Abstract
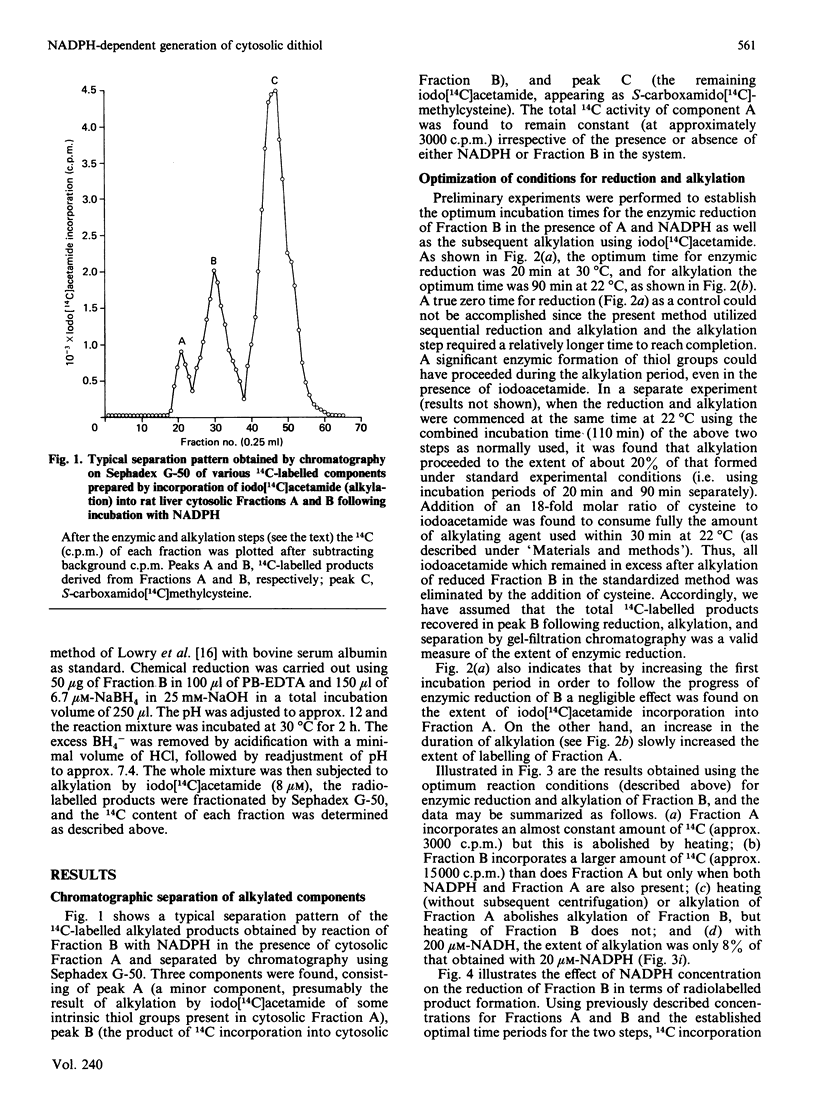
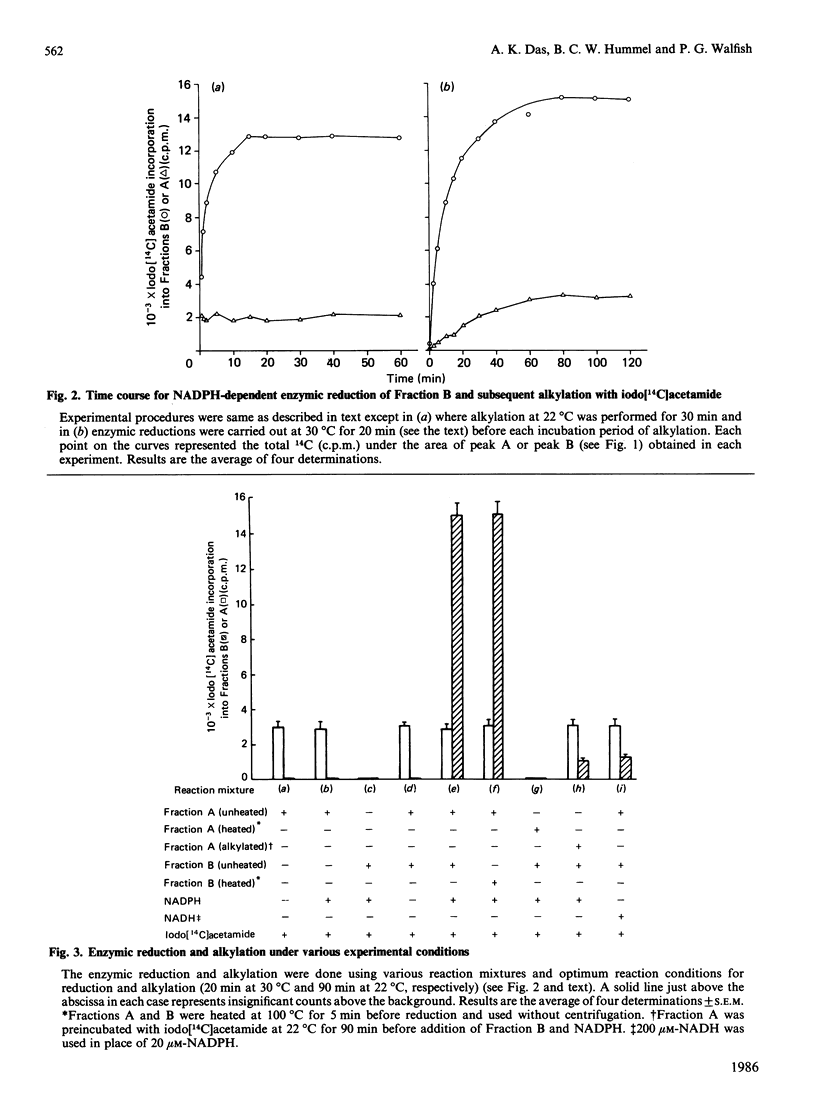
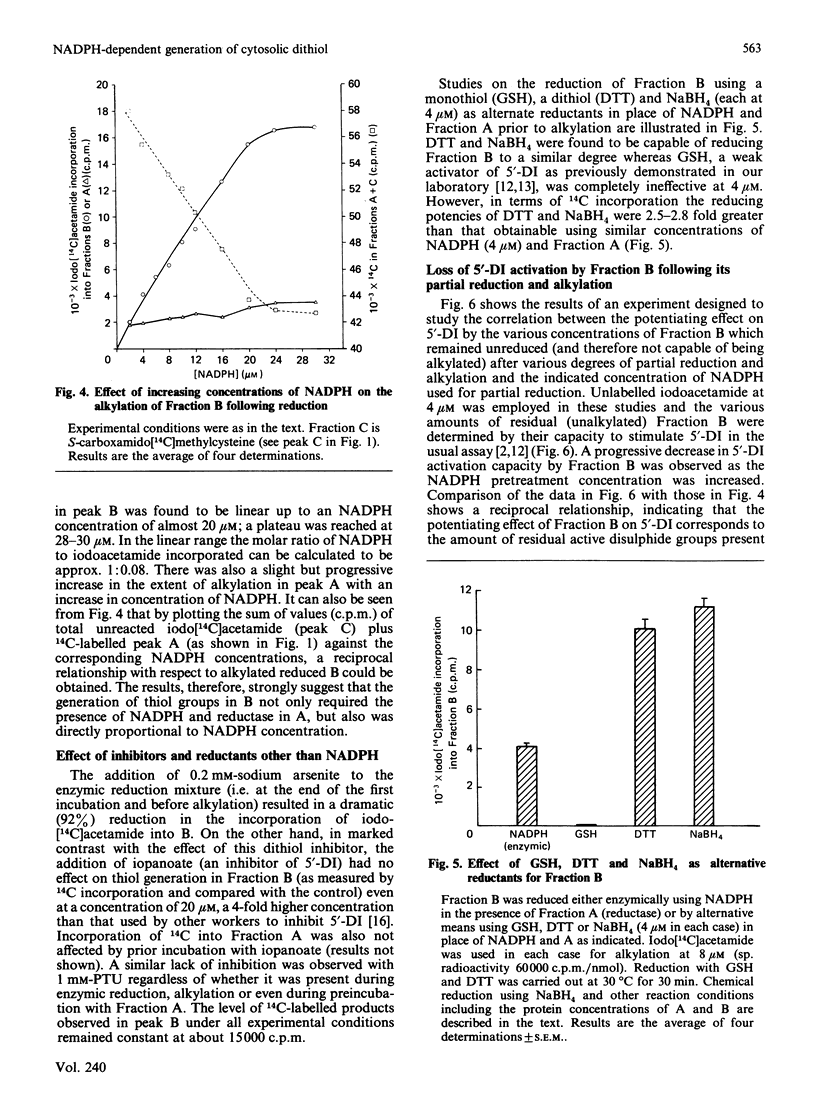
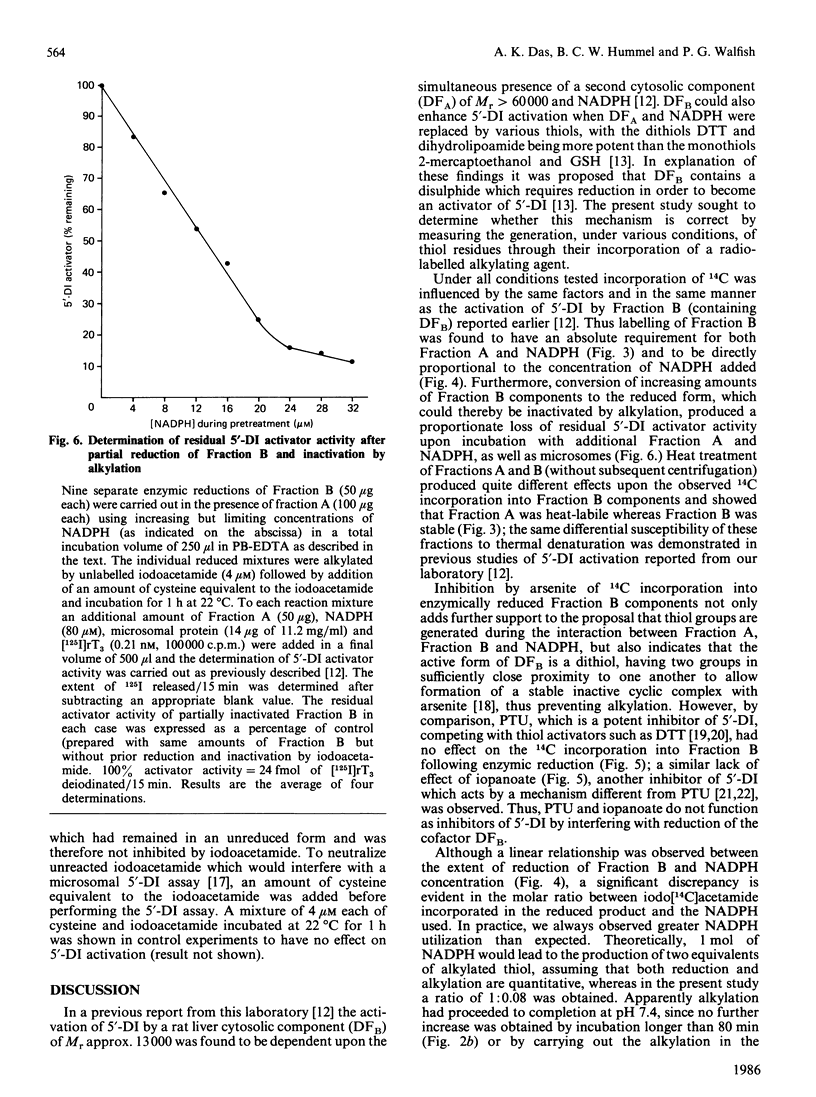
We have assessed a previously proposed mechanism mediating 5'-deiodinase activation involving enzymic reduction of disulphides to thiols in non-glutathione cytosolic components of Mr approx. 13,000 (Fraction B) catalysed by NADPH in the presence of other cytosolic components of Mr greater than 60,000 (Fraction A). The extent of Fraction B reduction under various experimental conditions was monitored by determining the amount of 14C incorporated into chromatographically isolated Fractions B and A after their alkylation with iodo[14C]acetamide. Incorporation of 14C into B was found to require the simultaneous presence of NADPH and A, to be directly proportional to the concentration of NADPH added, and to be unaffected by either propylthiouracil or iopanoate. Activation of 5'-deiodinase attainable using B after its partial reduction by various concentrations of NADPH and subsequent alkylation with non-radioactive iodoacetamide was inversely proportional to the previously added concentration of NADPH. Fraction B was stable at 100 degrees C for 5 min, while similar heat treatment of Fraction A or omission of NADPH resulted in a complete loss of 14C incorporation. A greater than 90% reduction in iodo[14C]acetamide incorporation was revealed when 0.2 mM-sodium arsenite was added after enzymic reduction of B, as well as when NADPH was replaced by NADH. Fraction B could be labelled more extensively after reduction non-specifically, with dithiothreitol or NaBH4, but not by GSH. These observations provide strong evidence for the