Abstract
Background
Published data on whether post-stroke delirium (PSD) is an independent predictor of outcomes in patients with acute stroke are inconsistent and have not yet been synthesized and quantified via meta-analyses.
Methods
This systematic review and meta-analysis followed the Meta-analysis of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (MOOSE) and Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA) guidelines. The study protocol involved a search of the PubMed, Embase, PsycINFO, and Medline databases from 1946 to November 1, 2023, of which prospective observational and case–control studies were included. The quality of the included studies was rated using the Newcastle Ottawa Scale. Pooled effect estimates calculated using a random-effects model were expressed as the odds ratios (ORs), hazard ratios (HRs), and standardized mean differences (SMDs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs). The protocol was registered in PROSPERO (CRD42023472551).
Results
The search yielded 39 eligible articles comprising 3295 and 9643 patients with and without PSD, respectively. Thirty studies were high quality, while 9 had moderate quality. The primary analyses, adequately adjusting for predefined confounders, showed that PSD was significantly associated with mortality risk (average follow-up of 19.50 months; OR, 3.47; 95% CI, 2.35–5.12; I2, 26.0%) and poor neurological function (average follow-up of 21.75 months; OR, 3.62; 95% CI, 2.15–6.09; I2, 0). Secondary analyses, with or without inadequate adjustment, showed that PSD was significantly associated with prolonged hospital length of stay, increased risk of institutionalization, poor cognitive outcomes, and quality of life after discharge.
Conclusions
This systematic review and meta-analysis provides evidence that PSD was independently associated with mortality and poor neurological function after controlling for pre-specified confounders. The prevention of PSD remains a high clinical and research priority.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1186/s12916-024-03689-1.
Keywords: Delirium, Post-stroke, Outcomes, Meta-analysis
Background
Delirium, a neuropsychiatric syndrome characterized by acute and fluctuating disturbances in consciousness and cognition, is the most common complication in elderly hospitalized patients [1, 2]. Numerous studies have shown that delirium is associated with increased morbidity and mortality, placing a considerable burden on healthcare services and expenditures [3, 4].
Delirium is usually associated with acute physical stressors, such as acute stroke [5]. Previous meta-analyses have shown that post-stroke delirium (PSD) affects approximately 25% of acute stroke patients [6] and is associated with higher mortality, longer hospitalization, and dependency post-discharge [7]. However, the potential fragility of PSD-outcomes association may depend on the choice of confounders included in adjusted models [3, 4]. To date, no meta-analyses have yet examined whether PSD is an independent predictor of adverse outcomes. Further, while functional and cognitive outcomes, as well as quality of life in patients with PSD, have attracted increasing attention [7], quantitative estimates of the associations between PSD and these outcomes have not yet been synthesized via meta-analysis.
These above-mentioned issues preclude drawing reliable conclusions regarding the prognosis of PSD, which may allow clinicians, policymakers, and researchers to pay more attention to PSD. Therefore, in the present study, we systematically reviewed and summarized data on the risk of various outcomes (mortality, length of stay [LOS], institutionalization, functional and cognitive outcomes, and quality of life) after delirium in acute stroke patients. Our primary objective was to explore the association between PSD and adverse outcomes, while controlling for important confounders.
Methods
Data sources and study selection
This study followed the Meta-analysis of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (MOOSE) [8] (Additional file 1) and the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses (PRISMA) [9] (Additional file 2) reporting guidelines for systematic reviews and meta-analyses. The protocol has been registered in PROSPERO (CRD42023472551) [10].
The following databases were searched for eligible studies: PubMed from 2006 to 2023, Embase from 1988 to 2023, PsycINFO from 1968 to 2023, and Medline from 1946 to 2023. The search keywords for delirium were combined with stroke-specific and outcome keywords (Additional file 3: eAppendix 1). The primary study outcome was the association between PSD and various outcomes (mortality, hospital LoS, institutionalization, functional outcomes, cognitive outcomes, and QoL) after adequate adjustment for important confounders during the follow-up period. The secondary outcome was the association between PSD and each outcome based on inadequate adjustment and non-adjustment.
Research articles examining the outcome of delirium in patients with acute stroke were included if they met the following criteria: (1) prospective observational cohort studies of acute stroke patients aged 18 years or older, and (2) studies using a definition of stroke based on the World Health Organization definition, including ischemic, hemorrhagic, transient ischemic attack, or subarachnoid hemorrhage [11]. Acute stroke was defined as the period from ictus to 6 weeks post-event [6]; (3) delirium was prospectively identified using any edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) [12] or the diagnostic tool validated against DSM, e.g., confusion assessment method (CAM) [13], confusion assessment method for the intensive care unit (CAM-ICU) [14], and intensive care delirium screening checklist (ICDSC) [15], Delirium Rating Scale (DRS) [16], DRS-R-98 [17], Delirium Observation Screening (DOS) [18], and 4A’s Test (4AT) [19]; (4) at least one of the following outcomes was reported: mortality, hospital LoS, institutionalization, neurological functional outcome, cognitive outcome and quality of life. Specifically, institutionalization was defined as admission to a care or nursing home following hospital discharge; neurological functional outcome was required to be measured after hospital discharge by the modified Rankin Scale score (mRS) [20]; the cognitive outcome was required to be measured after hospital discharge using validated cognition assessment scales, such as the Mini-Metal State Examination (MMSE) [21] or the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) [22] score; and the quality of life was required to be measured using validated scales, such as the Barthel Index (BI) [23], the Functional Independence Measure (FIM) [24], and the Instrumental Activities of Daily Living (ADL) Scale [25]. (5) The manuscript was written in English. The exclusion criteria were: studies with designs other than case–control, case studies or case series, studies without available raw data, and duplicate publications.
Data extraction
Three reviewers (H. W. H., J. M. L., and W. J. Y.) independently extracted data from each study. Initial data extraction was performed on 1 November 2023. The following information was recorded: study characteristics (country, publication year, setting, sample size, and delirium assessment tools), patient characteristics (age, sex, stroke subtype, stroke severity, comorbidity, baseline cognitive impairment, and baseline institutionalization), and any reported endpoints. For longitudinal studies, data from the last follow-up for each outcome were selected for our analysis. Disagreements were resolved through discussion with the corresponding author (G. B. Z.).
Quality assessment
The quality of the included studies was rated using the modified Newcastle–Ottawa Scale [26] (Additional file 3: eAppendix 2 and 3), which contains separate quality assessment instruments for cohort studies [27] (Additional file 3: eAppendix 2)and case–control(Additional file 3: eAppendix 3). The NOS comprises three sections: study population selection, comparability, and outcome measures. A maximum of nine scores was awarded to each study: four for selection, three for outcome, and two for comparability. The specific items and their scores are detailed in Additional file 3: eAppendix 2. Points were scored for each “yes” answer. Given the sum of the scores for each individual item, studies with a score of 7–9 points were classified as high quality, studies with scores of 3–5 points were classified as moderate quality, and studies with scores of less than 2 were classified as low quality.
Statistical analysis
All statistical analyses were conducted using the Comprehensive Meta-Analysis software (version 3.0). Dichotomous variables are presented as percentages, while continuous variables are presented as means with standard deviations. We determined the association between different outcome measures and PSD using pooled odds ratios (ORs), hazard ratios (HRs), and pooled standardized mean differences (SMD) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs). In keeping with previous studies [3, 4], our primary analysis included only studies adjusted for age and comorbidity. Given that the severity of stroke has been reported to be a predictor of post-stroke outcomes and PSD [6, 28], it was also included in our list of required adjusted variables for primary analysis. Control for confounding factors was determined to be inadequate if the aforementioned key variables were not included in the final adjusted model [29, 30]. Therefore, we further conducted secondary and tertiary analyses, in which we included estimates of associations that were inadequately adjusted and unadjusted. A random-effects meta-analysis was performed when two or more studies were pooled. Heterogeneity was measured using the chi-squared Cochran’s Q-test and I2 statistics; I2 > 50% indicated significant heterogeneity [31]. We further conducted a meta-regression to explore whether the a priori defined covariates explained the source of heterogeneity. Subgroup analyses were performed for stroke subtypes (Table 1). Publication bias was assessed by inspecting funnel plots, Egger’s test, and Duval and Tweedie’s trim-and-fill method [32]. Sensitivity analyses were performed to examine: (1) whether the pooled estimates between PSD and mortality were more conservative after excluding studies that reported hospitalized mortality, (2) whether the strength of the association between PSD and hospital LoS was affected after excluding studies that involved incident cases of ICU admission, (3) whether the association between PSD and institutionalization was affected after excluding studies that included incident cases who had resided in an institution at baseline, and (4) whether the association between PSD and cognitive outcome was affected after excluding studies that included patients with cognitive impairment at baseline. Outliers were identified if the CI did not overlap with that of the pooled effect [33]. All tests were 2-sided. Statistical significance was set at P < 0.05.
Table 1.
