Abstract
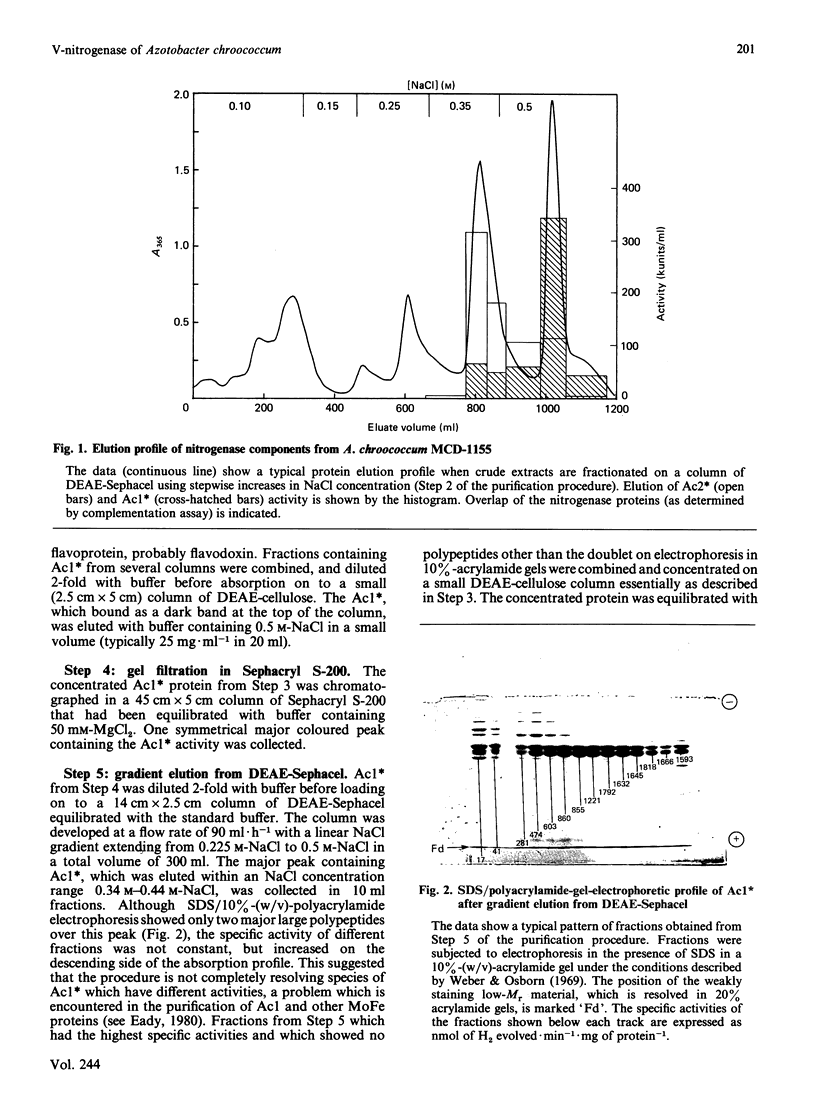
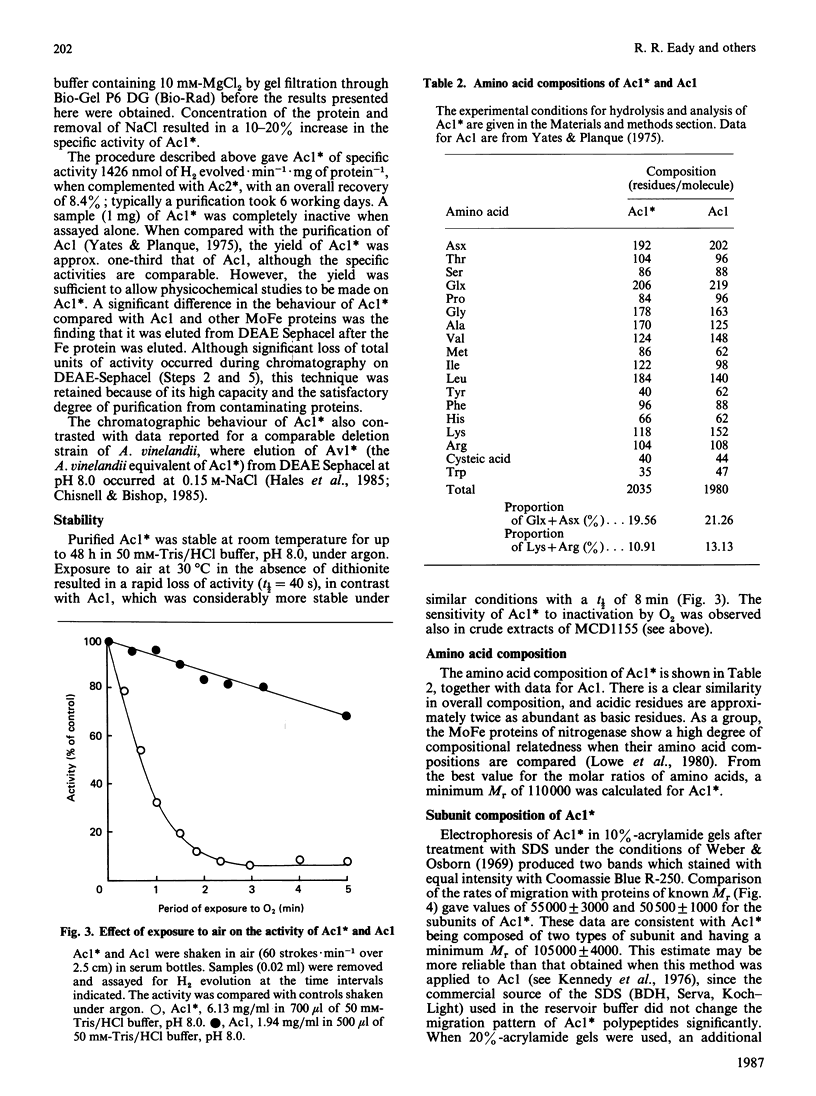
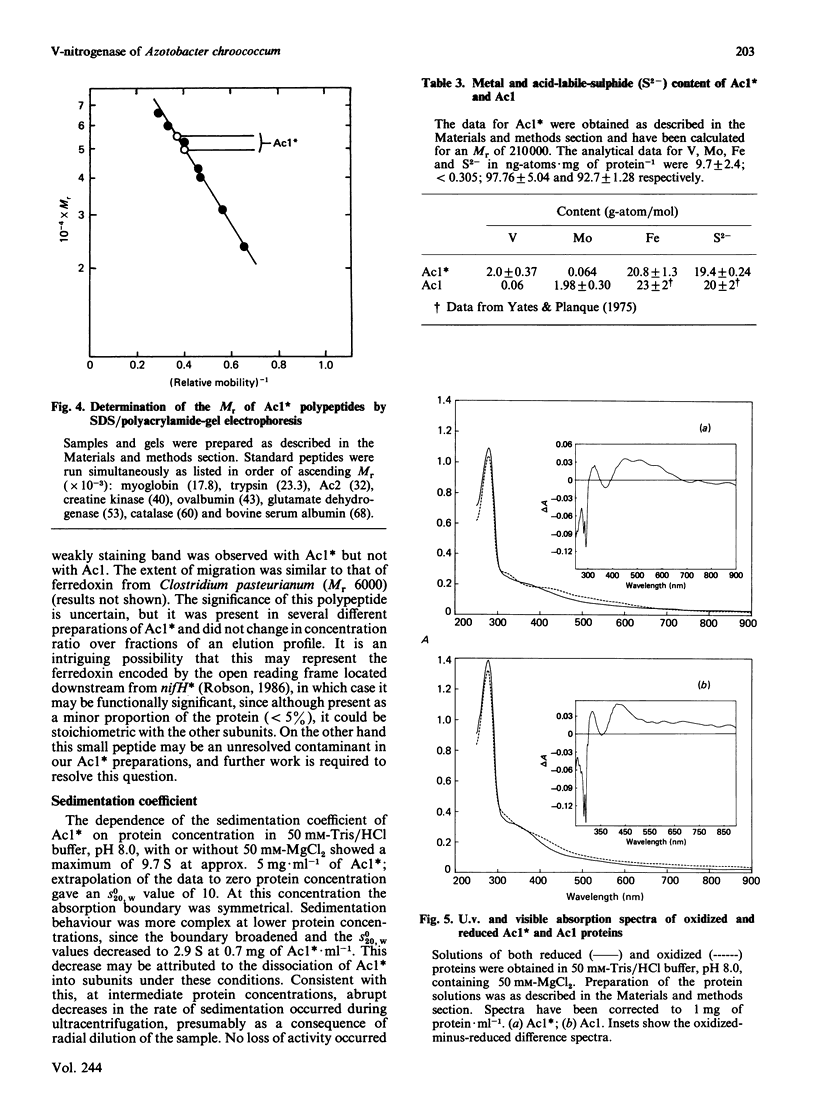
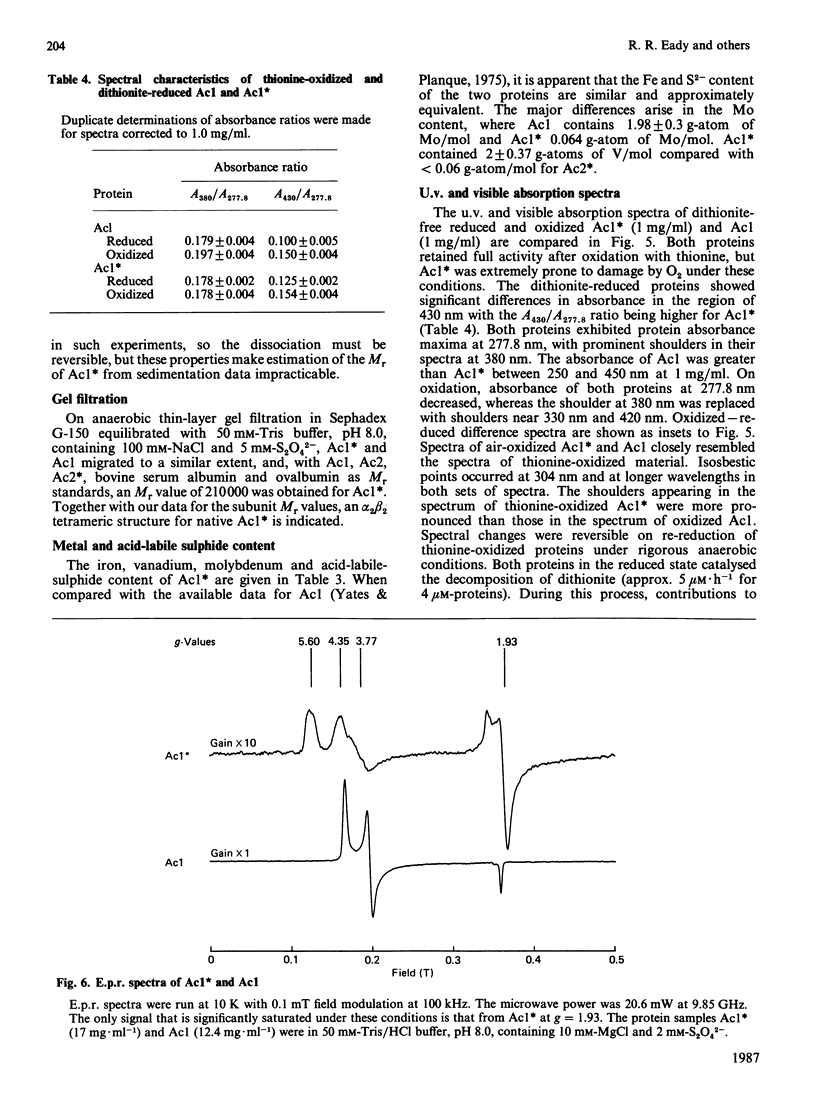
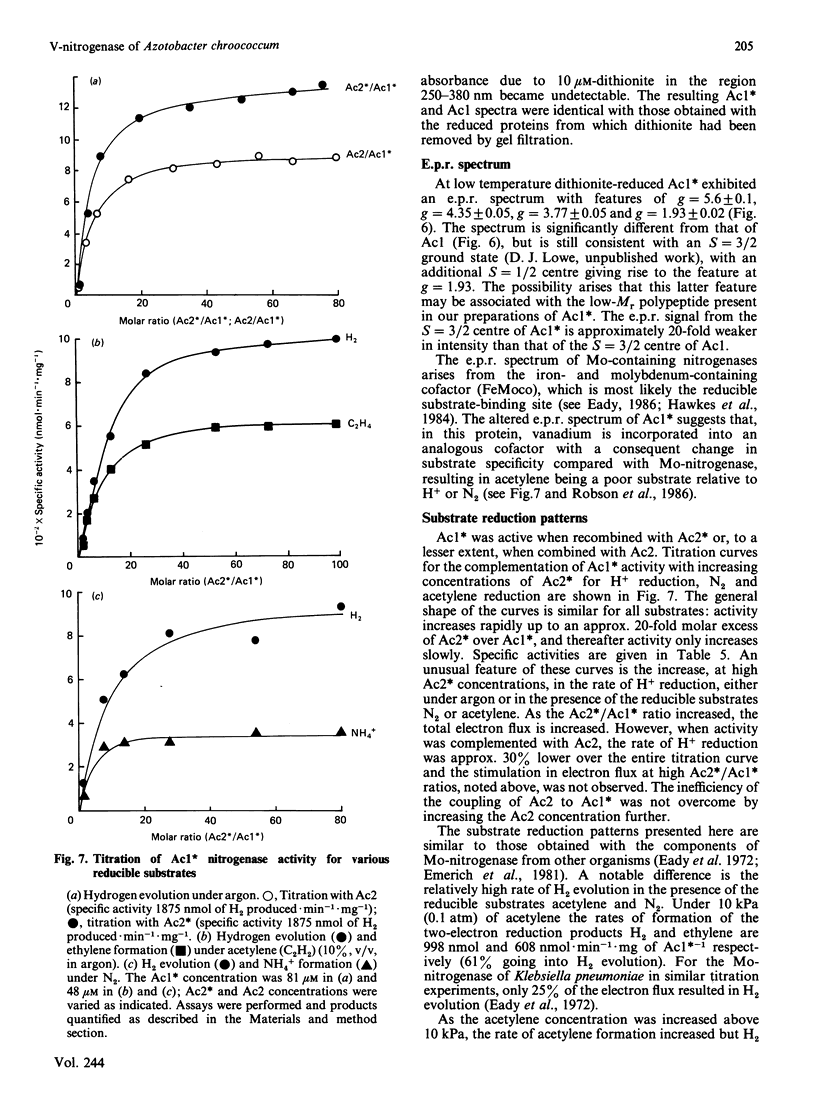
1. Nitrogenase activity of a strain of Azotobacter chroococcum lacking the structural genes for conventional nitrogenase (nifHDK) was separated into two components: an Fe-containing protein and a vanadoprotein. 2. The larger protein was purified to homogeneity by the criterion of electrophoresis of 10% (w/v) acrylamide gels in the presence of SDS. Two types of subunit, of Mr 50,000 and 55,000, were present in equal amounts. 3. The protein had an Mr of 210,000 and contained 2 V atoms, 23 Fe atoms and 20 acid-labile sulphide groups per molecule. The Mo content was less than 0.06 g-atom/mol. All the common amino acids were present, with a predominance of acidic residues. Ultracentrifugal analysis gave a maximum sedimentation coefficient of 9.7 S and a symmetrical boundary at 5 mg of protein X ml-1; dissociation occurred at lower concentrations. The specific activities (nmol of product/min per mg of protein), when assayed under optimum conditions with the complementary Fe protein from this strain, were 1348 for H2 evolution, 350 for NH3 formation and 608 for acetylene reduction. Activity was O2-labile, with a t1/2 of 40 s in air. At low temperatures the dithionite-reduced protein showed e.p.r. signals at g = 5.6, 4.35, 3.77 and 1.93, consistent with an S = 3/2 ground state with an additional S = 1/2 centre giving rise