Abstract
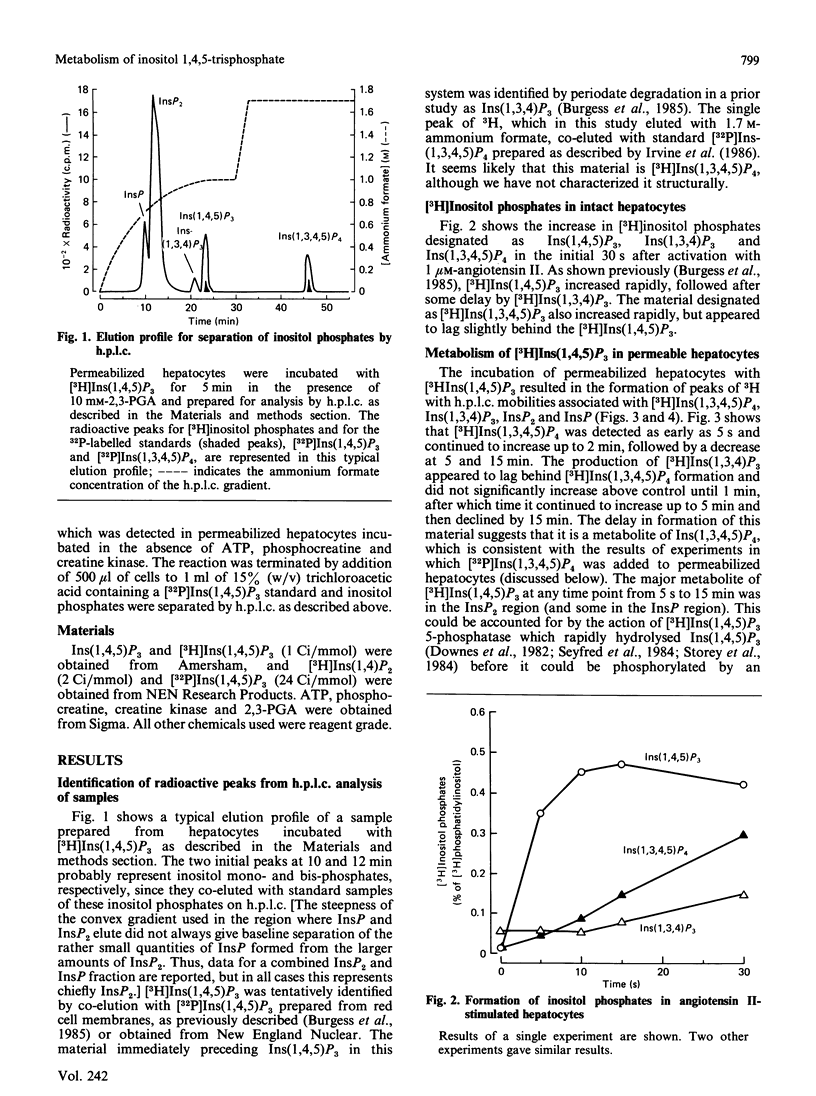
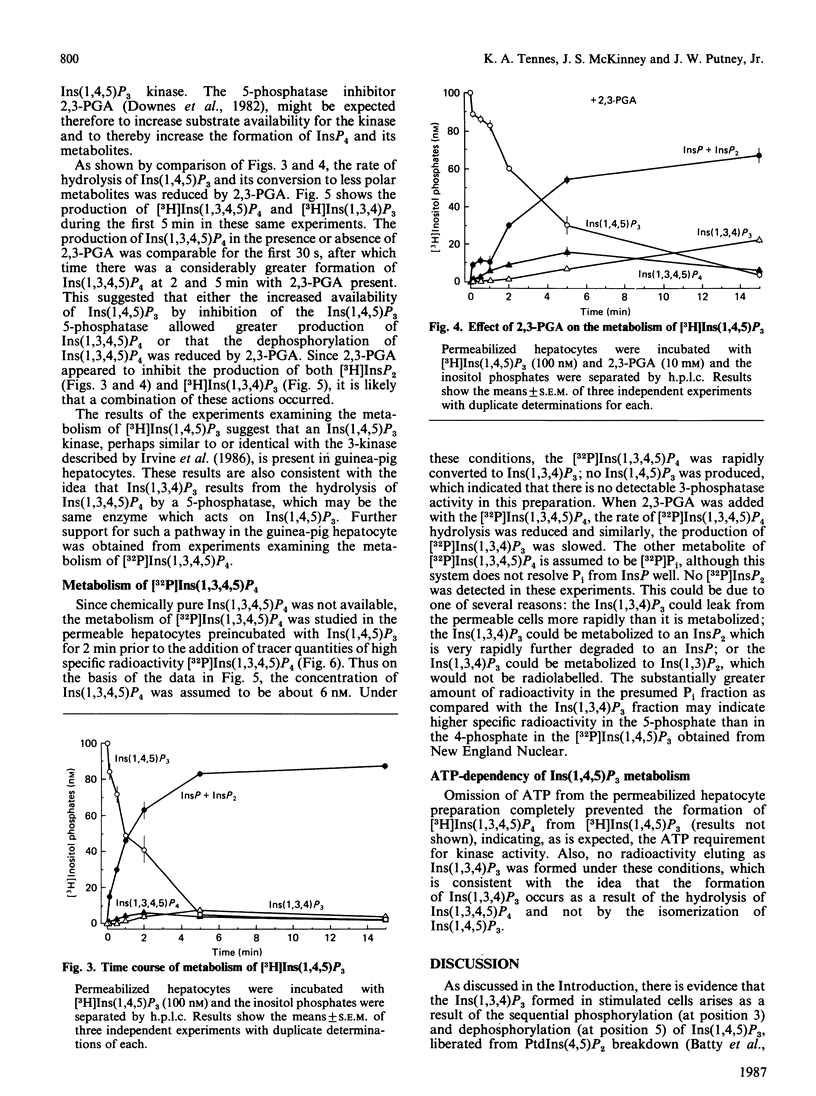
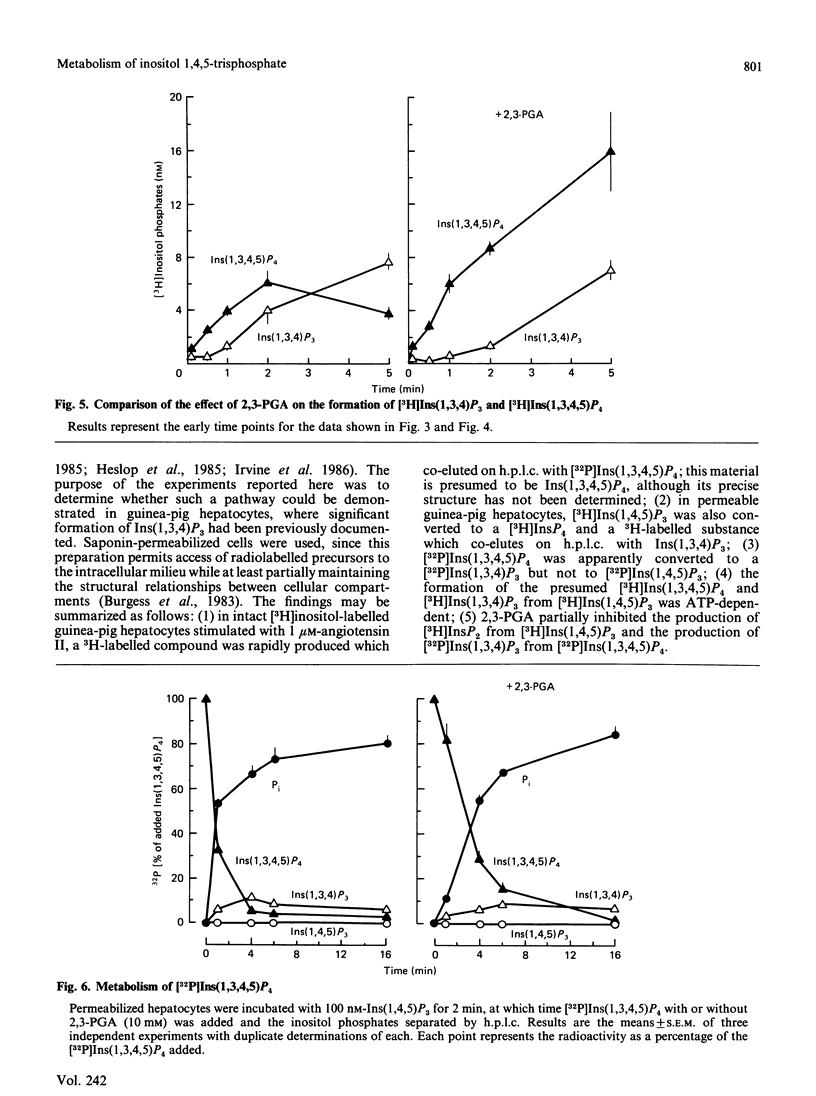
Metabolism of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate was investigated in permeabilized guinea-pig hepatocytes. The conversion of [3H]inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate to a more polar 3H-labelled compound occurred rapidly and was detected as early as 5 s. This material co-eluted from h.p.l.c. with inositol 1,3,4,5 tetrakis[32P]phosphate and is presumably an inositol tetrakisphosphate. A significant increase in the 3H-labelled material co-eluting from h.p.l.c. with inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate occurred only after a definite lag period. Incubation of permeabilized hepatocytes with inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakis[32P]phosphate resulted in the formation of 32P-labelled material that co-eluted with inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate; no inositol 1,4,5-tris[32P]phosphate was produced, suggesting the action of a 5-phosphomonoesterase. The half-time of hydrolysis of inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakis[32P]phosphate of approx. 1 min was increased to 3 min by 2,3-bisphosphoglyceric acid. Similarly, the rate of production of material tentatively designed as inositol 1,3,4-tris[32P]phosphate from the tetrakisphosphate was reduced by 10 mM-2,3-bisphosphoglyceric acid. In the absence of ATP there was no conversion of [3H]inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate to [3H]inositol tetrakisphosphate or to [3H]inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate, which suggests that the 1,3,4 isomer does not result from isomerization of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. The results of this study suggest that the origin of the 1,3,4 isomer of inositol trisphosphate in isolated hepatocytes is inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate and that inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate is rapidly converted to this tetrakisphosphate. The ability of 2,3-bisphosphoglyceric acid, an inhibitor of 5-phosphomonoesterase