Abstract
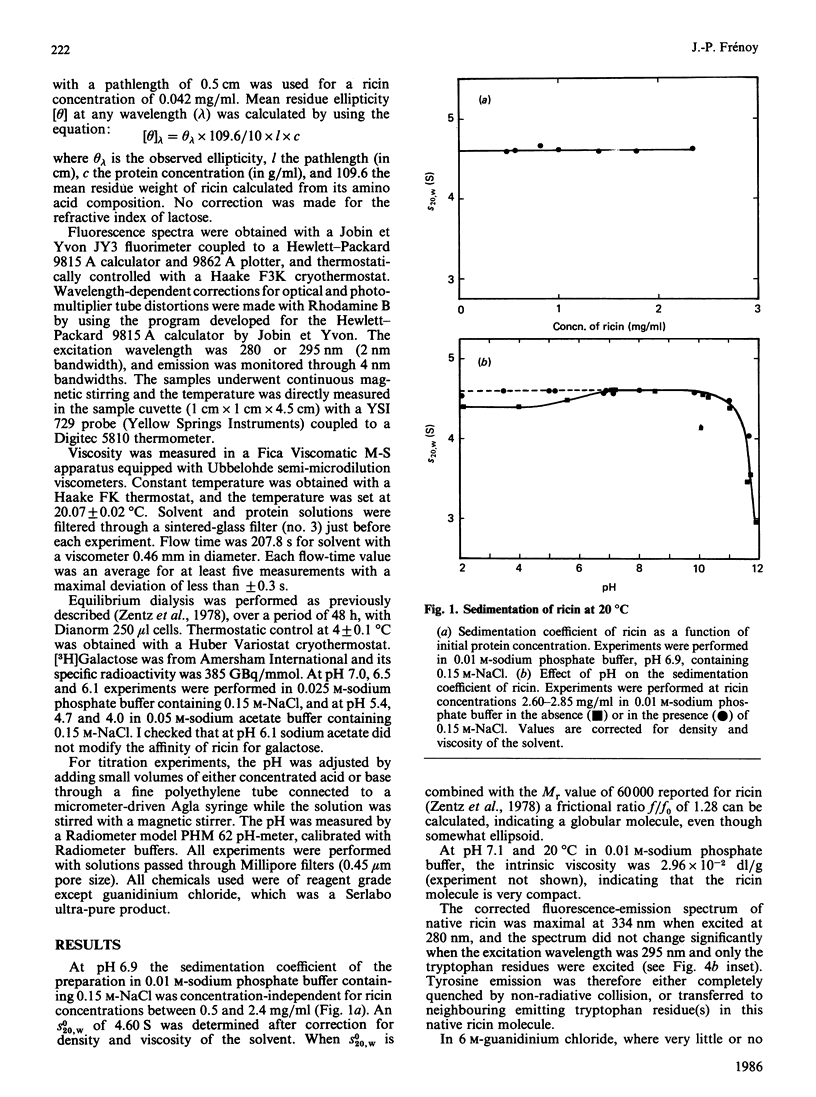
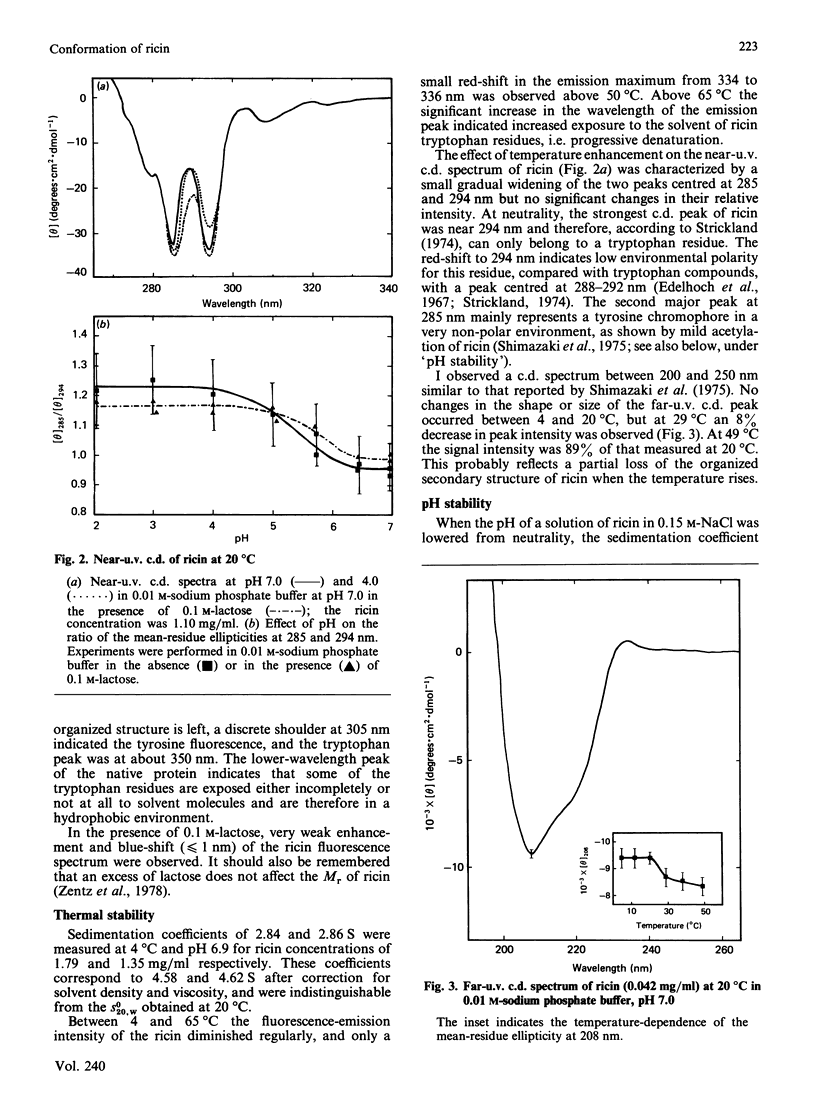
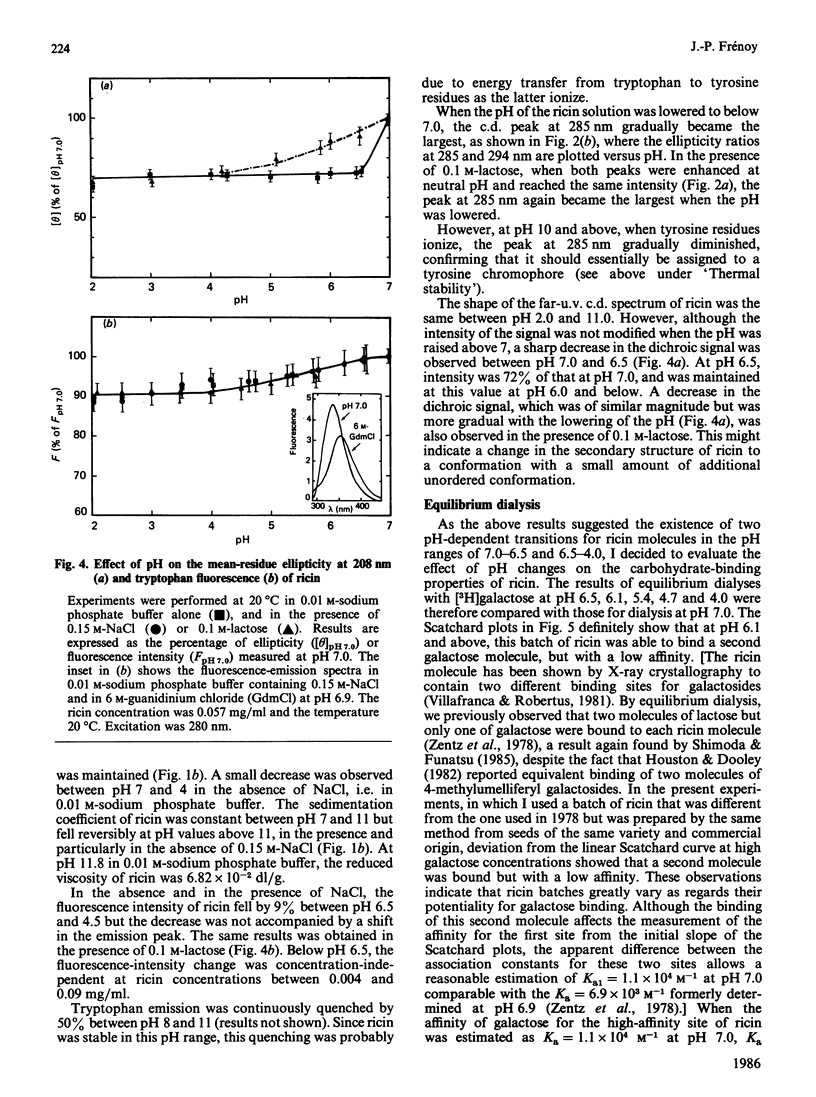
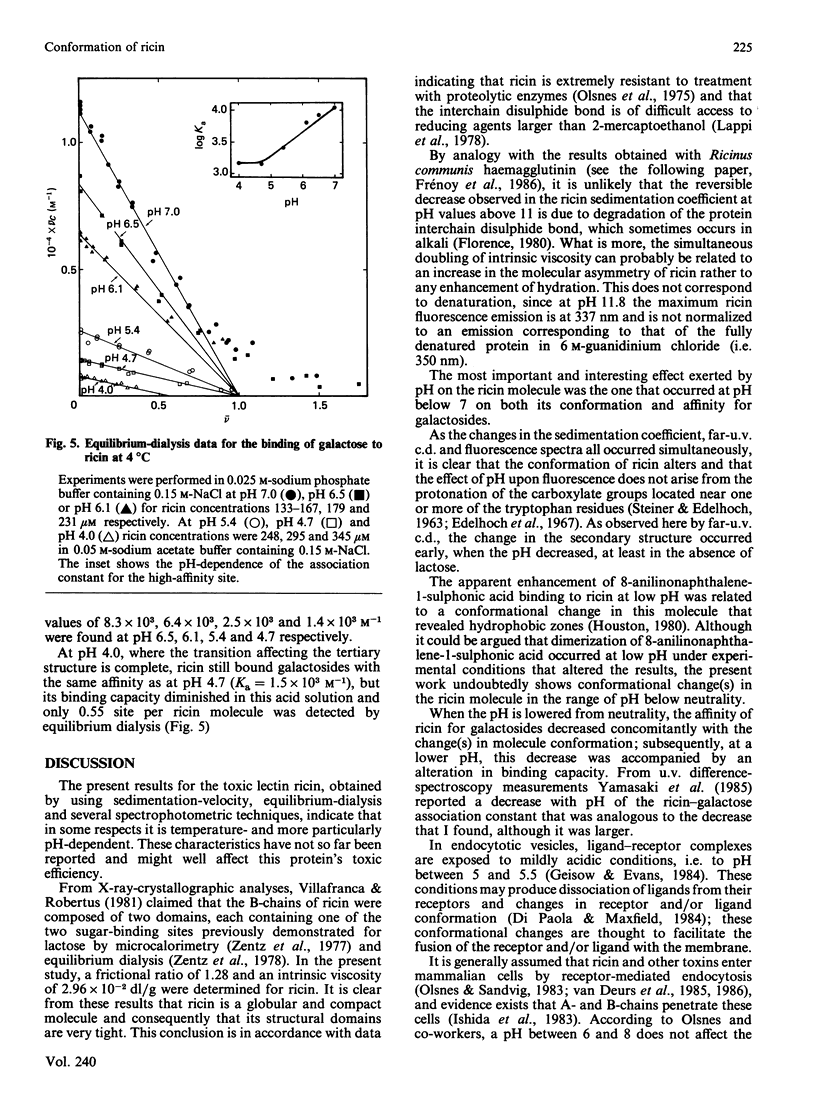
The molecular properties of ricin (the toxic lectin from Ricinus communis seeds, RCA II or RCA 60) were evaluated by analytical ultracentrifugation, viscosimetry, c.d., fluorescence and equilibrium dialysis. Measurements of sedimentation (S0(20,W) = 4.60 S) and viscosity (eta = 2.96 X 10(-2) dl/g) indicated that, at neutral pH, the ricin molecule is very compact. Various transitions were explored, and a pH-triggered change in the ricin conformation was observed between pH 7 and 4. In this range, the sedimentation coefficient, far-u.v. c.d. and fluorescence altered simultaneously without unfolding. Below pH 7 the change in the ricin conformation was accompanied by a decrease in the affinity of ricin for galactosides, and at pH 4.0 by an alteration in its binding capacity. These effects of low pH are discussed in relation to the physical conditions encountered by ricin molecules during their entry into living cells.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonfils C., Nato F., Bourrillon R., Balny C. Polyanionic character of plasma membrane sialoglycoproteins. FEBS Lett. 1981 Jan 26;123(2):222–224. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80292-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiPaola M., Maxfield F. R. Conformational changes in the receptors for epidermal growth factor and asialoglycoproteins induced by the mildly acidic pH found in endocytic vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 25;259(14):9163–9171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelhoch H., Brand L., Wilchek M. Fluorescence studies with tryptophyl peptides. Biochemistry. 