Abstract
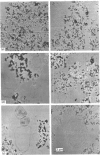
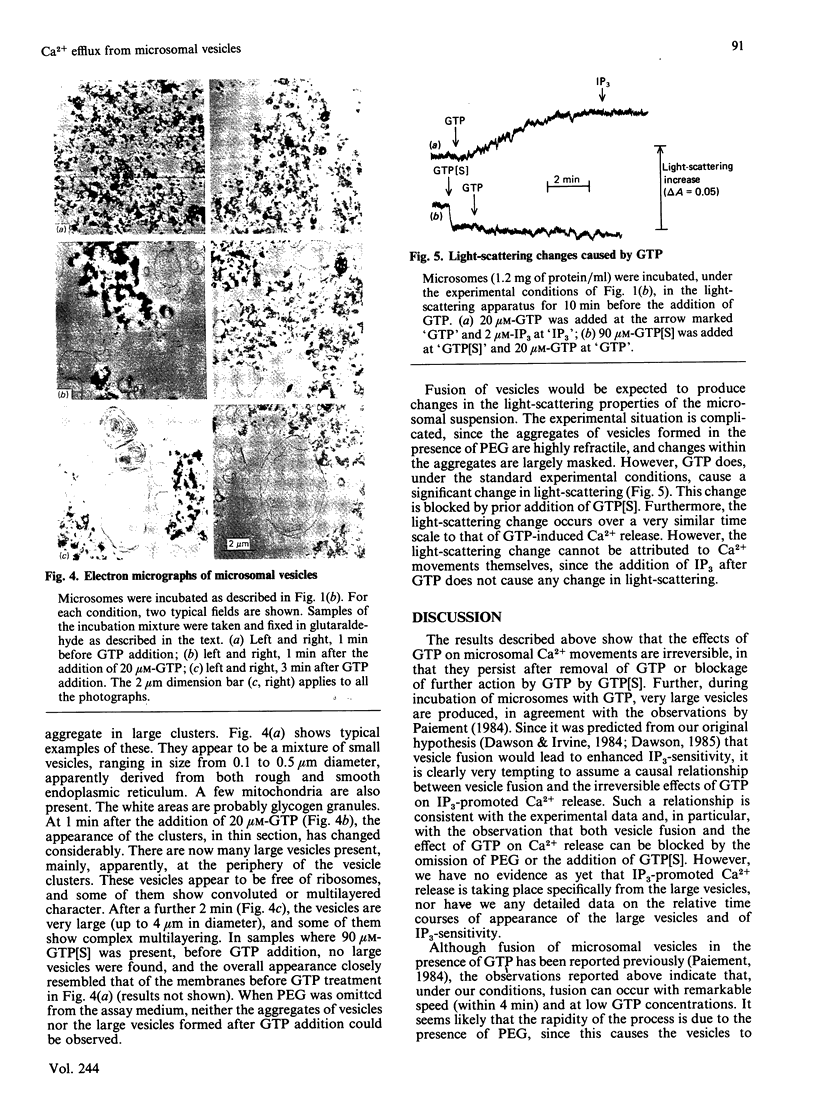
1. Guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate (GTP[S]), if added before GTP, blocks both Ca2+ efflux promoted by GTP and the effect of GTP on enhancement of inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate (IP3)-promoted Ca2+ release from preloaded microsomal vesicles. If, however, GTP[S] is added after GTP, it does not reverse the Ca2+ efflux promoted by GTP, nor does it inhibit IP3-promoted Ca2+ release. 2. The effect of GTP in enhancing IP3-promoted Ca2+ release is maintained after washing the microsomal vesicles free of added GTP. After this treatment, enhancement of IP3-promoted Ca2+ efflux can be observed in the absence of poly(ethylene glycol). 3. Electron microscopy shows that during GTP treatment of microsomal vesicles there is rapid production of very large vesicular structures, apparently produced by fusion of smaller vesicles. 4. Light-scattering changes are detectable during the fusion process. 5. Both Ca2+ efflux promoted by GTP and the enhancement of IP3-promoted Ca2+ release seen in the presence of GTP can probably be attributed to GTP-dependent vesicle fusion.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Authi K. S., Crawford N. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-induced release of sequestered Ca2+ from highly purified human platelet intracellular membranes. Biochem J. 1985 Aug 15;230(1):247–253. doi: 10.1042/bj2300247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biden T. J., Prentki M., Irvine R. F., Berridge M. J., Wollheim C. B. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate mobilizes intracellular Ca2+ from permeabilized insulin-secreting cells. Biochem J. 1984 Oct 15;223(2):467–473. doi: 10.1042/bj2230467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess G. M., Irvine R. F., Berridge M. J., McKinney J. S., Putney J. W., Jr Actions of inositol phosphates on Ca2+ pools in guinea-pig hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1984 Dec 15;224(3):741–746. doi: 10.1042/bj2240741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson A. P., Comerford J. G., Fulton D. V. The effect of GTP on inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-stimulated Ca2+ efflux from a rat liver microsomal fraction. Is a GTP-dependent protein phosphorylation involved? Biochem J. 1986 Mar 1;234(2):311–315. doi: 10.1042/bj2340311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson A. P. GTP enhances inositol trisphosphate-stimulated Ca2+ release from rat liver microsomes. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jun 3;185(1):147–150. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80759-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson A. P., Irvine R. F. Inositol (1,4,5)trisphosphate-promoted Ca2+ release from microsomal fractions of rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 May 16;120(3):858–864. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80186-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. L., Ueda T., Chueh S. H., Noel M. W. Ca2+ release from endoplasmic reticulum is mediated by a guanine nucleotide regulatory mechanism. Nature. 1986 Apr 3;320(6061):461–464. doi: 10.1038/320461a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henne V., Söling H. D. Guanosine 5'-triphosphate releases calcium from rat liver and guinea pig parotid gland endoplasmic reticulum independently of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jul 7;202(2):267–273. