Abstract
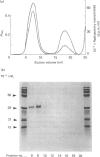
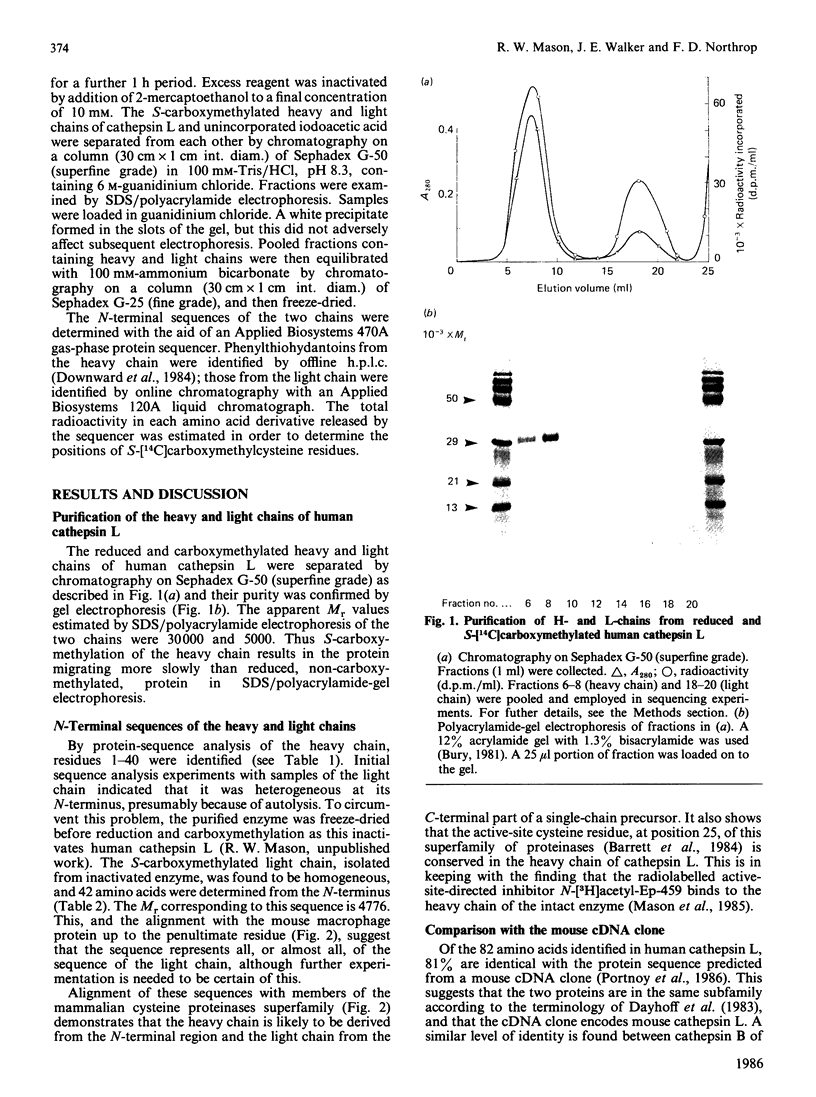
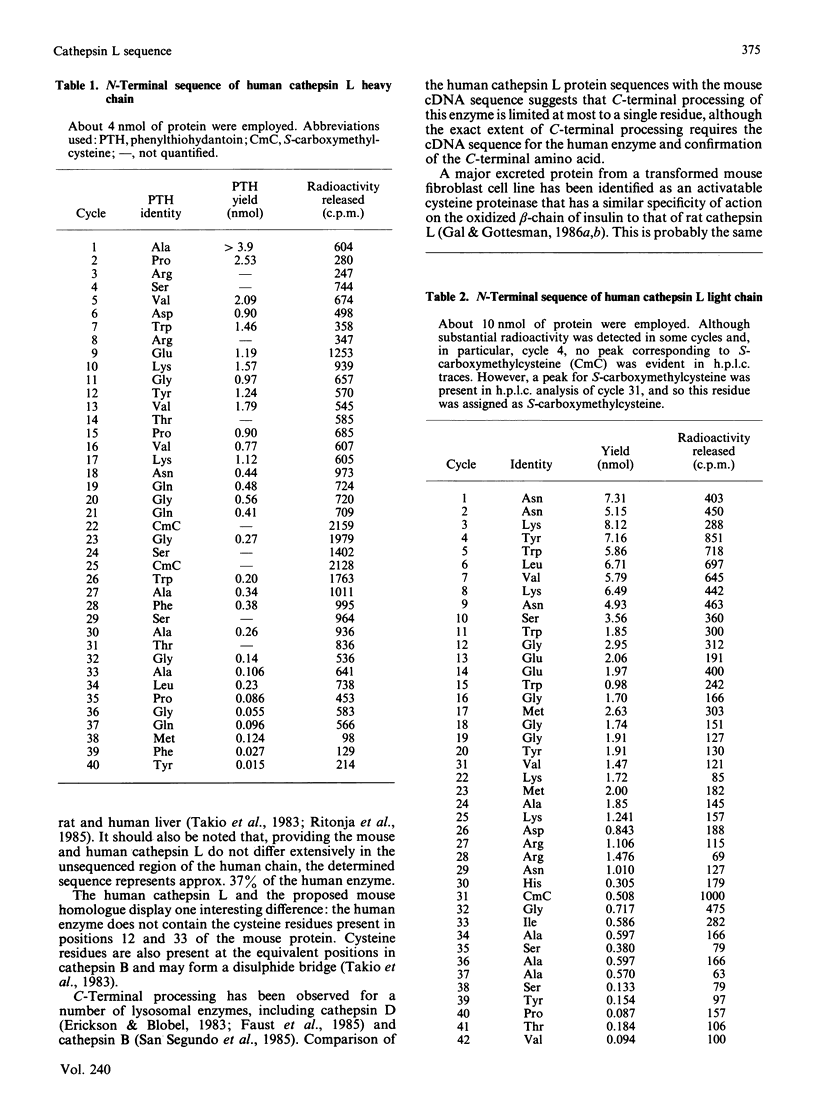
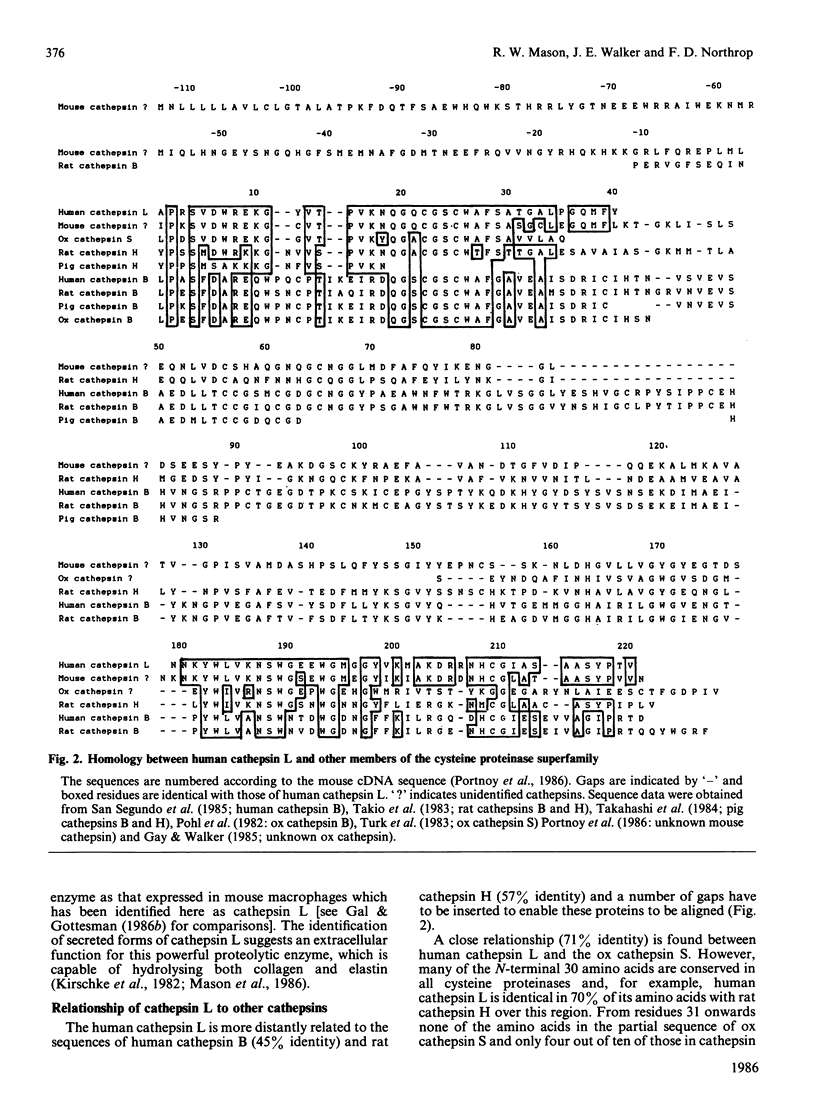
Human liver cathepsin L consists of a heavy chain and a light chain with Mr values of 25,000 and 5000 respectively. The chains have been purified and their N-terminal amino acid sequences have been determined. The 40 amino acids determined from the heavy chain and 42 amino acids sequenced in the light chain are homologous with the N-terminal and C-terminal regions respectively of the superfamily of cysteine proteinases. Therefore it is likely that the two chains of cathepsin L are derived by proteolysis of a single polypeptide precursor. Of the amino acids sequenced, 81% are identical with the homologous portions of a protein sequence for a major cysteine proteinase predicted from a cDNA clone from a mouse macrophage cell line. This is the closest relative amongst the known sequences in the superfamily and strongly indicates that the protein encoded by this mRNA is cathepsin L. The mouse protein is also probably the major excreted protein of a transformed cell line [Gal & Gottesman (1986) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 139, 156-162]. The heavy chain is identical in only 71% of its residues with the sequence of ox cathepsin S, providing further evidence that this latter enzyme is probably not a species variant of cathepsin L. The relationship with a second unidentified cathepsin cDNA clone from a bovine library is much weaker (41% identity), and so this clone remains unidentified.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrett A. J., Kirschke H. Cathepsin B, Cathepsin H, and cathepsin L. Methods Enzymol. 1981;80(Pt 100):535–561. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)80043-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayhoff M. O., Barker W. C., Hunt L. T. Establishing homologies in protein sequences. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:524–545. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91049-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J., Yarden Y., Mayes E., Scrace G., Totty N., Stockwell P., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J., Waterfield M. D. Close similarity of epidermal growth factor receptor and v-erb-B oncogene protein sequences. Nature. 