1967 Feb;6(2):547–559. doi: 10.1021/bi00854a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florence T. M. Degradation of protein disulphide bonds in dilute alkali. Biochem J. 1980 Sep 1;189(3):507–520. doi: 10.1042/bj1890507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frénoy J. P., Tran A. T., Bourrillon R. Structure and stability of Ricinus communis haemagglutinin. Biochem J. 1986 Nov 15;240(1):227–231. doi: 10.1042/bj2400227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisow M. J., Evans W. H. pH in the endosome. Measurements during pinocytosis and receptor-mediated endocytosis. Exp Cell Res. 1984 Jan;150(1):36–46. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(84)90699-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh P. C., Wellner R. B., Cragoe E. J., Jr, Wu H. C. Enhancement of ricin cytotoxicity in Chinese hamster ovary cells by depletion of intracellular K+: evidence for an Na+/H+ exchange system in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;101(2):350–357. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.2.350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houston L. L. Differential fluorescence enhancement of 8-anilino-1-napthalene sulfonic acid by ricin A and B chains. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Jan 15;92(1):319–326. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91555-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houston L. L., Dooley T. P. Binding of two molecules of 4-methylumbelliferyl galactose or 4-methylumbelliferyl N-acetylgalactosamine to the B chains of ricin and Ricinus communis agglutinin and to purified ricin B chain. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4147–4151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishida B., Cawley D. B., Reue K., Wisnieski B. J. Lipid-protein interactions during ricin toxin insertion into membranes. Evidence for A and B chain penetration. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5933–5937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lappi D. A., Kapmeyer W., Beglau J. M., Kaplan N. O. The disulfide bond connecting the chains of ricin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1096–1100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. Y., Tserng K. Y., Chen C. C., Lin L. T., Tung T. C. Abrin and ricin: new anti-tumour substances. Nature. 1970 Jul 18;227(5255):292–293. doi: 10.1038/227292a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moya M., Dautry-Varsat A., Goud B., Louvard D., Boquet P. Inhibition of coated pit formation in Hep2 cells blocks the cytotoxicity of diphtheria toxin but not that of ricin toxin. J Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;101(2):548–559. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.2.548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson G. L., Blaustein J., Etzler M. E. Characterization of two plant lectins from Ricinus communis and their quantitative interaction with a murine lymphoma. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 1;13(1):196–204. doi: 10.1021/bi00698a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson G. L., Blaustein J. The interaction of Ricinus communis agglutinin with normal and tumor cell surfaces. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 May 9;266(2):543–547. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90109-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsnes S., Refsnes K., Christensen T. B., Pihl A. Studies on the structure and properties of the lectins from Abrus precatorius and Ricinus communis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Sep 9;405(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(75)90308-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsnes S., Saltvedt E., Pihl A. Isolation and comparison of galactose-binding lectins from Abrus precatorius and Ricinus communis. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 10;249(3):803–810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardoe G. I., Bird G. W., Uhlenbruck G. On the specificity of lectins with a broad agglutination spectrum. I. The nature of the specific receptors for Ricinus communis and Solanum tuberosum Lectins. Z Immunitatsforsch Allerg Klin Immunol. 1969 May;137(5):442–457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEINER R. F., EDELHOCH H. The ultraviolet fluorescence of proteins. I. The influence of pH and temperature. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 May 21;66:341–355. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91203-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandvig K., Olsnes S. Effect of temperature on the uptake, excretion and degradation of abrin and ricin by HeLa cells. Exp Cell Res. 1979 Jun;121(1):15–25. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(79)90439-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandvig K., Olsnes S. Entry of the toxic proteins abrin, modeccin, ricin, and diphtheria toxin into cells. II. Effect of pH, metabolic inhibitors, and ionophores and evidence for toxin penetration from endocytotic vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7504–7513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandvig K., Olsnes S., Pihl A. Kinetics of binding of the toxic lectins abrin and ricin to surface receptors of human cells. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jul 10;251(13):3977–3984. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimazaki K., Walborg E. F., Jr, Neri G., Jirgensons B. Circular dichroism and saccharide-induced conformational transitions of lectins from Ricinus communis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Aug;169(2):731–736. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90218-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland E. H. Aromatic contributions to circular dichroism spectra of proteins. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1974 Jan;2(1):113–175. doi: 10.3109/10409237409105445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhr J. W. Immunotoxins: harnessing nature's poisons. J Immunol. 