Abstract
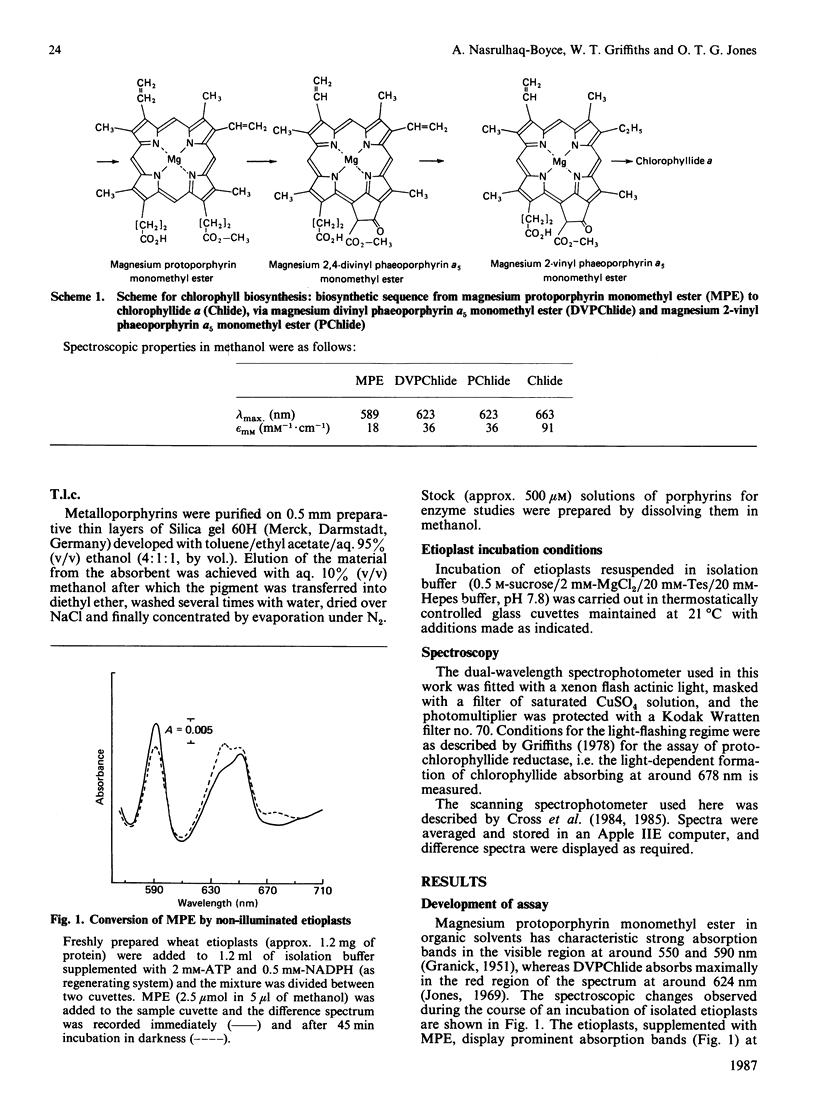
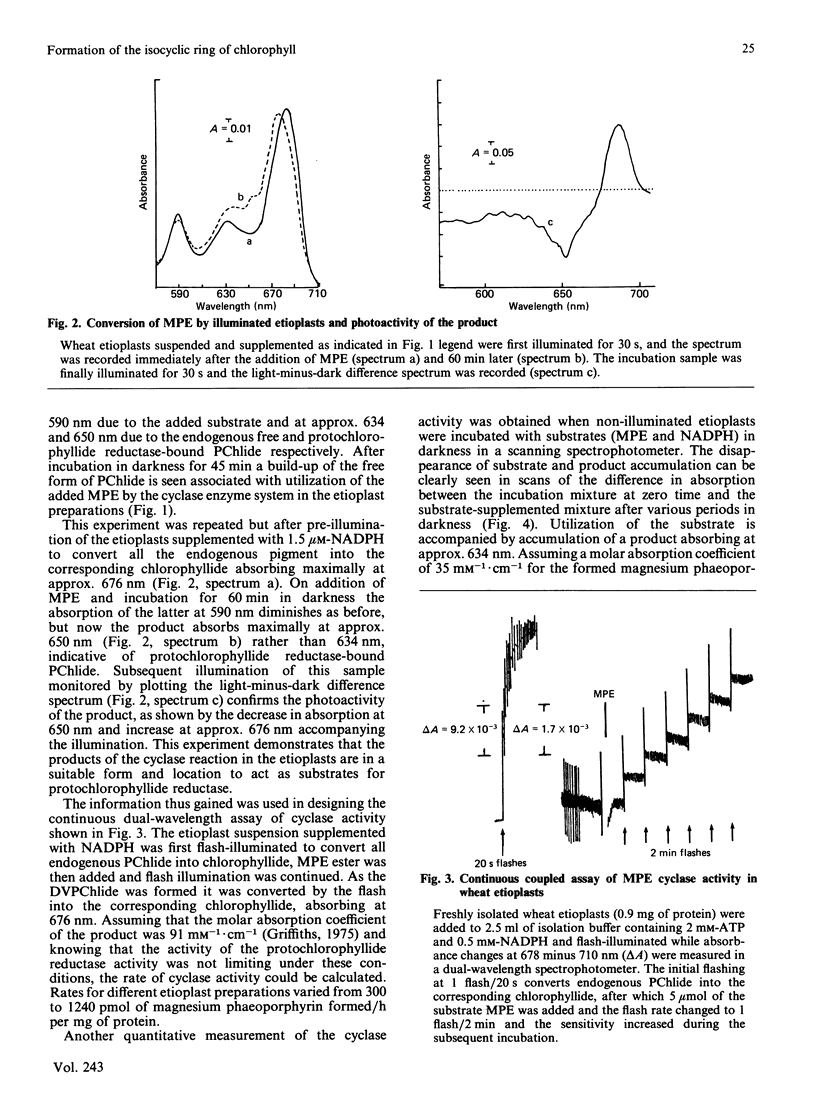
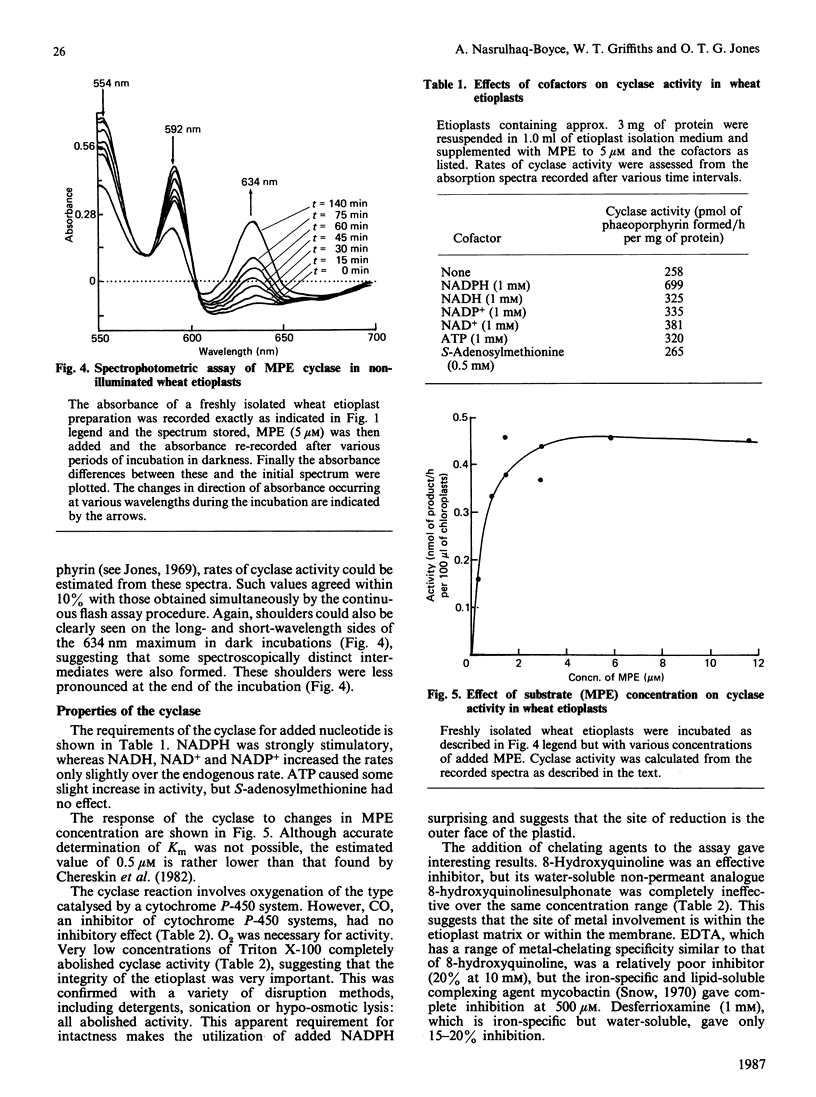
A continuous spectroscopic assay has been developed for magnesium protoporphyrin monomethyl ester oxidative cyclase, which records either the dark formation of both free and protein-bound magnesium phaeoporphyrin or, following flash illumination, its corresponding chlorin. The properties of the enzyme were studied in wheat etioplasts. When plastids were pre-illuminated in the presence of NADPH all endogenous protochlorophyllide was converted into chlorophyllide and the product of dark incubation with magnesium protoporphyrin monomethyl ester was protein-bound magnesium 2-vinyl phaeoporphyrin a5 monomethyl ester with either a vinyl or an ethyl group at position 4 of the macrocycle alone. Rates of chlorin production from magnesium protoporphyrin monomethyl ester (up to 1240 pmol/h per mg of protein) were adequate to support known rates of plant chlorophyll synthesis. The enzyme required NADPH and O2 and had an approximate Km of 0.5 microM for magnesium protoporphyrin IX monomethyl ester. Lipid-soluble metal-complexing agents inhibited enzyme activity: hydrophilic agents were ineffective. The strong inhibition of mycobactin suggested the involvement of iron ions. Zinc protoporphyrin monomethyl ester, but not copper or nickel or metal-free protoporphyrin monomethyl esters, was a substrate; magnesium protoporphyrin dimethyl ester was inhibitory. The activity of the enzyme was unchanged by prior greening of the plants. The activity in isolated etioplasts was very dependent upon intactness of the plastid structure.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chereskin B. M., Castelfranco P. A., Dallas J. L., Straub K. M. Mg-2,4-divinyl pheoporphyrin a5: the product of a reaction catalyzed in vitro by developing chloroplasts. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Oct 1;226(1):10–18. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90266-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chereskin B. M., Wong Y. S., Castelfranco P. A. In Vitro Synthesis of the Chlorophyll Isocyclic Ring : Transformation of Magnesium-Protoporphyrin IX and Magnesium-Protoporphyrin IX Monomethyl Ester into Magnesium-2,4-Divinyl Pheoporphyrin A(5). Plant Physiol. 1982 Oct;70(4):987–993. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.4.987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross A. R., Parkinson J. F., Jones O. T. Mechanism of the superoxide-producing oxidase of neutrophils. O2 is necessary for the fast reduction of cytochrome b-245 by NADPH. Biochem J. 1985 Mar 15;226(3):881–884. doi: 10.1042/bj2260881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross A. R., Parkinson J. F., Jones O. T. The superoxide-generating oxidase of leucocytes. NADPH-dependent reduction of flavin and cytochrome b in solubilized preparations. Biochem J. 1984 Oct 15;223(2):337–344. doi: 10.1042/bj2230337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellsworth R. K., Aronoff S. Investigations of the biogenesis of chlorophyll a. IV. Isolation and partial characterization of some biosynthetic intermediates between Mg-protoporphine IX monomethyl ester and Mg-vinylpheoporphine a5, obtained from Chlorella mutants. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Mar;130(1):374–383. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90047-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRANICK S. The structural and functional relationships between heme and chlorophyll. Harvey Lect. 1948 1949;Series 44:220–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths W. T. Characterization of the terminal stages of chlorophyll (ide) synthesis in etioplast membrane preparations. Biochem J. 1975 Dec;152(3):623–635. doi: 10.1042/bj1520623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths W. T., Jones O. T. Magnesium 2,4-divinylphaeoporphyrin alpha-5 as a substrate for chlorophyll biosynthesis in vitro. FEBS Lett. 1975 Feb 15;50(3):355–358. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80526-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths W. T. Reconstitution of chlorophyllide formation by isolated etioplast membranes. Biochem J. 1978 Sep 15;174(3):681–692. doi: 10.1042/bj1740681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths W. T. Substrate-specificity studies on protochlorophyllide reductase in barley (Hordeum vulgare) etioplast membranes. Biochem J. 1980 Jan 15;186(1):267–278. doi: 10.1042/bj1860267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones O. T., Saunders V. A. Energy-linked electron transfer reactions in Rhodopseudomonas viridis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Sep 20;275(3):427–436. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(72)90223-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mapleston R. E., Griffiths W. T. Effects of illumination of whole barley plants on the protochlorophyllide-activating system in the isolated plastids. Biochem Soc Trans. 1977;5(1):319–321. doi: 10.1042/bst0050319a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver R. P., Griffiths W. T. Pigment-protein complexes of illuminated etiolated leaves. Plant Physiol. 1982 Oct;70(4):1019–1025. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.4.1019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snow G. A. Mycobactins: iron-chelating growth factors from mycobacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1970 Jun;34(2):99–125. doi: 10.1128/br.34.2.99-125.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong Y. S., Castelfranco P. A., Goff D. A., Smith K. M. Intermediates in the formation of the chlorophyll isocyclic ring. Plant Physiol. 1985 Nov;79(3):725–729. doi: 10.1104/pp.79.3.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong Y. S., Castelfranco P. A. Properties of the Mg-Protoporphyrin IX Monomethyl Ester (Oxidative) Cyclase System. Plant Physiol. 1985 Nov;79(3):730–733. doi: 10.1104/pp.79.3.730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong Y. S., Castelfranco P. A. Resolution and Reconstitution of Mg-Protoporphyrin IX Monomethyl Ester (Oxidative) Cyclase, the Enzyme System Responsible for the Formation of the Chlorophyll Isocyclic Ring. Plant Physiol. 1984 Jul;75(3):658–661. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.3.658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