to the feature at g = 1.93. The u.v. spectra of dithionite-reduced and thionine-oxidized protein were very similar. Oxidation resulted in a general increase in absorbance in the visible region. The shoulder at 380 nm in the spectrum of reduced protein was replaced with shoulders near 330 nm and 420 nm on oxidation.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benemann J. R., McKenna C. E., Lie R. F., Traylor T. G., Kamen M. D. The vanadium effect in nitrogen fixation by azotobacter. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Mar 30;264(1):25–38. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(72)90113-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop P. E., Jarlenski D. M., Hetherington D. R. Evidence for an alternative nitrogen fixation system in Azotobacter vinelandii. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7342–7346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop P. E., Jarlenski D. M., Hetherington D. R. Expression of an alternative nitrogen fixation system in Azotobacter vinelandii. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jun;150(3):1244–1251. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.3.1244-1251.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop P. E., Premakumar R., Dean D. R., Jacobson M. R., Chisnell J. R., Rizzo T. M., Kopczynski J. Nitrogen Fixation by Azotobacter vinelandii Strains Having Deletions in Structural Genes for Nitrogenase. Science. 1986 Apr 4;232(4746):92–94. doi: 10.1126/science.232.4746.92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns R. C., Fuchsman W. H., Hardy R. W. Nitrogenase from vanadium-grown Azotobacter: isolation, characteristics, and mechanistic implications. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Feb 5;42(3):353–358. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90377-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. S., Mortenson L. E. Inhibition of methylene blue formation during determination of the acid-labile sulfide of iron-sulfur protein samples containing dithionite. Anal Biochem. 1977 May 1;79(1-2):157–165. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90390-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin J. L. Liquid chromatographic-fluorescence determination of ammonia from nitrogenase reactions: a 2-min assay. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 May;47(5):1027–1030. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.5.1027-1030.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. A. The genetic complexity of nitrogen fixation. The ninth Fleming lecture. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Nov;130(11):2745–2755. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-11-2745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eady R. R., Robson R. L. Characteristics of N2 fixation in Mo-limited batch and continuous cultures of Azotobacter vinelandii. Biochem J. 1984 Dec 15;224(3):853–862. doi: 10.1042/bj2240853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eady R. R., Smith B. E., Cook K. A., Postgate J. R. Nitrogenase