1984 Dec;133(6):i–x. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villafranca J. E., Robertus J. D. Ricin B chain is a product of gene duplication. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 25;256(2):554–556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wileman T., Harding C., Stahl P. Receptor-mediated endocytosis. Biochem J. 1985 Nov 15;232(1):1–14. doi: 10.1042/bj2320001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamasaki N., Hatakeyama T., Funatsu G. Ricin D-saccharide interaction as studied by ultraviolet difference spectroscopy. J Biochem. 1985 Dec;98(6):1555–1560. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zentz C., Frénoy J. P., Bourrillon R. Binding of galactose and lactose to ricin. Equilibrium studies. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Sep 26;536(1):18–26. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(78)90047-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zentz C., Frénoy J. P., Bourrillon R. Microcalorimetric measurements of ricin-saccharide binding. FEBS Lett. 1977 Sep 1;81(1):23–27. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80919-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Deurs B., Pedersen L. R., Sundan A., Olsnes S., Sandvig K. Receptor-mediated endocytosis of a ricin-colloidal gold conjugate in vero cells. Intracellular routing to vacuolar and tubulo-vesicular portions of the endosomal system. Exp Cell Res. 1985 Aug;159(2):287–304. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4827(85)80003-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Deurs B., Tønnessen T. I., Petersen O. W., Sandvig K., Olsnes S. Routing of internalized ricin and ricin conjugates to the Golgi complex. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;102(1):37–47. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


