Abstract
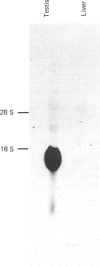
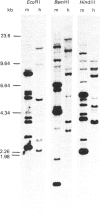
Mouse sperm-specific lactate dehydrogenase-C (LDH-C) cDNA was cloned and sequenced from lambda gt11 expression library. The LDH-C cDNA insert of 1236 bp consists of the protein-coding sequence (999 bp), the 5' (54 bp) and 3' (113 bp) non-coding regions, and the poly(A) tail (70 bp). The Northern blot analysis of poly(A)-containing RNAs from mouse testes and liver indicates that the LDH-C gene is expressed in testes but not in liver, and that its mRNA is approx. 1400 nucleotides in length. The nucleotide and amino acid sequences of the mouse LDH-C cDNA show 73% and 72% homologies, respectively, with those of the mouse LDH-A. The Southern blot analysis of genomic DNAs from mouse liver and human placenta indicates the presence of multiple LDH-C gene-related sequences.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akai K., Yagi K., Tiano H. F., Pan Y. C., Shimizu M., Fong K., Jungmann R. A., Li S. S. Isolation and characterization of a cDNA and a pseudogene for mouse lactate dehydrogenase-A isozyme. Int J Biochem. 1985;17(5):645–648. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(85)90298-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung F. Z., Tsujibo H., Bhattacharyya U., Sharief F. S., LI S. S. Genomic organization of human lactate dehydrogenase-A gene. Biochem J. 1985 Nov 1;231(3):537–541. doi: 10.1042/bj2310537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukasawa K. M., Li S. S. Nucleotide sequence of the putative regulatory region of mouse lactate dehydrogenase-A gene. Biochem J. 1986 Apr 15;235(2):435–439. doi: 10.1042/bj2350435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukasawa K. M., Li W. H., Yagi K., Luo C. C., Li S. S. Molecular evolution of mammalian lactate dehydrogenase-A genes and pseudogenes: association of a mouse processed pseudogene with a B1 repetitive sequence. Mol Biol Evol. 1986 Jul;3(4):330–342. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg E. Amino acid composition and properties of crystalline lactate dehydrogenase X from mouse testes. J Biol Chem. 1972 Apr 10;247(7):2044–2048. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg E. Infertility in female rabbits immunized with lactate dehydrogenase X. Science. 1973 Aug 3;181(4098):458–459. doi: 10.1126/science.181.4098.458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li S. S., Feldmann R. J., Okabe M., Pan Y. C. Molecular features and immunological properties of lactate dehydrogenase C4 isozymes from mouse and rat testes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):7017–7028. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li S. S., Fitch W. M., Pan Y. C., Sharief F. S. Evolutionary relationships of vertebrate lactate dehydrogenase isozymes A4 (muscle), B4 (heart), and C4 (testis). J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):7029–7032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li S. S., Tiano H. F., Fukasawa K. M., Yagi K., Shimizu M., Sharief F. S., Nakashima Y., Pan Y. E. Protein structure and gene organization of mouse lactate dehydrogenase-A isozyme. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Jun 3;149(2):215–225. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08914.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markert C. L., Shaklee J. B., Whitt G. S. Evolution of a gene. Multiple genes for LDH isozymes provide a model of the evolution of gene structure, function and regulation. Science. 1975 Jul 11;189(4197):102–114. doi: 10.1126/science.1138367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. A system for shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):309–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musick W. D., Rossmann M. G. The structure of mouse testicular lactate dehydrogenase isoenzyme C4 at 2.9 A resolution. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 25;254(16):7611–7620. doi: 10.2210/pdb1ldx/pdb. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okabe M., Akai K., Li S. S. Identification of lactate dehydrogenase-X translated in vitro from mouse testicular poly A-containing mRNA. Int J Biochem. 1982;14(5):371–375. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(82)90022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan Y. C., Sharief F. S., Okabe M., Huang S., Li S. S. Amino acid sequence studies on lactate dehydrogenase C4 isozymes from mouse and rat testes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):7005–7016. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Brownlee G. G. 3' non-coding region sequences in eukaryotic messenger RNA. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):211–214. doi: 10.1038/263211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark G. R., Williams J. G. Quantitative analysis of specific labelled RNA'S using DNA covalently linked to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jan;6(1):195–203. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.1.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujibo H., Tiano H. F., Li S. S. Nucleotide sequences of the cDNA and an intronless pseudogene for human lactate dehydrogenase-A isozyme. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Feb 15;147(1):9–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08711.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheat T. E., Goldberg E. Sperm-specific lactate dehydrogenase C4: antigenic structure and immunosuppression of fertility. Isozymes Curr Top Biol Med Res. 1983;7:113–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright L. L., Swofford J. H. Mouse lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) C4 (testis) is immunochemically cross-reactive with LDH A4 (muscle) and LDHB4 (heart). Scand J Immunol. 1984 Mar;19(3):247–254. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1984.tb00926.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]