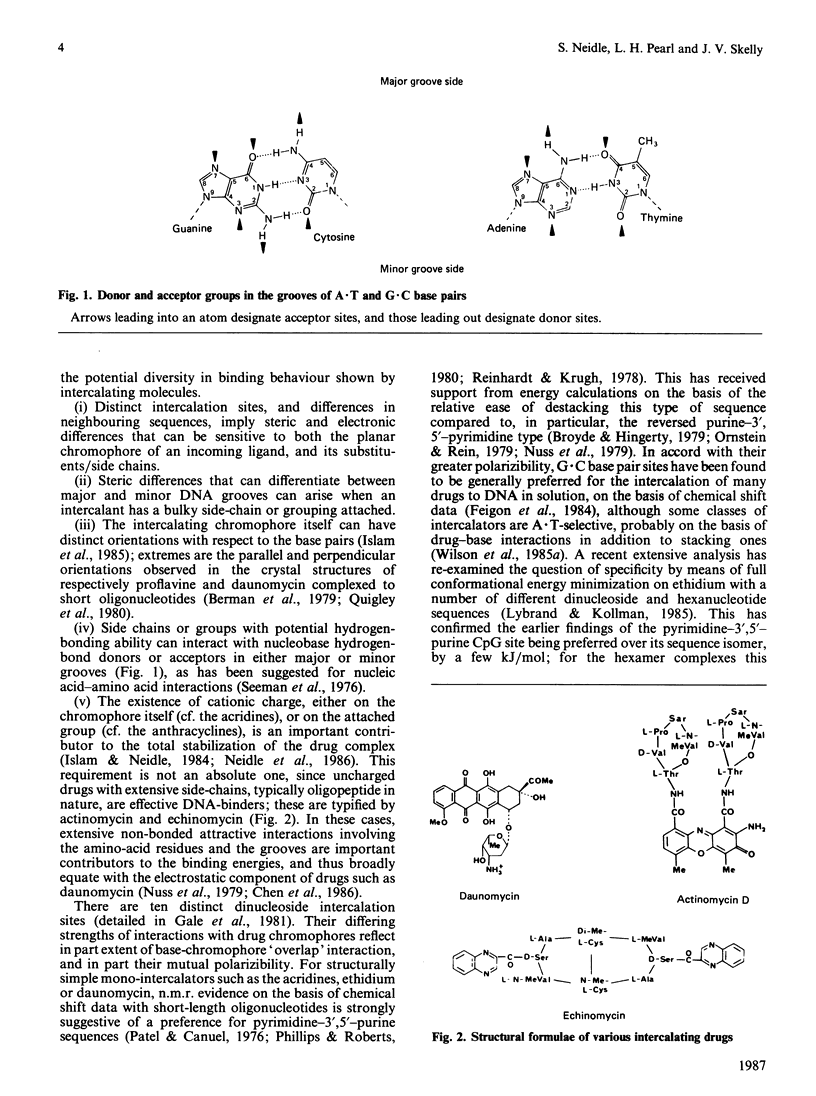
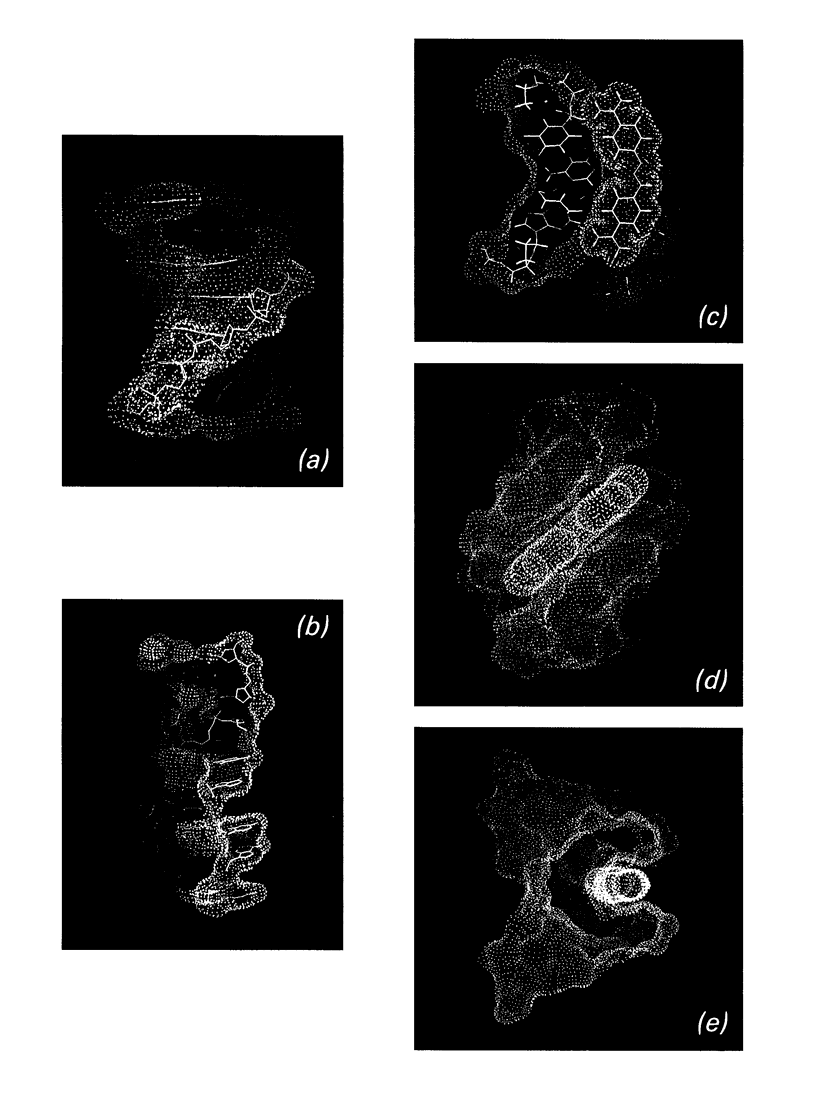
Full text
PDF




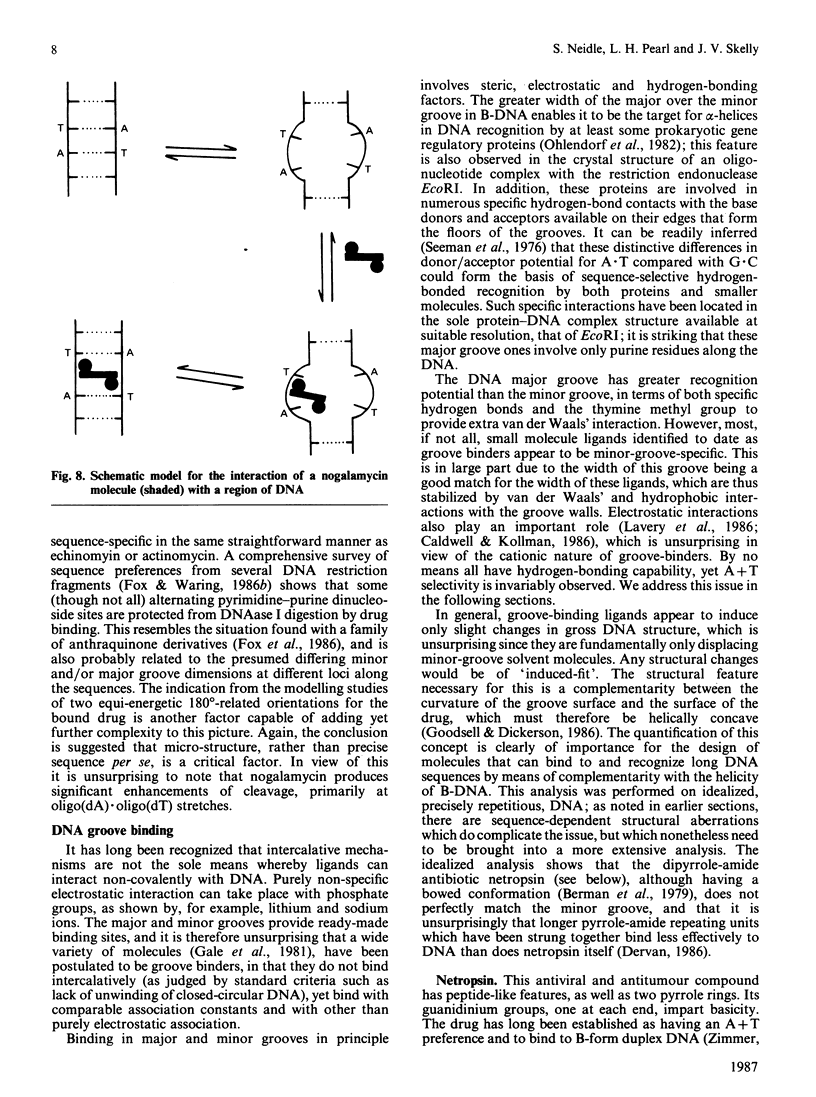
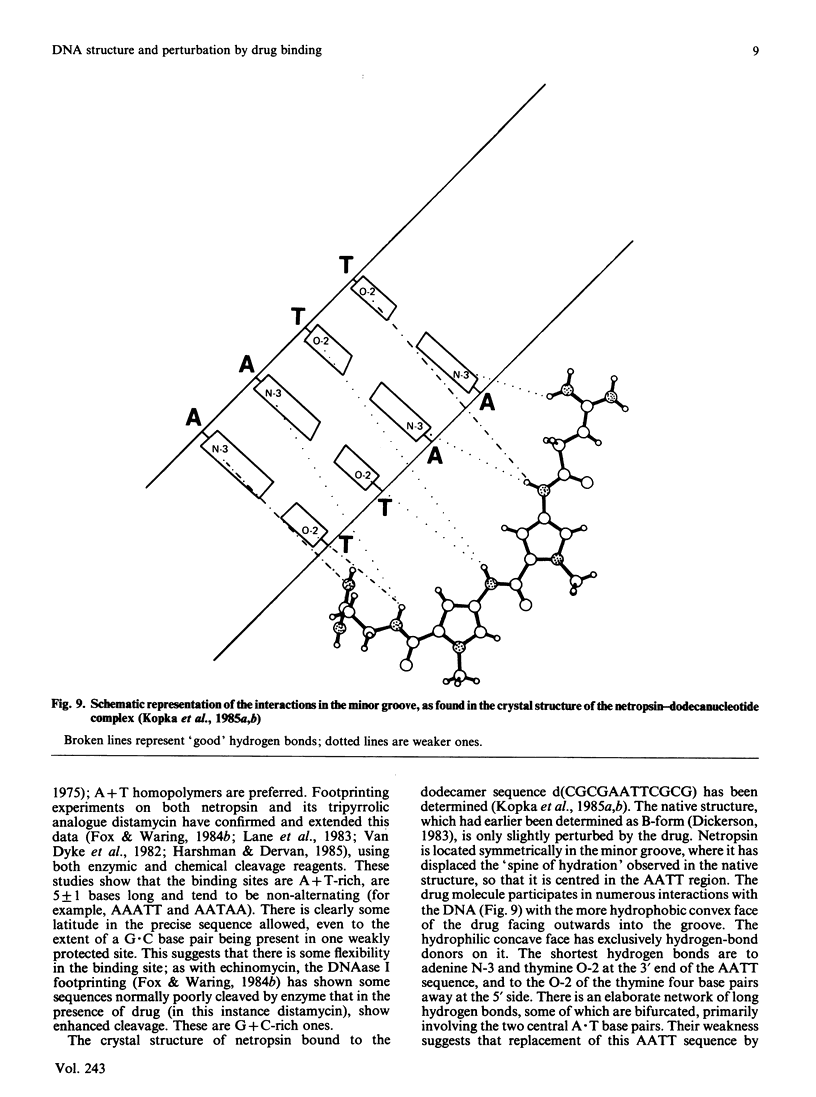

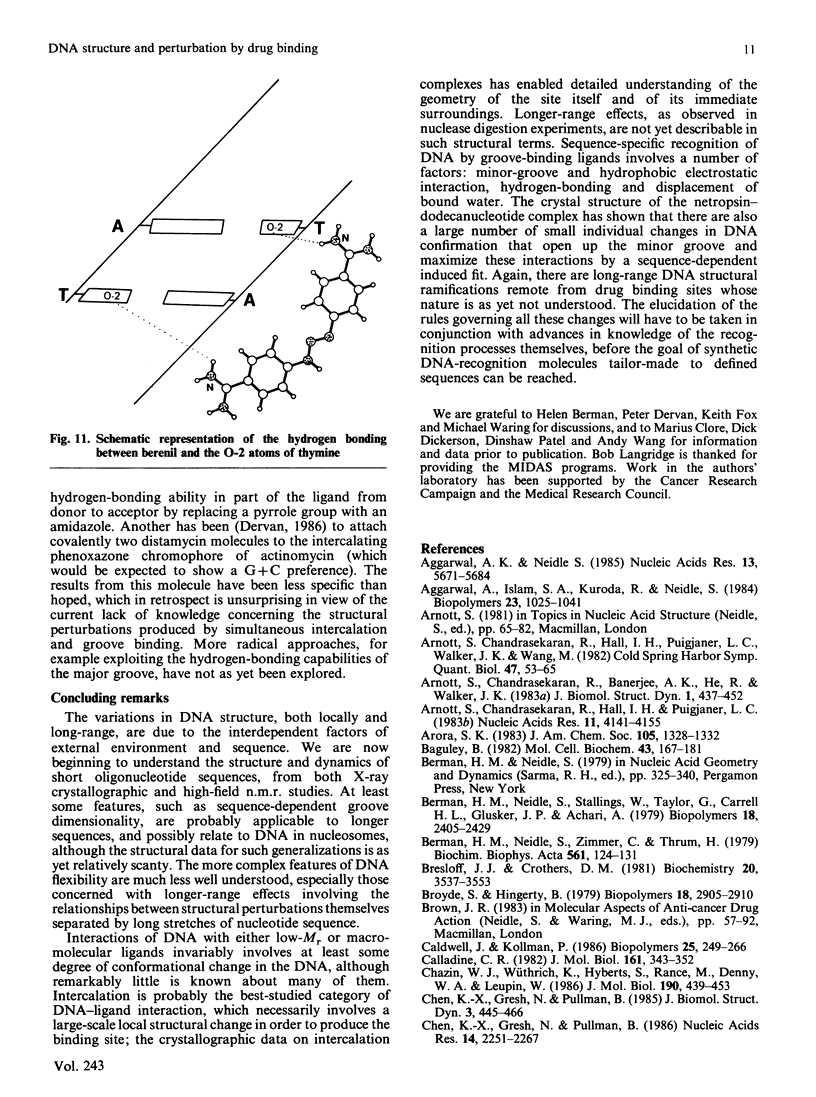


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aggarwal A. K., Neidle S. Nucleic acid binding drugs. Part XIII. Molecular motion in a drug-nucleic acid model system: thermal motion analysis of a proflavine-dinucleoside crystal structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Aug 12;13(15):5671–5684. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.15.5671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aggarwal A., Islam S. A., Kuroda R., Neidle S. X-ray crystallographic analysis of a ternary intercalation complex between proflavine and the dinucleoside monophosphates CpA and UpG. Biopolymers. 1984 Jun;23(6):1025–1041. doi: 10.1002/bip.360230605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnott S., Chandrasekaran R., Banerjee A. K., He R., Walker J. K. New wrinkles on polynucleotide duplexes. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1983 Oct;1(2):437–452. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1983.10507453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnott S., Chandrasekaran R., Hall I. H., Puigjaner L. C. Heteronomous DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jun 25;11(12):4141–4155. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.12.4141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnott S., Chandrasekaran R., Hall I. H., Puigjaner L. C., Walker J. K., Wang M. DNA secondary structures: helices, wrinkles, and junctions. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 1):53–65. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baguley B. C. Nonintercalative DNA-binding antitumour compounds. Mol Cell Biochem. 1982 Apr 2;43(3):167–181. doi: 10.1007/BF00223008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman H. M., Neidle S., Zimmer C., Thrum H. Netropsin, a DNA-binding oligopeptide structural and binding studies. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jan 26;561(1):124–131. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(79)90496-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bresloff J. L., Crothers D. M. Equilibrium studies of ethidium--polynucleotide interactions. Biochemistry. 1981 Jun 9;20(12):3547–3553. doi: 10.1021/bi00515a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broyde S., Hingerty B. Conformational origin of the pyrimidine (3'-5') purine base sequence preference for intercalation into RNAs. Biopolymers. 1979 Nov;18(11):2905–2910. doi: 10.1002/bip.1979.360181117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell J., Kollman P. A molecular mechanical study of netropsin-DNA interactions. Biopolymers. 1986 Feb;25(2):249–266. doi: 10.1002/bip.360250207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calladine C. R. Mechanics of sequence-dependent stacking of bases in B-DNA. J Mol Biol. 1982 Oct 25;161(2):343–352. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90157-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chazin W. J., Wüthrich K., Hyberts S., Rance M., Denny W. A., Leupin W. 1H nuclear magnetic resonance assignments for d-(GCATTAATGC)2 using experimental refinements of established procedures. J Mol Biol. 1986 Aug 5;190(3):439–453. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90014-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen K. X., Gresh N., Pullman B. A theoretical investigation on the sequence selective binding of daunomycin to double-stranded polynucleotides. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1985 Dec;3(3):445–466. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1985.10508434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clore G. M., Gronenborn A. M., Moss D. S., Tickle I. J. Refinement of the solution structure of the B DNA hexamer 5'd(C-G-T-A-C-G)2 on the basis of inter-proton distance data. J Mol Biol. 1985 Sep 5;185(1):219–226. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90195-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
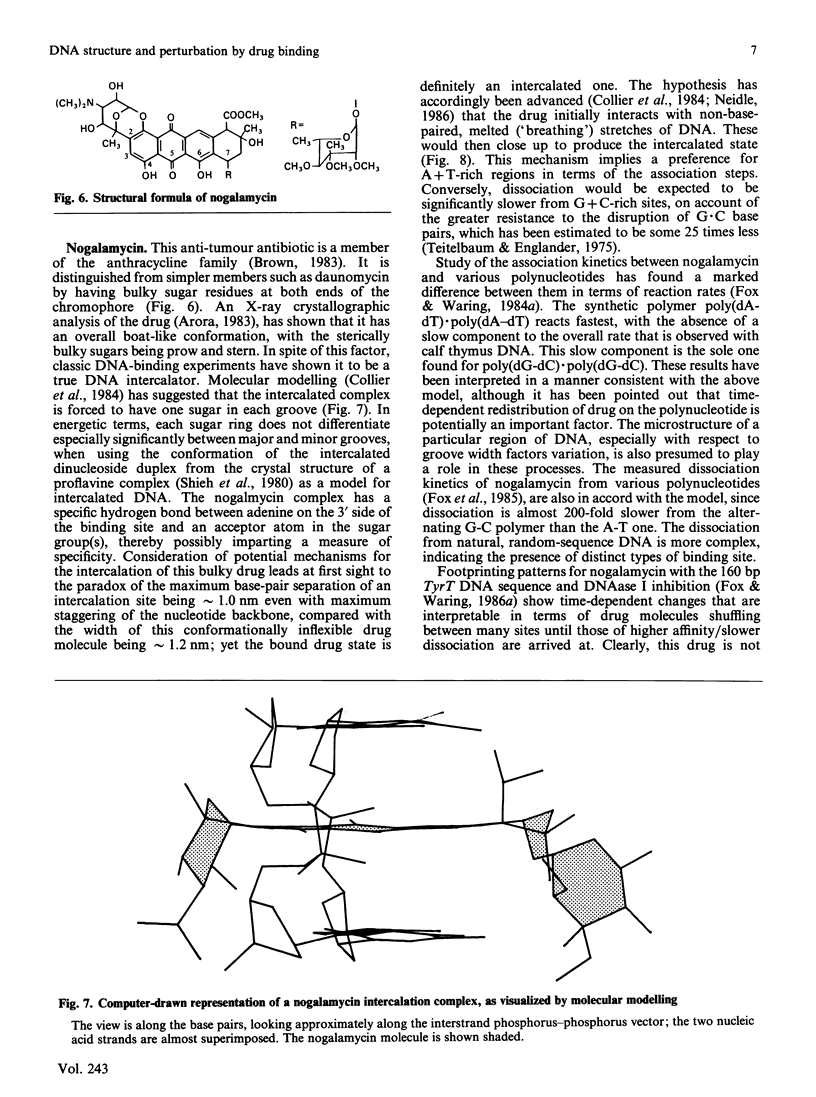
- Collier D. A., Neidle S., Brown J. R. Molecular models for the interaction of the anti-tumour drug nogalamycin with DNA. Biochem Pharmacol. 1984 Sep 15;33(18):2877–2880. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(84)90210-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dervan P. B. Design of sequence-specific DNA-binding molecules. Science. 1986 Apr 25;232(4749):464–471. doi: 10.1126/science.2421408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson R. E. Base sequence and helix structure variation in B and A DNA. J Mol Biol. 1983 May 25;166(3):419–441. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson R. E., Drew H. R. Kinematic model for B-DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7318–7322. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson R. E., Drew H. R. Structure of a B-DNA dodecamer. II. Influence of base sequence on helix structure. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jul 15;149(4):761–786. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90357-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson R. E., Kopka M. L. Nuclear Overhauser data and stereochemical considerations suggest that netropsin binds symmetrically within the minor groove of poly(dA).poly(dT), forming hydrogen bonds with both strands of the double helix. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1985 Dec;3(3):423–431. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1985.10508431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew H. R., Dickerson R. E. Structure of a B-DNA dodecamer. III. Geometry of hydration. J Mol Biol. 1981 Sep 25;151(3):535–556. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90009-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew H. R. Structural specificities of five commonly used DNA nucleases. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jul 15;176(4):535–557. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90176-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew H. R., Travers A. A. DNA structural variations in the E. coli tyrT promoter. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):491–502. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90379-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew H. R., Travers A. A. Structural junctions in DNA: the influence of flanking sequence on nuclease digestion specificities. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 25;13(12):4445–4467. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.12.4445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feigon J., Denny W. A., Leupin W., Kearns D. R. Interactions of antitumor drugs with natural DNA: 1H NMR study of binding mode and kinetics. J Med Chem. 1984 Apr;27(4):450–465. doi: 10.1021/jm00370a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feuerstein B. G., Pattabiraman N., Marton L. J. Spermine-DNA interactions: a theoretical study. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5948–5952. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox K. R., Brassett C., Waring M. J. Kinetics of dissociation of nogalamycin from DNA: comparison with other anthracycline antibiotics. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jul 5;840(3):383–392. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(85)90219-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox K. R., Waring M. J., Brown J. R., Neidle S. DNA sequence preferences for the anti-cancer drug mitoxanthrone and related anthraquinones revealed by DNase I footprinting. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jul 7;202(2):289–294. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80703-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox K. R., Waring M. J. DNA structural variations produced by actinomycin and distamycin as revealed by DNAase I footprinting. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 21;12(24):9271–9285. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.24.9271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox K. R., Waring M. J. Evidence of different binding sites for nogalamycin in DNA revealed by association kinetics. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Nov 28;802(2):162–168. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(84)90157-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox K. R., Waring M. J. Footprinting reveals that nogalamycin and actinomycin shuffle between DNA binding sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 11;14(5):2001–2014. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.5.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox K. R., Waring M. J. Kinetic evidence that echinomycin migrates between potential DNA binding sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jan 25;13(2):595–603. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.2.595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox K. R., Waring M. J. Nucleotide sequence binding preferences of nogalamycin investigated by DNase I footprinting. Biochemistry. 1986 Jul 29;25(15):4349–4356. doi: 10.1021/bi00363a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frederick C. A., Grable J., Melia M., Samudzi C., Jen-Jacobson L., Wang B. C., Greene P., Boyer H. W., Rosenberg J. M. Kinked DNA in crystalline complex with EcoRI endonuclease. Nature. 1984 May 24;309(5966):327–331. doi: 10.1038/309327a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodsell D., Dickerson R. E. Isohelical analysis of DNA groove-binding drugs. J Med Chem. 1986 May;29(5):727–733. doi: 10.1021/jm00155a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresh N., Pullman B. A theoretical study of the nonintercalative binding of berenil and stilbamidine to double-stranded (dA-dT)n oligomers. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 May;25(3):452–458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresh N. Theoretical study of the binding of aliphatic diamines to the minor groove of a B-DNA (dA-dT)11 oligomer. Biopolymers. 1985 Aug;24(8):1527–1542. doi: 10.1002/bip.360240809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harshman K. D., Dervan P. B. Molecular recognition of B-DNA by Hoechst 33258. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jul 11;13(13):4825–4835. