Abstract
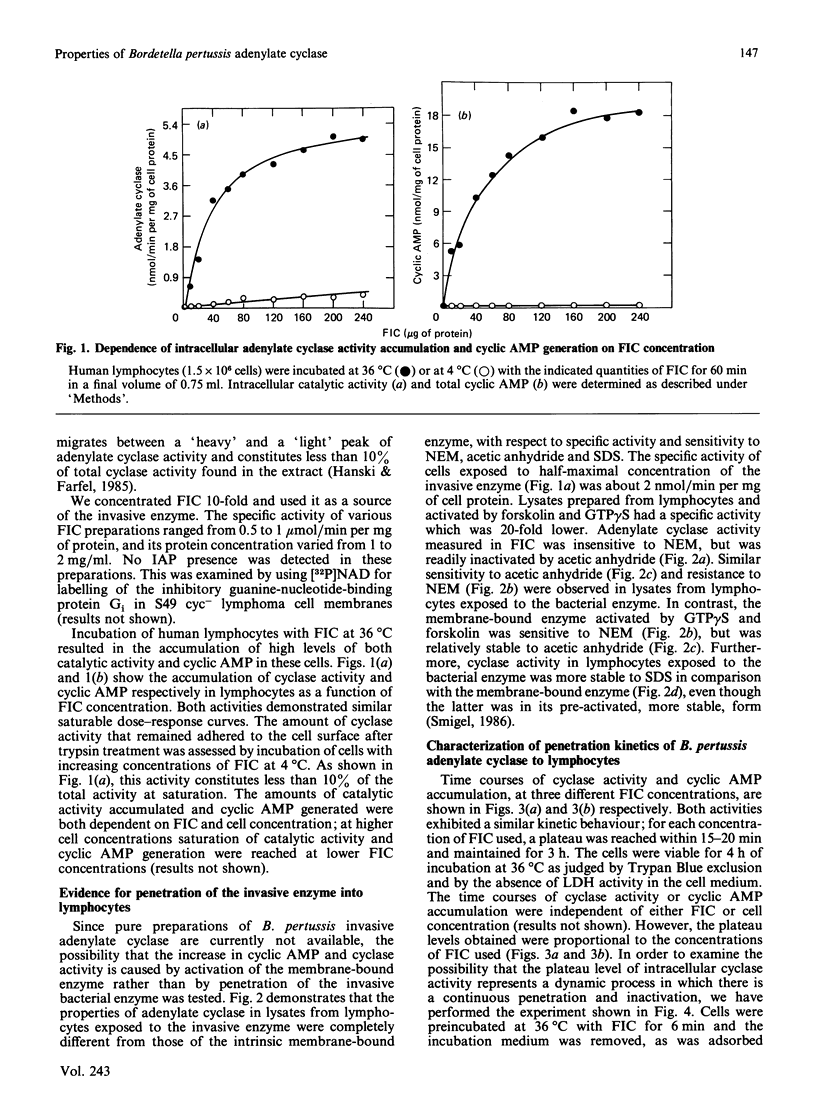
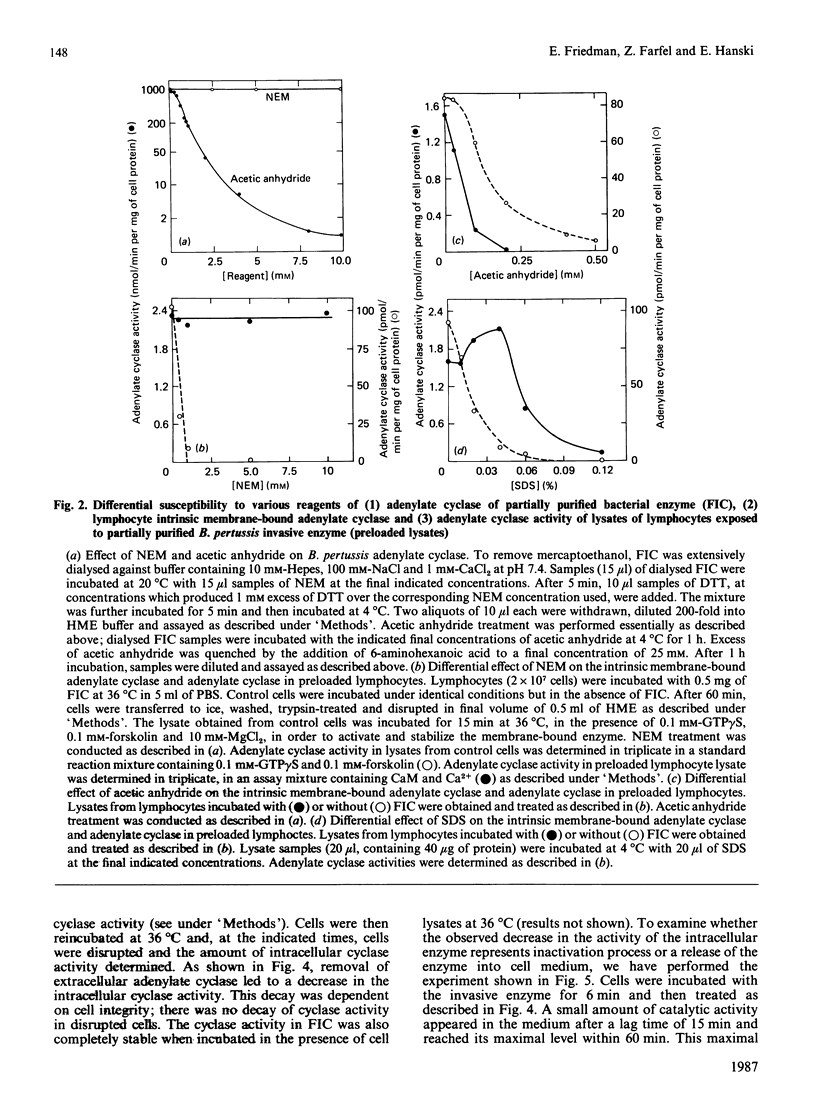
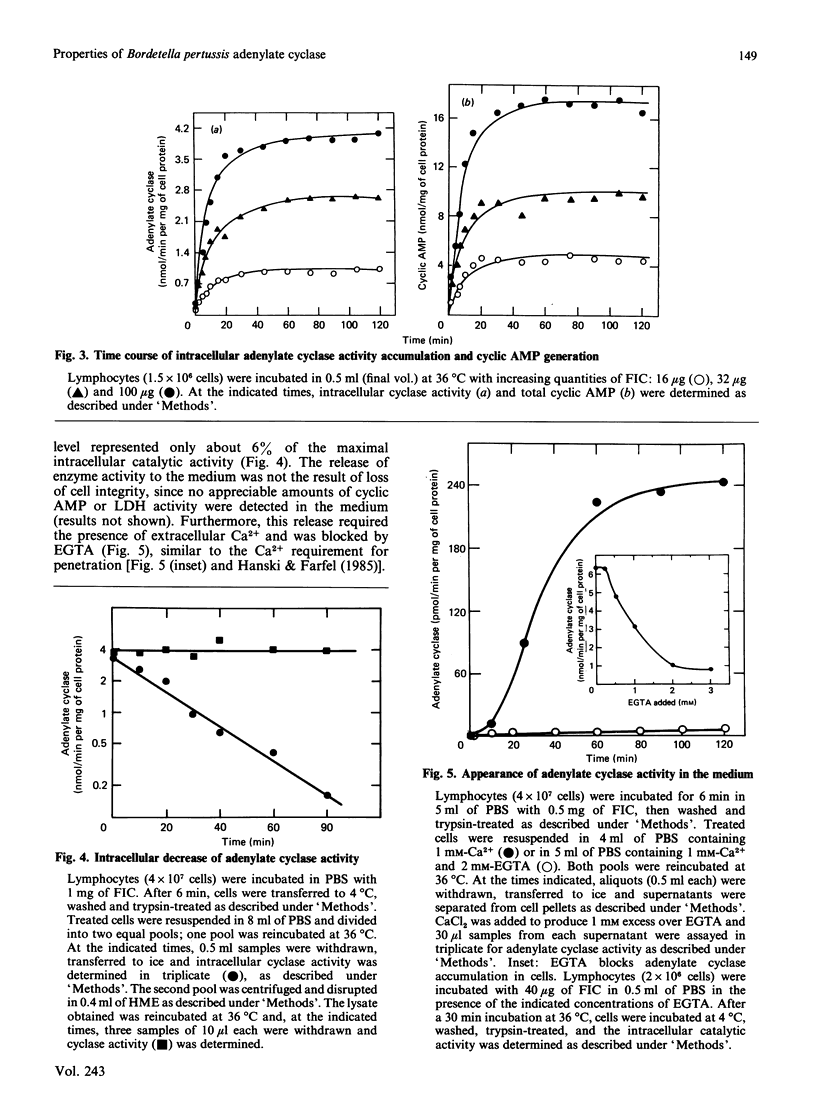
Bordetella pertussis, the causative organism of whooping cough, produces a calmodulin-sensitive adenylate cyclase. Confer & Eaton [(1982) Science 217, 948-950] have shown that an extract from B. pertussis increases intracellular cyclic AMP levels in neutrophils and suggested that this increase is caused by the bacterial adenylate cyclase which penetrates these cells. We demonstrate in the present study that adenylate cyclase activity in lysates from lymphocytes exposed to a partially purified preparation of the bacterial enzyme has properties completely different from those of the intrinsic membrane-bound enzyme. Adenylate cyclase activity in lysates from lymphocytes exposed to the invasive enzyme is insensitive to N-ethylmaleimide, readily inactivated by acetic anhydride and relatively stable to SDS. Similar properties are exhibited by the bacterial enzyme itself. By contrast, the intrinsic membrane-bound enzyme activated by forskolin and guanosine 5'-gamma-thiotriphosphate is sensitive to N-ethylmaleimide and SDS and relatively stable to acetic anhydride. This strongly supports the notion that B. pertussis adenylate cyclase penetrates cells. Using the partially purified preparation of the invasive enzyme, we have studied the kinetics of its penetration. The intracellular catalytic activity reaches a steady state within 20 min, irrespective of enzyme or cell concentration. Steady-state levels are maintained for at least 2 h provided that the invasive enzyme is present in the incubation medium. Upon its removal, a rapid decrease (t1/2 approximately equal to 15 min) in the intracellular cyclase level is observed. This decrease reflects intracellular inactivation of the bacterial enzyme and is not caused by the release of the enzyme to the cell medium.