Abstract
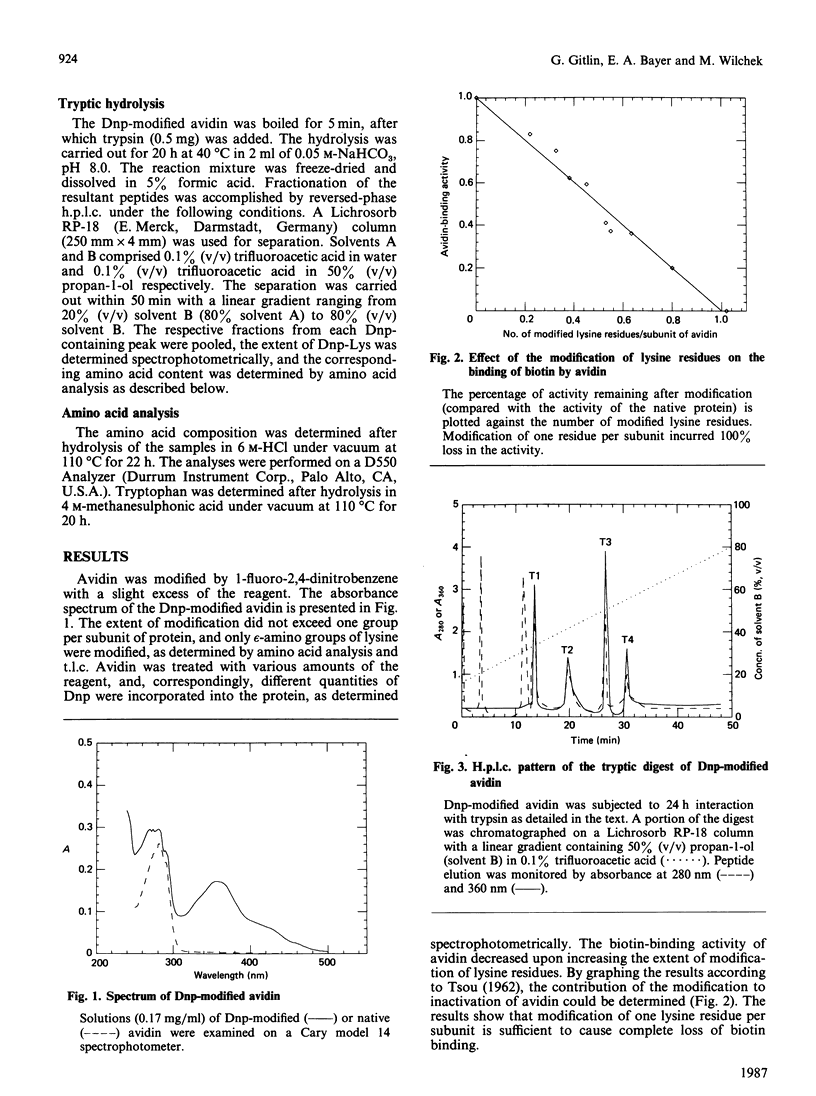
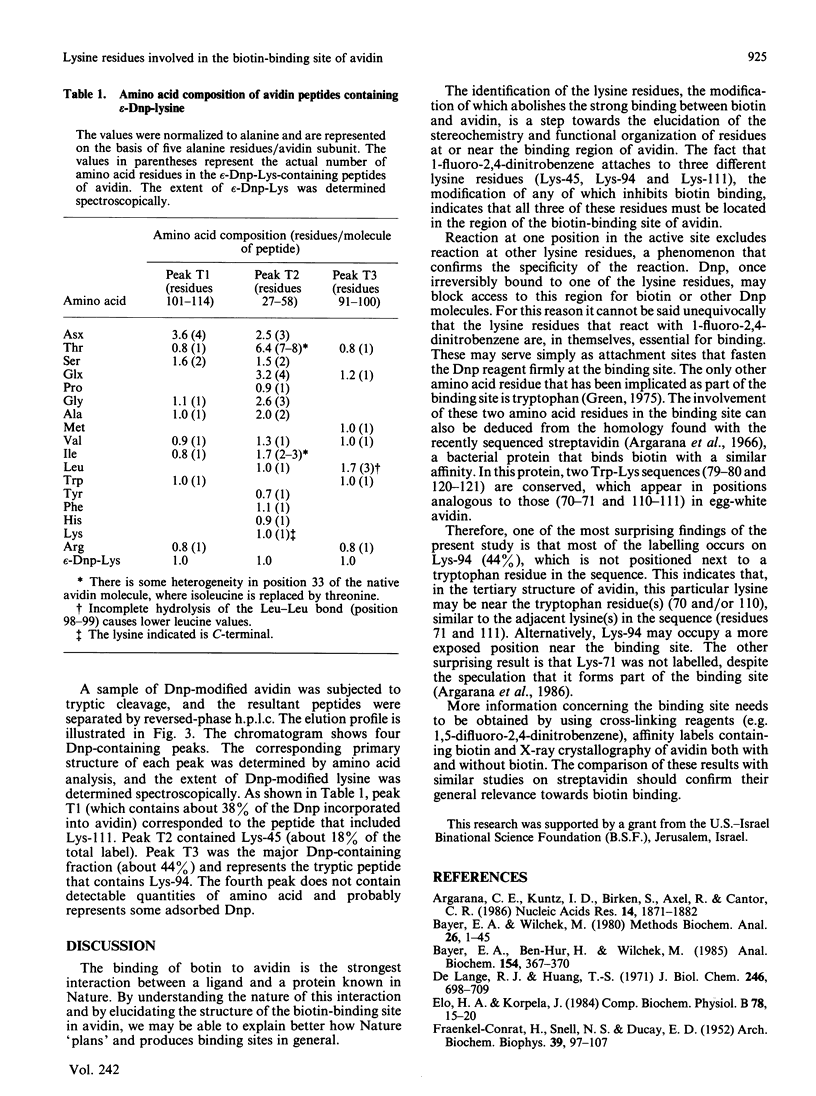
Egg-white avidin was treated with 1-fluoro-2,4-dinitrobenzene. Modification of an average of one lysine residue per avidin subunit caused the complete loss of biotin binding. Tryptic peptides obtained from the 2,4-dinitrophenylated avidin were fractionated by reversed-phase h.p.l.c. Three peptides contained the 2,4-dinitrophenyl group. Amino acid analysis revealed that lysine residues 45, 94 and 111 are modified and probably comprise part of the biotin-binding site.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Argaraña C. E., Kuntz I. D., Birken S., Axel R., Cantor C. R. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of the streptavidin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 25;14(4):1871–1882. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.4.1871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer E. A., Ben-Hur H., Wilchek M. A sensitive enzyme assay for biotin, avidin, and streptavidin. Anal Biochem. 1986 Apr;154(1):367–370. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90538-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer E. A., Wilchek M. The use of the avidin-biotin complex as a tool in molecular biology. Methods Biochem Anal. 1980;26:1–45. doi: 10.1002/9780470110461.ch1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLange R. J., Huang T. S. Egg white avidin. 3. Sequence of the 78-residue middle cyanogen bromide peptide. Complete amino acid sequence of the protein subunit. J Biol Chem. 1971 Feb 10;246(3):698–709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elo H. A., Korpela J. The occurrence and production of avidin: a new conception of the high-affinity biotin-binding protein. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1984;78(1):15–20. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(84)90137-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRAENKEL-CONRAT H., SNELL N. S., DUCAY E. D. Avidin. II. Composition and mode of action of avidin A. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1952 Jul;39(1):97–107. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(52)90264-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN N. M. AVIDIN. 3. THE NATURE OF THE BIOTIN-BINDING SITE. Biochem J. 1963 Dec;89:599–609. doi: 10.1042/bj0890599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN N. M. Spectroscopic evidence for the participation of tryptophan residues in the binding of biotin by avidin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 May 7;59:244–246. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90726-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green N. M. Avidin. Adv Protein Chem. 1975;29:85–133. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60411-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TSOU C. L. Relation between modification of functional groups of proteins and their biological activity. I.A graphical method for the determination of the number and type of essential groups. Sci Sin. 1962 Nov;11:1535–1558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