Unadjusted meta-analysis of outcomes for post-stroke delirium
| Outcomes | No. of studies | Pooled effect size (95% CI) | p-value | Q-value, p-value, I2 (%) | p-value for Egger’s regression |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mortality | |||||
| Main analysis, OR | 26 | 4.69 (3.55 to 6.20) | < 0.001 | 65.47, < 0.001, 61.82 | 0.82 |
| Subgroup analyses | |||||
| ICH | 1 | 29.67 (7.19 to 1222.33) | < 0.001 | 0.00, 1.000, 0.00 | |
| IS | 5 | 5.45 (4.39 to 6.77) | < 0.001 | 2.41, 0.661, 0.00 | |
| LOS | |||||
| Main analysis, SMD | 20 | 1.21 (0.54 to 1.89) * | < 0.001 | 1588.27, < 0.001, 98.81 | < 0.001 |
| Subgroup analyses | |||||
| ICH | 2 | 2.56 (2.16 to 2.97) | < 0.001 | 2.20, 0.13, 54.61 | |
| IS | 5 | 0.69 (− 0.03 to 1.43) | 0.06 | 118.65, < 0.001, 96.62 | |
| Institutionalization | |||||
| Main analysis, OR | 11 | 4.14 (2.68 to 6.38) | < 0.001 | 60.75, < 0.001, 83.53 | 0.34 |
| Subgroup analyses | |||||
| ICH | 1 | 27.04 (6.55 to 111.63) | < 0.001 | 0.00, 1.000, 0.00 | |
| IS | 2 | 1.59 (1.16 to 2.16) | 0.003 | 1.39, 0.23, 28.34 | |
| Cognitive decline | |||||
| Main analysis | |||||
| Dichotomized, OR | 5 | 5.68 (3.24 to 9.93) | < 0.001 | 10.76, 0.096, 44.23 | 0.79 |
| Continuous, SMD | 4 | − 2.43 (− 3.92 to 0.93) | 0.001 | 73.21, < 0.001, 95.90 | 0.14 |
| Dementia | |||||
| Main analysis, OR | 4 | 4.74 (2.08 to 10.79) | < 0.001 | 6.80, 0.078, 55.89 | 0.82 |
| Neurological functional outcomes | |||||
| Main analysis | |||||
| Dichotomized, OR | 7 | 8.13 (5.74 to 11.50) | < 0.001 | 10.97, 0.089, 45.34 | 0.49 |
| Continuous, SMD | 10 | 3.36 (1.57 to 5.15) | < 0.001 | 2136.14, < 0.001, 99.58 | 0.40 |
| Subgroup analyses | |||||
| ICH | 2 | 5.34 (2.05 to 12.75) | 0.157 | 415.78, < 0.001, 99.75 | |
| IS | 4 | 2.23 (0.60 to 5.08) | 0.123 | 903.77, < 0.001, 99.66 | |
| Poor quality of life | |||||
| Dichotomized, OR | 1 | 4.97 (2.26 to 10.94) | < 0.001 | - | - |
| Continuous, SMD | 8 | -2.56 (-4.44 to 0.68) | 0.007 | 1068.74, < 0.001, 99.34 | 0.46 |
Boldface type indicates statistical significance with two-sided p < 0.05
*Pooled effect size was adjusted by the trim-and-filled method
Abbreviations: CI confidence interval, LOS length of stay, OR odds ratio, SMD standardized mean difference, ICH intracerebral hemorrhage, IS ischemic stroke
Results
Study selection and study characteristics
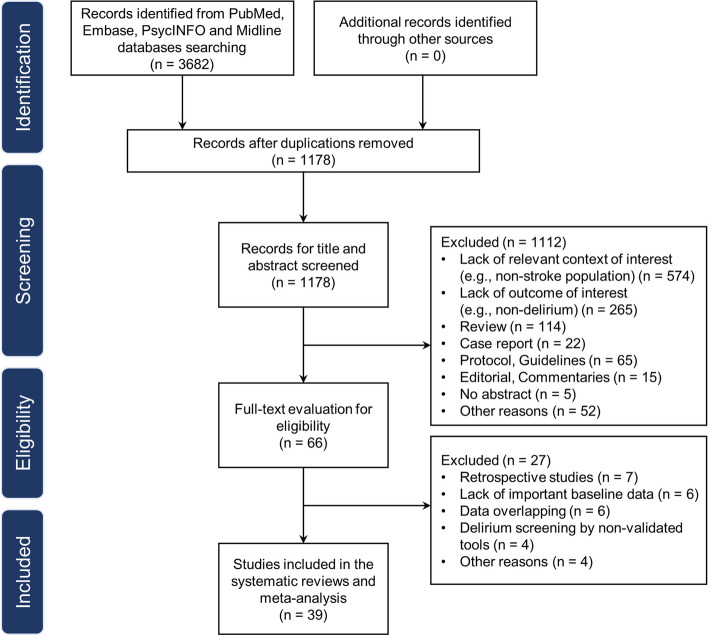
Initially, 3682 articles were identified through the primary search. Following the removal of duplicate articles, 1178 articles were reviewed in the title and abstract screening stage. Subsequently, 66 articles underwent full-text screening, of which 27 were excluded as they were deemed ineligible for inclusion. Ultimately, 39 studies were eligible for inclusion in the analysis (Fig. 1) [34–72]. The main characteristics of the selected studies are summarized in Table 2. There were 35 prospective cohort [34–42, 44–69] and 4 case–control studies [43, 70–72]. The sample size ranged from 50 to 1487. The follow-up period ranged from hospital discharge to 5 years.
Fig. 1.
PRISMA flowchart of the study
Table 2.
Characteristics of included studies
| Author | Country | Setting | Center | Stroke type | Total sample, n | Delirium cases, n | Average age, mean (SD) |
Gender (M/F) | Delirium assessment | Quality assessment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gustafson et al., 1991 | Sweden | Stroke Unit | Single | Acute IS or ICH | 145 | 69 | 73.0 (10.2) | 90/55 | DSM-III | 5 |
| Henon et al., 1999 | France | Stroke Unit | Single | Acute IS or ICH | 202 | 49 | 75.0 (10.7) | 97/105 | DSM-IV | 8 |
| Caeiro et al., 2004 | Portugal | Stroke Unit | Single | All stroke | 218 | 29 | NA | 130/88 | DSM-IV/DRS | 5 |
| Sheng et al., 2006 | Australia | Stroke Unit | Single | Acute IS or ICH | 156 | 39 | 79.2 (6.7) | 83/73 | DSM-IV | 8 |
| Dostovic et al., 2009 | Bosnia and Herzegovina | Neurology | Single | Acute IS or ICH and SAH | 233 | 59 | NA | NA | DSM-IV/DRS-98 | 5 |
| Manus et al., 2009 | UK | Stroke Unit | Single | Acute IS or ICH excluding SAH | 82 | 23 | 66.4 (15.9) | 51/31 | DSM-III/CAM | 7 |
| Dahl MH, 2010 | Norway | Stroke Unit | Single | All stroke | 178 | 18 | 73.0 | 102/76 | DSM-IV/CAM | 7 |
| Mcmanus et al., 2011 | UK | Stroke Unit | Single | Acute IS or ICH excluding SAH | 82 | 23 | 66.4 (15.9) | 51/31 | DSM-III/CAM | 9 |
| Rijsbergen et al., 2011 | Netherlands | Stroke Unit | Multi-center | Acute IS or ICH excluding SAH | 122 | 61 | 75.1 (10.7) | 29/21 | CAM | 9 |
| Oldenbeuving et al., 2011 | Netherlands | Stroke Unit | Multi-center | Acute IS or ICH excluding SAH and TIA | 527 | 62 | 72 (11.2) | 288/239 | CAM/DRS | 9 |
| Miu et al., 2012 | China | Stroke Unit | Single | Acute IS excluding TIA or ICH | 314 | 86 | 72.9 (10.3) | 163/151 | DSM-III/CAM | 8 |
| Melkas et al., 2012 | Finland | Helsinki Stroke Aging Memory Cohort | Single | Acute IS | 263 | 50 | 70.8 (7.4) | 135/128 | DSM-IV | 9 |
| Mitasova et al., 2012 | Czech Republic | Stroke Unit | Single | Acute IS excluding TIA or ICH excluding SAH | 129 | 55 | 71.2 (11.5) | 72/57 |
DSM-IV/ CAM-ICU |
8 |
| Naidech et al., 2013 | USA |
ICU and Stroke Unit |
Single | Acute ICH | 114 | 31 | 62.4 (13.8) | 62/52 |
DSM-IV/ CAM-ICU |
8 |
| Kozak et al., 2016 | Turkey | Stroke Unit | Single | Acute IS excluding TIA | 60 | 11 | 66.2 (12.5) | 29/31 | DSM-IV/DRS | 6 |
| Chan et al., 2017 | Australia | Stroke Unit | Single | Acute IS excluding TIA or ICH excluding SAH | 156 | 39 | 79.2 (6.7) | 83/73 | DSM-IV | 8 |
| Rosenthal et al., 2017 | USA | Neuro/Spine ICU | Single | Acute ICH | 174 | 53 | 63.5 | 92/82 | CAM-ICU | 7 |
| Lim et al., 2017 | Korea | Stroke Unit | Single | Acute IS | 576 | 38 | 65.2 (11.7) | 368/208 |
CAM/ DRS-R-98 |
8 |
| Nydahl et al., 2017 | Germany | Stroke Unit | Single | Acute IS and ICH including TIA | 309 | 33 | 73.4 (4.7) | NA | CAM | 8 |
| Ojagbemi et al., 2017 | Nigeria | Neurology Department | Single | Acute IS or ICH | 99 | 33 | 61.1 (12.9) | 52/47 | CAM/DRS | 7 |