of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Purification and properties of the component proteins. Biochem J. 1972 Jul;128(3):655–675. doi: 10.1042/bj1280655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerich D. W., Hageman R. V., Burris R. H. Interactions of dinitrogenase and dinitrogenase reductase. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1981;52:1–22. doi: 10.1002/9780470122976.ch1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hales B. J., Case E. E., Morningstar J. E., Dzeda M. F., Mauterer L. A. Isolation of a new vanadium-containing nitrogenase from Azotobacter vinelandii. Biochemistry. 1986 Nov 18;25(23):7251–7255. doi: 10.1021/bi00371a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes T. R., McLean P. A., Smith B. E. Nitrogenase from nifV mutants of Klebsiella pneumoniae contains an altered form of the iron-molybdenum cofactor. Biochem J. 1984 Jan 1;217(1):317–321. doi: 10.1042/bj2170317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy C., Eady R. R., Kondorosi E., Rekosh D. K. The molybdenum--iron protein of Klebsiella pneumoniae nitrogenase. Evidence for non-identical subunits from peptide 'mapping'. Biochem J. 1976 May 1;155(2):383–389. doi: 10.1042/bj1550383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenna C. E., Benemann J. R., Traylor T. G. A vanadium containing nitrogenase preparation: implications for the role of molybdenum in nitrogen fixation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Dec 24;41(6):1501–1508. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90557-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robson R. L., Postgate J. R. Oxygen and hydrogen in biological nitrogen fixation. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1980;34:183–207. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.34.100180.001151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson F. B., Burris R. H. A nitrogen pressure of 50 atmospheres does not prevent evolution of hydrogen by nitrogenase. Science. 1984 Jun 8;224(4653):1095–1097. doi: 10.1126/science.6585956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorneley R. N., Eady R. R., Yates M. G. Nitrogenases of Klebsiella pneumoniae and Azotobacter chroococum. Complex formation between the component proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Oct 22;403(2):269–284. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(75)90057-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorneley R. N., Lowe D. J. The mechanism of Klebsiella pneumoniae nitrogenase action. Simulation of the dependences of H2-evolution rate on component-protein concentration and ratio and sodium dithionite concentration. Biochem J. 1984 Dec 15;224(3):903–909. doi: 10.1042/bj2240903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates M. G., Planqué K. Nitrogenase from Azotobacter chroococcum. Purification and properties of the component proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Dec 15;60(2):467–476. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb21025.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]