Abstract
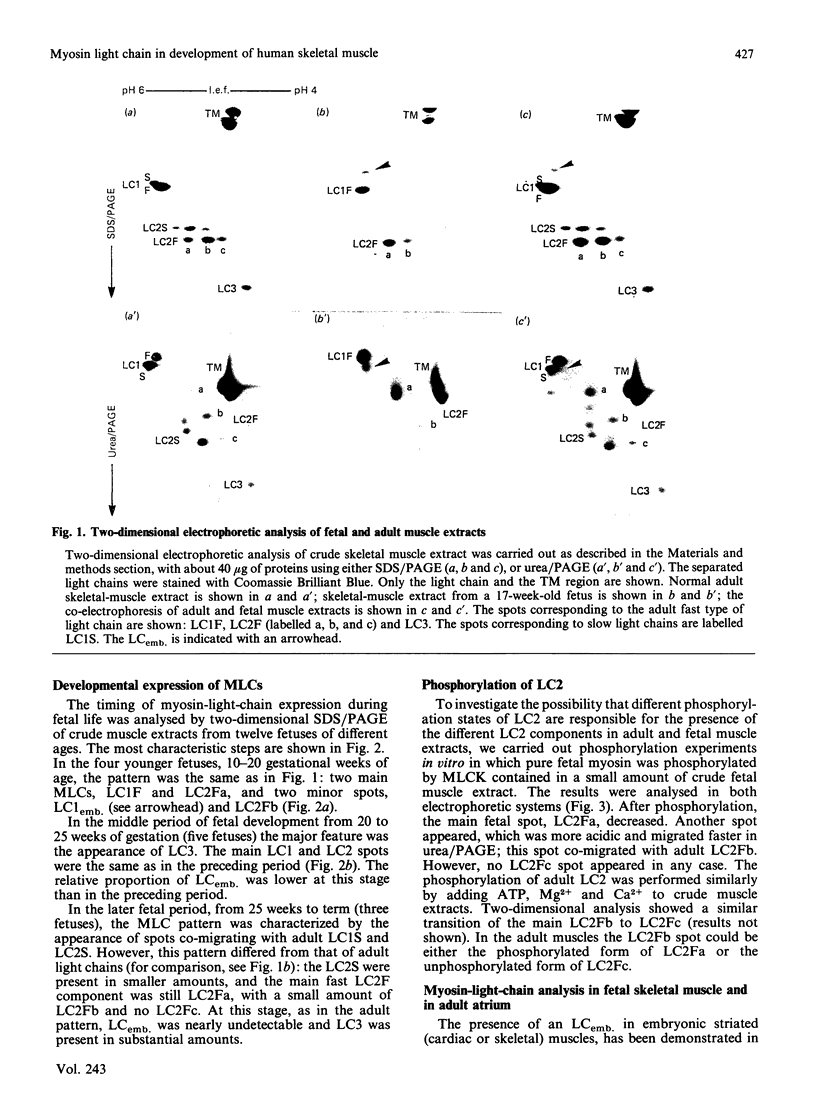
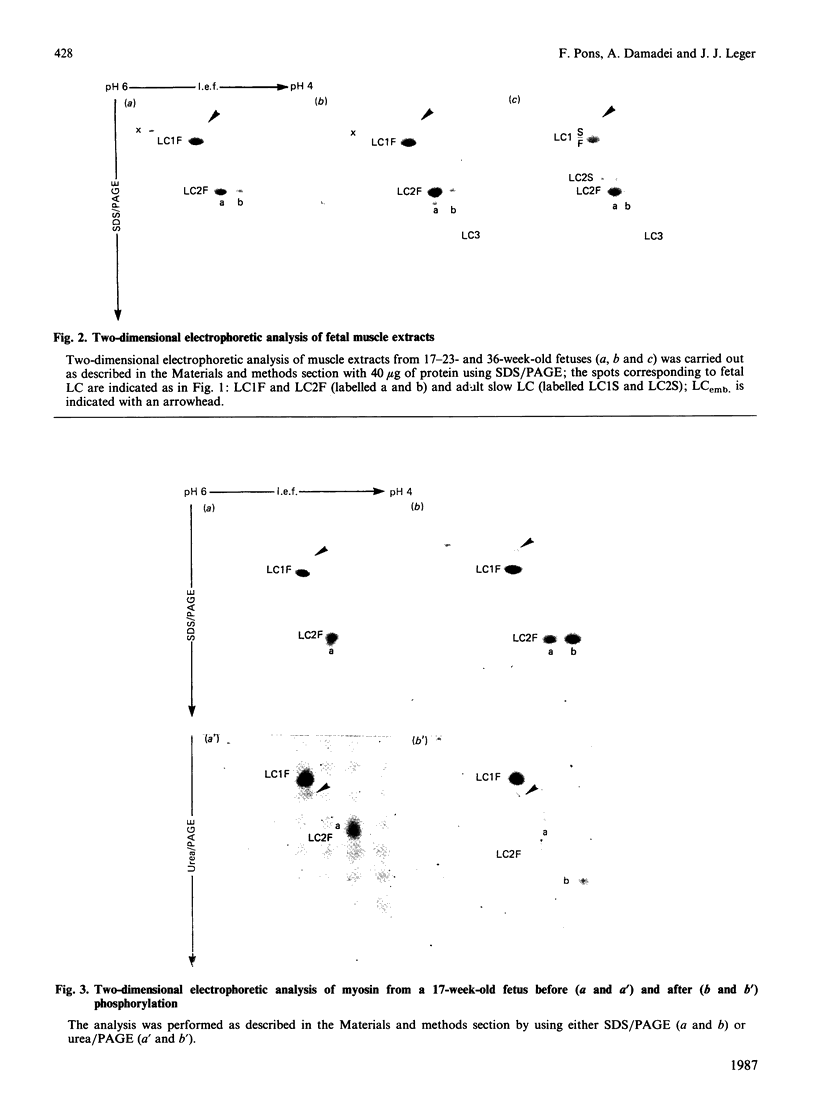
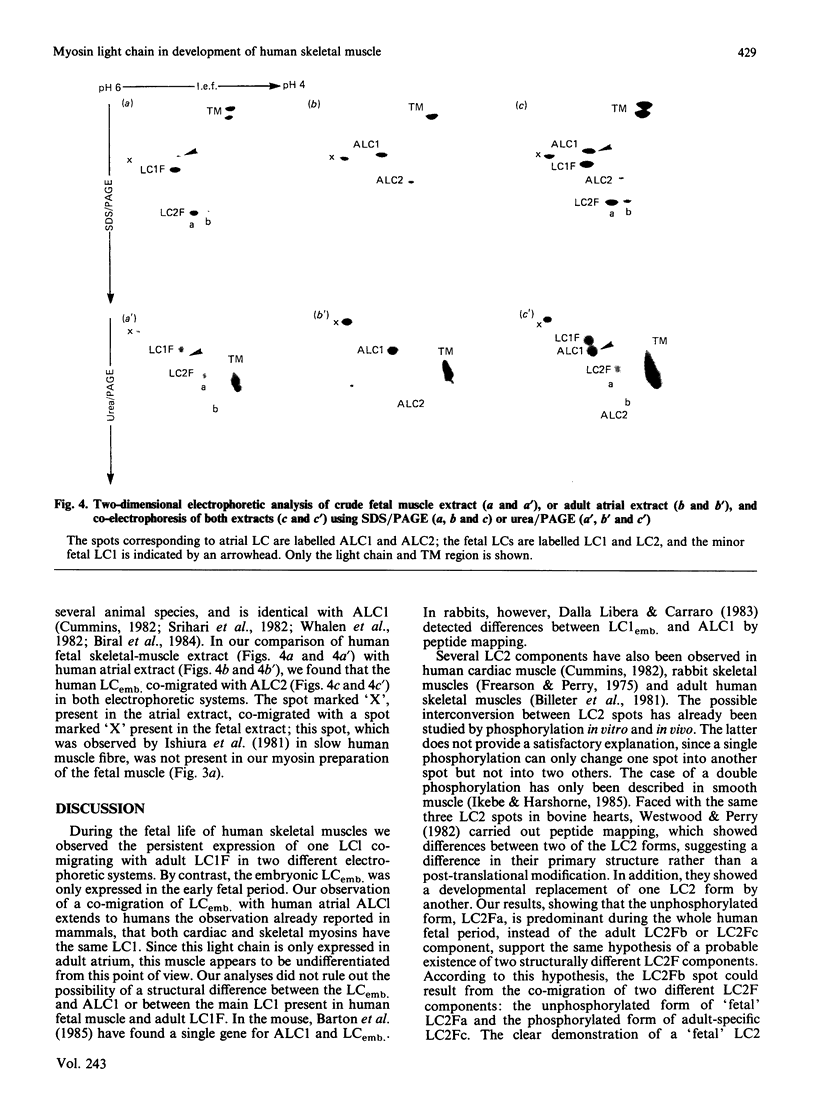
The expression of myosin light chains (MLCs) during the development of human skeletal muscle was investigated by using two different two-dimensional electrophoretic techniques. In both electrophoretic systems the predominant light chain 1 (LC1) expressed during the whole fetal period was found to co-migrate with the adult fast LC1 (LC1F). The main LC2 expressed during the whole fetal period was found to be different from the main fast LC2 (LC2F) and slow LC2 (LC2S) usually present in adult muscle, but co-migrated with a minor component often present in adult muscle. This fetal LC2 was phosphorylatable, and the phosphorylated form co-migrated with the main component of LC2F expressed in the adult. The adult fast LC3 appeared as early as week 20 of gestation, whereas the adult slow light chains (LC1S and LC2S) appeared only during the late fetal period. A minor component of LC1, previously described in humans as an 'embryonic LC' (LCemb.) [Strohman, Micou-Eastwood, Glass & Matsuda (1983) Science 221, 955-957], was only expressed in the early fetal period and was found to co-migrate with atrial LC1 (ALC1). We discuss the expression of these specific developmental forms of MLCs co-existing with immature myosin heavy chains during fetal life.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bandman E., Matsuda R., Strohman R. C. Developmental appearance of myosin heavy and light chain isoforms in vivo and in vitro in chicken skeletal muscle. Dev Biol. 1982 Oct;93(2):508–518. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90138-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barton P. J., Robert B., Fiszman M. Y., Leader D. P., Buckingham M. E. The same myosin alkali light chain gene is expressed in adult cardiac atria and in fetal skeletal muscle. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1985 Aug;6(4):461–475. doi: 10.1007/BF00712583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billeter R., Heizmann C. W., Howald H., Jenny E. Analysis of myosin light and heavy chain types in single human skeletal muscle fibers. Eur J Biochem. 1981 May 15;116(2):389–395. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05347.