| Qu et al., 2018 | China | Neurology Department | Single | Acute IS | 261 | 38 | 61.3 (12.0) | 184/77 | CAM/DRS | 8 |
| Dostovic et al., 2018 | Bosnia and Herzegovina | Neurology Department | Single | Acute IS or ICH | 200 | 100 | NA | NA | DSM-IV/DRS-98 | 7 |
| Kotfis et al., 2019 | Poland | Stroke Unit | Single | Acute IS | 760 | 121 | 71.6 (12.5) | 393/367 | DSM-V/CAM-ICU | 8 |
| Kotfis et al., 2019 | Poland | Neurology Department | Single | Acute IS | 1001 | 172 | 71.0 (3.0) | 523/478 |
DSM-V/ CAM-ICU |
8 |
| Zipser et al., 2019 | Switzerland | Neurology Department | Single | All stroke | 1487 | 356 | 71.2 (13.3) | 836/651 | DSM-V/DOS | 5 |
| Pasinska et al., 2019 | Poland | Stroke Unit | Single | Acute IS or ICH including TIA | 750 | 203 | 71.8 (13.1) | 352/398 | DSM-V/CAM/CAM-ICU | 9 |
| Zaitoun et al., 2019 | Egypt | ICU, Stroke Unit and Neurology | Single | All stroke excluding TIA | 74 | 15 | 60.7 (11.5) | 40/34 | DSM-IV | 7 |
| Aizen et al., 2019 | Israel | Rehabilitation | Single | All stroke | 110 | 30 | 80.2 (8.0) | 53/57 |
CAM/ DRS-R-98 |
6 |
| Kowalska et al., 2020 | Poland | Stroke Unit | Single | Acute IS or ICH including TIA | 750 | 203 | 71.8 (13.1) | 352/398 | DSM-V/CAM/CAM-ICU | 8 |
| Reznik et al., 2021 | USA | Neurocritical Care and Stroke Unit | Single | Acute ICH | 590 | 348 | 70.5 (15.5) | 309/281 | DSM-V | 9 |
| Zipser et al., 2021 | Switzerland | Neurology Department | Single | All stroke | 567 | 221 | 72.3 (4.2) | 331/236 | DSM-V/DOS | 9 |
| Silva et al., 2021 | Brazil | Stroke Unit | Single | Acute IS or ICH | 227 | 71 | 62.5 (13.5) | 121/106 | CAM-ICU | 9 |
| Czyzycki et al., 2021 | Poland | Neurology Department | Single | Acute IS or ICH including TIA | 688 | 169 | 72.4 (5.1) | 318/370 | CAM/CAM-ICU/DSM-V/DRS-R-98 | 8 |
| Stokholm et al., 2021 | Denmark | Neurology Department | Single | Acute IS | 64 | 8 | 70 (9.8) | 42/22 | CAM | 5 |
| Dostovic et al., 2021 | Croatia | Neurology Department | Single | Acute IS or ICH | 200 | 100 | NA | NA | DRS-R-98 | 6 |
| Mansutti et al., 2022 | Italy | Stroke Unit | Multi-center | Acute IS or ICH | 78 | 27 | 73.1 (11.5) | 46/32 | 4AT | 5 |
| Rollo et al.,2022 | Italy | Stroke Unit | Single | Acute IS or ICH | 103 | 36 | 75 (3.0) | 62/41 | RASS / CAM-ICU | 8 |
| Nerdal et al., 2022 | Norway | Stroke Unit | Multi-center | Acute IS or ICH | 139 | 13 | 71.4 (13.4) | 73/68 | CAM | 8 |
| Droś et al., 2023 | Poland | Stroke Unit | Single | Acute IS or ICH including TIA | 750 | 203 | 74 (3.16) | 352/398 | bCAM/CAM-ICU/DSM-V | 9 |
Abbreviations: 4AT 4 A’s Test, bCAM abbreviated version of the Confusion Assessment Method, CAM Confusion Assessment Method, CAM-ICU Confusion Assessment Method of the Intensive Care Unit, CAM-S Confusion Assessment Method of Severity, DOS Delirium Observation Screening, DRS Delirium Rating Scale, DSM Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, ICH intracranial cerebral hemorrhage, ICU Intensive Care Unit, IS ischemic stroke, NA not available, RASS Richmond Agitation Sedation Scale, SAH subarachnoid hemorrhage, TIA transient ischemic attack, USA United States of America, UK United Kingdom
The studies included 3295 (25.5%) patients with PSD and 9643 patients without PSD. For PSD screening, 16 studies [39–42, 46, 48, 51–53, 57, 58, 62, 64, 65, 70] used the CAM, 11 [45, 47, 50, 54, 55, 57, 58, 61, 62, 67, 69] used the CAM-ICU, while 25 [34–41, 44–49, 54–60, 62, 63, 69, 71] used DSM. Ten studies [41, 42, 47, 57, 59–62, 67, 69] used multivariate approaches to adjust for the association between PSD and the outcomes. Three studies provided separate data on the risk of hemorrhagic stroke [47, 50, 59], 8 provided separate risk data for ischemic stroke[44, 49, 51, 53–55, 62, 65], and 28 provided risk data for hemorrhagic and ischemic stroke[34–43, 45, 46, 48, 52, 56–58, 60, 61, 63, 64, 66–72].
Quality assessment
According to the NOS score, 31 studies [35, 37, 39–48, 50–55, 57–63, 67–72] were rated as high-quality and eight [34, 36, 38, 49, 56, 64–66] as moderate-quality (Additional file 3: Table S1). Of the 35 cohort studies, the majority were observational cohort studies (n = 27) considered to have an overall high quality [73], while the remaining cohort studies (n = 8) were only of moderate quality [34, 36, 38, 49, 56, 64–66] due to controlling for insufficient covariates [34, 36, 38, 49, 56, 64–66], experiencing more than 20% loss to follow-up [34, 36, 38, 49, 56, 64–66], inadequate follow-up [34, 36, 38, 49, 56, 65, 66], and insufficient follow-up length to allow outcomes to occur [34, 36, 38, 56, 64–66]. The four case–control studies were of high quality [43, 70–72].
Mortality
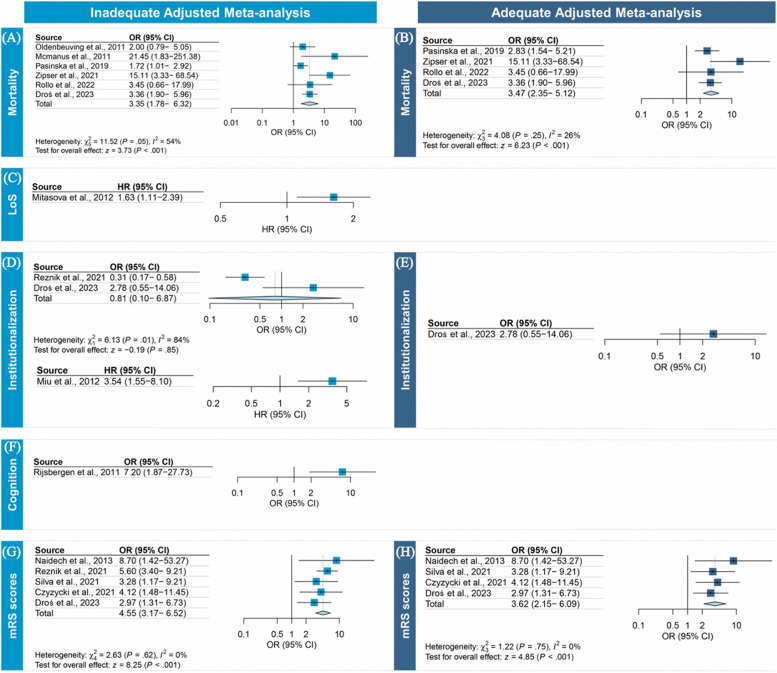
Twenty-six studies (n = 10,421) [34, 35, 37–39, 42, 43, 45, 46, 48, 51, 53–55, 70, 71] examined the association between PSD and mortality. Four studies (n = 2187) [57, 60, 67, 69] were included in the primary analysis, and 30.1% (n = 663) of the patients developed PSD. The overall adequately adjusted ORs showed a significant association between PSD and mortality following a mean (SD) follow-up of 19.50 (27.30) months (range, 3–60 months) (OR, 3.47 [95% CI, 2.35–5.12]; I2, 26.0%) (Fig. 2B). No publication bias (Additional file 3: Fig. S1) or outliers were identified.
Fig. 2.
Forest plots of the associations of post-stroke delirium with outcomes
The secondary analysis of inadequately adjusted ORs included 6 studies [41, 42, 57, 60, 67, 69], with results indicating that PSD was associated with a threefold increase in the odds of mortality (OR, 3.35 [95% CI, 1.78–6.32]; I2, 54.0%) after a mean (SD) follow-up of 17.16 (22.67) months (range, 1–60 months). Significant publication bias was observed using the Egger test (P = 0.030), and the trim-and-filled method simulated 1 missing study (OR, 2.92 [95% CI, 1.51–5.64]) (Additional file 3: Fig. S1). No outliers were identified.
