Abstract
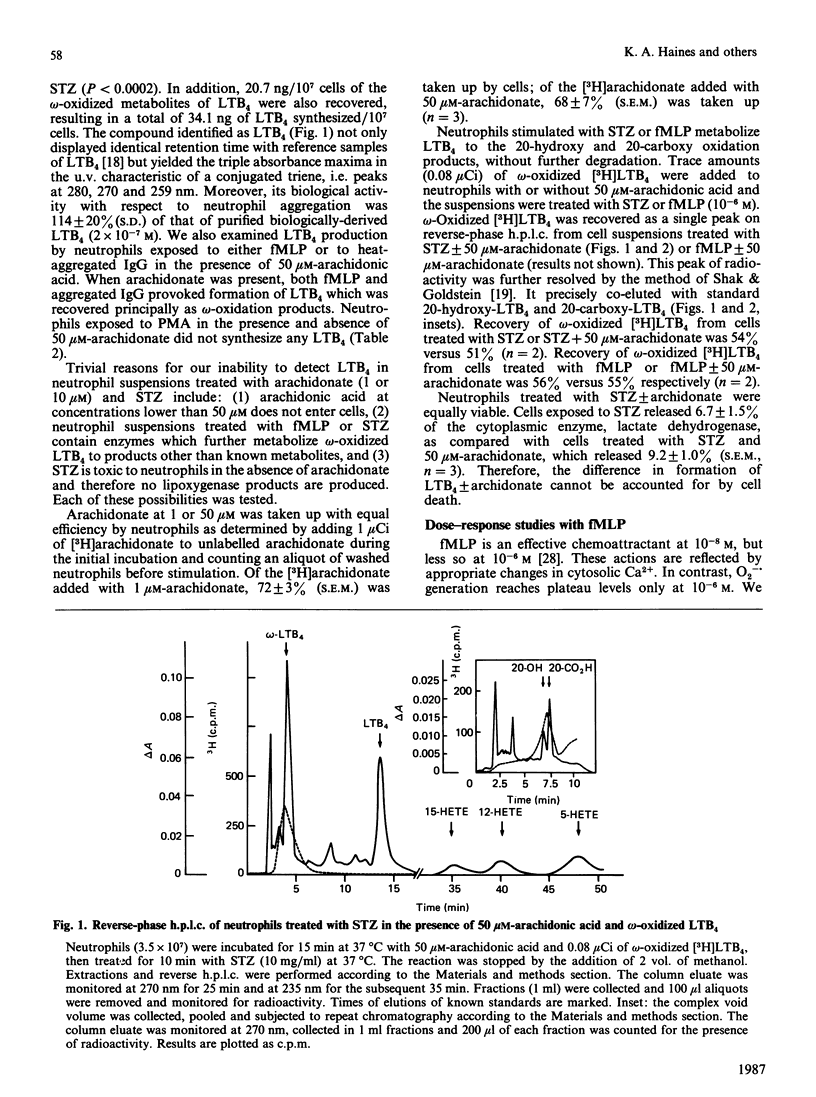
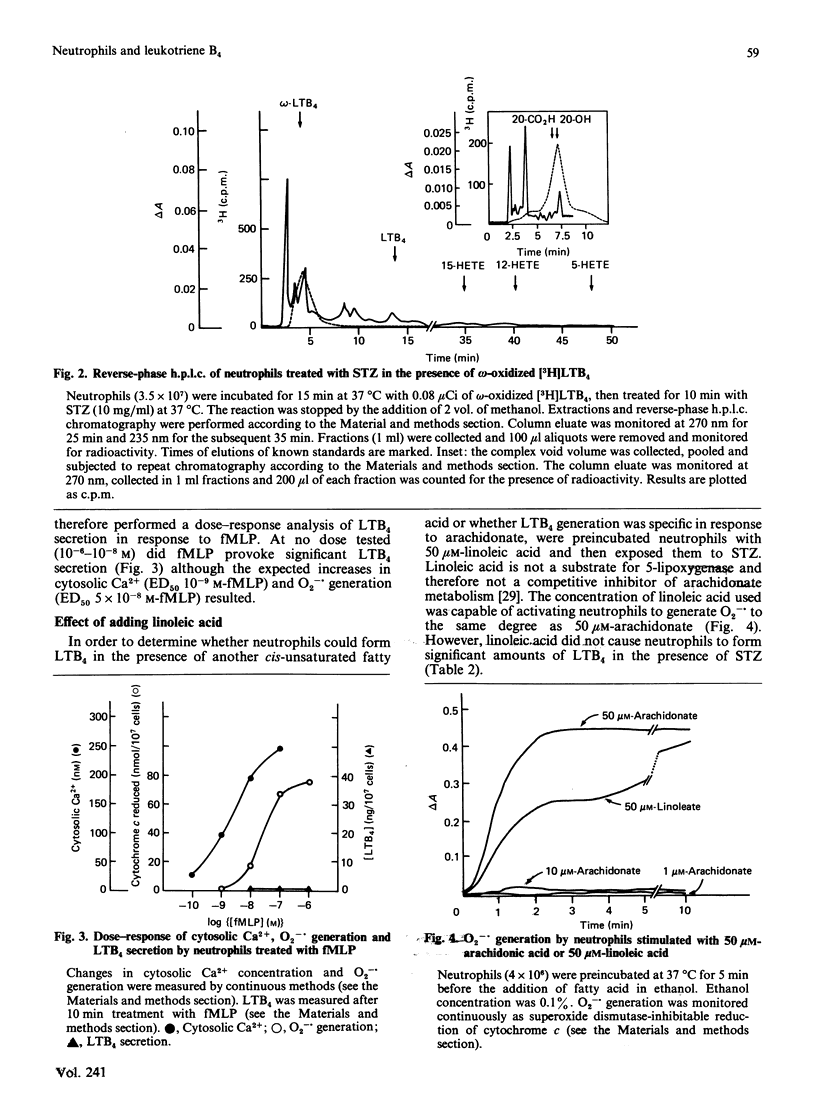
Leukotriene B4 (5S,12R-dihydroxy-6,14-cis,8,10-trans-eicosatetraenoic acid, LTB4) is released from neutrophils exposed to calcium ionophores. To determine whether LTB4 might be produced by ligand-receptor interactions at the plasmalemma, we treated human neutrophils with serum-treated zymosan (STZ), heat-aggregated IgG and fMet-Leu-Phe (fMLP), agonists at the C3b, Fc and fMLP receptors respectively. STZ (10 mg/ml) provoked the formation of barely detectable amounts of LTB4 (0.74 ng/10(7) cells); no omega-oxidized metabolites of LTB4 were found. Adding 10 microM-arachidonate did not significantly increase production of LTB4 or its metabolites. Addition of 50 microM-arachidonate (an amount which activates protein kinase C) before STZ caused a 40-fold increase in the quantity of LTB4 and its omega-oxidation products. Neither phorbol myristate acetate (PMA, 200 ng/ml) nor linoleic acid (50 microM), also activators of protein kinase C, augmented generation of LTB4 by cells stimulated with STZ. Neither fMLP (10(-6) M) nor aggregated IgG (0.3 mg/ml) induced LTB4 formation (less than 0.01 ng/10(7) cells). Moreover, cells exposed to STZ, fMLP, or IgG did not form all-trans-LTB4 or 5-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid; their failure to make LTB4 was therefore due to inactivity of neutrophil 5-lipoxygenase. However, adding 50 microM-arachidonate to neutrophil suspensions before fMLP or IgG triggered LTB4 production, the majority of which was metabolized to its omega-oxidized products (fMLP, 20.2 ng/10(7) cells; IgG, 17.1 ng/10(7) cells). The data show that neutrophils exposed to agonists at defined cell-surface receptors produce significant quantities of LTB4 only when treated with non-physiological concentrations of arachidonate.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Badwey J. A., Curnutte J. T., Karnovsky M. L. cis-Polyunsaturated fatty acids induce high levels of superoxide production by human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 25;256(24):12640–12643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker E. L., Stossel T. P. Chemotaxis. Fed Proc. 1980 Oct;39(12):2949–2952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgeat P., Fruteau de Laclos B., Picard S., Vallerand P., Sirois P. Double dioxygenation of arachidonic acid in leukocytes by lipoxygenases. Adv Prostaglandin Thromboxane Leukot Res. 1982;9:45–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgeat P., Samuelsson B. Arachidonic acid metabolism in polymorphonuclear leukocytes: effects of ionophore A23187. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2148–2152. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgeat P., Samuelsson B. Transformation of arachidonic acid by rabbit polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Formation of a novel dihydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 25;254(8):2643–2646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claesson H. E., Lundberg U., Malmsten C. Serum-coated zymosan stimulates the synthesis of leukotriene B4 in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Inhibition by cyclic AMP. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Apr 30;99(4):1230–1237. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)90751-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clancy R. M., Dahinden C. A., Hugli T. E. Arachidonate metabolism by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes stimulated by N-formyl-Met-Leu-Phe or complement component C5a is independent of phospholipase activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7200–7204. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craddock P. R., Hammerschmidt D., White J. G., Dalmosso A. P., Jacob H. S. Complement (C5-a)-induced granulocyte aggregation in vitro. A possible mechanism of complement-mediated leukostasis and leukopenia. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jul;60(1):260–264. doi: 10.1172/JCI108763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahinden C. A., Clancy R. M., Gross M., Chiller J. M., Hugli T. E. Leukotriene C4 production by murine mast cells: evidence of a role for extracellular leukotriene A4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6632–6636. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzpatrick F., Haeggström J., Granström E., Samuelsson B. Metabolism of leukotriene A4 by an enzyme in blood plasma: a possible leukotactic mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(17):5425–5429. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.17.5425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goetzl E. J., Pickett W. C. Novel structural determinants of the human neutrophil chemotactic activity of leukotriene B. J Exp Med. 1981 Feb 1;153(2):482–487. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.2.482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman D. W., Goetzl E. J. Specific binding of leukotriene B4 to receptors on human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Immunol. 1982 Oct;129(4):1600–1604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein I. M., Hoffstein S. T., Weissmann G. Mechanisms of lysosomal enzyme release from human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Effects of phorbol myristate acetate. J Cell Biol. 1975 Sep;66(3):647–652. doi: 10.1083/jcb.66.3.647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein I. M., Horn J. K., Kaplan H. B., Weissmann G. Calcium-induced lysozyme secretion from human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Sep 23;60(2):807–812. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90312-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein I. M., Roos D., Kaplan H. B., Weissmann G. Complement and immunoglobulins stimulate superoxide production by human leukocytes independently of phagocytosis. J Clin Invest. 1975 Nov;56(5):1155–1163. doi: 10.1172/JCI108191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hafstrom I., Palmblad J., Malmsten C. L., Rådmark O., Samuelsson B. Leukotriene B4--a stereospecific stimulator for release of lysosomal enzymes from neutrophils. FEBS Lett. 1981 Jul 20;130(1):146–148. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80684-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haines K. A., Giedd K. N., Weissmann G. Leukotriene B4 synthesis and metabolism by neutrophils and granule-free cytoplasts. Biochem J. 1986 Jan 15;233(2):583–588. doi: 10.1042/bj2330583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson A., Serhan C. N., Haeggström J., Ingelman-Sundberg M., Samuelsson B. Activation of protein kinase C by lipoxin A and other eicosanoids. Intracellular action of oxygenation products of arachidonic acid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Feb 13;134(3):1215–1222. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90380-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jubiz W., Rådmark O., Malmsten C., Hansson G., Lindgren J. A., Palmblad J., Udén A. M., Samuelsson B. A novel leukotriene produced by stimulation of leukocytes with formylmethionylleucylphenylalanine. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6106–6110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreisle R. A., Parker C. W. Specific binding of leukotriene B4 to a receptor on human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Exp Med. 1983 Feb 1;157(2):628–641. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.2.628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus A. J., Broekman M. J., Safier L. B., Ullman H. L., Islam N., Sherhan C. N., Rutherford L. E., Korchak H. M., Weissmann G. Formation of leukotrienes and other hydroxy acids during platelet-neutrophil interactions in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Nov 16;109(1):130–137. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91575-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPhail L. C., Clayton C. C., Snyderman R. A potential second messenger role for unsaturated fatty acids: activation of Ca2+-dependent protein kinase. Science. 1984 May 11;224(4649):622–625. doi: 10.1126/science.6231726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naccache P. H., Molski T. F., Borgeat P., Sha'afi R. I. Mechanism of action of leukotriene B4: intracellular calcium redistribution in rabbit neutrophils. J Cell Physiol. 1984 Jan;118(1):13–18. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041180104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flaherty J. T., Hammett M. J., Shewmake T. B., Wykle R. L., Love S. H., McCall C. E., Thomas M. J. Evidence for 5, 12-dihydroxy-6,8,10,14-eicosatetraenoate as a mediator of human neutrophil aggregation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Nov 30;103(2):552–558. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)90487-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. M., Salmon J. A. Release of leukotriene B4 from human neutrophils and its relationship to degranulation induced by N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine, serum-treated zymosan and the ionophore A23187. Immunology. 1983 Sep;50(1):65–73. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell W. S. Rapid extraction of arachidonic acid metabolites from biological samples using octadecylsilyl silica. Methods Enzymol. 1982;86:467–477. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)86218-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouzer C. A., Samuelsson B. On the nature of the 5-lipoxygenase reaction in human leukocytes: enzyme purification and requirement for multiple stimulatory factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6040–6044. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuelsson B. Leukotrienes: mediators of immediate hypersensitivity reactions and inflammation. Science. 1983 May 6;220(4597):568–575. doi: 10.1126/science.6301011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serhan C. N., Lundberg U., Weissmann G., Samuelsson B. Formation of leukotrienes and hydroxy acids by human neutrophils and platelets exposed to monosodium urate. Prostaglandins. 1984 Apr;27(4):563–581. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(84)90092-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serhan C. N., Smolen J. E., Korchak H. M., Weissmann G. Leukotriene B4 is a complete secretagogue in human neutrophils: Ca2+ translocation in liposomes and kinetics of neutrophil activation. Adv Prostaglandin Thromboxane Leukot Res. 1983;11:53–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sha'afi R. I., Naccache P. H., Molski T. F., Borgeat P., Goetzl E. J. Cellular regulatory role of leukotriene B4: its effects on cation homeostasis in rabbit neutrophils. J Cell Physiol. 