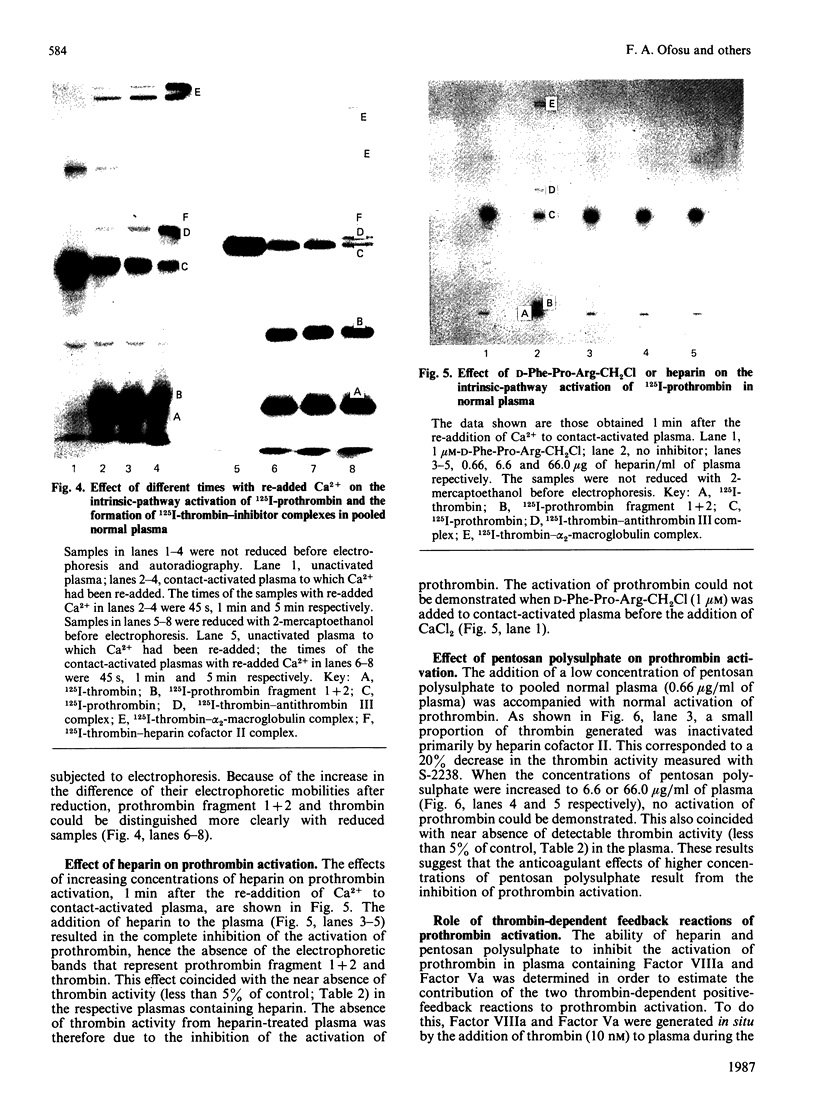
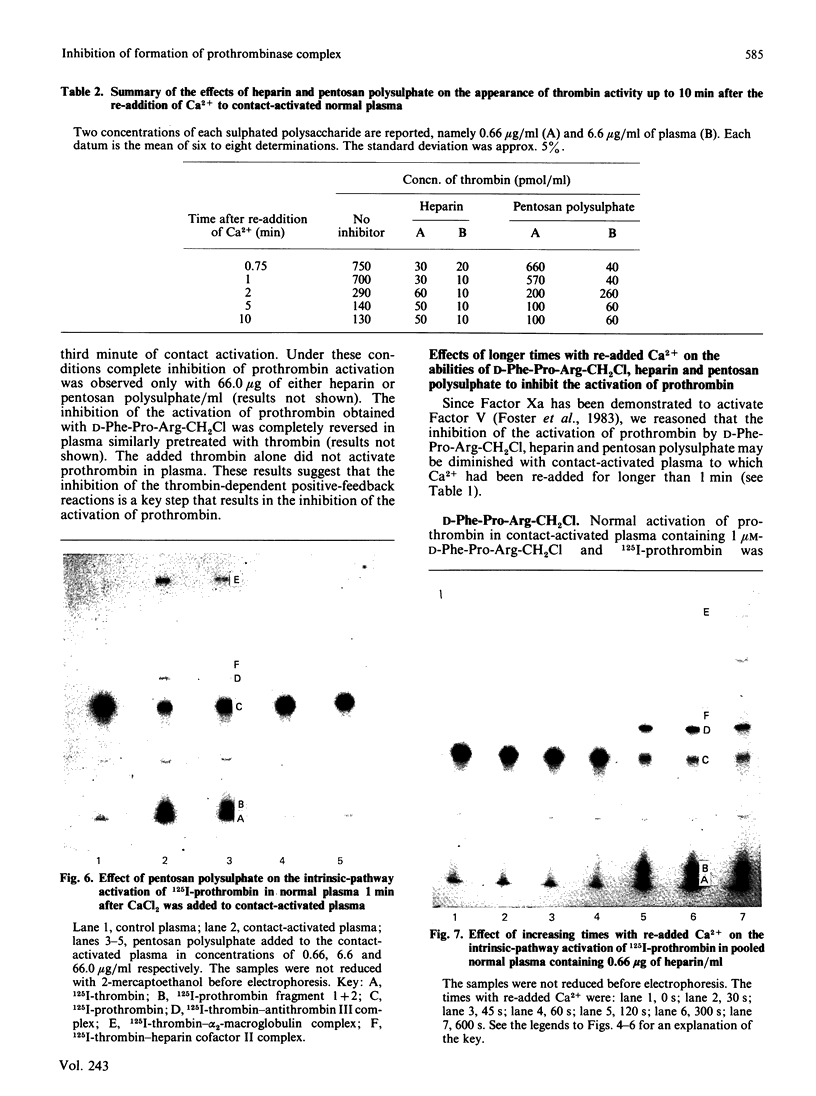
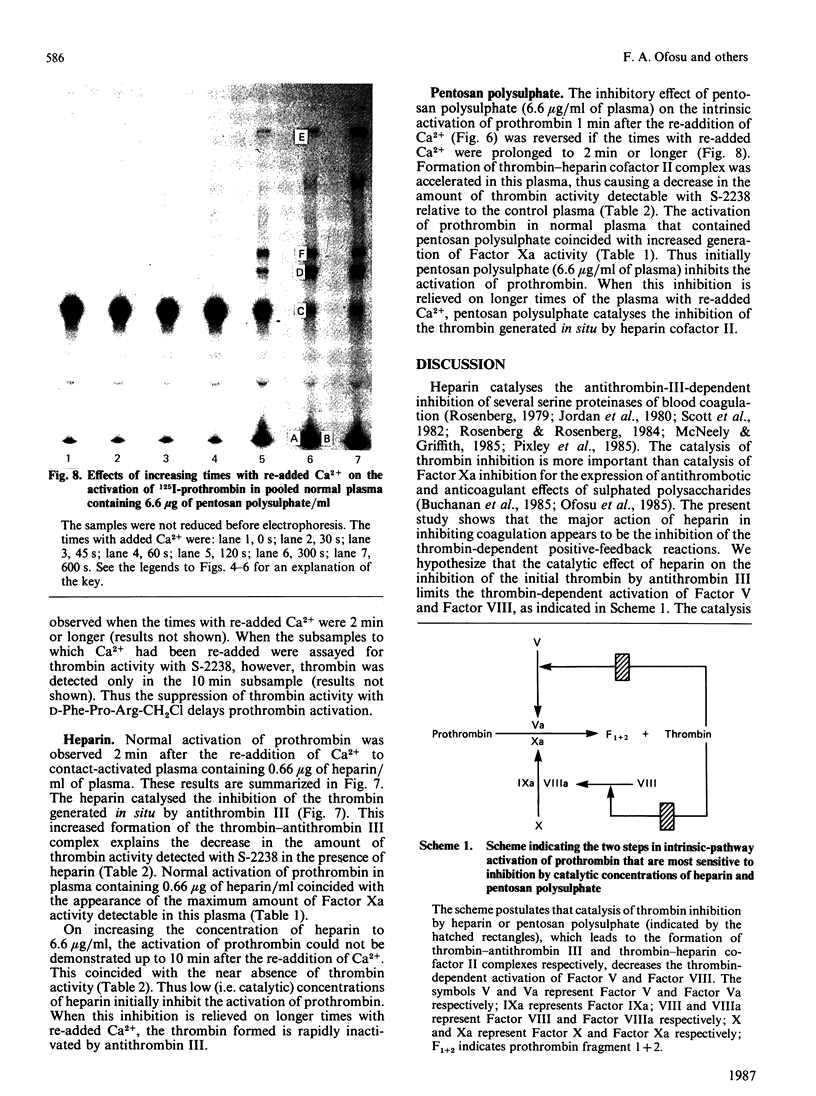
Abstract
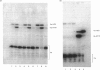
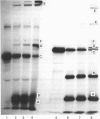
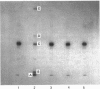
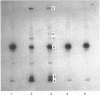
Heparin catalyses the inhibition of two key enzymes of blood coagulation, namely Factor Xa and thrombin, by enhancing the antiproteinase activities of plasma antithrombin III and heparin cofactor II. In addition, heparin can directly inhibit the activation of Factor X and prothrombin. The contributions of each of these effects to the anticoagulant activity of heparin have not been delineated. We therefore performed experiments to assess how each of these effects of heparin contributes to its anticoagulant activity by comparing the effects of