The tertiary analysis included 26 studies [34, 35, 37–39, 42, 43, 45, 46, 48, 51, 53–55, 70, 71], and yielded results showing that the overall unadjusted OR for mortality in patients with PSD was 4.69 (OR, 4.69 [95% CI, 3.55–6.20]; I2, 61.8%) after a mean (SD) follow-up of 11.09 (12.93) months (range, 1–60 months) (Table 3). No publication bias was detected (Additional file 3: Fig. S1). We identified 3 outlier studies [35, 57, 59], and the significant association was retained after removing studies with reduced heterogeneity (I2, 34.2%) (Additional file 3: Table S3). Meta-regression analysis showed that the stroke type and follow-up duration accounted for 16% of the heterogeneity (Table 4). We conducted subgroup analysis based on stroke types and observed that both delirium after ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke (OR, 5.45; 95% CI, 4.39–6.77, P < 0.001 vs OR, 29.67; 95% CI, 7.19–122.33) were significantly associated with mortality (Table 3). Finally, we conducted sensitivity analyses, which showed that the direction and strength of the results of all ORs remained the same when excluding the studies which reported hospitalized mortality (Additional file 3: Table S5).
Table 3.
Unadjusted meta-analysis of outcomes for post-stroke delirium
| Outcomes | No. of studies | Pooled effect size (95% CI) | p-value | Q-value, p-value, I2 (%) | p-value for Egger’s regression |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mortality | |||||
| Main analysis, OR | 26 | 4.69 (3.55 to 6.20) | < 0.001 | 65.47, < 0.001, 61.82 | 0.82 |
| Subgroup analyses | |||||
| ICH | 1 | 29.67 (7.19 to 1222.33) | < 0.001 | 0.00, 1.000, 0.00 | |
| IS | 5 | 5.45 (4.39 to 6.77) | < 0.001 | 2.41, 0.661, 0.00 | |
| LOS | |||||
| Main analysis, SMD | 20 | 1.21 (0.54 to 1.89)* | < 0.001 | 1588.27, < 0.001, 98.81 | < 0.001 |
| Subgroup analyses | |||||
| ICH | 2 | 2.56 (2.16 to 2.97) | < 0.001 | 2.20, 0.13, 54.61 | |
| IS | 5 | 0.69 (− 0.03 to 1.43) | 0.06 | 118.65, < 0.001, 96.62 | |
| Institutionalization | |||||
| Main analysis, OR | 11 | 4.14 (2.68 to 6.38) | < 0.001 | 60.75, < 0.001, 83.53 | 0.34 |
| Subgroup analyses | |||||
| ICH | 1 | 27.04 (6.55 to 111.63) | < 0.001 | 0.00, 1.000, 0.00 | |
| IS | 2 | 1.59 (1.16 to 2.16) | 0.003 | 1.39, 0.23, 28.34 | |
| Cognitive decline | |||||
| Main analysis | |||||
| Dichotomized, OR | 5 | 5.68 (3.24 to 9.93) | < 0.001 | 10.76, 0.096, 44.23 | 0.79 |
| Continuous, SMD | 4 | − 2.43 (− 3.92 to 0.93) | 0.001 | 73.21, < 0.001, 95.90 | 0.14 |
| Dementia | |||||
| Main analysis, OR | 4 | 4.74 (2.08 to 10.79) | < 0.001 | 6.80, 0.078, 55.89 | 0.82 |
| Neurological functional outcomes | |||||
| Main analysis | |||||
| Dichotomized, OR | 7 | 8.13 (5.74 to 11.50) | < 0.001 | 10.97, 0.089, 45.34 | 0.49 |
| Continuous, SMD | 10 | 3.36 (1.57 to 5.15) | < 0.001 | 2136.14, < 0.001, 99.58 | 0.40 |
| Subgroup analyses | |||||
| ICH | 2 | 5.34 (− 2.05 to 12.75) | 0.157 | 415.78, < 0.001, 99.75 | |
| IS | 4 | 2.23 (0.60 to 5.08) | 0.123 | 903.77, < 0.001, 99.66 | |
| Poor quality of life | |||||
| Dichotomized, OR | 1 | 4.97 (2.26 to 10.94) | < 0.001 | - | - |
| Continuous, SMD | 8 | − 2.56 (− 4.44 to 0.68) | 0.007 | 1068.74, < 0.001, 99.34 | 0.46 |
Boldface type indicates statistical significance with two-sided p < 0.05
*Pooled effect size was adjusted by the trim-and-filled method
Abbreviations: CI confidence interval, LOSlength of stay, OR odds ratio, SMD standardized mean difference, ICH intracerebral hemorrhage, ISischemic stroke
Table 4.
Uni- and multivariable meta-regression for heterogeneity-originated covariates of outcomes
| Outcomes | Univariable | Multivariable | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β | SE | 95% CI | z-value | p-value | R2 (%) | β | z-value | p-value | R2 (%) | |
| Mortality | ||||||||||
| Age at baseline, year | − 0.03 | 0.03 | − 0.10 to 0.03 | − 1.09 | 0.276 | 0 | 16 | |||
| NIHSS | − 0.03 | 0.07 | − 0.18 to 0.10 | − 0.52 | 0.606 | 0 | ||||
| Measure of delirium | 0.557 | 0 | ||||||||
| CAM | Ref | - | - | - | - | |||||
| DSM | − 0.28 | 0.57 | − 1.42 to 0.84 | − 0.49 | 0.621 | |||||
| Other | 1.25 | 1.66 | − 2.01 to 4.53 | 0.75 | 0.450 | |||||
| Mix | 0.20 | 0.47 | − 0.73 to 1.13 | 0.42 | 0.676 | |||||
| Stroke type | 10.0 | |||||||||
| ICH | Ref | - | - | - | - | Ref | - | - | ||
| IS | − 1.69 | 0.90 | − 3.47 to − 0.08 | − 1.87 | 0.061 | − 1.01 | − 1.07 | 0.284 | ||
| IS and ICH | − 1.95 | 0.87 | − 3.67 to − 0.24 | − 2.24 | 0.025 | − 1.51 | − 1.70 | 0.089 | ||
| Neuropsychiatric disorders excluded | 0 | |||||||||
| No | Ref | - | - | - | - | |||||
| Yes | − 0.07 | 0.29 | − 0.65 to 0.51 | − 0.24 | 0.808 | |||||
| Duration of follow-up, m | 1.0 | |||||||||
| < 3 | Ref | - | - | - | - | Ref | - | - | ||
| ≥ 3 | − 0.69 | 0.30 | − 1.29 to − 0.09 | − 2.26 | 0.023 | − 0.69 | − 2.18 | 0.029 | ||
| NOS scores | − 0.10 | 0.11 | − 0.33 to 0.13 | − 0.86 | 0.390 | 0 | ||||
| LoS | ||||||||||
| Age at baseline, years | − 0.03 | 0.04 | − 0.11 to 0.05 | − 0.74 | 0.458 | 0 | 41 | |||
| NIHSS | − 0.08 | 0.08 | − 0.25 to 0.08 | − 0.99 | 0.324 | 0 | ||||
| Measure of delirium | 0.218 | 0 | ||||||||
| CAM | Ref | - | - | - | - | |||||
| DSM | − 0.98 | 0.70 | − 2.36 to 0.39 | − 1.40 | 0.161 | |||||
| Other | − 1.40 | 0.99 | − 3.36 to 0.55 | − 1.41 | 0.159 | |||||
| Mix | − 0.14 | 0.55 | − 1.23 to 0.95 | − 0.25 | 0.801 | |||||
| Stroke type | 0.004 | 37 | 0.012 | |||||||
| ICH | Ref | - | - | - | - | Ref | - | - | ||
| IS | − 1.81 | 0.57 | − 2.94 to − 0.68 | − 3.14 | 0.001 | − 1.62 | − 2.79 | 0.005 | ||
| IS and ICH | − 1.60 | 0.52 | − 2.62 to − 0.58 | − 3.09 | 0.002 | − 1.48 | − 2.83 | 0.004 | ||
| Neuropsychiatric disorders excluded | 5 | |||||||||
| No | Ref | - | - | - | - | Ref | - | - | ||
| Yes | 0.50 | 0.53 | − 0.53 to 1.54 | 0.95 | 0.340 | 0.96 | 2.18 | 0.029 | ||
| NOS scores | 0.27 | 0.13 | 0.01 to 0.53 | 2.11 | 0.035 | 4 | 0.25 | 2.29 | 0.022 | |
| Institutionalization | ||||||||||
| Age at baseline, years | − 0.01 | 0.06 | − 0.13 to 0.10 | − 0.30 | 0.760 | 0 | 100 | |||
| NIHSS | − 0.01 | 0.15 | − 0.31 to 0.28 | − 0.10 | 0.920 | 0 | ||||
| Measure of delirium | 0.830 | 0 | ||||||||
| DSM | Ref | - | - | - | - | |||||
| Other | − 0.59 | 0.98 | − 2.52 to 1.34 | − 0.60 | 0.550 | |||||
| Mix | − 0.12 | 0.62 | − 1.34 to 1.09 | − 0.21 | 0.836 | |||||
| Stroke type | < 0.001 | 100 | < 0.001 | |||||||
| ICH | Ref | - | - | - | - | Ref | - | - | ||
| IS | − 2.84 | 0.73 | − 4.28 to − 1.39 | − 3.86 | < 0.001 | − 2.84 | − 3.86 | < 0.001 | ||
| IS and ICH | − 1.75 | 0.72 | − 3.18 to − 0.32 | − 2.40 | 0.016 | − 1.75 | − 2.40 | 0.016 | ||
