Abstract
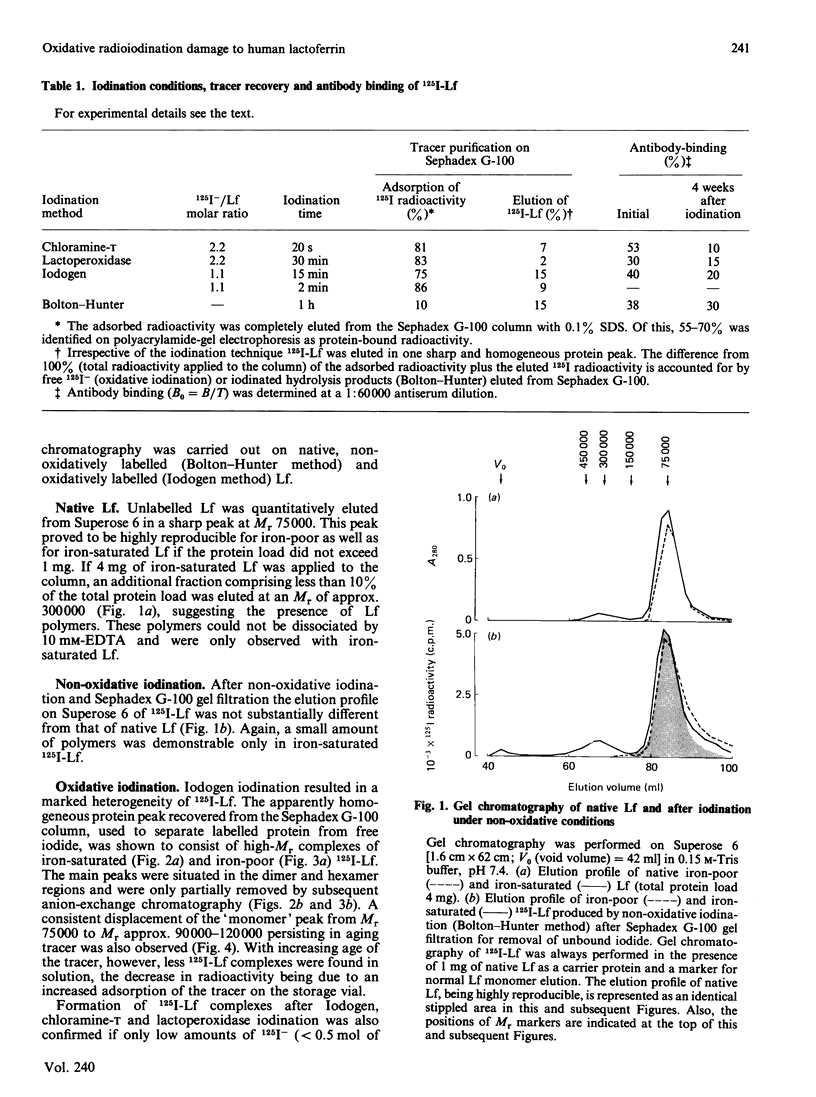
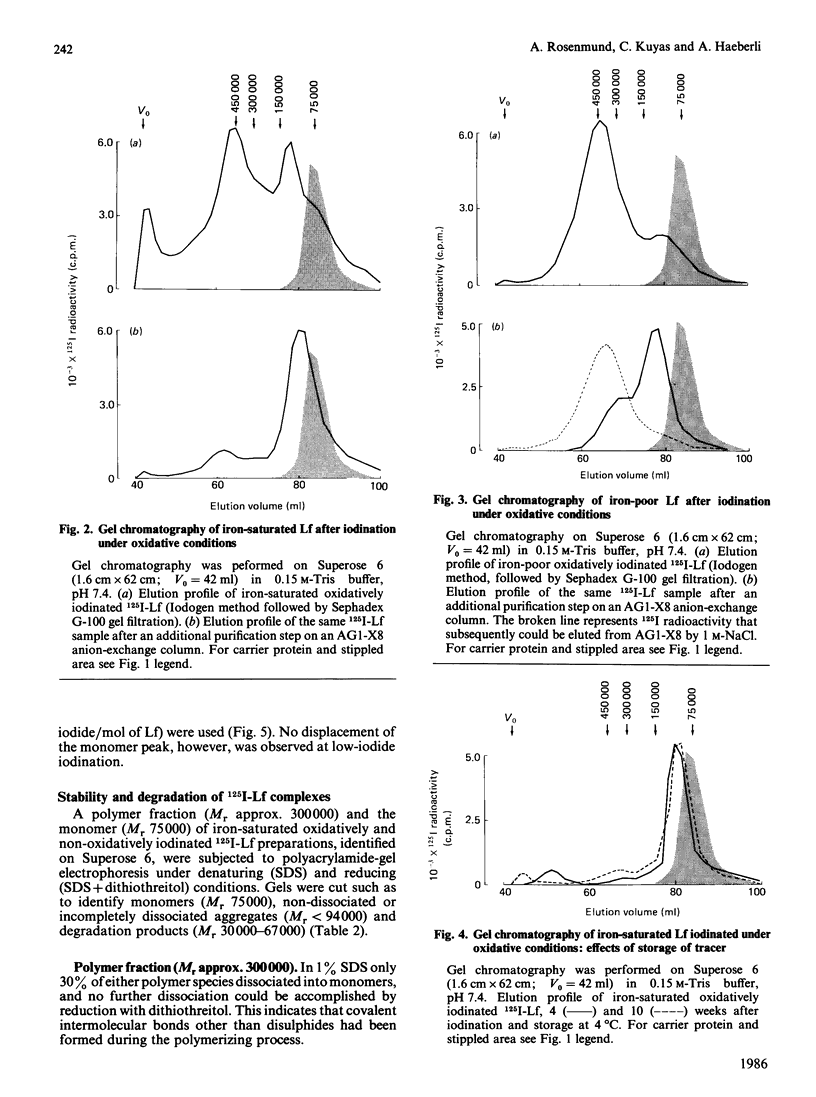
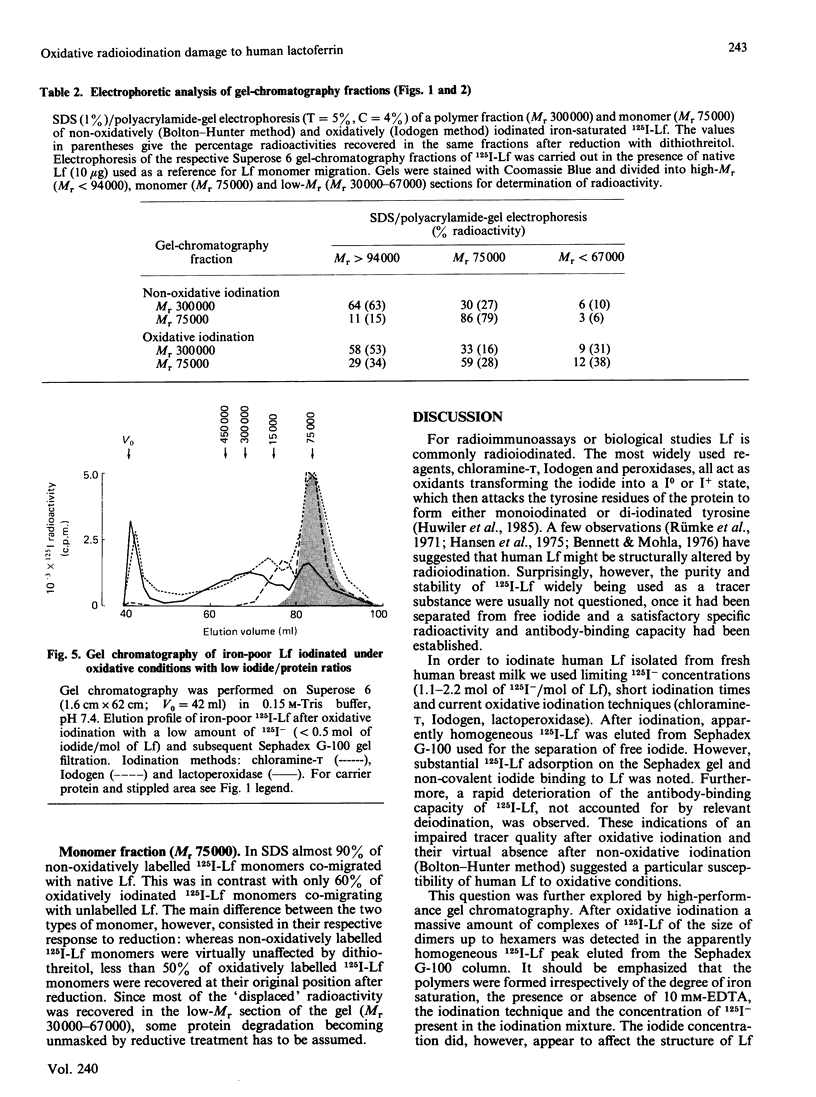
Oxidative iodination of human lactoferrin (Lf) as commonly performed by using the chloramine-T, the Iodogen or the lactoperoxidase method produces an unreliable tracer protein because of excessive and heterogeneous polymer formation. Before iodination a minor tetramer fraction may be demonstrable in iron-saturated Lf only. Iodination-induced polymerization of iron-poor as well as iron-saturated Lf occurs independently of the presence or absence of 10 mM-EDTA and the 125I-/Lf molar ratio used for iodination. 125I-Lf polymers are mainly covalently linked, as suggested by the lack of substantial dissociation in SDS/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis. Damage to the 125I-Lf monomer may be another consequence of oxidative iodination. This is demonstrated in SDS/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis where 50% of the radioactivity of apparently normal monomer (Mr 75,000) is displaced to a lower-Mr region (30,000-67,000) after reduction with dithiothreitol. Non-oxidative iodination by the Bolton-Hunter technique produces an antigenetically stable tracer that is not being subjected to polymerization and monomer degradation as judged by high-performance gel chromatography and SDS/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis with and without dithiothreitol treatment. It is concluded that oxidation in itself leads to covalent non-disulphide cross-linking between human Lf molecules and, possibly, to intramolecular peptide-bond breaking becoming unmasked under reducing conditions. In biological experiments with human 125I-Lf this problem should be carefully considered.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aeschbach R., Amadò R., Neukom H. Formation of dityrosine cross-links in proteins by oxidation of tyrosine residues. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Aug 9;439(2):292–301. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(76)90064-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexander N. M. Oxidative cleavage of tryptophanyl peptide bonds during chemical- and peroxidase-catalyzed iodinations. J Biol Chem. 1974 Mar 25;249(6):1946–1952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambruso D. R., Johnston R. B., Jr Lactoferrin enhances hydroxyl radical production by human neutrophils, neutrophil particulate fractions, and an enzymatic generating system. J Clin Invest. 1981 Feb;67(2):352–360. doi: 10.1172/JCI110042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagby G. C., Jr, Bennett R. M. Feedback regulation of granulopoiesis: polymerization of lactoferrin abrogates its ability to inhibit CSA production. Blood. 