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.13.4825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Islam S. A., Neidle S., Gandecha B. M., Partridge M., Patterson L. H., Brown J. R. Comparative computer graphics and solution studies of the DNA interaction of substituted anthraquinones based on doxorubicin and mitoxantrone. J Med Chem. 1985 Jul;28(7):857–864. doi: 10.1021/jm00145a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain S. C., Sobell H. M. Visualization of drug-nucleic acid interactions at atomic resolution. VIII. Structures of two ethidium/dinucleoside monophosphate crystalline complexes containing ethidium: cytidylyl(3'-5') guanosine. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1984 Mar;1(5):1179–1194. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1984.10507511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain S. C., Tsai C. C., Sobell H. M. Visualization of drug-nucleic acid interactions at atomic resolution. II. Structure of an ethidium/dinucleoside monophosphate crystalline complex, ethidium:5-iodocytidylyl (3'-5') guanosine. J Mol Biol. 1977 Aug 15;114(3):317–331. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90253-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kollman P. A., Weiner P. K., Dearing A. Studies of nucleotide conformations and interactions. The relative stabilities of double-helical B-DNA sequence isomers. Biopolymers. 1981 Dec;20(12):2583–2621. doi: 10.1002/bip.1981.360201208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo H. S., Wu H. M., Crothers D. M. DNA bending at adenine . thymine tracts. Nature. 1986 Apr 10;320(6062):501–506. doi: 10.1038/320501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopka M. L., Yoon C., Goodsell D., Pjura P., Dickerson R. E. Binding of an antitumor drug to DNA, Netropsin and C-G-C-G-A-A-T-T-BrC-G-C-G. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jun 25;183(4):553–563. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90171-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopka M. L., Yoon C., Goodsell D., Pjura P., Dickerson R. E. The molecular origin of DNA-drug specificity in netropsin and distamycin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(5):1376–1380. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.5.1376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LERMAN L. S. Structural considerations in the interaction of DNA and acridines. J Mol Biol. 1961 Feb;3:18–30. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(61)80004-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane M. J., Dabrowiak J. C., Vournakis J. N. Sequence specificity of actinomycin D and Netropsin binding to pBR322 DNA analyzed by protection from DNase I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3260–3264. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavery R., Pullman B. The molecular electrostatic potential, steric accessibility and hydration of Dickerson's B-DNA dodecamer d(CpGpCpGpApApTpTpCpGpCpG). Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 11;9(15):3765–3777. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.15.3765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low C. M., Drew H. R., Waring M. J. Sequence-specific binding of echinomycin to DNA: evidence for conformational changes affecting flanking sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 25;12(12):4865–4879. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.12.4865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lown J. W., Krowicki K., Balzarini J., De Clercq E. Structure-activity relationship of novel oligopeptide antiviral and antitumor agents related to netropsin and distamycin. J Med Chem. 1986 Jul;29(7):1210–1214. doi: 10.1021/jm00157a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lybrand T., Kollman P. Molecular mechanical calculations on the interaction of ethidium cation with double-helical DNA. Biopolymers. 