| Neuropsychiatric disorders excluded | 0 | |||||||||
| No | Ref | - | - | - | ||||||
| Yes | 0.43 | 0.45 | − 0.46 to 1.33 | 0.95 | 0.340 | |||||
| NOS scores | 0.06 | 0.17 | − 0.28 to 0.41 | 0.34 | 0.732 | 0 | ||||
| Cognitive decline | ||||||||||
| Measure of delirium | 97 | 97 | ||||||||
| CAM | Ref | - | - | - | - | Ref | - | - | ||
| DSM | 6.00 | 0.77 | 4.48 to 7.51 | 7.75 | < 0.001 | 6.00 | 7.75 | < 0.001 | ||
| Functional outcome | ||||||||||
| Age at baseline, years | 0.21 | 0.23 | − 0.24 to 0.66 | 0.90 | 0.367 | 0 | 14 | |||
| NIHSS | − 0.13 | 0.34 | − 0.81 to 0.55 | − 0.37 | 0.709 | 0 | ||||
| Measure of delirium | 0.613 | 0 | ||||||||
| CAM | Ref | - | - | - | - | |||||
| DSM | − 0.14 | 4.39 | − 8.75 to 8.45 | − 0.03 | 0.972 | |||||
| Other | 0.54 | 4.39 | − 8.06 to 9.16 | 0.12 | 0.900 | |||||
| Mix | 2.98 | 3.32 | − 3.53 to 9.50 | 0.90 | 0.368 | |||||
| Stroke type | 0.482 | 0 | ||||||||
| ICH | Ref | - | - | - | - | |||||
| IS | − 3.10 | 2.58 | − 8.16 to 1.95 | − 1.20 | 0.229 | |||||
| IS and ICH | − 1.84 | 2.58 | − 6.90 to − 3.21 | − 0.72 | 0.474 | |||||
| Neuropsychiatric disorders excluded | 0 | |||||||||
| No | Ref | - | - | - | - | |||||
| Yes | 0.42 | 2.06 | − 3.61 to − 4.46 | 0.21 | 0.836 | |||||
| Duration of follow-up, m | 0 | |||||||||
| < 3 | Ref | - | - | - | - | |||||
| ≥ 3 | − 0.26 | 2.43 | − 5.04 to 4.51 | − 0.11 | 0.913 | |||||
| NOS scores | 1.06 | 0.59 | − 0.11 to 2.23 | 1.77 | 0.076 | 14 | 1.06 | 1.77 | 0.076 | |
| Quality of life | ||||||||||
| Age at baseline, y | − 0.00 | 0.17 | − 0.34 to 0.32 | − 0.05 | 0.961 | 0 | 79 | |||
| NIHSS | − 1.23 | 1.20 | − 3.58 to 1.12 | − 0.10 | 0.306 | 0 | ||||
| Measure of delirium | 0.548 | 0 | ||||||||
| DSM | Ref | - | - | - | - | |||||
| Other | − 0.14 | 3.48 | − 6.97 to 6.67 | − 0.04 | 0.966 | |||||
| Mix | − 2.36 | 2.30 | − 6.88 to 2.14 | − 1.03 | 0.303 | |||||
| Stroke type | 0 | |||||||||
| IS | ||||||||||
| IS and ICH | − 2.46 | 3.03 | − 8.41 to 3.48 | − 0.81 | 0.417 | |||||
| Measure tools | < 0.001 | 79 | < 0.001 | |||||||
| BI | Ref | - | - | - | - | Ref | - | - | ||
| FIM | 0.63 | 1.06 | − 1.44 to 2.70 | 0.59 | 0.551 | 0.53 | 0.48 | 0.629 | ||
| IADL | − 8.15 | 1.39 | − 10.89 to − 5.41 | − 5.84 | < 0.001 | − 7.77 | − 4.97 | < 0.001 | ||
| NOS scores | − 1.10 | 0.69 | − 2.47 to 0.25 | − 1.60 | 0.110 | 8 | − 0.24 | − 0.62 | 0.534 | |
Boldface type indicates statistical significance with two-sided p < 0.05
Abbreviations: BI Barthel Index, CAM Confusion Assessment Method, CAM Confusion Assessment Method, CI confidence interval, DSM Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, FIM Functional Independence Measure, IADL Instrumental Activities of Daily Living, ICH intracranial cerebral hemorrhage, IS ischemic stroke, LoS length of stay, NA not available, NIHSS, National Institute of Health stroke scale, m month, RASS, Richmond Agitation Sedation Scale, Ref., reference, SAH subarachnoid hemorrhage, TIA transient ischemic attack, USA United States of America, UK United Kingdom, y year
Hospital LoS
Twenty-one studies [34, 35, 37, 39, 42, 45–47, 49, 51, 54–57, 59–61, 65–67, 70] assessed the association between PSD and hospital LOS. Only 1 study [45] adequately adjusted for prespecified confounders, with results showing that the PSD was significantly associated with longer hospital LoS (HR, 1.63 [95% CI, 1.11–2.39]) (Fig. 2C).
Twenty studies [34, 35, 37, 39, 42, 46, 47, 49, 51, 54–57, 59–61, 65–67, 70] were used for pooled unadjusted analysis, which revealed that patients with PSD had significantly increased hospital LoS compared to those without (SMD, 1.03, 95% CI, 0.65 to 1.40; I2, 98.8%). We further identified a significant publication bias (Egger test P < 0.001), while the trim-and-filled method simulated 3 missing studies (SMD, 1.21 [95% CI, 0.54–1.89]) (Additional file 3: Table S2, Fig. S2). We identified eight outlier studies [35, 39, 47, 54, 55, 59, 61, 67], and the results remained the same after removing studies with reduced heterogeneity (I2 = 57.7%) (Additional file 3: Table S2). Sensitivity analysis showed that the association between PSD and hospital LOS remained when patients admitted to the ICU at baseline were excluded (Additional file 3: Table S3). The meta-regression analysis showed that stroke type, history of neuropsychiatric disorders, and quality assessment together accounted for 41% of the heterogeneity (Table 4). Subgroup analysis by stroke type showed risks of 0.69 (95% CI, − 0.03–1.43, P = 0.06) and 2.56 (95% CI, 2.16–2.97, P < 0.001) for ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke, respectively, indicating that stroke type may be an important source of heterogeneity (Table 3).
Institutionalization
Eleven studies [35, 37, 39, 46, 54–56, 59, 60, 66, 69] examined the association between PSD and institutionalization. However, only one [69] adequately adjusted for key confounders, with this study suggesting that PSD was not significantly associated with the risk of institutionalization (OR, 2.78 [95% CI, 0.55–14.06], P = 0.2) (Fig. 2D). Two studies were inadequately adjusted for prespecified confounders. A pooled analysis of these three studies was not possible, as one study [46] reported the results as adjusted HRs (HR, 3.54 [95% CI, 1.55–8.10]) (Fig. 2D), while two [59, 69] reported the adjusted ORs. The pooled inadequately adjusted OR suggested PSD was not associated with an increased institutionalization risk (OR, 0.81 [95% CI, 0.10–6.87]) (Fig. 2D). Eleven studies [35, 37, 39, 46, 54–56, 59, 60, 66, 69] presented unadjusted event rates, and the pooled OR indicated that PSD was associated with a fourfold increased institutionalization risk (OR, 4.14 [95% CI, 2.68–6.38]; I2, 83.5%) after a mean (SD) follow-up of 13.44 (18.04) months (range, 1–60 months) (Table 3). No publication bias was identified (Additional file 3: Fig. S3). We identified two outlier studies [55, 59], and the significant association persisted after removing these studies with reduced heterogeneity (I2 = 63.8%) (Additional file 3: Table S2). Sensitivity analysis showed that the association between PSD and institutionalization remained when only patients who had not resided in an institution at baseline were considered (Additional file 3: Table S3). Meta-regression analysis showed that the stroke type accounted for 100% of the heterogeneity (Table 4). Subgroup analysis by types of stroke showed a risk of 1.59 (95% CI, 1.16–2.16, P = 0.003) and 27.04 (95% CI, 6.55–111.63, P < 0.001) for ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke, respectively (Table 3).
