Abstract
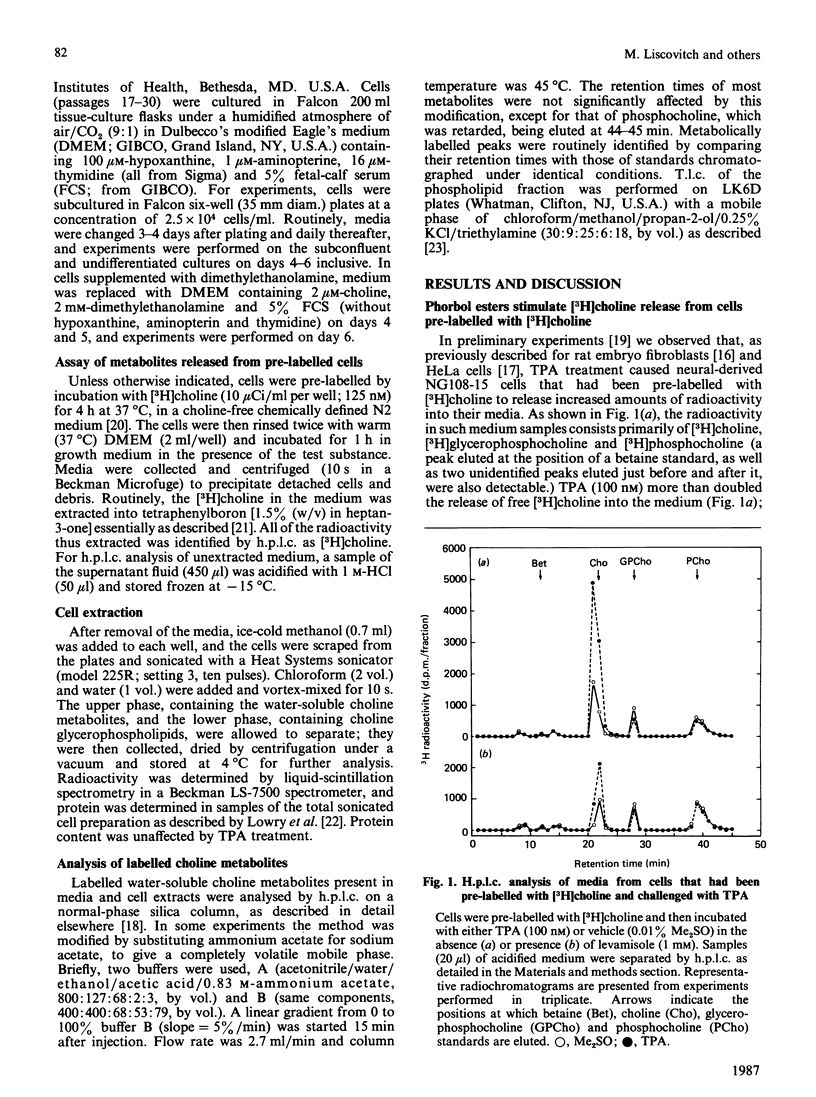
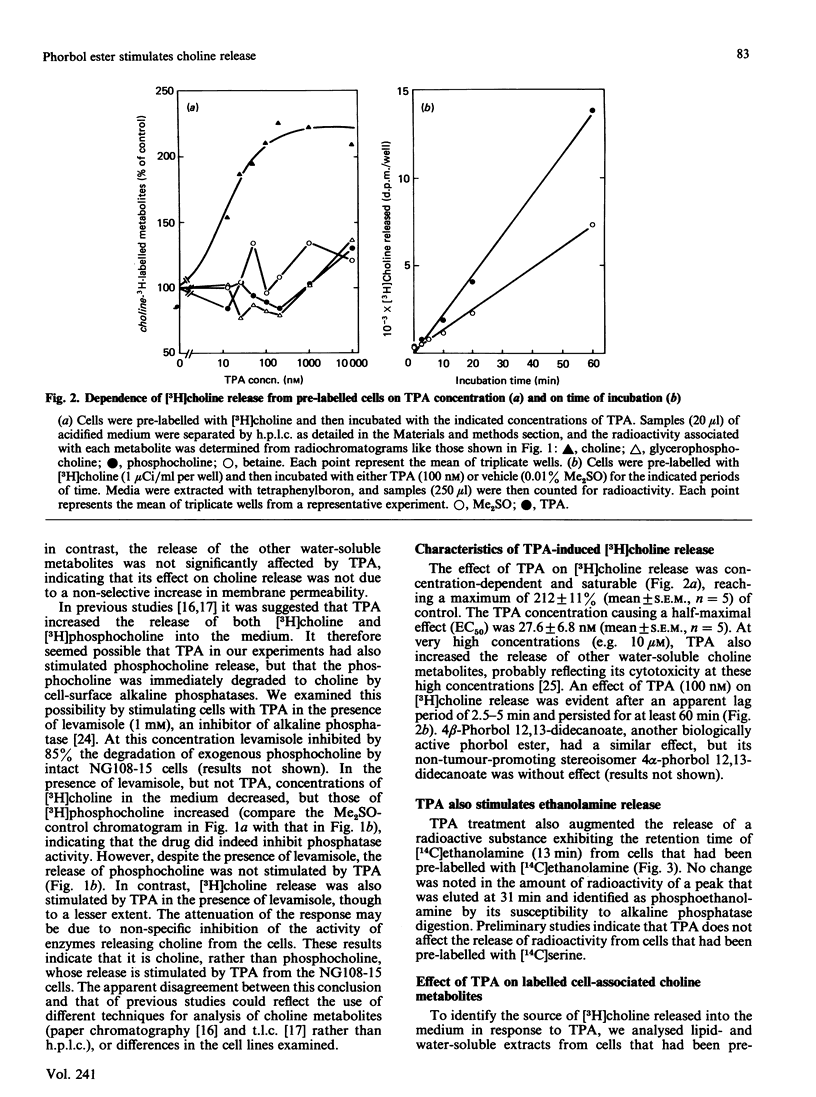
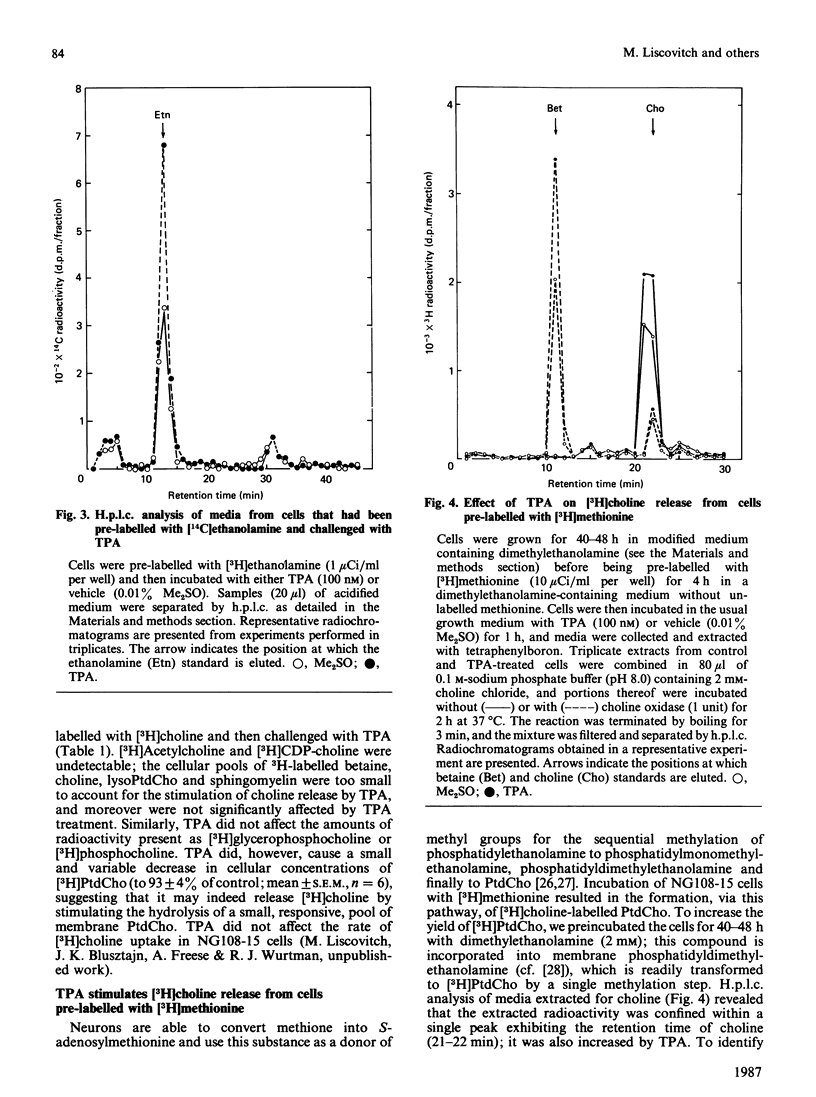
The effects of the potent tumour-promoting phorbol ester 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate (TPA) on phosphatidylcholine (PtdCho) metabolism were investigated in the neuroblastoma X glioma hybrid cell line NG108-15. TPA (100 nM) stimulated by 150-200% the release into the medium of 3H radioactivity from cells that had been pre-labelled with [3H]choline. H.p.l.c. analysis of the medium revealed that TPA stimulated the release of only free [3H]choline (212 +/- 11% of control), without affecting such other labelled metabolites as [3H]phosphocholine and [3H]glycerophosphocholine. This effect was concentration-dependent, with a half-maximal effect obtained at 27.5 +/- 6.8 nM, and was observable as early as 5-10 min after exposure to TPA. The TPA-induced release of [3H]choline into the medium was accompanied by a small and variable decrease in cellular [3H]PtdCho (to 93 +/- 4% of control). However, the radioactivity associated with water-soluble cellular choline metabolites (mainly [3H]phosphocholine and [3H]glycerophosphocholine) remained unchanged. TPA also stimulated the release of [3H]choline derived from [3H]PtdCho that had been produced via the methylation pathway from [3H]methionine. These data suggest that phosphatidylcholine may serve as the source of free choline released from the cells in response to TPA. The possible enzymic mechanisms underlying this response are discussed.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson R. E., Maude M. B., Pu G. A., Hollyfield J. G. Effect of light on the metabolism of lipids in the rat retina. J Neurochem. 1985 Mar;44(3):773–778. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb12882.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blusztajn J. K., Wurtman R. J. Choline biosynthesis by a preparation enriched in synaptosomes from rat brain. Nature. 1981 Apr 2;290(5805):417–418. doi: 10.1038/290417a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blusztajn J. K., Zeisel S. H., Wurtman R. J. Synthesis of lecithin (phosphatidylcholine) from phosphatidylethanolamine in bovine brain. Brain Res. 1979 Dec 28;179(2):319–327. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottenstein J. E., Sato G. H. Growth of a rat neuroblastoma cell line in serum-free supplemented medium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):514–517. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carney D. H., Scott D. L., Gordon E. A., LaBelle E. F. Phosphoinositides in mitogenesis: neomycin inhibits thrombin-stimulated phosphoinositide turnover and initiation of cell proliferation. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):479–488. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90105-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castagna M., Takai Y., Kaibuchi K., Sano K., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Direct activation of calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase by tumor-promoting phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7847–7851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fonnum F. Radiochemical micro assays for the determination of choline acetyltransferase and acetylcholinesterase activities. Biochem J. 1969 Nov;115(3):465–472. doi: 10.1042/bj1150465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy G. R., Murray A. W. Tumor promoter stimulation of phosphatidylcholine turnover in HeLa cells. Cancer Res. 1982 May;42(5):1980–1985. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori H., Kanfer J. N. Synaptosomal phospholipase D potential role in providing choline for acetylcholine synthesis. J Neurochem. 1985 Nov;45(5):1578–1584. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb07229.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinzel V., Kreibich G., Hecker E., Süss R. Stimulation of choline incorporation in cell cultures by phorbol derivatives and its correlation with their irritant and tumor-promoting activity. Cancer Res. 1979 Jul;39(7 Pt 1):2743–2750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreibich G., Hecker E., Süss R., Kinzel V. Phorbol ester stimulates choline incorporation. Naturwissenschaften. 1971 Jun;58(6):323–323. doi: 10.1007/BF00624744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreutter D., Caldwell A. B., Morin M. J. Dissociation of protein kinase C activation from phorbol ester-induced maturation of HL-60 leukemia cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):5979–5984. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liscovitch M., Freese A., Blusztajn J. K., Wurtman R. J. High-performance liquid chromatography of water-soluble choline metabolites. Anal Biochem. 1985 Nov 15;151(1):182–187. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90069-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahadevappa V. G., Holub B. J. Relative degradation of different molecular species of phosphatidylcholine in thrombin-stimulated human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 10;259(15):9369–9373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mozzi R., Porcellati G. Conversion of phosphatidylethanolamine to phosphatidylcholine in rat brain by the methylation pathway. FEBS Lett. 1979 Apr 15;100(2):363–366. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80370-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mufson R. A., Okin E., Weinstein I. B. Phorbol esters stimulate the rapid release of choline from prelabelled cells. Carcinogenesis. 1981;2(11):1095–1102. doi: 10.1093/carcin/2.11.1095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rana R. S., Mertz R. J., Kowluru A., Dixon J. F., Hokin L. E., MacDonald M. J. Evidence for glucose-responsive and -unresponsive pools of phospholipid in pancreatic islets. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 5;260(13):7861–7867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Süss R., Kinzel V., Kreibich G. Cocarcinogenic croton oil factor A1 stimulates lipid synthesis in cell cultures. Experientia. 1971 Jan 15;27(1):46–47. doi: 10.1007/BF02137733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Süss R., Kreibich G., Kinzel V. Phorbol esters as a tool in cell research? Eur J Cancer. 1972 Jun;8(3):299–304. doi: 10.1016/0014-2964(72)90024-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Belle H. Kinetics and inhibition of alkaline phosphatases from canine tissues. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Nov 10;289(1):158–168. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(72)90118-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein I. B. Current concepts and controversies in chemical carcinogenesis. J Supramol Struct Cell Biochem. 1981;17(2):99–120. doi: 10.1002/jsscb.380170202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein I. B., Lee L. S., Fisher P. B., Mufson A., Yamasaki H. Action of phorbol esters in cell culture: mimicry of transformation, altered differentiation, and effects on cell membranes. J Supramol Struct. 1979;12(2):195–208. doi: 10.1002/jss.400120206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto S., Gotoh H., Aizu E., Kato R. Failure of 1-oleoyl-2-acetylglycerol to mimic the cell-differentiating action of 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate in HL-60 cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 15;260(26):14230–14234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yavin E., Zutra A. Translocation and turnover of phospholipid analogs in plasma membrane-derived vesicles from cell cultures. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jun 2;553(3):424–437. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90298-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