1981 Sep;108(3):401–408. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041080314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shak S., Goldstein I. M. Omega-oxidation is the major pathway for the catabolism of leukotriene B4 in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 25;259(16):10181–10187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Showell H. J., Freer R. J., Zigmond S. H., Schiffmann E., Aswanikumar S., Corcoran B., Becker E. L. The structure-activity relations of synthetic peptides as chemotactic factors and inducers of lysosomal secretion for neutrophils. J Exp Med. 1976 May 1;143(5):1154–1169. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.5.1154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Showell H. J., Naccache P. H., Borgeat P., Picard S., Vallerand P., Becker E. L., Sha'afi R. I. Characterization of the secretory activity of leukotriene B4 toward rabbit neutrophils. J Immunol. 1982 Feb;128(2):811–816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smolen J. E., Weissmann G. Effects of indomethacin, 5,8,11,14-eicosatetraynoic acid, and p-bromophenacyl bromide on lysosomal enzyme release and superoxide anion generation by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1980 Feb 15;29(4):533–538. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(80)90373-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soberman R. J., Harper T. W., Betteridge D., Lewis R. A., Austen K. F. Characterization and separation of the arachidonic acid 5-lipoxygenase and linoleic acid omega-6 lipoxygenase (arachidonic acid 15-lipoxygenase) of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 10;260(7):4508–4515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun F. F., McGuire J. C. Metabolism of arachidonic acid by human neutrophils. Characterization of the enzymatic reactions that lead to the synthesis of leukotriene B4. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jun 6;794(1):56–64. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(84)90297-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tripp C. S., Mahoney M., Needleman P. Calcium ionophore enables soluble agonists to stimulate macrophage 5-lipoxygenase. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):5895–5898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh C. E., Waite B. M., Thomas M. J., DeChatelet L. R. Release and metabolism of arachidonic acid in human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 25;256(14):7228–7234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. D., Lee T. H., Lewis R. A., Austen F. Intracellular retention of the 5-lipoxygenase pathway product, leukotriene B4, by human neutrophils activated with unopsonized zymosan. J Immunol. 1985 Apr;134(4):2624–2630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wynkoop E. M., Broekman M. J., Korchak H. M., Marcus A. J., Weissmann G. Phospholipid metabolism in human neutrophils activated by N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine. Degranulation is not required for release of arachidonic acid: studies with neutrophils and neutrophil-derived cytoplasts. Biochem J. 1986 Jun 15;236(3):829–837. doi: 10.1042/bj2360829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


