Abstract
DL-alpha-Difluoromethylornithine (DFMO), an irreversible inhibitor of ornithine decarboxylase, prevented the increases in putrescine and spermidine, but not in spermine, in human erythrocytes infected with the malarial parasite Plasmodium falciparum. The addition of putrescine to these polyamine-depleted cultures restored the normal concentrations of spermidine, whereas that of putrescine even exceeded that of the control cultures. DFMO also inhibited the incorporation of radioactive amino acids into the proteins of parasitized erythrocytes. Electrophoresis on polyacrylamide gels revealed that the synthesis of some proteins was completely blocked by DFMO, but the synthesis of others was not affected. DFMO also caused a partial inhibition of RNA synthesis, and DNA synthesis was completely blocked in polyamine-depleted parasitized erythrocytes. It has been suggested that putrescine and/or spermidine are required for the synthesis of certain proteins in parasitized erythrocytes and that at least one of those proteins is related to the synthesis of DNA of the malarial parasite. It appears that polyamines regulate the schizogony process of P. falciparum.
Full text
PDF

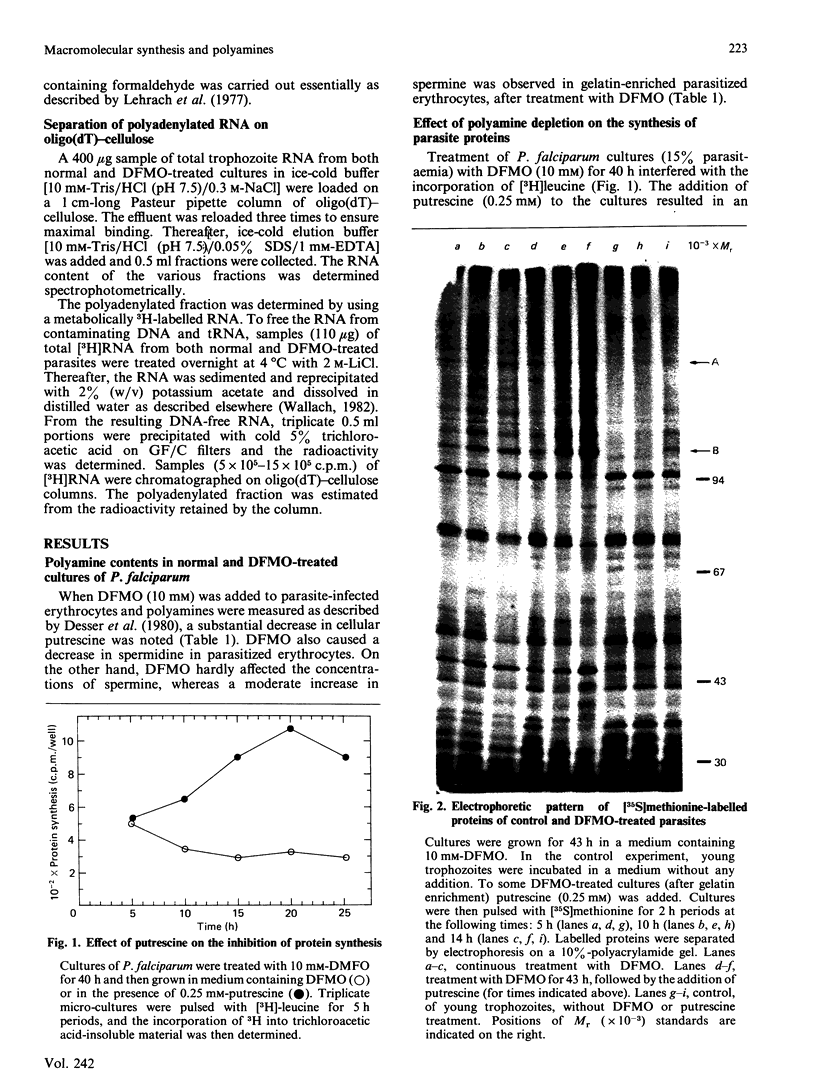

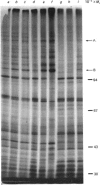
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Assaraf Y. G., Golenser J., Spira D. T., Bachrach U. Plasmodium falciparum: synchronization of cultures with DL-alpha-difluoromethylornithine, an inhibitor of polyamine biosynthesis. Exp Parasitol. 1986 Apr;61(2):229–235. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(86)90156-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Assaraf Y. G., Golenser J., Spira D. T., Bachrach U. Polyamine levels and the activity of their biosynthetic enzymes in human erythrocytes infected with the malarial parasite, Plasmodium falciparum. Biochem J. 1984 Sep 15;222(3):815–819. doi: 10.1042/bj2220815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair D. G. Activation of mammalian RNA polymerases by polyamines. Int J Biochem. 1985;17(1):23–30. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(85)90081-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desser H., Lutz D., Krieger O., Stierer M. Rapid detection of polyamines in the sera of patients with colorectal carcinoma by liquid ion-exchange chromatography. Oncology. 1980;37(6):376–380. doi: 10.1159/000225476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gritzmacher C. A., Reese R. T. Protein and nucleic acid synthesis during synchronized growth of Plasmodium falciparum. J Bacteriol. 1984 Dec;160(3):1165–1167. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.3.1165-1167.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igarashi K., Hashimoto S., Miyake A., Kashiwagi K., Hirose S. Increase of fidelity of polypeptide synthesis by spermidine in eukaryotic cell-free systems. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Nov 15;128(2-3):597–604. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb07006.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igarashi K., Morris D. R. Physiological effects in bovine lymphocytes of inhibiting polyamine synthesis with ethylglyoxal bis(guanylhydrazone). Cancer Res. 1984 Nov;44(11):5332–5337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inselburg J., Banyal H. S. Synthesis of DNA during the asexual cycle of Plasmodium falciparum in culture. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1984 Jan;10(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(84)90020-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen J. B. Concentration from continuous culture of erythrocytes infected with trophozoites and schizonts of Plasmodium falciparum. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1978 Nov;27(6):1274–1276. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1978.27.1274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jänne J., Hölttä E., Kallio A., Käpyaho K. Role of polyamines and their antimetabolites in clinical medicine. Spec Top Endocrinol Metab. 1983;5:227–293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutson J. C., Morris D. R. Cellular polyamine depletion reduces DNA synthesis in isolated lymphocyte nuclei. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Sep 27;520(2):291–301. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(78)90228-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K., Favre M. Maturation of the head of bacteriophage T4. I. DNA packaging events. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 15;80(4):575–599. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambros C., Vanderberg J. P. Synchronization of Plasmodium falciparum erythrocytic stages in culture. J Parasitol. 1979 Jun;65(3):418–420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiler N. Use of the dansyl reaction in biochemical analysis. Methods Biochem Anal. 1970;18:259–337. doi: 10.1002/9780470110362.ch5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor C. W., Tabor H. Polyamines. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:749–790. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.003533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trager W., Jensen J. B. Human malaria parasites in continuous culture. Science. 1976 Aug 20;193(4254):673–675. doi: 10.1126/science.781840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vezza A. C., Trager W. Preliminary characterization of the major RNA species from Plasmodium falciparum. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1981 Dec;4(3-4):149–162. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(81)90014-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallach M. Efficient extraction and translation of Plasmodium falciparum messenger RNA. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1982 Dec;6(6):335–342. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(82)90023-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallach M., Kilejian A. The importance of tRNA for the in vitro cell-free translation of messenger RNA isolated from the malaria parasite Plasmodium lophurae. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1982 Apr;5(4):245–261. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(82)90033-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whaun J. M., Brown N. D. Ornithine decarboxylase inhibition and the malaria-infected red cell: a model for polyamine metabolism and growth. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 May;233(2):507–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Rojas M. O., Wasserman M. Temporal relationships on macromolecular synthesis during the asexual cell cycle of Plasmodium falciparum. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1985;79(6):792–796. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(85)90119-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]