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80699-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata M., Suematsu E., Hashimoto T., Hamachi T., Koga T. Release of Ca2+ from a non-mitochondrial store site in peritoneal macrophages treated with saponin by inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Biochem J. 1984 Oct 1;223(1):229–236. doi: 10.1042/bj2230229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph S. K., Thomas A. P., Williams R. J., Irvine R. F., Williamson J. R. myo-Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. A second messenger for the hormonal mobilization of intracellular Ca2+ in liver. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 10;259(5):3077–3081. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph S. K., Williams R. J., Corkey B. E., Matschinsky F. M., Williamson J. R. The effect of inositol trisphosphate on Ca2+ fluxes in insulin-secreting tumor cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):12952–12955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muallem S., Schoeffield M., Pandol S., Sachs G. Inositol trisphosphate modification of ion transport in rough endoplasmic reticulum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4433–4437. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Rourke F. A., Halenda S. P., Zavoico G. B., Feinstein M. B. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate releases Ca2+ from a Ca2+-transporting membrane vesicle fraction derived from human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):956–962. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paiement J. Physiological concentrations of GTP stimulate fusion of the endoplasmic reticulum and the nuclear envelope. Exp Cell Res. 1984 Apr;151(2):354–366. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(84)90386-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentki M., Biden T. J., Janjic D., Irvine R. F., Berridge M. J., Wollheim C. B. Rapid mobilization of Ca2+ from rat insulinoma microsomes by inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate. Nature. 1984 Jun 7;309(5968):562–564. doi: 10.1038/309562a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentki M., Corkey B. E., Matschinsky F. M. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and the endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ cycle of a rat insulinoma cell line. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 5;260(16):9185–9190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentki M., Wollheim C. B., Lew P. D. Ca2+ homeostasis in permeabilized human neutrophils. Characterization of Ca2+-sequestering pools and the action of inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13777–13782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selwyn M. J., Dawson A. P., Stockdale M., Gains N. Chloride-hydroxide exchange across mitochondrial, erythrocyte and artificial lipid membranes mediated by trialkyl- and triphenyltin compounds. Eur J Biochem. 1970 May 1;14(1):120–126. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00268.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streb H., Bayerdörffer E., Haase W., Irvine R. F., Schulz I. Effect of inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate on isolated subcellular fractions of rat pancreas. J Membr Biol. 1984;81(3):241–253. doi: 10.1007/BF01868717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streb H., Irvine R. F., Berridge M. J., Schulz I. Release of Ca2+ from a nonmitochondrial intracellular store in pancreatic acinar cells by inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate. Nature. 1983 Nov 3;306(5938):67–69. doi: 10.1038/306067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda T., Chueh S. H., Noel M. W., Gill D. L. Influence of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and guanine nucleotides on intracellular calcium release within the N1E-115 neuronal cell line. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 5;261(7):3184–3192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]