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biral D., Damiani E., Margreth A., Scarpini E. Myosin subunit composition in human developing muscle. Biochem J. 1984 Dec 15;224(3):923–931. doi: 10.1042/bj2240923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biral D., Damiani E., Volpe P., Salviati G., Margreth A. Polymorphism of myosin light chains. An electrophoretic and immunological study of rabbit skeletal-muscle myosins. Biochem J. 1982 Jun 1;203(3):529–540. doi: 10.1042/bj2030529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. E., Salmons S., Whalen R. G. The sequential replacement of myosin subunit isoforms during muscle type transformation induced by long term electrical stimulation. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14686–14692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardinaud R. A simple and rapid preparation of fully phosphorylated and fully dephosphorylated skeletal muscle myosin. Application to the preparation of a phosphorylated LC2-modified artificial isozyme. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1986 Oct;7(5):455–466. doi: 10.1007/BF01753588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crow M. T., Olson P. S., Stockdale F. E. Myosin light-chain expression during avian muscle development. J Cell Biol. 1983 Mar;96(3):736–744. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.3.736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummins P. Transitions in human atrial and ventricular myosin light-chain isoenzymes in response to cardiac-pressure-overload-induced hypertrophy. Biochem J. 1982 Jul 1;205(1):195–204. doi: 10.1042/bj2050195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalla Libera L., Carraro U. The suggested identity of myosin light chain of cardiac atrial muscle and embryonic skeletal muscle may be excluded by proteolytic mapping. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1983 Apr;7(4):271–273. doi: 10.1016/0309-1651(83)90061-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzsimons R. B., Hoh J. F. Embryonic and foetal myosins in human skeletal muscle. The presence of foetal myosins in duchenne muscular dystrophy and infantile spinal muscular atrophy. J Neurol Sci. 1981 Nov-Dec;52(2-3):367–384. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(81)90018-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frearson N., Perry S. V. Phosphorylation of the light-chain components of myosin from cardiac and red skeletal muscles. Biochem J. 1975 Oct;151(1):99–107. doi: 10.1042/bj1510099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikebe M., Hartshorne D. J. Phosphorylation of smooth muscle myosin at two distinct sites by myosin light chain kinase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 25;260(18):10027–10031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiura S., Takagi A., Nonaka I., Sugita H. Heterogeneous expression of myosin light chain 1 in a human slow-twitch muscle fiber. J Biochem. 