Cognitive outcomes
Eight studies [35, 37, 43, 44, 48, 52, 68, 72] investigated the association between PSD and cognitive outcomes, including 4 on dementia and 5 on cognitive decline. However, 1 study [43], which suggested that PSD was significantly associated the risk of dementia at 24 months (OR, 7.20 [95% CI, 1.87–27.73]), was inadequately adjusted for the prespecified confounders (Fig. 2F). Five studies reported unadjusted dichotomous cognitive outcomes, while the pooled unadjusted OR for poorer cognitive outcomes in patients with PSD was 5.68 (95% CI, 3.24–9.93; I2, 44.23%) after a mean (SD) follow-up of 33 (34.20) months (range, 3–90 months) (Table 3). No publication bias (Additional file 3: Fig. S4) or outliers were identified. Four studies reported continuous cognitive outcomes, revealing significantly worse outcomes in patients with PSD (SMD − 2.43, 95% CI − 3.92 to − 0.93; I2, 95.9%) compared with those without (Table 3). No publication bias was identified (Additional file 3, Fig. S4). We identified one outlier study, and the results remained the same after removing studies with reduced heterogeneity (I2 = 46.8%) (Additional file 3: Table S2). Meta-regression analysis revealed that delirium accounted for 97% of the heterogeneity (Table 4). Four studies reported dementia as an outcome, and the pooled unadjusted OR in patients with PSD was 4.74 (95% CI, 2.08–10.79; I2, 55.9%) after a mean (SD) follow-up of 32.25 (39.45) months (range, 3–90 months) (Table 3). No publication biases or outliers were identified (Additional file 3: Fig. S5). We further conducted sensitivity analyses of the unadjusted ORs of poorer cognitive outcomes and dementia, finding that the associations remained when patients with cognitive impairment at baseline were excluded (Additional file 3: Table S3).
Functional outcome
Fifteen studies [35, 36, 47, 48, 51, 53–55, 57, 59, 60, 65, 66] investigated the association between PSD and functional outcomes (i.e., modified Rankin Scale [mRS] scores). The aggregated analysis of adequately adjusted ORs in 4 studies revealed that PSD was associated with poorer functional outcome after a mean (SD) follow-up of 21.75 (25.85) months (range, 3–60 months) (OR, 3.62 [95% CI, 2.15–6.09]; I2, 0%) (Fig. 2H). The pooled inadequately adjusted OR in 5 studies indicated that PSD was associated with a 4.5-fold increase in the odds of poor functional outcome (OR, 4.55 [95% CI, 3.17–6.52]; I2, 0%) after a mean (SD) follow-up of 18 (23.90) months (range, 3–60 months) (Fig. 2G). The pooled unadjusted OR in 7 studies indicated PSD was associated with an eightfold increased risk of poor functional outcomes (OR, 8.13 [95% CI, 5.74–11.50]; I2, 45.3%) after a mean (SD) follow-up of 14.50 (22.56) months (range, 3–60 months) (Table 3). In the above meta-analyses, no publication biases (Additional file 3: Fig. S6) or outlier studies were identified. Sensitivity analyses indicated that the direction and strength of all the results remained the same when patients with higher baseline mRS scores were excluded (Additional file 3: Table S3).
Ten studies reported on continuous functional outcomes, presenting results that indicated poorer functional outcomes in patients with delirium (SMD 3.36, 95% CI 1.57 to 5.15; p < 0.001; I2, 99.6%) compared with those without (Table 3). No publication bias or outliers were identified (Additional file 3: Fig. S6). Meta-regression analysis revealed that the quality assessment accounted for 14% of the heterogeneity (Table 4). Subgroup analysis further showed that both delirium after ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke (OR, 2.23; 95% CI, 0.60–5.08, P = 0.123 vs. OR, 5.34; 95% CI, − 2.05–12.75, P = 0.157) was numerically associated with neurological functional outcomes (Table 3). Sensitivity analyses revealed that the direction and strength of the results remained the same when patients with higher baseline mRS scores were excluded (Additional file 3: Table S3).
Quality of life
Nine studies [35, 37, 42, 51, 53, 57, 63, 64, 66] examined the association between PSD and quality of life. One that presented unadjusted event rates indicated that PSD was associated with an unadjusted fourfold increase in the odds of poor quality of life (OR, 4.97 [95% CI, 2.26–10.94]) (Table 3). Eight studies that reported continuous outcomes reported significantly worse outcomes in patients with PSD (SMD − 2.56, 95% CI − 4.44 to − 0.68; p = 0.007; I2, 99.3%) compared with those without (Table 3). No publication bias was identified (Additional file 3, Fig. S7). We identified one outlier study, in which the association persisted after removing this study with reduced heterogeneity (Additional file 3: Table S2). Meta-regression analysis showed that the measures of quality of life and study quality accounted for 79% of the heterogeneity (Table 4). Sensitivity analyses revealed that the direction and strength of the results remained the same when only patients with poor quality of life at baseline were excluded (Additional file 3: Fig. S3).
Discussion
This study comprised a comprehensive review of PSD outcome data obtained from 39 studies, including 35 prospective observational studies and 4 case–control studies. Overall, the results suggested that delirium identified in acute stroke patients is strongly associated with mortality and functional outcomes, even after adjusting for age, comorbid illnesses, and stroke severity. On an inadequately adjusted and unadjusted basis, PSD was found to be associated with a significantly increased risk of death, longer LoS, institutionalization, poor function, cognition, and quality of life. Compared with a previous meta-analysis [7], our investigation included a larger number of studies and patients (10 vs. 39 studies; 2004 vs 12,938 patients) and included more comprehensive endpoints. More importantly, this is the first meta-analysis to quantify the association between PSD and outcomes after controlling for key confounders that may have influenced the association between delirium and poor outcomes.
Our meta-analysis has several practical clinical implications. Delirium has been suggested to reflect the quality of inpatient care [74]; however, it is frequently overlooked and poorly documented among patients with neurological symptoms [75]. Although no intervention has been found to improve long-term outcomes of delirium, our results indicate that PSD is a potentially modifiable risk factor for adverse outcomes. Therefore, delirium may be a promising target for outcome optimization. For example, multicomponent interventions aimed at addressing the risk factors for delirium could diminish the risk of delirium and improve outcomes associated with delirium (i.e., a trend toward reduced LOS and institutionalization) [76]. Identifying high-risk populations and implementing strategies to prevent delirium may improve PSD-associated adverse outcomes in patients with acute stroke.
This study highlights several directions for future clinical studies on PSD. First, patients with acute stroke who develop delirium tend to differ substantially from patients without delirium at baseline, and these differences (e.g., age, comorbidity, and severity of stroke) are closely associated with adverse outcomes. Therefore, any attempt to identify the association between PSD and its outcomes requires careful control of these variables. One prior meta-analysis by Salluh et al. demonstrated a significant increase in the risk of mortality associated with delirium in critically ill patients, after controlling for age, sex, and illness [4]. Another meta-analysis by Hamilton et al. concluded that POD had no significant effect on mortality after controlling for confounders specific to the perioperative setting [77]. These two conflicting findings indicate that there are potential differences in the pathophysiology of delirium due to different causes. In our study, the association between PSD, mortality, and function persisted even after adjusting for several key confounders, supporting the independent nature of delirium as an exposure to outcomes in stroke patients. However, our predefined confounders were not sufficient to control for confounding factors in the association between delirium and other outcomes, indicating that more high-quality studies with adequate adjustment for confounders are warranted. Second, our results underline the need for prospective cohort studies with standardized methods to assess the impact of delirium on endpoints (cognition and quality of life) in acute stroke patients. Third, we found that the stroke type could account for the heterogeneity of several endpoints. As such, future studies should be designed to allow for discriminative analysis according to stroke type. Finally, high-quality clinical trials are required to evaluate the efficacy of single and bundled interventions in reducing the prevalence and burden of delirium in patients with acute stroke.
This study has some limitations. First, most of the included studies were unadjusted or inadequately adjusted for the selected covariates. To overcome this, we performed a meta-analysis of inadequately adjusted and unadjusted effect estimates to validate the results of the PSD-outcomes relationship. Second, there is insufficient evidence regarding the most suitable screening tool for assessing delirium in acute stroke patients [75]. Patients who are comatose or have other cognitive dysfunctions may be excluded from neurocognitive assessment, or misclassified as having delirium. Third, all the included studies were observational; therefore, the causation between PSD and poor outcomes could not be determined.
Conclusions
The results of this meta-analysis suggest that PSD is independently associated with an increased risk of mortality and poor function. Furthermore, the unadjusted results indicated that PSD was associated with longer hospitalization, more institutionalization, cognitive impairment, and worse quality of life. PSD prevention is a high clinical and research priority, meaning that collaborative scientific efforts should be directed towards addressing these challenges.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1: MOOSE Checklist of the study
Additional file 2: PRISMA Checklist of the study
Additional file 3: Table S1-S5. Table S1: Characteristics of included studies. Table S2: Methodological quality for outcomes of poststroke delirium. Table S3: The meta-analysis of outcomes for post-stroke delirium with excluding outliers. Table S4: Uni- and multivariable Meta-regression for heterogeneity-originated covariates of outcomes. Table S5: Sensitivity analysis. Figure S1: Funnel plot assessing publication bias on mortality of post-stroke delirium Figure S2: Funnel plot assessing publication bias on hospital stay of post-stroke delirium Figure S3: Funnel plot assessing publication bias on institutionalization of post-stroke delirium Figure S4: Funnel plot assessing publication bias on cognitive outcomes of post-stroke delirium Figure S5: Funnel plot assessing publication bias on dementia of post-stroke delirium Figure S6: Funnel plot assessing publication bias on functional outcomes of post-stroke delirium Figure S7: Funnel plot assessing publication bias on life quality of post-stroke delirium
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- PSD
Post-stroke delirium
- ORs
Odds ratios
- CIs
Confidence intervals
- SMDs
Standardized mean differences
- HRs
Hazard ratios
- SD
Standard deviation
- LoS
Length of stay
- MOOSE
Meta-analysis of Observational Studies in Epidemiology
- DSN
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders
- CAM
Confusion assessment method
- CAM-ICU
Confusion assessment method for the intensive care unit
- ICDSC
Intensive care delirium screening checklist
- mRS
Modifiable Rankin scale
Authors’ contributions
G.B.Z., G.Z.S., H.W.H. contributed to the conception and design of the study; G.B.Z., W.J.Y., J.M.L., H.Y.L., L.W., S.L.Z. contributed to acquiring the data; G.B.Z., W.J.Y., J.M.L., H.Y.L. contributed to analyzing and interpreting the data; H.W.H., G.Z.S., G.B.Z. contributed to writing the original draft and supervision. G.Z.S. and H.W.H. contributed to writing, reviewing and editing. All the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
Dr Huawei Huang supported this work, granted by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81801042), Beijing Hospital Authority Youth Programme (20190504), and Beijing Municipal Administration of Hospitals Incubating Program (PX2023021). Dr Guobin Zhang also supported this work, granted by the Beijing Municipal Administration of Hospitals Incubating Program (PX2023018).