1982 Jul;60(1):108–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagby G. C., Jr, Rigas V. D., Bennett R. M., Vandenbark A. A., Garewal H. S. Interaction of lactoferrin, monocytes, and T lymphocyte subsets in the regulation of steady-state granulopoiesis in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1981 Jul;68(1):56–63. doi: 10.1172/JCI110254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett R. M., Bagby G. C., Davis J. Calcium-dependent polymerization of lactoferrin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Jul 16;101(1):88–95. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(81)80014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett R. M., Davis J., Campbell S., Portnoff S. Lactoferrin binds to cell membrane DNA. Association of surface DNA with an enriched population of B cells and monocytes. J Clin Invest. 1983 Mar;71(3):611–618. doi: 10.1172/JCI110807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett R. M., Kokocinski T. Lactoferrin turnover in man. Clin Sci (Lond) 1979 Nov;57(5):453–460. doi: 10.1042/cs0570453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett R. M., Mohla C. A solid-phase radioimmunoassay for the measurement of lactoferrin in human plasma: variations with age, sex, and disease. J Lab Clin Med. 1976 Jul;88(1):156–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birgens H. S., Hansen N. E., Karle H., Kristensen L. O. Receptor binding of lactoferrin by human monocytes. Br J Haematol. 1983 Jul;54(3):383–391. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1983.tb02113.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bläckberg L., Hernell O. Isolation of lactoferrin from human whey by a single chromatographic step. FEBS Lett. 1980 Jan 14;109(2):180–183. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)81081-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton A. E., Hunter W. M. The labelling of proteins to high specific radioactivities by conjugation to a 125I-containing acylating agent. Biochem J. 1973 Jul;133(3):529–539. doi: 10.1042/bj1330529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton A. E., Lee-Own V., McLean R. K., Challand G. S. Three different radioiodination methods for human spleen ferritin compared. Clin Chem. 1979 Oct;25(10):1826–1830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boxer L. A., Coates T. D., Haak R. A., Wolach J. B., Hoffstein S., Baehner R. L. Lactoferrin deficiency associated with altered granulocyte function. N Engl J Med. 1982 Aug 12;307(7):404–410. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198208123070704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broxmeyer H. E., Gentile P., Bognacki J., Ralph P. Lactoferrin, transferrin and acidic isoferritins: regulatory molecules with potential therapeutic value in leukemia. Blood Cells. 1983;9(1):83–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broxmeyer H. E. Lactoferrin acts on Ia-like antigen-positive subpopulations of human monocytes to inhibit production of colony stimulatory activity in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1979 Dec;64(6):1717–1720. doi: 10.1172/JCI109635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgett M. W., Fairfield S. J., Monthony J. F. A solid phase fluorescent immunossay for the quantitation of the C4 component of human complement. J Immunol Methods. 1977;16(3):211–219. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90199-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comens P. G., Simmer R. L., Baker J. B. Direct linkage of 125I-EGF to cell surface receptors. A useful artifact of chloramine-T treatment. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 10;257(1):42–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen N. E., Malmquist J., Thorell J. Plasma myeloperoxidase and lactoferrin measured by radioimmunoassay: relations to neutrophil kinetics. Acta Med Scand. 1975 Dec;198(6):437–443. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1975.tb19572.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hekman A. Association of lactoferrin with other proteins, as demonstrated by changes in electrophoretic mobility. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Dec 28;251(3):380–387. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(71)90126-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huwiler M., Bürgi U., Kohler H. Mechanism of enzymatic and non-enzymatic tyrosine iodination. Inhibition by excess hydrogen peroxide and/or iodide. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Mar 15;147(3):469–476. doi: 10.1111/j.0014-2956.1985.00469.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imber M. J., Pizzo S. V. Clearance and binding of native and defucosylated lactoferrin. Biochem J. 1983 May 15;212(2):249–257. doi: 10.1042/bj2120249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Junek H., Kirk K. L., Cohen L. A. The oxidative cleavage of tyrosyl-peptide bonds during iodination. Biochemistry. 1969 May;8(5):1844–1848. doi: 10.1021/bi00833a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karle H., Hansen N. E., Malmquist J., Karle A. K., Larsson I. Turnover of human lactoferrin in the rabbit. Scand J Haematol. 