of red blood cell membrane, to inhibit the breakdown of the tetrakisphosphate suggests that the enzyme which removes the 5-phosphate from inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate may also act to convert the tetrakisphosphate to inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate. It is not known if the role of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate kinase is to inactivate inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate or whether the tetrakisphosphate product may have a messenger function in the cell.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Batty I. R., Nahorski S. R., Irvine R. F. Rapid formation of inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate following muscarinic receptor stimulation of rat cerebral cortical slices. Biochem J. 1985 Nov 15;232(1):211–215. doi: 10.1042/bj2320211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess G. M., Claret M., Jenkinson D. H. Effects of quinine and apamin on the calcium-dependent potassium permeability of mammalian hepatocytes and red cells. J Physiol. 1981 Aug;317:67–90. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess G. M., McKinney J. S., Irvine R. F., Putney J. W., Jr Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate formation in Ca2+-mobilizing-hormone-activated cells. Biochem J. 1985 Nov 15;232(1):237–243. doi: 10.1042/bj2320237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downes C. P., Mussat M. C., Michell R. H. The inositol trisphosphate phosphomonoesterase of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochem J. 1982 Apr 1;203(1):169–177. doi: 10.1042/bj2030169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen C. A., Mah S., Williamson J. R. Formation and metabolism of inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate in liver. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8100–8103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heslop J. P., Irvine R. F., Tashjian A. H., Jr, Berridge M. J. Inositol tetrakis- and pentakisphosphates in GH4 cells. J Exp Biol. 1985 Nov;119:395–401. doi: 10.1242/jeb.119.1.395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Anggård