presence in vivo of a cytosolic disulphide (DFBS2) in Fraction B which can be reduced enzymically to a dithiol [DFB(SH)2] by NADPH and cytosolic components in Fraction A. The degree of activation of hepatic 5'-deiodinase correlated with the amount of available (unalkylated) Fraction B.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balsam A., Ingbar S. H. Observations on the factors that control the generation of triiodothyronine from thyroxine in rat liver and the nature of the defect induced by fasting. J Clin Invest. 1979 Jun;63(6):1145–1156. doi: 10.1172/JCI109408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balsam A., Sexton F., Ingbar S. H. On the mechanism of impaired in vitro generation of 3,5,3'-triiodothyronine from thyroxine in the livers of hypothyroid rats. Endocrinology. 1979 Nov;105(5):1115–1121. doi: 10.1210/endo-105-5-1115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burch H. B., Bradley M. E., Lowry O. H. The measurement of triphosphopyridine nucleotide and reduced triphosphopyridine nucleotide and the role of hemoglobin in producing erroneous triphosphopyridine nucleotide values. J Biol Chem. 1967 Oct 10;242(19):4546–4554. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fekkes D., Hennemann G., Visser T. J. Evidence for a single enzyme in rat liver catalysing the deiodination of the tyrosyl and the phenolic ring of iodothyronines. Biochem J. 1982 Mar 1;201(3):673–676. doi: 10.1042/bj2010673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fekkes D., Hennemann G., Visser T. J. One enzyme for the 5'-deiodination of 3,3',5'-triiodothyronine and 3',5'-diiodothyronine in rat liver. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 May 1;31(9):1705–1709. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90672-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavin L. A., McMahon F. A., Moeller M. Dietary modification of thyroxine deiodination in rat liver is not mediated by hepatic sulfhydryls. J Clin Invest. 1980 Apr;65(4):943–946. doi: 10.1172/JCI109751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goswami A., Rosenberg I. N. Purification and characterization of a cytosolic protein enhancing GSH-dependent microsomal iodothyronine 5'-monodeiodination. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):6012–6019. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris A. R., Fang S. L., Hinerfeld L., Braverman L. E., Vagenakis A. G. The role of sulfhydryl groups on the impaired hepatic 3',3,5-triiodothyronine generation from thyroxine in the hypothyroid, starved, fetal, and neonatal rodent. J Clin Invest. 1979 Mar;63(3):516–524. doi: 10.1172/JCI109330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren A. Thioredoxin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:237–271. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.001321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallis G. B., Holmgren A. Differential reactivity of the functional sulfhydryl groups of cysteine-32 and cysteine-35 present in the reduced form of thioredoxin from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10261–10265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan M. M. Changes in the particulate subcellular component of hepatic thyroxine-5'-monodeiodinase in hyperthyroid and hypothyroid rats. Endocrinology. 1979 Aug;105(2):548–554. doi: 10.1210/endo-105-2-548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan M. M. Subcellular alterations causing reduced hepatic thyroxine-5'-monodeiodinase activity in fasted fats. Endocrinology. 1979 Jan;104(1):58–64. doi: 10.1210/endo-104-1-58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., PASSONNEAU J. V., ROCK M. K. The stability of pyridine nucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1961 Oct;236:2756–2759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard J. L., Rosenberg I. N. Characterization of essential enzyme sulfhydryl groups of thyroxine 5'-deiodinase from rat kidney. Endocrinology. 1980 Feb;106(2):444–451. doi: 10.1210/endo-106-2-444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard J. L., Rosenberg I. N. Thyroxine 5'-deiodinase activity of rat kidney: observations on activation by thiols and inhibition by propylthiouracil. Endocrinology. 1978 Dec;103(6):2137–2144. doi: 10.1210/endo-103-6-2137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard J. L., Visser T. J. Selective modification of the active center of renal iodothyronine 5'-deiodinase by iodoacetate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jun 14;787(2):122–130. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(84)90070-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luthman M., Holmgren A. Rat liver thioredoxin and thioredoxin reductase: purification and characterization. Biochemistry. 1982 Dec 21;21(26):6628–6633. doi: 10.1021/bi00269a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato K., Robbins J. Does glutathione regulate thyroxine deiodinase activity in cells? Horm Metab Res Suppl. 1984;14:30–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato K., Robbins J. Glutathione deficiency induced by cystine and/or methionine deprivation does not affect thyroid hormone deiodination in cultured rat hepatocytes and monkey hepatocarcinoma cells. Endocrinology. 