Abstract
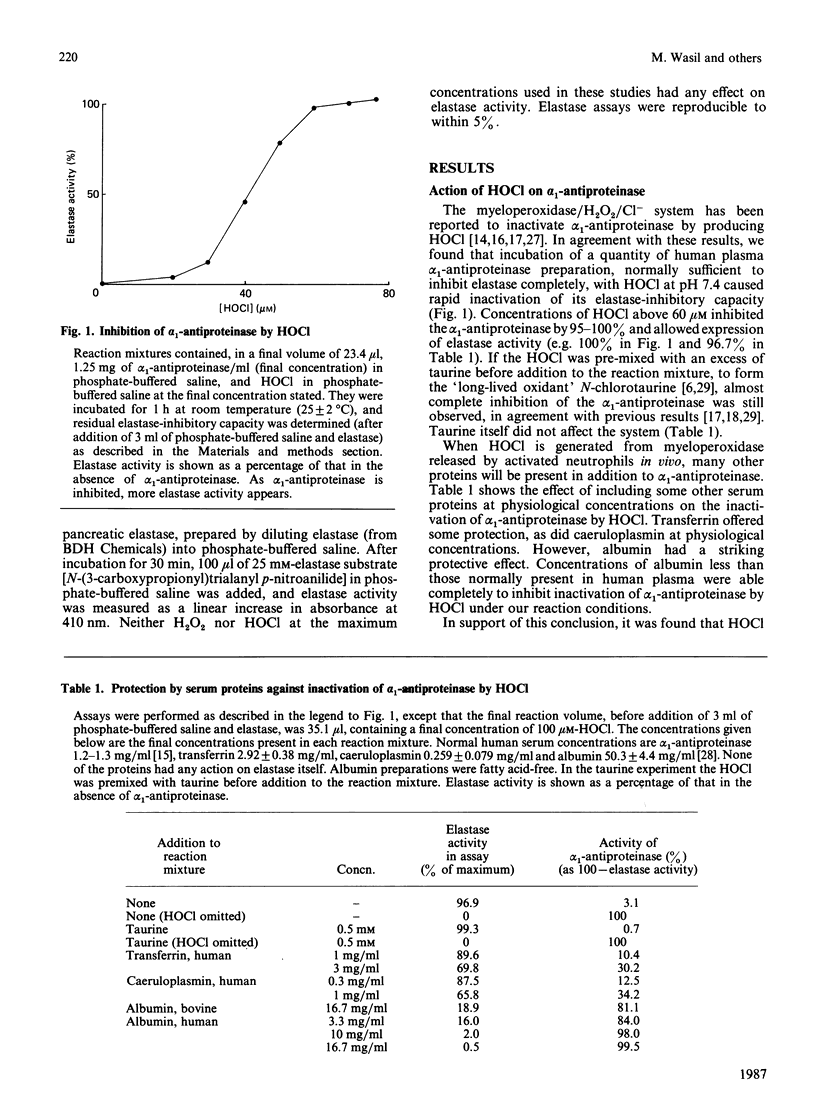
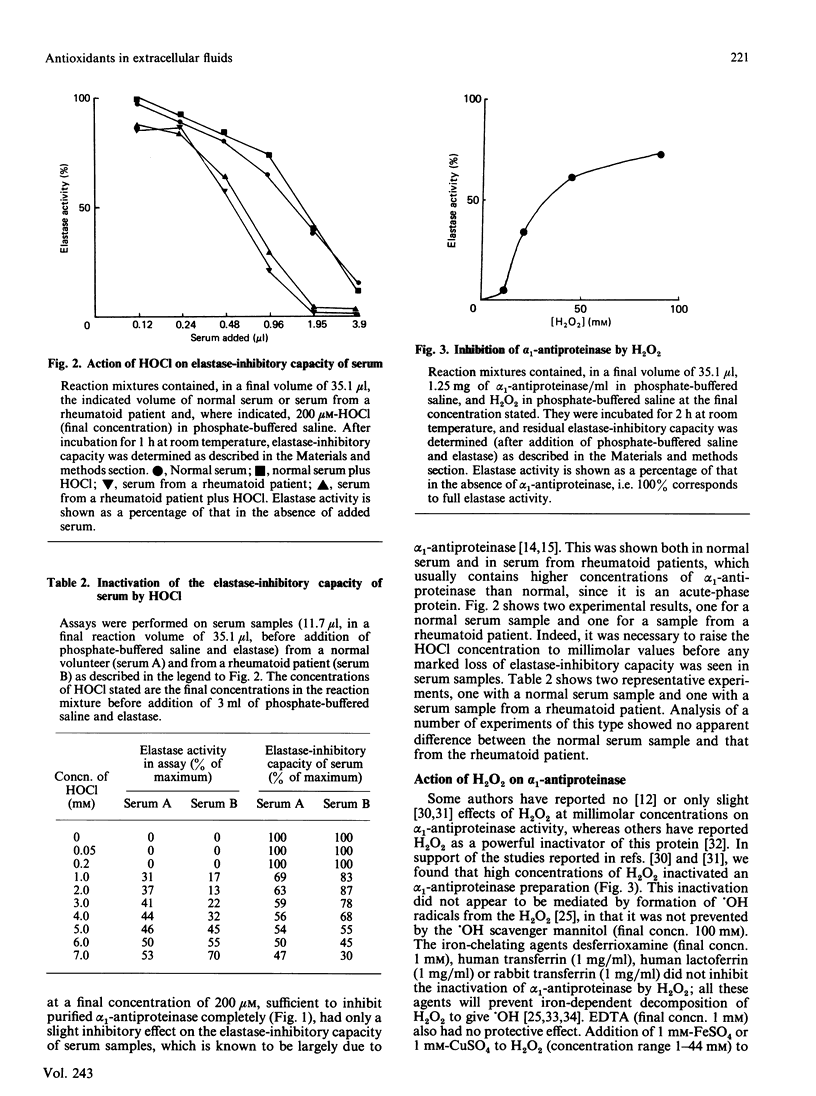
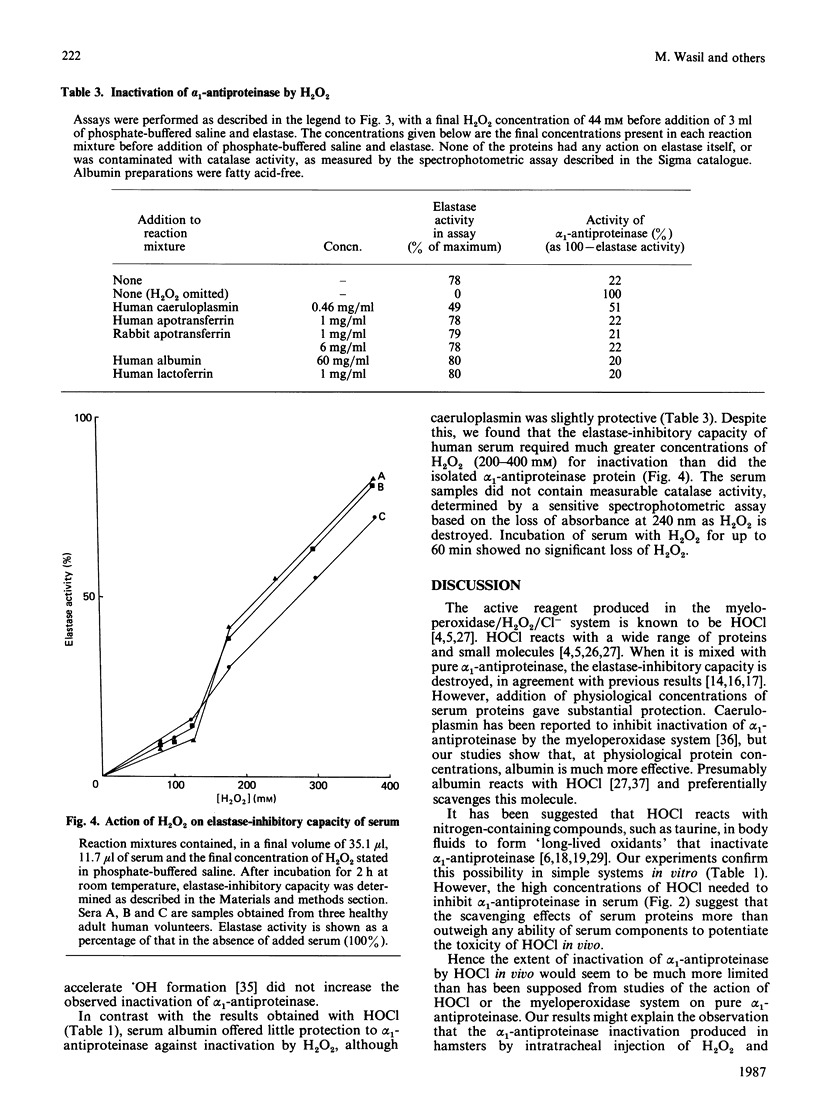
The elastase-inhibitory capacity of purified human alpha 1-antiproteinase is inactivated by low concentrations of the myeloperoxidase-derived oxidant hypochlorous acid, but much higher concentrations are required to inhibit the elastase-inhibitory capacity of serum samples. The protective effect of serum appears to be largely due to albumin. High concentrations of H2O2 also inactivate the elastase-inhibitory capacity of alpha 1-antiproteinase, by a mechanism not involving formation of hydroxyl radicals. Serum offers protection against H2O2 inactivation of alpha 1-antiproteinase. The relevance of these results to the tissue damage produced by activated phagocytes is discussed.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abboud R. T., Fera T., Richter A., Tabona M. Z., Johal S. Acute effect of smoking on the functional activity of alpha1-protease inhibitor in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Jan;131(1):79–85. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.131.1.79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albrich J. M., Hurst J. K. Oxidative inactivation of Escherichia coli by hypochlorous acid. Rates and differentiation of respiratory from other reaction sites. FEBS Lett. 1982 Jul 19;144(1):157–161. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80591-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albrich J. M., McCarthy C. A., Hurst J. K. Biological reactivity of hypochlorous acid: implications for microbicidal mechanisms of leukocyte myeloperoxidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):210–214. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aruoma O. I., Halliwell B. Superoxide-dependent and ascorbate-dependent formation of hydroxyl radicals from hydrogen peroxide in the presence of iron. Are lactoferrin and transferrin promoters of hydroxyl-radical generation? Biochem J. 1987 Jan 1;241(1):273–278. doi: 10.1042/bj2410273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babior B. M. Oxygen-dependent microbial killing by phagocytes (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1978 Mar 23;298(12):659–668. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197803232981205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell E. J., Senior R. M., McDonald J. A., Cox D. L. Proteolysis by neutrophils. Relative importance of cell-substrate contact and oxidative inactivation of proteinase inhibitors in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1982 Oct;70(4):845–852. doi: 10.1172/JCI110681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carp H., Janoff A. In vitro suppression of serum elastase-inhibitory capacity by reactive oxygen species generated by phagocytosing polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Clin Invest. 