1981 Jul;90(1):279–282. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIELLEY W. W., BRADLEY L. B. The relationship between sulfhydryl groups and the activation of myosin adenosinetriphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1956 Feb;218(2):653–659. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowey S., Benfield P. A., LeBlanc D. D., Waller G. S. Myosin isozymes in avian skeletal muscles. I. Sequential expression of myosin isozymes in developing chicken pectoralis muscles. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1983 Dec;4(6):695–716. doi: 10.1007/BF00712161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maréchal G., Schwartz K., Beckers-Bleukx G., Ghins E. Isozymes of myosin in growing and regenerating rat muscles. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jan 16;138(2):421–428. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb07932.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrifield P. A., Konigsberg I. R. Reflective densitometry of Western blots to quantitate the developmentally regulated accumulation of myosin light chain 3. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Mar 28;135(3):778–784. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90996-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrie W. T., Perry S. V. An electrophoretic study of the low-molecular-weight components of myosin. Biochem J. 1970 Aug;119(1):31–38. doi: 10.1042/bj1190031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pons F., Leger J., Georgesco M., Bonnel F., Leger J. J. Myosin light chains in normal and pathological human skeletal muscles. Muscle Nerve. 1983 Jan;6(1):40–47. doi: 10.1002/mus.880060107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pons F., Léger J. O., Chevallay M., Tomé F. M., Fardeau M., Léger J. J. Immunocytochemical analysis of myosin heavy chains in human fetal skeletal muscles. J Neurol Sci. 1986 Dec;76(2-3):151–163. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(86)90165-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiaffino S., Gorza L., Dones I., Cornelio F., Sartore S. Fetal myosin immunoreactivity in human dystrophic muscle. Muscle Nerve. 