Abstract
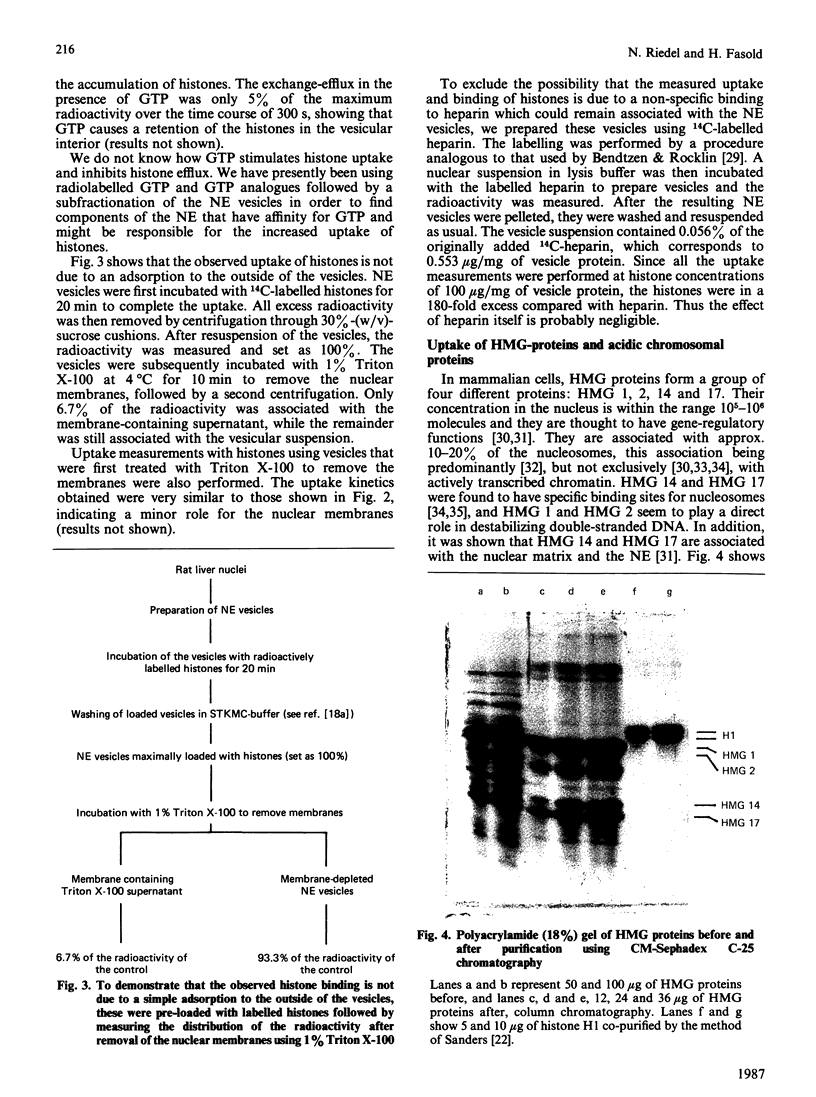
In the preceding paper [Riedel & Fasold (1987) Biochem. J. 241, 203-212] we have described a procedure for the preparation of nuclear-envelope vesicles (NE vesicles) from rat liver nuclei. These vesicles, which are largely free of components of the nuclear interior, were employed in an assay system in vitro to study protein translocation across the NE. We found that nuclear proteins such as histones, high-mobility-group proteins and acidic chromosomal proteins are specifically taken up and accumulated in the NE vesicles, whereas there is little or no affinity for non-nuclear proteins like immunoglobulin, myoglobin and cytochrome c. The kinetics of histone uptake into the NE vesicles are similar to those obtained for whole rat liver nuclei, and comparative studies with non-vesicular NEs prepared by deoxyribonuclease I-treatment (DNAase-NEs) indicate that the NE of the vesicles affects the uptake kinetics and increases the capacity for nuclear proteins. The uptake of histones into NE vesicles, but not the binding to DNAase-NEs, can be stimulated by GTP and GDP. Furthermore, we found that even very large molecules can be entrapped in the vesicles during their preparation. These results indicate that the NE vesicles might provide a useful system in vitro with which to investigate the structures and mechanisms involved in protein translocation across the NE.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AFZELIUS B. A. The ultrastructure of the nuclear membrane of the sea urchin oocyte as studied with the electron microscope. Exp Cell Res. 1955 Feb;8(1):147–158. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(55)90051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendtzen K., Rocklin R. E. Use of benzoyl-L-phenylalanyl-L-valyl-L-arginine (3H) methyl ester as a sensitive and selective substrate for the human lymphokine, leukocyte migration inhibitory factor (LIF). J Immunol. 1980 Oct;125(4):1775–1781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M. Protein migration into nuclei. I. Frog oocyte nuclei in vivo accumulate microinjected histones, allow entry to small proteins, and exclude large proteins. J Cell Biol. 1975 Feb;64(2):421–430. doi: 10.1083/jcb.64.2.421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M. Protein migration into nuclei. II. Frog oocyte nuclei accumulate a class of microinjected oocyte nuclear proteins and exclude a class of microinjected oocyte cytoplasmic proteins. J Cell Biol. 1975 Feb;64(2):431–437. doi: 10.1083/jcb.64.2.431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clawson G. A., James J., Woo C. H., Friend D. S., Moody D., Smuckler E. A. Pertinence of nuclear envelope nucleoside triphosphatase activity to ribonucleic acid transport. Biochemistry. 1980 Jun 10;19(12):2748–2756. doi: 10.1021/bi00553a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clawson G. A., Smuckler E. A. A model for nucleocytoplasmic transport of ribonucleoprotein particles. J Theor Biol. 1982 Apr 21;95(4):607–613. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(82)90344-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox G. S. Discrimination in the uptake of soluble proteins by isolated nuclei. J Cell Sci. 1982 Dec;58:363–384. doi: 10.1242/jcs.58.1.363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dabauvalle M. C., Franke W. W. Karyophilic proteins: polypeptides synthesized in vitro accumulate in the nucleus on microinjection into the cytoplasm of amphibian oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5302–5306. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Robertis E. M., Longthorne R. F., Gurdon J. B. Intracellular migration of nuclear proteins in Xenopus oocytes. Nature. 1978 Mar 16;272(5650):254–256. doi: 10.1038/272254a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C., Sharnick S. V., Laskey R. A. A polypeptide domain that specifies migration of nucleoplasmin into the nucleus. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):449–458. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90242-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dwyer N., Blobel G. A modified procedure for the isolation of a pore complex-lamina fraction from rat liver nuclei. J Cell Biol. 1976 Sep;70(3):581–591. doi: 10.1083/jcb.70.3.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgin S. C., Weintraub H. Chromosomal proteins and chromatin structure. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:725–774. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.003453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FELDHERR C. M. THE EFFECT OF THE ELECTRON-OPAQUE PORE MATERIAL ON EXCHANGES THROUGH THE NUCLEAR ANNULI. J Cell Biol. 1965 Apr;25:43–53. doi: 10.1083/jcb.25.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fawcett D. W. On the occurrence of a fibrous lamina on the inner aspect of the nuclear envelope in certain cells of vertebrates. Am J Anat. 1966 Jul;119(1):129–145. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001190108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldherr C. M., Cohen R. J., Ogburn J. A. Evidence for mediated protein uptake by amphibian oocyte nuclei. J Cell Biol. 1983 May;96(5):1486–1490. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.5.1486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein L., Ko C. Distribution of proteins between nucleus and cytoplasm of Amoeba proteus. J Cell Biol. 1981 Mar;88(3):516–525. doi: 10.1083/jcb.88.3.516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin G. H., Johns E. W. Are the high mobility group non-histone chromosomal proteins associated with 'active' chromatin? Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jun 22;519(1):279–284. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(78)90081-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green N. M. The nuclear pore--a biological grommet? Nature. 1982 May 27;297(5864):287–288. doi: 10.1038/297287a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurdon J. B. Nuclear transplantation and the control of gene activity in animal development. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1970 Dec 1;176(1044):303–314. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1970.0050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall M. N., Hereford L., Herskowitz I. Targeting of E. coli beta-galactosidase to the nucleus in yeast. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):1057–1065. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90055-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz S. B. The permeability of the amphibian oocyte nucleus, in situ. J Cell Biol. 1972 Sep;54(3):609–625. doi: 10.1083/jcb.54.3.609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johns E. W. Studies on histones. 7. Preparative methods for histone fractions from calf thymus. Biochem J. 1964 Jul;92(1):55–59. doi: 10.1042/bj0920055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalderon D., Roberts B. L., Richardson W. D., Smith A. E. A short amino acid sequence able to specify nuclear location. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):499–509. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90457-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kletzien R. F. Nucleocytoplasmic transport of RNA. The effect of 3'-deoxyadenosine triphosphate on RNA release from isolated nuclei. Biochem J. 1980 Nov 15;192(2):753–759. doi: 10.1042/bj1920753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondor-Koch C., Riedel N., Valentin R., Fasold H., Fischer H. Characterization of an ATPase on the inside of rat-liver nuclear envelopes by affinity labeling. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Oct;127(2):285–289. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06868.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mardian J. K., Paton A. E., Bunick G. J., Olins D. E. Nucleosome cores have two specific binding sites for nonhistone chromosomal proteins HMG 14 and HMG 17. Science. 1980 Sep 26;209(4464):1534–1536. doi: 10.1126/science.7433974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W., De Robertis E. M. Nuclear segregation of U2 snRNA requires binding of specific snRNP proteins. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):111–118. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90314-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moffett R. B., Webb T. E. Regulated transport of messenger ribonucleic acid from isolated liver nuclei by nucleic acid binding proteins. Biochemistry. 1981 May 26;20(11):3253–3262. doi: 10.1021/bi00514a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paine P. L., Feldherr C. M. Nucleocytoplasmic exchange of macromolecules. Exp Cell Res. 1972 Sep;74(1):81–98. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(72)90483-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paine P. L., Moore L. C., Horowitz S. B. Nuclear envelope permeability. Nature. 