Abstract
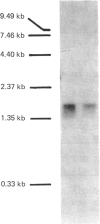
cDNA clones coding for the medium-chain S-acyl fatty acid synthetase thioester hydrolase (thioesterase II) from rat mammary gland were identified in a bacteriophage lambda gt11 library and their nucleotide sequences were determined. The predicted coding region spans 263 amino acid residues and includes a sequence identical with that of a peptide derived from the enzyme active site. The rat thioesterase II cDNA sequence exhibits homology with that of a thioesterase found in duck uropygial glands.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnstiel M. L., Busslinger M., Strub K. Transcription termination and 3' processing: the end is in site! Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):349–359. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross R. H. A DNA sequence analysis program for the Apple Macintosh. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 10;14(1):591–596. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.1.591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori M., Sakaki Y. Dideoxy sequencing method using denatured plasmid templates. Anal Biochem. 1986 Feb 1;152(2):232–238. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90403-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinzel R., Appelhans H., Gassen G., Seemüller U., Machleidt W., Fritz H., Steffens G. Molecular cloning and expression of cDNA for human antileukoprotease from cervix uterus. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Oct 1;160(1):61–67. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09940.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knudsen J., Clark S., Dils R. Purification and some properties of a medium-chain acyl-thioester hydrolase from lactating-rabbit mammary gland which terminates chain elongation in fatty acid synthesis. Biochem J. 1976 Dec 15;160(3):683–691. doi: 10.1042/bj1600683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libertini L. J., Smith S. Purification and properties of a thioesterase from lactating rat mammary gland which modifies the product specificity of fatty acid synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 10;253(5):1393–1401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libertini L. J., Smith S. Synthesis of long chain acyl-enzyme thioesters by modified fatty acid synthetases and their hydrolysis by a mammary gland thioesterase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1979 Jan;192(1):47–60. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(79)90070-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locker J. Analytical and preparative electrophoresis of RNA in agarose-urea. Anal Biochem. 1979 Oct 1;98(2):358–367. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90154-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. A system for shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):309–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikkelsen J., Witkowski A., Smith S. Interaction of rat mammary gland thioesterase II with fatty acid synthetase is dependent on the presence of acyl chains on the synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1570–1574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayama H., Berg P. High-efficiency cloning of full-length cDNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;2(2):161–170. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.2.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawlak J., Smith S. Evaluation of thioesterase II as a serum marker for rat mammary cancer. Cancer Res. 1986 Sep;46(9):4712–4719. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulose A. J., Rogers L., Cheesbrough T. M., Kolattukudy P. E. Cloning and sequencing of the cDNA for S-acyl fatty acid synthase thioesterase from the uropygial gland of mallard duck. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15953–15958. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. The end of the message and beyond. Nature. 1984 Feb 2;307(5950):412–413. doi: 10.1038/307412a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randhawa Z. I., Naggert J., Blacher R. W., Smith S. Amino acid sequence of the serine active-site region of the medium-chain S-acyl fatty acid synthetase thioester hydrolase from rat mammary gland. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Feb 2;162(3):577–581. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb10678.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Efficient isolation of genes by using antibody probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Yeast RNA polymerase II genes: isolation with antibody probes. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):778–782. doi: 10.1126/science.6356359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]