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
Declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All authors provided consent for publication.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Guo-Bin Zhang, Jia-Mei Lv, and Wei-Jie Yu contributed equally to this work.
Contributor Information
Guang-Zhi Shi, Email: sgzttyy@126.com.
Hua-Wei Huang, Email: huanghw0403@163.com.
References
- 1.Zou Y, Cole MG, Primeau FJ, McCusker J, Bellavance F, Laplante J. Detection and diagnosis of delirium in the elderly: psychiatrist diagnosis, confusion assessment method, or consensus diagnosis?. Int Psychogeriatr. 1998;10(3):303–8. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 2.Siddiqi N, House AO, Holmes JD. Occurrence and outcome of delirium in medical in-patients: A systematic literature review. Age ageing. 2006;35(4):350–64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Witlox J, Eurelings LS, de Jonghe JF, Kalisvaart KJ, Eikelenboom P, van Gool WA. Delirium in elderly patients and the risk of postdischarge mortality, institutionalization, and dementia: A meta-analysis. JAMA. 2010;304(4):443–51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Salluh JI, Wang H, Schneider EB, Nagaraja N, Yenokyan G, Damluji A, et al. Outcome of delirium in critically ill patients: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2015;350:h2538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Inouye SK, Westendorp RGJ, Saczynski JS. Delirium in elderly people. The lancet. 2014;383(9920):911–22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 6.Shaw RC, Walker G, Elliott E, Quinn TJ. Occurrence rate of delirium in acute stroke settings: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Stroke. 2019;50(11):3028–36. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Shi Q, Presutti R, Selchen D, Saposnik G. Delirium in acute stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Stroke. 2012;43(3):645–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Stroup DF, Berlin JA, Morton SC, Olkin I, Williamson GD, Rennie D, et al. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: A proposal for reporting Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology (moose) group. Jama. 2000;283(15):2008–12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The prisma statement. PLoS Med. 2009;6(7):e1000097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Huang. H, Yu. W, Li. H. Outcomes of post-stroke delirium: Meta-analysis and systematic review. Accessed october 27, 2023.. https://www.Crd.York.Ac.Uk/prospero/recordemail.Php
- 11.Investigators WMP. The world health organization monica project (monitoring trends and determinants in cardiovascular disease): A major international collaboration Who monica project principal investigators. J Clin Epidemiol. 1988;41(2):105–14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Bell CC. DSM-IV: diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. Jama.1994;272(10):828–9.
- 13.Inouye SK, van Dyck CH, Alessi CA, Balkin S, Siegal AP, Horwitz RI. Clarifying confusion: The confusion assessment method A new method for detection of delirium. Ann Intern Med. 1990;113(12):941–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ely EW, Inouye SK, Bernard GR, Gordon S, Francis J, May L, et al. Delirium in mechanically ventilated patients: Validity and reliability of the confusion assessment method for the intensive care unit (cam-icu). JAMA. 2001;286(21):2703–10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Bergeron N, Dubois MJ, Dumont M, Dial S, Skrobik Y. Intensive care delirium screening checklist: Evaluation of a new screening tool. Intensive Care Med. 2001;27(5):859–64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Trzepacz PT, Mulsant BH, Dew MA, Pasternak R, Sweet RA, Zubenko GS. Is delirium different when it occurs in dementia? A study using the delirium rating scale. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 1998;10(2):199–204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Trzepacz PT, Mittal D, Torres R, Kanary K, Norton J, Jimerson N. Validation of the delirium rating scale-revised-98: Comparison with the delirium rating scale and the cognitive test for delirium. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2001;13(2):229–42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Schuurmans MJ, Shortridge-Baggett LM, Duursma SA. The delirium observation screening scale: A screening instrument for delirium. Res Theory Nurs Pract. 2003;17(1):31–50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Bellelli G, Morandi A, Davis DH, Mazzola P, Turco R, Gentile S, et al. Validation of the 4at, a new instrument for rapid delirium screening: A study in 234 hospitalised older people. Age ageing. 2014;43(4):496–502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.van Swieten JC, Koudstaal PJ, Visser MC, Schouten HJ, van Gijn J. Interobserver agreement for the assessment of handicap in stroke patients. Stroke. 1988;19(5):604–7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR. “Mini-mental state” A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res. 1975;12(3):189–98. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Nasreddine ZS, Phillips NA, Bédirian V, Charbonneau S, Whitehead V, Collin I, et al. The montreal cognitive assessment, moca: A brief screening tool for mild cognitive impairment. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2005;53(4):695–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Mahoney FI, Barthel DW. Functional Evaluation: The Barthel Index. Md State Med J. 1965;14:61–5. [PubMed]
- 24.van der Putten JJ, Hobart JC, Freeman JA, Thompson AJ. Measuring change in disability after inpatient rehabilitation: Comparison of the responsiveness of the barthel index and the functional independence measure. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1999;66(4):480–4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Lawton MP, Brody EM. Assessment of older people: Self-maintaining and instrumental activities of daily living. Gerontologist. 1969;9(3):179–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Stang A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol. 2010;25(9):603–5. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 27.Chan A, Jamieson C, Draper H, O'Callaghan S, Guinn BA. Cancer screening attendance rates in transgender and gender-diverse patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Evid Based Med. 2024:bmjebm-2023:112719. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 28.Tang S, Xiong L, Fan Y, Mok VCT, Wong KS, Leung TW. Stroke outcome prediction by blood pressure variability, heart rate variability, and baroreflex sensitivity. Stroke. 2020;51(4):1317–20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Hernán MA, Hernández-Díaz S, Werler MM, Mitchell AA. Causal knowledge as a prerequisite for confounding evaluation: An application to birth defects epidemiology. Am J Epidemiol. 2002;155(2):176–84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Sun GW, Shook TL, Kay GL. Inappropriate use of bivariable analysis to screen risk factors for use in multivariable analysis. J Clin Epidemiol. 1996;49(8):907–16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Higgins JPT, Thompson SG, Decks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ. 2003;327(7414):557–60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M, Minder C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ. 1997;315(7109):629–34. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 33.Viechtbauer W, Cheung MW. Outlier and influence diagnostics for meta-analysis. Res Synth Methods. 2010;1(2):112–25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Gustafson Y, Olsson T, Eriksson S, Asplund K, Bucht G, Ouml, et al. Acute confusional states (delirium) in stroke patients. Cerebrovascular Diseases. 1991;1(5):257–264.