heparin, pentosan polysulphate and D-Phe-Pro-Arg-CH2Cl on the intrinsic pathway of coagulation. Unlike heparin, pentosan polysulphate catalyses only the inhibition of thrombin by plasma. D-Phe-Pro-Arg-CH2Cl is rapid enough an inhibitor of thrombin so that when added to plasma no complexes of thrombin with its inhibitors are formed, whether or not the plasma also contains heparin. Heparin (0.66 microgram/ml) and pentosan polysulphate (6.6 micrograms/ml) completely inhibited the intrinsic-pathway activation of 125I-prothrombin to 125I-prothrombin fragment 1 + 2 and 125I-thrombin. On the addition of thrombin, a good Factor V activator, to the plasma before each sulphated polysaccharide, the inhibition of prothrombin activation was demonstrable only in the presence of higher concentrations of the sulphated polysaccharide. D-Phe-Pro-Arg-CH2Cl also completely inhibited the intrinsic-pathway activation of prothrombin in normal plasma. The inhibitory effect of D-Phe-Pro-Arg-CH2Cl was reversed if thrombin was added to the plasma before D-Phe-Pro-Arg-CH2Cl. The inhibition of the activation of prothrombin by the three agents was also abolished with longer times with re-added Ca2+. Reversal of the inhibitory effects of heparin and pentosan polysulphate was associated with the accelerated formation of 125I-thrombin-antithrombin III and 125I-thrombin-heparin cofactor complexes respectively. These results suggest that the anticoagulant effects of heparin and pentosan polysulphate are mediated primarily by their ability to inhibit the thrombin-dependent activation of Factor V, thereby inhibiting the formation of prothrombinase complex, the physiological activator of prothrombin.