1984 Feb 9;307(5951):521–527. doi: 10.1038/307521a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson A. H., Blobel G. Carboxyl-terminal proteolytic processing during biosynthesis of the lysosomal enzymes beta-glucuronidase and cathepsin D. Biochemistry. 1983 Oct 25;22(22):5201–5205. doi: 10.1021/bi00291a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faust P. L., Kornfeld S., Chirgwin J. M. Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA for human cathepsin D. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):4910–4914. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.4910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gal S., Gottesman M. M. The major excreted protein (MEP) of transformed mouse cells and cathepsin L have similar protease specificity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Aug 29;139(1):156–162. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80093-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gal S., Gottesman M. M. The major excreted protein of transformed fibroblasts is an activable acid-protease. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 5;261(4):1760–1765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay N. J., Walker J. E. Molecular cloning of a bovine cathepsin. Biochem J. 1985 Feb 1;225(3):707–712. doi: 10.1042/bj2250707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschke H., Kembhavi A. A., Bohley P., Barrett A. J. Action of rat liver cathepsin L on collagen and other substrates. Biochem J. 1982 Feb 1;201(2):367–372. doi: 10.1042/bj2010367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschke H., Langner J., Wiederanders B., Ansorge S., Bohley P. Cathepsin L. A new proteinase from rat-liver lysosomes. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Apr 1;74(2):293–301. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11393.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschke H., Locnikar P., Turk V. Species variations amongst lysosomal cysteine proteinases. FEBS Lett. 1984 Aug 20;174(1):123–127. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)81089-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason R. W., Green G. D., Barrett A. J. Human liver cathepsin L. Biochem J. 1985 Feb 15;226(1):233–241. doi: 10.1042/bj2260233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason R. W., Johnson D. A., Barrett A. J., Chapman H. A. Elastinolytic activity of human cathepsin L. Biochem J. 1986 Feb 1;233(3):925–927. doi: 10.1042/bj2330925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason R. W., Taylor M. A., Etherington D. J. The purification and properties of cathepsin L from rabbit liver. Biochem J. 1984 Jan 1;217(1):209–217. doi: 10.1042/bj2170209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murachi T. Calcium-dependent proteinases and specific inhibitors: calpain and calpastatin. Biochem Soc Symp. 1984;49:149–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno S., Emori Y., Imajoh S., Kawasaki H., Kisaragi M., Suzuki K. Evolutionary origin of a calcium-dependent protease by fusion of genes for a thiol protease and a calcium-binding protein? Nature. 1984 Dec 6;312(5994):566–570. doi: 10.1038/312566a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohl J., Baudys M., Tomásek V., Kostka V. Identification of the active site cysteine and of the disulfide bonds in the N-terminal part of the molecule of bovine spleen cathepsin B. FEBS Lett. 1982 Jun 1;142(1):23–26. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80210-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritonja A., Popovic T., Turk V., Wiedenmann K., Machleidt W. Amino acid sequence of human liver cathepsin B. FEBS Lett. 1985 Feb 11;181(1):169–172. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)81136-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- San Segundo B., Chan S. J., Steiner D. F. Identification of cDNA clones encoding a precursor of rat liver cathepsin B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2320–2324. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi T., Dehdarani A. H., Schmidt P. G., Tang J. Cathepsins B and H from porcine spleen. Purification, polypeptide chain arrangements, and carbohydrate content. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 10;259(15):9874–9882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takio K., Towatari T., Katunuma N., Teller D. C., Titani K. Homology of amino acid sequences of rat liver cathepsins B and H with that of papain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3666–3670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]