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Confer D. L., Eaton J. W. Phagocyte impotence caused by an invasive bacterial adenylate cyclase. Science. 1982 Sep 3;217(4563):948–950. doi: 10.1126/science.6287574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Confer D. L., Slungaard A. S., Graf E., Panter S. S., Eaton J. W. Bordetella adenylate cyclase toxin: entry of bacterial adenylate cyclase into mammalian cells. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphorylation Res. 1984;17:183–187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farfel Z., Friedman E., Hanski E. The invasive adenylate cyclase of Bordetella pertussis. Intracellular localization and kinetics of penetration into various cells. Biochem J. 1987 Apr 1;243(1):153–158. doi: 10.1042/bj2430153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanski E., Farfel Z. Bordetella pertussis invasive adenylate cyclase. Partial resolution and properties of its cellular penetration. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 10;260(9):5526–5532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewlett E. L., Urban M. A., Manclark C. R., Wolff J. Extracytoplasmic adenylate cyclase of Bordetella pertussis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):1926–1930. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.1926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewlett E., Wolff J. Soluble adenylate cyclase from the culture medium of Bordetella pertussis: purification and characterization. J Bacteriol. 1976 Aug;127(2):890–898. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.2.890-898.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Ui M. Slow interaction of islet-activating protein with pancreatic islets during primary culture to cause reversal of alpha-adrenergic inhibition of insulin secretion. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 25;255(20):9580–9588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leppla S. H. Anthrax toxin edema factor: a bacterial adenylate cyclase that increases cyclic AMP concentrations of eukaryotic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3162–3166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss J., Vaughan M. Activation of adenylate cyclase by choleragen. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:581–600. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.003053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandvig K., Olsnes S. Effect of temperature on the uptake, excretion and degradation of abrin and ricin by HeLa cells. Exp Cell Res. 1979 Jun;121(1):15–25. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(79)90439-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shattuck R. L., Storm D. R. Calmodulin inhibits entry of Bordetella pertussis adenylate cyclase into animal cells. Biochemistry. 1985 Nov 5;24(23):6323–6328. doi: 10.1021/bi00344a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smigel M. D. Purification of the catalyst of adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 5;261(4):1976–1982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. A., Hewlett E. L., Myers G. A., Falkow S. Pertussis toxin and extracytoplasmic adenylate cyclase as virulence factors of Bordetella pertussis. J Infect Dis. 1984 Aug;150(2):219–222. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.2.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff J., Cook G. H., Goldhammer A. R., Berkowitz S. A. Calmodulin activates prokaryotic adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3841–3844. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff J., Cook G. H., Goldhammer A. R., Londos C., Hewlett E. L. Bordetella pertussis: multiple attacks on host cell cyclic AMP regulation. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphorylation Res. 1984;17:161–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