Full text
PDF
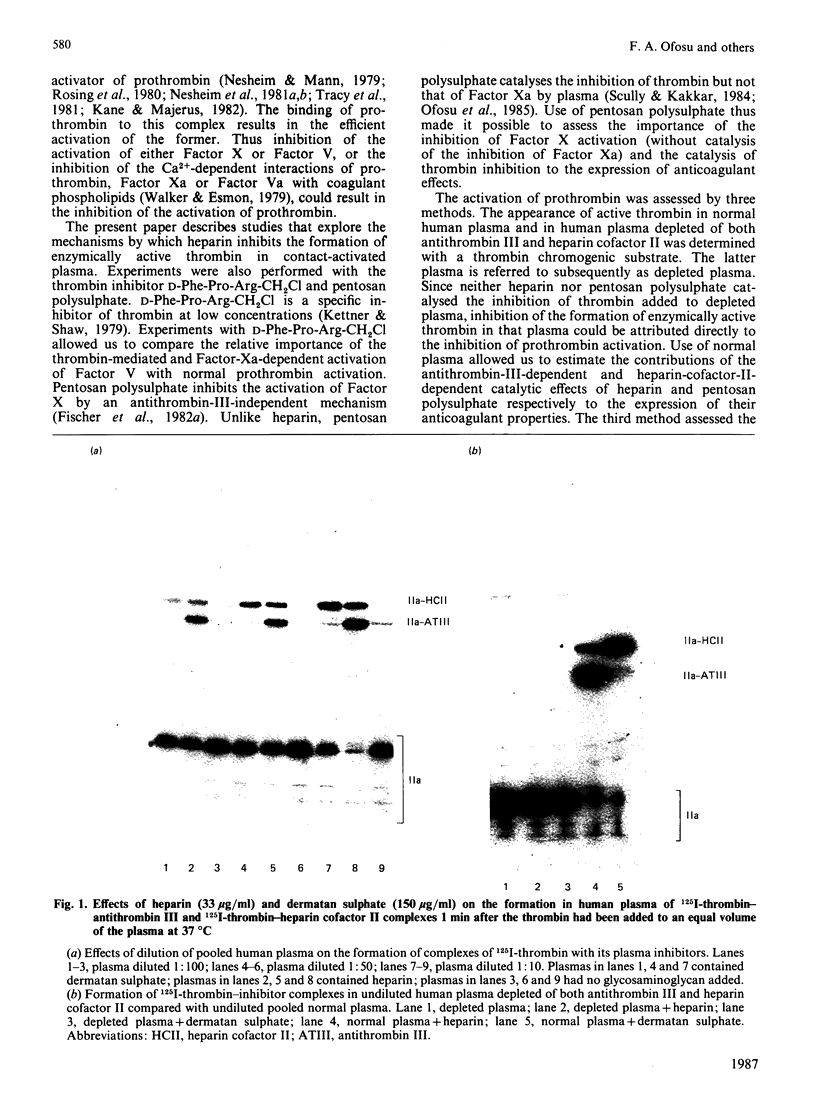

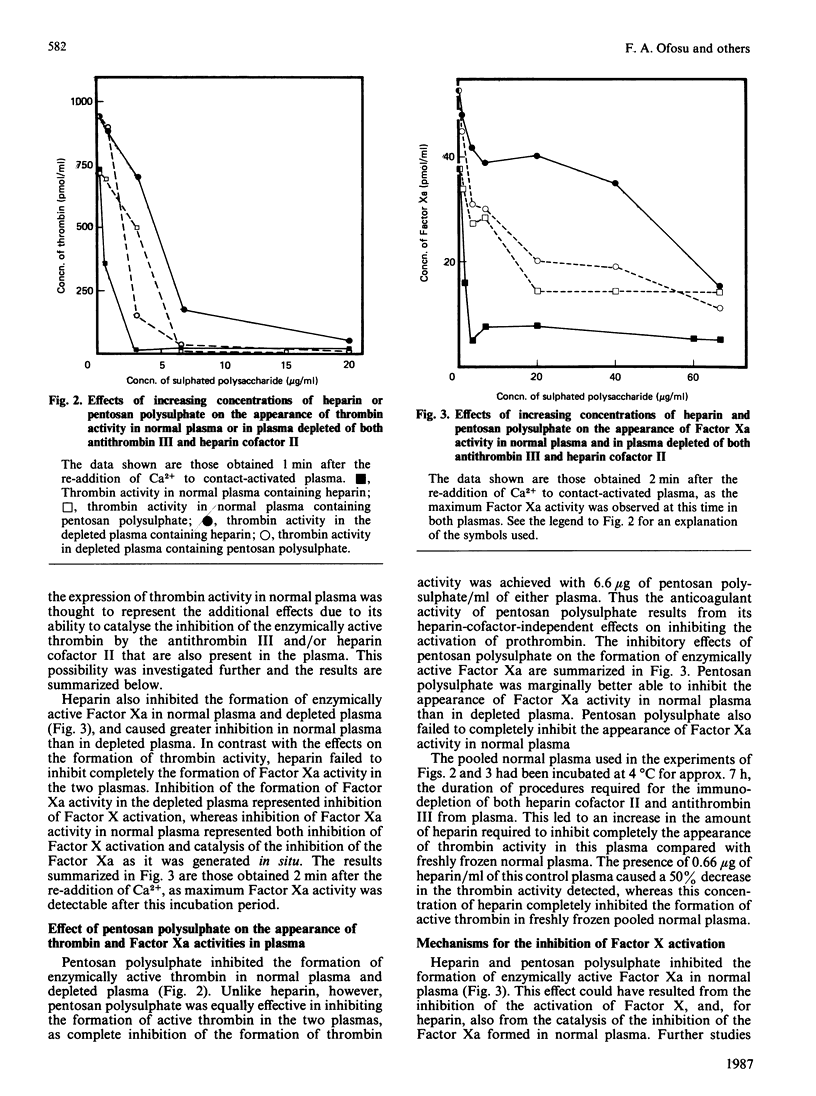



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrowcliffe T. W., Merton R. E., Havercroft S. J., Thunberg L., Lindahl U., Thomas D. P. Low-affinity heparin potentiates the action of high-affinity heparin oligosaccharides. Thromb Res. 1984 Apr 15;34(2):125–133. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(84)90069-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baruch D., Lindhout T., Wagenvoord R., Hemker H. C. Inhibition of thrombin-catalyzed reactions in blood coagulation and platelet activation by heparin fractions in the absence of antithrombin III. Haemostasis. 1986;16(2):71–81. doi: 10.1159/000215276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergqvist D., Efsing H. O., Hallbök T., Lindblad B. Prevention of postoperative thromboembolic complications. A prospective comparison between dextran 70, dihydroergotamine heparin and a sulphated polysaccharide. Acta Chir Scand. 1980;146(8):559–568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan M. R., Boneu B., Ofosu F., Hirsh J. The relative importance of thrombin inhibition and factor Xa inhibition to the antithrombotic effects of heparin. Blood. 1985 Jan;65(1):198–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer A. M., Barrowcliffe T. W., Thomas D. P. A comparison of pentosan polysulphate (SP54) and heparin. I: Mechanism of action on blood coagulation. Thromb Haemost. 1982 Apr 30;47(2):104–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer A. M., Merton R. E., Marsh N. A., Williams S., Gaffney P. J., Barrowcliffe T. W., Thomas D. P. A comparison of pentosan polysulphate and heparin. II: Effects of subcutaneous injection. Thromb Haemost. 1982 Apr 30;47(2):109–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan R. E., Oosta G. M., Gardner W. T., Rosenberg R. D. The kinetics of hemostatic enzyme-antithrombin interactions in the presence of low molecular weight heparin. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10081–10090. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane W. H., Majerus P. W. The interaction of human coagulation factor Va with platelets. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 10;257(7):3963–3969. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kettner C., Shaw E. D-Phe-Pro-ArgCH2C1-A selective affinity label for thrombin. Thromb Res. 1979;14(6):969–973. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(79)90014-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeely T. B., Griffith M. J. The anticoagulant mechanism of action of heparin in contact-activated plasma: inhibition of factor X activation. Blood. 