E. E., Letcher A. J., Downes C. P. Metabolism of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate in rat parotid glands. Biochem J. 1985 Jul 15;229(2):505–511. doi: 10.1042/bj2290505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Letcher A. J., Heslop J. P., Berridge M. J. The inositol tris/tetrakisphosphate pathway--demonstration of Ins(1,4,5)P3 3-kinase activity in animal tissues. Nature. 1986 Apr 17;320(6063):631–634. doi: 10.1038/320631a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Letcher A. J., Lander D. J., Downes C. P. Inositol trisphosphates in carbachol-stimulated rat parotid glands. Biochem J. 1984 Oct 1;223(1):237–243. doi: 10.1042/bj2230237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Moor R. M. Micro-injection of inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate activates sea urchin eggs by a mechanism dependent on external Ca2+. Biochem J. 1986 Dec 15;240(3):917–920. doi: 10.1042/bj2400917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merritt J. E., Taylor C. W., Rubin R. P., Putney J. W., Jr Evidence suggesting that a novel guanine nucleotide regulatory protein couples receptors to phospholipase C in exocrine pancreas. Biochem J. 1986 Jun 1;236(2):337–343. doi: 10.1042/bj2360337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seyfred M. A., Farrell L. E., Wells W. W. Characterization of D-myo-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate phosphatase in rat liver plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13204–13208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storey D. J., Shears S. B., Kirk C. J., Michell R. H. Stepwise enzymatic dephosphorylation of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate to inositol in liver. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):374–376. doi: 10.1038/312374a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas A. P., Marks J. S., Coll K. E., Williamson J. R. Quantitation and early kinetics of inositol lipid changes induced by vasopressin in isolated and cultured hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5716–5725. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