1979 Oct;23(4):303–312. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1979.tb02865.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keough D. T., Dionysius D. A., de Jersey J., Zerner B. Iron-containing acid phosphatases: characterization of the metal-ion binding site of the enzyme from pig allantoic fluid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 May 30;94(2):600–605. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91274-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy R. C., Markowitz H. Characterization of human prostatic acid phosphatase radioiodinated by four different procedures. Clin Chim Acta. 1983 Aug 31;132(3):277–286. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(83)90006-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rümke P., Visser D., Kwa H. G., Hart A. A. Radio-immuno assay of lactoferrin in blood plasma of breast cancer patients, lactating and normal women; prevention of false high levels caused by leakage from neutrophile leucocytes in vitro. Folia Med Neerl. 1971 Aug-Sep;14(4):156–168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salacinski P. R., McLean C., Sykes J. E., Clement-Jones V. V., Lowry P. J. Iodination of proteins, glycoproteins, and peptides using a solid-phase oxidizing agent, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3 alpha,6 alpha-diphenyl glycoluril (Iodogen). Anal Biochem. 1981 Oct;117(1):136–146. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90703-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturgeon C. M., Beynon L., Seth J., Chisholm G. D. Comparison of Bolton-Hunter and chloramine-T techniques for the radioiodination of prostatic acid phosphatase. Ann Clin Biochem. 1983 Mar;20(Pt 2):112–115. doi: 10.1177/000456328302000210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Snick J. L., Masson P. L., Heremans J. F. The involvement of lactoferrin in the hyposideremia of acute inflammation. J Exp Med. 1974 Oct 1;140(4):1068–1084. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.4.1068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Snick J. L., Masson P. L. The binding of human lactoferrin to mouse peritoneal cells. J Exp Med. 1976 Dec 1;144(6):1568–1580. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.6.1568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. G., Wachter C., Scriba P. C. Experiences using chloramine-T and 1, 3, 4, 6-tetrachloro-3 alpha, 6 alpha-diphenylglycoluril (Iodogen) for radioiodination of materials for radioimmunoassay. J Clin Chem Clin Biochem. 1981 Oct;19(10):1051–1056. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