1985 May;65(5):1226–1231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modi G. J., Blajchman M. A., Ofosu F. A. The isolation of prothrombin, Factor IX and Factor X from human Factor IX concentrates. Thromb Res. 1984 Dec 15;36(6):537–547. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(84)90193-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesheim M. E. A simple rate law that describes the kinetics of the heparin-catalyzed reaction between antithrombin III and thrombin. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14708–14717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesheim M. E., Eid S., Mann K. G. Assembly of the prothrombinase complex in the absence of prothrombin. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 10;256(19):9874–9882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesheim M. E., Kettner C., Shaw E., Mann K. G. Cofactor dependence of factor Xa incorporation into the prothrombinase complex. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):6537–6540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesheim M. E., Mann K. G. Thrombin-catalyzed activation of single chain bovine factor V. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 25;254(4):1326–1334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofosu F. A., Blajchman M. A., Modi G. J., Smith L. M., Buchanan M. R., Hirsh J. The importance of thrombin inhibition for the expression of the anticoagulant activities of heparin, dermatan sulphate, low molecular weight heparin and pentosan polysulphate. Br J Haematol. 1985 Aug;60(4):695–704. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1985.tb07474.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofosu F. A., Blajchman M. A., Modi G., Cerskus A. L., Hirsh J. Activation of factor X and prothrombin in antithrombin-III depleted plasma: the effects of heparin. 1981 Aug 15-Sep 1Thromb Res. 23(4-5):331–345. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(81)90194-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofosu F. A., Cerskus A. L., Hirsh J., Smith L. M., Modi G. J., Blajchman M. A. The inhibition of the anticoagulant activity of heparin by platelets, brain phospholipids, and tissue factor. Br J Haematol. 1984 Jun;57(2):229–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofosu F. A., Modi G. J., Smith L. M., Cerskus A. L., Hirsh J., Blajchman M. A. Heparan sulfate and dermatan sulfate inhibit the generation of thrombin activity in plasma by complementary pathways. Blood. 1984 Sep;64(3):742–747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofosu F. A., Modi G., Cerskus A. L., Hirsh J., Blajchman M. A. Heparin with low affinity to antithrombin III inhibits the activation of prothrombin in normal plasma. Thromb Res. 1982 Nov 15;28(4):487–497. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(82)90165-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofosu F., Blajchman M. A., Hirsh J. The inhibition by heparin of the intrinsic pathway activation of factor X in the absence of antithrombin-III. Thromb Res. 1980 Nov 15;20(4):391–403. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(80)90278-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pixley R. A., Schapira M., Colman R. W. Effect of heparin on the inactivation rate of human activated factor XII by antithrombin III. Blood. 1985 Jul;66(1):198–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg R. D. Chemistry of the hemostatic mechanism and its relationship to the action of heparin. Fed Proc. 1977 Jan;36(1):10–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg R. D., Rosenberg J. S. Natural anticoagulant mechanisms. J Clin Invest. 1984 Jul;74(1):1–6. doi: 10.1172/JCI111389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosing J., Tans G., Govers-Riemslag J. W., Zwaal R. F., Hemker H. C. The role of phospholipids and factor Va in the prothrombinase complex. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 10;255(1):274–283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott C. F., Schapira M., Colman R. W. Effect of heparin on the inactivation rate of human factor XIa by antithrombin-III. Blood. 1982 Oct;60(4):940–947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scully M. F., Kakkar V. V. Identification of heparin cofactor II as the principal plasma cofactor for the antithrombin activity of pentosan polysulphate (SP54). Thromb Res. 1984 Oct 15;36(2):187–194. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(84)90340-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tollefsen D. M., Pestka C. A., Monafo W. J. Activation of heparin cofactor II by dermatan sulfate. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):6713–6716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracy P. B., Nesheim M. E., Mann K. G. Coordinate binding of factor Va and factor Xa to the unstimulated platelet. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 25;256(2):743–751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vehar G. A., Davie E. W. Preparation and properties of bovine factor VIII (antihemophilic factor). Biochemistry. 1980 Feb 5;19(3):401–410. doi: 10.1021/bi00544a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker F. J., Esmon C. T. Interactions between heparin and factor Xa. Inhibition of prothrombin activation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jul 4;585(3):405–415. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(79)90085-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]