1979 Apr;63(4):793–797. doi: 10.1172/JCI109364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carp H., Janoff A. Potential mediator of inflammation. Phagocyte-derived oxidants suppress the elastase-inhibitory capacity of alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1980 Nov;66(5):987–995. doi: 10.1172/JCI109968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A., Stone P. J., El Hag A., Calore J. D., Franzblau C. Myeloperoxidase-catalyzed inactivation of alpha 1-protease inhibitor by human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 10;256(7):3348–3353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson K., Slight J., Hannant D., Bolton R. E. Increased release of hydrogen peroxide and superoxide anion from asbestos-primed macrophages. Effect of hydrogen peroxide on the functional activity of alpha 1-protease inhibitor. Inflammation. 1985 Jun;9(2):139–147. doi: 10.1007/BF00917586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dooley M. M., Pryor W. A. Free radical pathology: inactivation of human alpha-1-proteinase inhibitor by products from the reaction of nitrogen dioxide with hydrogen peroxide and the etiology of emphysema. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jun 15;106(3):981–987. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91807-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foote C. S., Goyne T. E., Lehrer R. I. Assessment of chlorination by human neutrophils. Nature. 1983 Feb 24;301(5902):715–716. doi: 10.1038/301715a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forman H. J., Thomas M. J. Oxidant production and bactericidal activity of phagocytes. Annu Rev Physiol. 1986;48:669–680. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.48.030186.003321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green T. R., Fellman J. H., Eicher A. L. Myeloperoxidase oxidation of sulfur-centered and benzoic acid hydroxyl radical scavengers. FEBS Lett. 1985 Nov 11;192(1):33–36. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80037-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutteridge J. M. Antioxidant properties of the proteins caeruloplasmin, albumin and transferrin. A study of their activity in serum and synovial fluid from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jan 30;869(2):119–127. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(86)90286-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutteridge J. M., Richmond R., Halliwell B. Inhibition of the iron-catalysed formation of hydroxyl radicals from superoxide and of lipid peroxidation by desferrioxamine. Biochem J. 1979 Nov 15;184(2):469–472. doi: 10.1042/bj1840469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halliwell B., Gutteridge J. M., Blake D. Metal ions and oxygen radical reactions in human inflammatory joint disease. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1985 Dec 17;311(1152):659–671. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1985.0171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halliwell B., Gutteridge J. M. Oxygen free radicals and iron in relation to biology and medicine: some problems and concepts. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 May 1;246(2):501–514. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(86)90305-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halliwell B., Gutteridge J. M. The importance of free radicals and catalytic metal ions in human diseases. Mol Aspects Med. 1985;8(2):89–193. doi: 10.1016/0098-2997(85)90001-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halliwell B. Production of superoxide, hydrogen peroxide and hydroxyl radicals by phagocytic cells: a cause of chronic inflammatory disease? Cell Biol Int Rep. 1982 Jun;6(6):529–542. doi: 10.1016/0309-1651(82)90175-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamers M. N., Bot A. A., Weening R. S., Sips H. J., Roos D. Kinetics and mechanism of the bactericidal action of human neutrophils against Escherichia coli. Blood. 1984 Sep;64(3):635–641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janoff A. Proteases and lung injury. A state-of-the-art minireview. Chest. 1983 May;83(5 Suppl):54S–58S. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebanoff S. J. Myeloperoxidase-halide-hydrogen peroxide antibacterial system. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):2131–2138. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.2131-2138.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matheson N. R., Travis J. Differential effects of oxidizing agents on human plasma alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor and human neutrophil myeloperoxidase. Biochemistry. 1985 Apr 9;24(8):1941–1945. doi: 10.1021/bi00329a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison H. M., Burnett D., Stockley R. A. The effect of reducing agents on proteolytic enzymes and oxidation of alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1986 Mar;367(3):177–182. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1986.367.1.177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ossanna P. J., Test S. T., Matheson N. R., Regiani S., Weiss S. J. Oxidative regulation of neutrophil elastase-alpha-1-proteinase inhibitor interactions. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jun;77(6):1939–1951. doi: 10.1172/JCI112523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passo S. A., Weiss S. J. Oxidative mechanisms utilized by human neutrophils to destroy Escherichia coli. Blood. 1984 Jun;63(6):1361–1368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pryor W. A., Dooley M. M., Church D. F. Mechanisms of cigarette smoke toxicity: the inactivation of human alpha-1-proteinase inhibitor by nitric oxide/isoprene mixtures in air. Chem Biol Interact. 1985 Jul;54(2):171–183. doi: 10.1016/s0009-2797(85)80161-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stockley R. A. Proteolytic enzymes, their inhibitors and lung diseases. Clin Sci (Lond) 1983 Feb;64(2):119–126. doi: 10.1042/cs0640119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone P. J., Calore J. D., McGowan S. E., Bernardo J., Snider G. L., Franzblau C. Functional alpha 1-protease inhibitor in the lower respiratory tract of cigarette smokers is not decreased. Science. 1983 Sep 16;221(4616):1187–1189. doi: 10.1126/science.6612333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. C., Oey L. Ceruloplasmin: plasma inhibitor of the oxidative inactivation of alpha 1-protease inhibitor. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 Sep;126(3):476–482. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.126.3.476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas E. L., Grisham M. B., Melton D. F., Jefferson M. M. Evidence for a role of taurine in the in vitro oxidative toxicity of neutrophils toward erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3321–3329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travis J., Salvesen G. S. Human plasma proteinase inhibitors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:655–709. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.003255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vissers M. C., Day W. A., Winterbourn C. C. Neutrophils adherent to a nonphagocytosable surface (glomerular basement membrane) produce oxidants only at the site of attachment. Blood. 1985 Jul;66(1):161–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner D. K., Collins-Lech C., Sohnle P. G. Inhibition of neutrophil killing of Candida albicans pseudohyphae by substances which quench hypochlorous acid and chloramines. Infect Immun. 1986 Mar;51(3):731–735. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.3.731-735.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wayner D. D., Burton G. W., Ingold K. U., Locke S. Quantitative measurement of the total, peroxyl radical-trapping antioxidant capability of human blood plasma by controlled peroxidation. The important contribution made by plasma proteins. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jul 22;187(1):33–37. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)81208-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J., Klein R., Slivka A., Wei M. Chlorination of taurine by human neutrophils. Evidence for hypochlorous acid generation. J Clin Invest. 1982 Sep;70(3):598–607. doi: 10.1172/JCI110652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J., Lampert M. B., Test S. T. Long-lived oxidants generated by human neutrophils: characterization and bioactivity. Science. 1983 Nov 11;222(4624):625–628. doi: 10.1126/science.6635660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winterbourn C. C. Comparative reactivities of various biological compounds with myeloperoxidase-hydrogen peroxide-chloride, and similarity of the oxidant to hypochlorite. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jun 18;840(2):204–210. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(85)90120-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff S. P., Dean R. T. Fragmentation of proteins by free radicals and its effect on their susceptibility to enzymic hydrolysis. Biochem J. 1986 Mar 1;234(2):399–403. doi: 10.1042/bj2340399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaslow M. C., Clark R. A., Stone P. J., Calore J., Snider G. L., Franzblau C. Myeloperoxidase-induced inactivation of alpha 1-antiprotease in hamsters. J Lab Clin Med. 1985 Feb;105(2):178–184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