1986 Jan;9(1):51–58. doi: 10.1002/mus.880090108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srihari T., Tuchschmid C. R., Schaub M. C. Isoforms of heavy and light chains of cardiac myosins from rat and rabbit. Basic Res Cardiol. 1982 Nov-Dec;77(6):599–609. doi: 10.1007/BF01908313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strohman R. C., Micou-Eastwood J., Glass C. A., Matsuda R. Human fetal muscle and cultured myotubes derived from it contain a fetal-specific myosin light chain. Science. 1983 Sep 2;221(4614):955–957. doi: 10.1126/science.6879193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syrový I. Changes in light chains of myosin during animal development. Int J Biochem. 1979;10(3):223–227. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(79)90038-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornell L. E., Billeter R., Butler-Browne G. S., Eriksson P. O., Ringqvist M., Whalen R. G. Development of fiber types in human fetal muscle. An immunocytochemical study. J Neurol Sci. 1984 Oct;66(1):107–115. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(84)90146-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpe P., Biral D., Damiani E., Margreth A. Characterization of human muscle myosins with respect to the light chains. Biochem J. 1981 Apr 1;195(1):251–258. doi: 10.1042/bj1950251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westwood S. A., Perry S. V. Two forms of the p light chain of myosin in rabbit and bovine hearts. FEBS Lett. 1982 Jun 1;142(1):31–34. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80212-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whalen R. G., Butler-Browne G. S., Gros F. Identification of a novel form of myosin light chain present in embryonic muscle tissue and cultured muscle cells. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 15;126(3):415–431. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90049-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whalen R. G., Sell S. M., Butler-Browne G. S., Schwartz K., Bouveret P., Pinset-Härstöm I. Three myosin heavy-chain isozymes appear sequentially in rat muscle development. Nature. 1981 Aug 27;292(5826):805–809. doi: 10.1038/292805a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whalen R. G., Sell S. M., Eriksson A., Thornell L. E. Myosin subunit types in skeletal and cardiac tissues and their developmental distribution. Dev Biol. 1982 Jun;91(2):478–484. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90055-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]