1981 Sep;109(3):844–852. doi: 10.1210/endo-109-3-844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato T., Maruyama S., Nomura K. On the role of NADPH and glutathione in the catalytic mechanism of hepatic thyroxine 5'-deiodination. Endocrinol Jpn. 1981 Aug;28(4):451–459. doi: 10.1507/endocrj1954.28.451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawada K., Hummel B. C., Walfish P. G. Cytosolic cofactors and dihydrolipoamide stimulate hepatic microsomal 5'-deiodination. Endocrinology. 1985 Sep;117(3):1259–1263. doi: 10.1210/endo-117-3-1259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawada K., Hummel B. C., Walfish P. G. Intermediate Mr cytosolic components potentiate hepatic 5'-deiodinase activation by thiols. Biochem J. 1986 Sep 15;238(3):787–791. doi: 10.1042/bj2380787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawada K., Hummel B. C., Walfish P. G. Properties of cytosolic components activating rat hepatic 5' [corrected]-deiodination in the presence of NADPH. Biochem J. 1986 Mar 1;234(2):391–398. doi: 10.1042/bj2340391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visser T. J., Does-Tobé I., Docter R., Hennemann G. Subcellular localization of a rat liver enzyme converting thyroxine into tri-iodothyronine and possible involvement of essential thiol groups. Biochem J. 1976 Aug 1;157(2):479–482. doi: 10.1042/bj1570479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahler W. L., Cleland W. W. A specific and sensitive assay for disulfides. J Biol Chem. 1968 Feb 25;243(4):716–719. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