- 35.Hénon H, Lebert F, Durieu I, Godefroy O, Lucas C, Pasquier F, et al. Confusional state in stroke: Relation to preexisting dementia, patient characteristics, and outcome. Stroke. 1999;30(4):773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Caeiro L, Ferro JM, Albuquerque R, Figueira ML. Delirium in the first days of acute stroke. J Neurol. 2004;251(2):171–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Sheng AZ, Shen Q, Cordato D, Zhang YY, Yin Chan DK. Delirium within three days of stroke in a cohort of elderly patients. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2006;54(8):1192–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Dostović Z, Smajlović D, Sinanović O, Vidović M. Duration of delirium in the acute stage of stroke. Acta Clin Croat. 2009;48(1):13–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.McManus J, Pathansali R, Hassan H, Ouldred E, Cooper D, Stewart R, et al. The course of delirium in acute stroke. Age ageing. 2009;38(4):385–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Dahl MH, Rønning OM, Thommessen B. Delirium in acute stroke–prevalence and risk factors. Acta Neurol Scand Suppl. 2010;190:39–43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Mc Manus JT, Pathansali R, Ouldred E, Stewart R, Jackson SH. Association of delirium post-stroke with early and late mortality. Age ageing. 2011;40(2):271–4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Oldenbeuving AW, de Kort PL, Jansen BP, Algra A, Kappelle LJ, Roks G. Delirium in the acute phase after stroke: Incidence, risk factors, and outcome. Neurology. 2011;76(11):993–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.van Rijsbergen MW, Oldenbeuving AW, Nieuwenhuis-Mark RE, Nys GM, Las SG, Roks G, et al. Delirium in acute stroke: A predictor of subsequent cognitive impairment? A two-year follow-up study. J Neurol Sci. 2011;306(1–2):138–42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Melkas S, Laurila JV, Vataja R, Oksala N, Jokinen H, Pohjasvaara T, et al. Post-stroke delirium in relation to dementia and long-term mortality. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2012;27(4):401–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Mitasova A, Kostalova M, Bednarik J, Michalcakova R, Kasparek T, Balabanova P, et al. Poststroke delirium incidence and outcomes: Validation of the confusion assessment method for the intensive care unit (cam-icu). Crit Care Med. 2012;40(2):484–90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Miu DK, Yeung JC. Incidence of post-stroke delirium and 1-year outcome. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2013;13(1):123–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Naidech AM, Beaumont JL, Rosenberg NF, Maas MB, Kosteva AR, Ault ML, et al. Intracerebral hemorrhage and delirium symptoms Length of stay, function, and quality of life in a 114-patient cohort. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013;188(11):1331–7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Chan EKW, Shen Q, Cordato D, Kneebone I, Xu YH, Chan DKY. Delirium post-stroke: Short- to long-term effect on anxiety and depression compared to effect on cognition. Top Stroke Rehabil. 2017;24(8):597–600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Kozak HH, Uğuz F, Kılınç İ, Uca AU, Serhat Tokgöz O, Akpınar Z, et al. Delirium in patients with acute ischemic stroke admitted to the non-intensive stroke unit: Incidence and association between clinical features and inflammatory markers. Neurol Neurochir Pol. 2017;51(1):38–44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Rosenthal LJ, Francis BA, Beaumont JL, Cella D, Berman MD, Maas MB, et al. Agitation, delirium, and cognitive outcomes in intracerebral hemorrhage. Psychosomatics. 2017;58(1):19–27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Lim TS, Lee JS, Yoon JH, Moon SY, Joo IS, Huh K, et al. Cigarette smoking is an independent risk factor for post-stroke delirium. BMC Neurol. 2017;17(1):56. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Ojagbemi A, Owolabi M, Bello T. Baiyewu O. Stroke severity predicts poststroke delirium and its association with dementia: Longitudinal observation from a low income setting. J Neurol Sci; 2017. p. 375376–81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Qu J, Chen Y, Luo G, Zhong H, Xiao W, Yin H. Delirium in the acute phase of ischemic stroke: Incidence, risk factors, and effects on functional outcome. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2018;27(10):2641–7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Kotfis K, Bott-Olejnik M, Szylińska A, Listewnik M, Rotter I. Characteristics, risk factors and outcome of early-onset delirium in elderly patients with first ever acute ischemic stroke - a prospective observational cohort study. Clin Interv Aging. 2019;14:1771–82. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Kotfis K, Bott-Olejnik M, Szylińska A, Rotter I. Could neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (nlr) serve as a potential marker for delirium prediction in patients with acute ischemic stroke? A prospective observational study. J Clin Med. 2019;8(7):1075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Zipser CM, Deuel J, Ernst J, Schubert M, Weller M, von Känel R, et al. Predisposing and precipitating factors for delirium in neurology: A prospective cohort study of 1487 patients. J Neurol. 2019;266(12):3065–75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Pasińska P, Wilk A, Kowalska K, Szyper-Maciejowska A, Klimkowicz-Mrowiec A. The long-term prognosis of patients with delirium in the acute phase of stroke: Prospective observational polish study (propolis). J Neurol. 2019;266(11):2710–7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Kowalska K, Droś J, Mazurek M, Pasińska P, Gorzkowska A, Klimkowicz-Mrowiec A. Delirium post-stroke: Short- and long-term effect on depression, anxiety, apathy and aggression (research study-part of propolis study). J Clin Med. 2020;9(7):2232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Reznik ME, Margolis SA, Mahta A, Wendell LC, Thompson BB, Stretz C, et al. Impact of delirium on outcomes after intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke. 2022;53(2):505–13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Zipser CM, Deuel JW, Held JPO, Ernst J, Schubert M, Weller M, et al. Economic impact of poststroke delirium and associated risk factors: Findings from a prospective cohort study. Stroke. 2021;52(10):3325–34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Fialho Silva IT, Assis Lopes P, Timotio Almeida T, Ramos SC, Caliman Fontes AT, Guimarães Silva D, et al. Impact of delirium and its motor subtypes on stroke outcomes. Stroke. 2021;52(4):1322–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Czyzycki M, Klimiec-Moskal E, Chrobak AA, Pera J, Slowik A, Dziedzic T. Subtypes of delirium after ischaemic stroke-predisposing factors and outcomes: A prospective observational study (propolis). Eur J Neurol. 2022;29(2):478–85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Zaitoun AM, Elsayed DAF, Ramadan BM, et al. Assessment of the risk factors and functional outcome of delirium in acute stroke. Egypt J Neurol Psychiat Neurosurg. 2019;55:1–6.
- 64.Aizen E, Yalonnitsky I, Zalyesov E, Shugaev I. Cognitive and functional outcomes in elderly patients with post-stroke delirium. Aging Med Healthc. 2019;10(4):122–7.
- 65.Stokholm J, Birkmose LKH, Ahmed A, Csillag C, Kjær TW, Christensen T. Changes in autonomic tone during delirium in acute stroke patients assessed by pupillometry and skin conductance. J Neurol Sci. 2021;428:117582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Mansutti I, Saiani L, Cargnelutti D, Petrucco S, Giannina V, Di Domenico C, et al. Delirium prevalence, risk factors and outcomes among patients with acute stroke: A multi-centre observational study. J Vasc Nurs. 2022;40(4):172–80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Rollo E, Brunetti V, Scala I, Callea A, Marotta J, Vollono C, et al. Impact of delirium on the outcome of stroke: A prospective, observational, cohort study. J Neurol. 2022;269(12):6467–75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Nerdal V, Gjestad E, Saltvedt I, Munthe-Kaas R, Ihle-Hansen H, Ryum T, et al. The relationship of acute delirium with cognitive and psychiatric symptoms after stroke: A longitudinal study. BMC Neurol. 2022;22(1):234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Droś J, Segiet N, Początek G, Klimkowicz-Mrowiec A. Five-year stroke prognosis. Influence of post-stroke delirium and post-stroke dementia on mortality and disability (Research Study - Part of the PROPOLIS Study). Neurol Sci. 2024;45(3):1109–19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 70.Nydahl P, Bartoszek G, Binder A, Paschen L, Margraf NG, Witt K, et al. Prevalence for delirium in stroke patients: A prospective controlled study. Brain Behav. 2017;7(8):e00748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Dostovic Z, Smajlovic D, Ibrahimagic OC, Dostovic A. Mortality and functional disability of poststroke delirium. Mater Sociomed. 2018;30(2):95–7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Dostović Z, Ibrahimagić O, Smajlović D, Kunić S, Čustović A. Cognitive functionality of patients with delirium after stroke. Psychiatr Danub. 2021;33(Suppl 4):503–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Droś J, Segiet N, Początek G, Klimkowicz-Mrowiec A. Five-year stroke prognosis Influence of post-stroke delirium and post-stroke dementia on mortality and disability (Research Study - Part of the PROPOLIS Study). Neurol Sci. 2024;45(3):1109–19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Inouye SK, Schlesinger MJ, Lydon TJ. Delirium: A symptom of how hospital care is failing older persons and a window to improve quality of hospital care. Am J Med. 1999;106(5):565–73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Patel MB, Bednarik J, Lee P, Shehabi Y, Salluh JI, Slooter AJ, et al. Delirium monitoring in neurocritically ill patients: A systematic review. Crit Care Med. 2018;46(11):1832–41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Inouye SK, Bogardus ST Jr, Charpentier PA, Leo-Summers L, Acampora D, Holford TR, et al. A multicomponent intervention to prevent delirium in hospitalized older patients. N Engl J Med. 1999;340(9):669–76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Hamilton GM, Wheeler K, Di Michele J, Lalu MM, McIsaac DI. A systematic review and meta-analysis examining the impact of incident postoperative delirium on mortality. Anesthesiology. 2017;127(1):78–88. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Additional file 1: MOOSE Checklist of the study
Additional file 2: PRISMA Checklist of the study
Additional file 3: Table S1-S5. Table S1: Characteristics of included studies. Table S2: Methodological quality for outcomes of poststroke delirium. Table S3: The meta-analysis of outcomes for post-stroke delirium with excluding outliers. Table S4: Uni- and multivariable Meta-regression for heterogeneity-originated covariates of outcomes. Table S5: Sensitivity analysis. Figure S1: Funnel plot assessing publication bias on mortality of post-stroke delirium Figure S2: Funnel plot assessing publication bias on hospital stay of post-stroke delirium Figure S3: Funnel plot assessing publication bias on institutionalization of post-stroke delirium Figure S4: Funnel plot assessing publication bias on cognitive outcomes of post-stroke delirium Figure S5: Funnel plot assessing publication bias on dementia of post-stroke delirium Figure S6: Funnel plot assessing publication bias on functional outcomes of post-stroke delirium Figure S7: Funnel plot assessing publication bias on life quality of post-stroke delirium
Data Availability Statement
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.