1985 Oct;24(10):1863–1879. doi: 10.1002/bip.360241003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahendrasingam A., Forsyth V. T., Hussain R., Greenall R. J., Pigram W. J., Fuller W. Time-resolved X-ray diffraction studies of the B in equilibrium D structural transition in the DNA double helix. Science. 1986 Jul 11;233(4760):195–197. doi: 10.1126/science.3726529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCall M., Brown T., Hunter W. N., Kennard O. The crystal structure of d(GGATGGGAG): an essential part of the binding site for transcription factor IIIA. Nature. 1986 Aug 14;322(6080):661–664. doi: 10.1038/322661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCall M., Brown T., Kennard O. The crystal structure of d(G-G-G-G-C-C-C-C). A model for poly(dG).poly(dC). J Mol Biol. 1985 Jun 5;183(3):385–396. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90009-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller W., Crothers D. M. Studies of the binding of actinomycin and related compounds to DNA. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jul 28;35(2):251–290. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(68)80024-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidle S., Abraham Z. Structural and sequence-dependent aspects of drug intercalation into nucleic acids. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1984;17(1):73–121. doi: 10.3109/10409238409110270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidle S., Berman H. M. X-ray crystallographic studies of nucleic acids and nucleic acid-drug complexes. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1983;41(2):43–66. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(83)90025-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson L., Clore G. M., Gronenborn A. M., Brünger A. T., Karplus M. Structure refinement of oligonucleotides by molecular dynamics with nuclear Overhauser effect interproton distance restraints: application to 5' d(C-G-T-A-C-G)2. J Mol Biol. 1986 Apr 5;188(3):455–475. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90168-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlendorf D. H., Anderson W. F., Fisher R. G., Takeda Y., Matthews B. W. The molecular basis of DNA-protein recognition inferred from the structure of cro repressor. Nature. 1982 Aug 19;298(5876):718–723. doi: 10.1038/298718a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ornstein R. L., Rein R. Energetics of intercalation specificity. I. Backbone unwinding. Biopolymers. 1979 May;18(5):1277–1291. doi: 10.1002/bip.1979.360180517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel D. J., Canuel L. L. Ethidium bromide-(dC-dG-dC-dG)2 complex in solution: intercalation and sequence specificity of drug binding at the tetranucleotide duplex level. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3343–3347. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel D. J., Kozlowski S. A., Bhatt R. Sequence dependence of base-pair stacking in right-handed DNA in solution: proton nuclear Overhauser effect NMR measurements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3908–3912. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel D. J., Kozlowski S. A., Marky L. A., Broka C., Rice J. A., Itakura K., Breslauer K. J. Premelting and melting transitions in the d(CGCGAATTCGCG) self-complementary duplex in solution. Biochemistry. 