1975 Mar 13;254(5496):109–114. doi: 10.1038/254109a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paine P. L. Nucleocytoplasmic movement of fluorescent tracers microinjected into living salivary gland cells. J Cell Biol. 1975 Sep;66(3):652–657. doi: 10.1083/jcb.66.3.652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palayoor T., Schumm D. E., Webb T. E. Transport of functional messenger RNA from liver nuclei in a reconstituted cell-free system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jul 27;654(2):201–210. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(81)90173-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabbani A., Goodwin G. H., Johns E. W. High mobility group non-histone chromosomal proteins from chicken erythrocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Mar 30;81(2):351–358. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91540-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves R., Chang D. Investigations of the possible functions for glycosylation in the high mobility group proteins. Evidence for a role in nuclear matrix association. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):679–687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson W. D., Roberts B. L., Smith A. E. Nuclear location signals in polyoma virus large-T. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):77–85. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90486-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riedel N., Fasold H. Preparation and characterization of nuclear-envelope vesicles from rat liver nuclei. Biochem J. 1987 Jan 1;241(1):203–212. doi: 10.1042/bj2410203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders C. A method for the fractionation of the high-mobility-group non-histome chromosomal proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Oct 10;78(3):1034–1042. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90525-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger J. W., Sanger J. M., Kreis T. E., Jockusch B. M. Reversible translocation of cytoplasmic actin into the nucleus caused by dimethyl sulfoxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5268–5272. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumm D. E., Webb T. E. Insulin-modulated transport of RNA from isolated live nuclei. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Aug;210(1):275–279. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90190-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelton K. R., Egle P. M., Cochran D. L. Nuclear envelope proteins: identification of lamin B subtypes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Dec 15;103(3):975–981. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)90905-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver P. A., Keegan L. P., Ptashne M. Amino terminus of the yeast GAL4 gene product is sufficient for nuclear localization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):5951–5955. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.5951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spelsberg T. C., Hnilica L. S. Proteins of chromatin in template restriction. I. RNA synthesis in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jan 1;228(1):202–211. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(71)90560-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uberbacher E. C., Mardian J. K., Rossi R. M., Olins D. E., Bunick G. J. Neutron scattering studies and modeling of high mobility group 14 core nucleosome complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5258–5262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unwin P. N., Milligan R. A. A large particle associated with the perimeter of the nuclear pore complex. J Cell Biol. 1982 Apr;93(1):63–75. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.1.63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisbrod S. T. Properties of active nucleosomes as revealed by HMG 14 and 17 chromatography. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Mar 25;10(6):2017–2042. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.6.2017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson E. M., Spelsberg T. C. Methods for isolation and characterization of acidic chromatin proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1975;40:171–176. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(75)40015-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




