FIGURE 3.
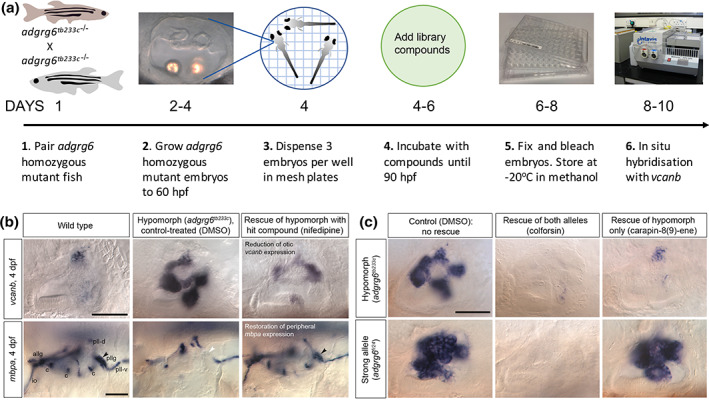
Design and proof‐of‐principle for a whole‐animal compound screen to identify agonists of the zebrafish Adgrg6 pathway. (a) Overview of screen pipeline. Batches of 100% homozygous embryos are dispensed into 96‐well plates, with three embryos (biological replicates) per well. Embryos are incubated in control and test compounds from a library of choice at an optimum time for rescue of the mutant phenotype. Effects of compounds on gene expression are measured by semi‐automated in situ hybridisation. (b) Example results from a two‐part in situ hybridization screen using the hypomorphic (adgrg6 tb233c−/− ) alelle. Here, an example hit compound (nifedipine, a dihydropyridine) reduces vcanb expression in the ear (top panels) and restores mpba expression in Schwann cells of the lateral line nerves in the vicinity of the ear. Several areas of mbpa expression are rescued, in particular that associated with the posterior lateral line ganglion (pllg, arrowhead). Lateral views; anterior to the left, dorsal to the top. Abbreviations: allg, anterior lateral line ganglion; c, expression associated with the sensory cristae of the ear; DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide; dpf, days post fertilization; io, infraorbital ramus of the anterior lateral line nerve; pll‐d, pll‐v, dorsal and ventral rami of the posterior lateral line nerve; pllg, posterior lateral line ganglion. Scale bars, 50 μm (top row); 50 μm (bottom row). (c) Use of hypomorphic and strong alleles to differentiate hit compound classes in the vcanb expression assay. Effects of example compounds are shown. Colforsin, a forskolin derivative, rescues both alleles efficiently, and is likely to act downstream of the pathway to raise cAMP levels. Carapin‐8(9)‐ene rescues the hypomorph, but has no effect on the stronger fr24 allele. Compounds such as this may interact directly with the Adgrg6 receptor. Scale bar, 50 μm. Images reproduced from Diamantopoulou et al., 2019