1982 Feb 2;21(3):428–436. doi: 10.1021/bi00532a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel D. J., Kozlowski S. A., Rice J. A. Hydrogen bonding, overlap geometry, and sequence specificity in anthracycline antitumor antibiotic.DNA complexes in solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3333–3337. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel D. J., Pardi A., Itakura K. DNA conformation, dynamics, and interactions in solution. Science. 1982 May 7;216(4546):581–590. doi: 10.1126/science.6280281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel D. J., Shapiro L., Hare D. Sequence-dependent conformation of DNA duplexes. The AATT segment of the d(G-G-A-A-T-T-C-C) duplex in aqueous solution. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 25;261(3):1223–1229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel D. J., Shapiro L. Molecular recognition in noncovalent antitumor agent-DNA complexes: NMR studies of the base and sequence dependent recognition of the DNA minor groove by netropsin. Biochimie. 1985 Jul-Aug;67(7-8):887–915. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(85)80181-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel D. J., Shapiro L. Sequence-dependent recognition of DNA duplexes. Netropsin complexation to the AATT site of the d(G-G-A-A-T-T-C-C) duplex in aqueous solution. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 25;261(3):1230–1240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel D. J., Shapiro L. Sequence-dependent recognition of DNA duplexes: netropsin complexation to the TATA site of the d(G-G-T-A-T-A-C-C) duplex in aqueous solution. Biopolymers. 1986 Apr;25(4):707–727. doi: 10.1002/bip.360250413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peck L. J., Wang J. C. Sequence dependence of the helical repeat of DNA in solution. Nature. 1981 Jul 23;292(5821):375–378. doi: 10.1038/292375a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. R., Roberts G. C. Proton nuclear magnetic resonance study of the self-complementary hexanucleotide d(pTpA)3 and its interaction with daunomycin. Biochemistry. 1980 Oct 14;19(21):4795–4801. doi: 10.1021/bi00562a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quigley G. J., Ughetto G., van der Marel G. A., van Boom J. H., Wang A. H., Rich A. Non-Watson-Crick G.C and A.T base pairs in a DNA-antibiotic complex. Science. 1986 Jun 6;232(4755):1255–1258. doi: 10.1126/science.3704650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quigley G. J., Wang A. H., Ughetto G., van der Marel G., van Boom J. H., Rich A. Molecular structure of an anticancer drug-DNA complex: daunomycin plus d(CpGpTpApCpG). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7204–7208. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhardt C. G., Krugh T. R. A comparative study of ethidium bromide complexes with dinucleotides and DNA: direct evidence for intercalation and nucleic acid sequence preferences. Biochemistry. 1978 Nov 14;17(23):4845–4854. doi: 10.1021/bi00616a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes D., Klug A. An underlying repeat in some transcriptional control sequences corresponding to half a double helical turn of DNA. Cell. 1986 Jul 4;46(1):123–132. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90866-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes D., Klug A. Sequence-dependent helical periodicity of DNA. Nature. 1981 Jul 23;292(5821):378–380. doi: 10.1038/292378a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder K., Silver S., DeLucia A. L., Fanning E., Tegtmeyer P. An altered DNA conformation in origin region I is a determinant for the binding of SV40 large T antigen. Cell. 1986 Mar 14;44(5):719–725. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90838-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarma M. H., Gupta G., Sarma R. H. Netropsin specifically recognizes one of the two conformationally equivalent strands of poly(dA).poly(dT). One dimensional NMR study at 500 MHz involving NOE transfer between netropsin and DNA protons. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1985 Jun;2(6):1085–1095. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1985.10507625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman N. C., Rosenberg J. M., Rich A. Sequence-specific recognition of double helical nucleic acids by proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):804–808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seibel G. L., Singh U. C., Kollman P. A. A molecular dynamics simulation of double-helical B-DNA including counterions and water. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6537–6540. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shakked Z., Rabinovich D., Kennard O., Cruse W. B., Salisbury S. A., Viswamitra M. A. Sequence-dependent conformation of an A-DNA double helix. The crystal structure of the octamer d(G-G-T-A-T-A-C-C). J Mol Biol. 1983 May 15;166(2):183–201. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shieh H. S., Berman H. M., Dabrow M., Neidle S. The structure of drug-deoxydinucleoside phosphate complex; generalized conformational behavior of intercalation complexes with RNA and DNA fragments. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 11;8(1):85–97. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.1.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. T., Künzler P. Cromatin and core particles formed from the inner histones and synthetic polydeoxyribonucleotides of defined sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Apr;6(4):1387–1415. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.4.1387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh U. C., Weiner S. J., Kollman P. Molecular dynamics simulations of d(C-G-C-G-A) X d(T-C-G-C-G) with and without "hydrated" counterions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):755–759. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suck D., Oefner C. Structure of DNase I at 2.0 A resolution suggests a mechanism for binding to and cutting DNA. Nature. 1986 Jun 5;321(6070):620–625. doi: 10.1038/321620a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takusagawa F., Dabrow M., Neidle S., Berman H. M. The structure of a pseudo intercalated complex between actinomycin and the DNA binding sequence d(GpC). Nature. 1982 Apr 1;296(5856):466–469. doi: 10.1038/296466a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor E. R., Olson W. K. Theoretical studies of nucleic acid interactions. I. Estimates of conformational mobility in intercalated chains. Biopolymers. 1983 Dec;22(12):2667–2702. doi: 10.1002/bip.360221213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teitelbaum H., Englander S. W. Open states in native polynucleotides. I. Hydrogen-exchange study of adenine-containing double helices. J Mol Biol. 1975 Feb 15;92(1):55–78. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90091-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ughetto G., Wang A. H., Quigley G. J., van der Marel G. A., van Boom J. H., Rich A. A comparison of the structure of echinomycin and triostin A complexed to a DNA fragment. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 11;13(7):2305–2323. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.7.2305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke M. M., Dervan P. B. Echinomycin binding sites on DNA. Science. 1984 Sep 14;225(4667):1122–1127. doi: 10.1126/science.6089341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke M. W., Hertzberg R. P., Dervan P. B. Map of distamycin, netropsin, and actinomycin binding sites on heterogeneous DNA: DNA cleavage-inhibition patterns with methidiumpropyl-EDTA.Fe(II). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5470–5474. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. H., Fujii S., van Boom J. H., Rich A. Molecular structure of the octamer d(G-G-C-C-G-G-C-C): modified A-DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):3968–3972. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.3968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. H., Gessner R. V., van der Marel G. A., van Boom J. H., Rich A. Crystal structure of Z-DNA without an alternating purine-pyrimidine sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3611–3615. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. H., Quigley G. J., Kolpak F. J., Crawford J. L., van Boom J. H., van der Marel G., Rich A. Molecular structure of a left-handed double helical DNA fragment at atomic resolution. Nature. 1979 Dec 13;282(5740):680–686. doi: 10.1038/282680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. H., Ughetto G., Quigley G. J., Hakoshima T., van der Marel G. A., van Boom J. H., Rich A. The molecular structure of a DNA-triostin A complex. Science. 1984 Sep 14;225(4667):1115–1121. doi: 10.1126/science.6474168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westhof E., Rao S. T., Sundaralingam M. Crystallographic studies of drug-nucleic acid interactions: proflavine intercalation between the non-complementary base-pairs of cytidilyl-3',5'-adenosine. J Mol Biol. 1980 Sep 25;142(3):331–361. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90276-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson W. D., Wang Y. H., Krishnamoorthy C. R., Smith J. C. Poly(dA).poly(dT) exists in an unusual conformation under physiological conditions: propidium binding to poly(dA).poly(dT) and poly[d(A-T)].poly[d(A-T)]. Biochemistry. 1985 Jul 16;24(15):3991–3999. doi: 10.1021/bi00336a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wing R., Drew H., Takano T., Broka C., Tanaka S., Itakura K., Dickerson R. E. Crystal structure analysis of a complete turn of B-DNA. Nature. 1980 Oct 23;287(5784):755–758. doi: 10.1038/287755a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakrzewska K., Lavery R., Pullman B. The solvation contribution to the binding energy of DNA with non-intercalating antibiotics. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Aug 24;12(16):6559–6574. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.16.6559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakrzewska K., Lavery R., Pullman B. Theoretical studies of the selective binding to DNA of two non-intercalating ligands: netropsin and SN 18071. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Dec 20;11(24):8825–8839. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.24.8825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmer C. Effects of the antibiotics netropsin and distamycin A on the structure and function of nucleic acids. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1975;15(0):285–318. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60122-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]