Abstract
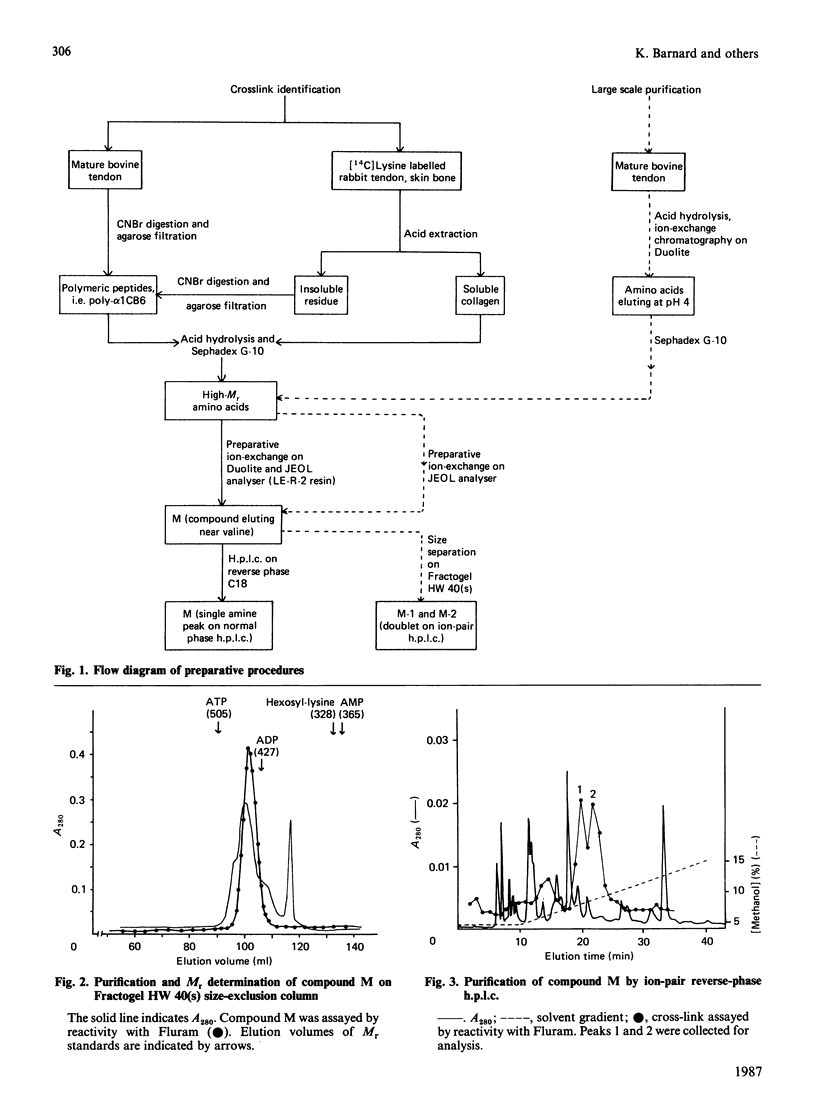
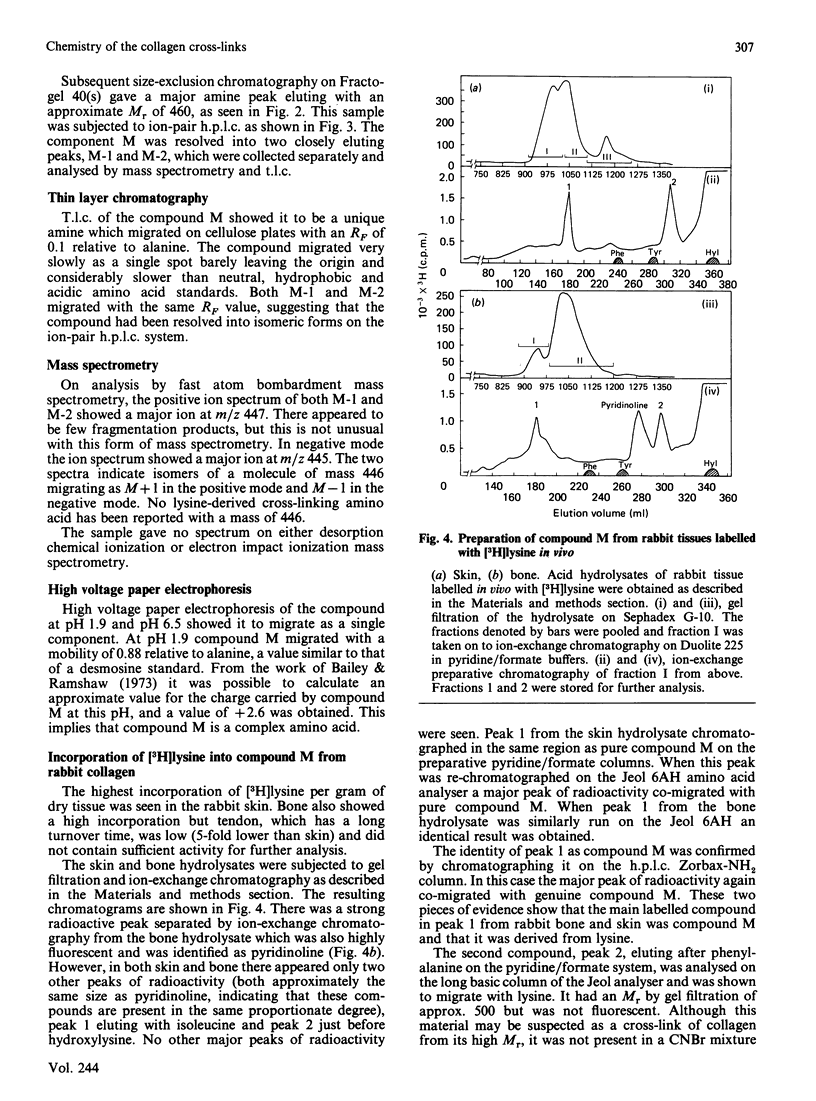
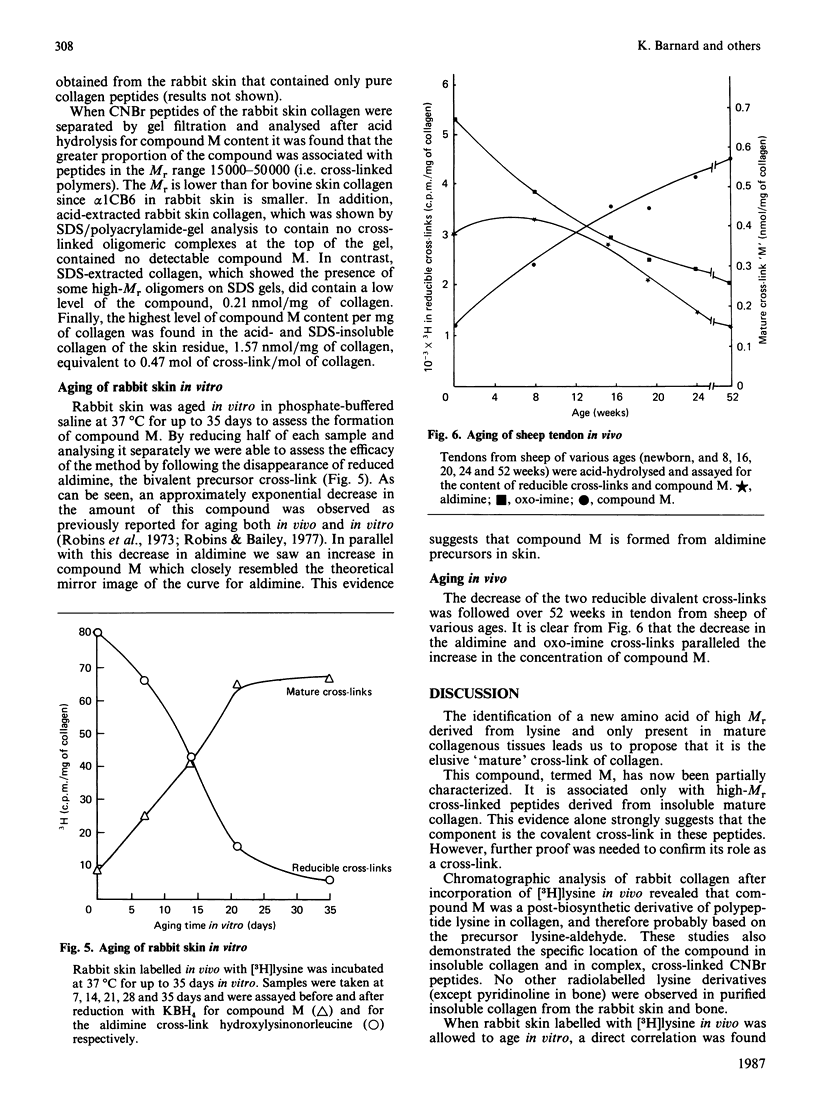
The conversion of the reducible divalent cross-links in collagen to non-reducible multivalent cross-links in mature collagen has resulted in the identification of several new amino acids as the putative mature cross-link. None of these compounds has completely satisfied the necessary criteria. We have now isolated an amino acid of high Mr, derived from lysine, that is only present in high-Mr peptides derived from mature collagen. Its increase with age of the tissue correlates with the decrease in the reducible cross-links, and it is present both in mature skin and bone, which are initially cross-linked through the aldimine and oxo-imine divalent cross-link respectively. We propose that this amino acid, as yet incompletely characterized and designated compound M, is a major cross-link of mature collagen.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailey A. J., Light N. D., Atkins E. D. Chemical cross-linking restrictions on models for the molecular organization of the collagen fibre. Nature. 1980 Nov 27;288(5789):408–410. doi: 10.1038/288408a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey A. J., Peach C. M. Isolation and structural identification of a labile intermolecular crosslink in collagen. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Dec 9;33(5):812–819. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90233-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey A. J., Robins S. P., Balian G. Biological significance of the intermolecular crosslinks of collagen. Nature. 1974 Sep 13;251(5471):105–109. doi: 10.1038/251105a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey C. J., Ramshaw J. A. The electrophoretic mobility of peptides on paper at pH 1.9. Biochem J. 1973 Dec;135(4):889–891. doi: 10.1042/bj1350889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyre D. R., Oguchi H. The hydroxypyridinium crosslinks of skeletal collagens: their measurement, properties and a proposed pathway of formation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Jan 29;92(2):403–410. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90347-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyre D. R., Paz M. A., Gallop P. M. Cross-linking in collagen and elastin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:717–748. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.003441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimoto D. Evidence for natural existence of pyridinoline crosslink in collagen. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Apr 14;93(3):948–953. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91167-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimoto D. Isolation and characterization of a fluorescent material in bovine achilles tendon collagen. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jun 20;76(4):1124–1129. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90972-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Housley T., Tanzer M. L., Henson E., Gallop P. M. Collagen crosslinking: isolation of hydroxyaldol-histidine, a naturally-occurring crosslink. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Nov 17;67(2):824–830. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90887-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Light N. D., Bailey A. J. Changes in crosslinking during aging in bovine tendon collagen. FEBS Lett. 1979 Jan 1;97(1):183–188. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80080-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Light N. D., Bailey A. J. Covalent cross-links in collagen. Methods Enzymol. 1982;82(Pt A):360–372. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)82073-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Light N. D., Bailey A. J. Polymeric C-terminal cross-linked material from type-I collagen. A modified method for purification, anomalous behaviour on gel filtration, molecular weight estimation, carbohydrate content and lipid content. Biochem J. 1980 Jul 1;189(1):111–124. doi: 10.1042/bj1890111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Light N. D., Bailey A. J. The chemistry of the collagen cross-links. Purification and characterization of cross-linked polymeric peptide material from mature collagen containing unknown amino acids. Biochem J. 1980 Feb 1;185(2):373–381. doi: 10.1042/bj1850373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Light N. D. Estimation of types I and III collagens in whole tissue by quantitation of CNBr peptides on SDS-polyacrylamide gels. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Mar 18;702(1):30–36. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(82)90024-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Light N., Bailey A. J. Collagen cross-links: location of pyridinoline in type I collagen. FEBS Lett. 1985 Mar 25;182(2):503–508. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80363-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mechanic G., Gallop P. M., Tanzer M. L. The nature of crosslinking in collagens from mineralized tissues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Nov 5;45(3):644–653. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90465-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriguchi T., Fujimoto D. Age-related changes in the content of the collagen crosslink, pyridinoline. J Biochem. 1978 Oct;84(4):933–935. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins S. P., Bailey A. J. Relative stabilities of the intermediate reducible crosslinks present in collagen fibres. FEBS Lett. 1973 Jul 1;33(2):167–174. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80184-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins S. P., Bailey A. J. Some observations on the ageing in vitro of reprecipitated collagen fibres. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jun 24;492(2):408–414. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(77)90092-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins S. P., Bailey A. J. The chemistry of the collagen cross-links. The mechanism of stabilization of the reducible intermediate cross-links. Biochem J. 1975 Aug;149(2):381–385. doi: 10.1042/bj1490381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins S. P., Duncan A. Cross-linking of collagen. Location of pyridinoline in bovine articular cartilage at two sites of the molecule. Biochem J. 1983 Oct 1;215(1):175–182. doi: 10.1042/bj2150175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins S. P., Shimokomaki M., Bailey A. J. The chemistry of the collagen cross-links. Age-related changes in the reducible components of intact bovine collagen fibres. Biochem J. 1973 Apr;131(4):771–780. doi: 10.1042/bj1310771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smolenski K. A., Avery N. C., Light N. D. A new rapid method for the identification of reducible collagen cross-links in small tissue samples. Biochem J. 1983 Aug 1;213(2):525–532. doi: 10.1042/bj2130525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes B. C., Bailey A. J. Molecular weight heterogeneity of the alpha-chain sub-units of collagen. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Apr 16;43(2):340–345. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90758-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzer M. L., Waite J. H. Collagen cross-linking. Coll Relat Res. 1982 Mar;2(2):177–180. doi: 10.1016/s0174-173x(82)80032-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


