Abstract
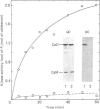
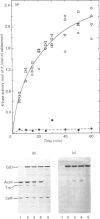
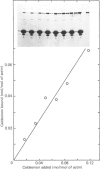
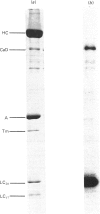
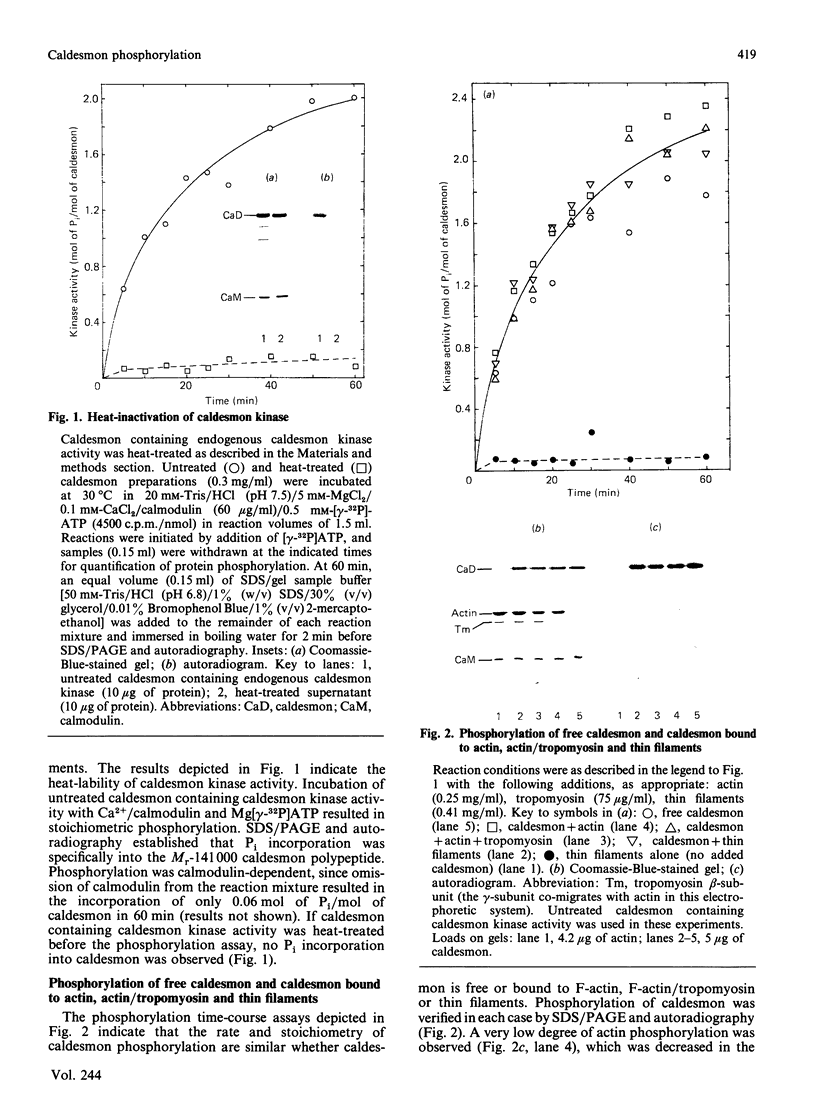
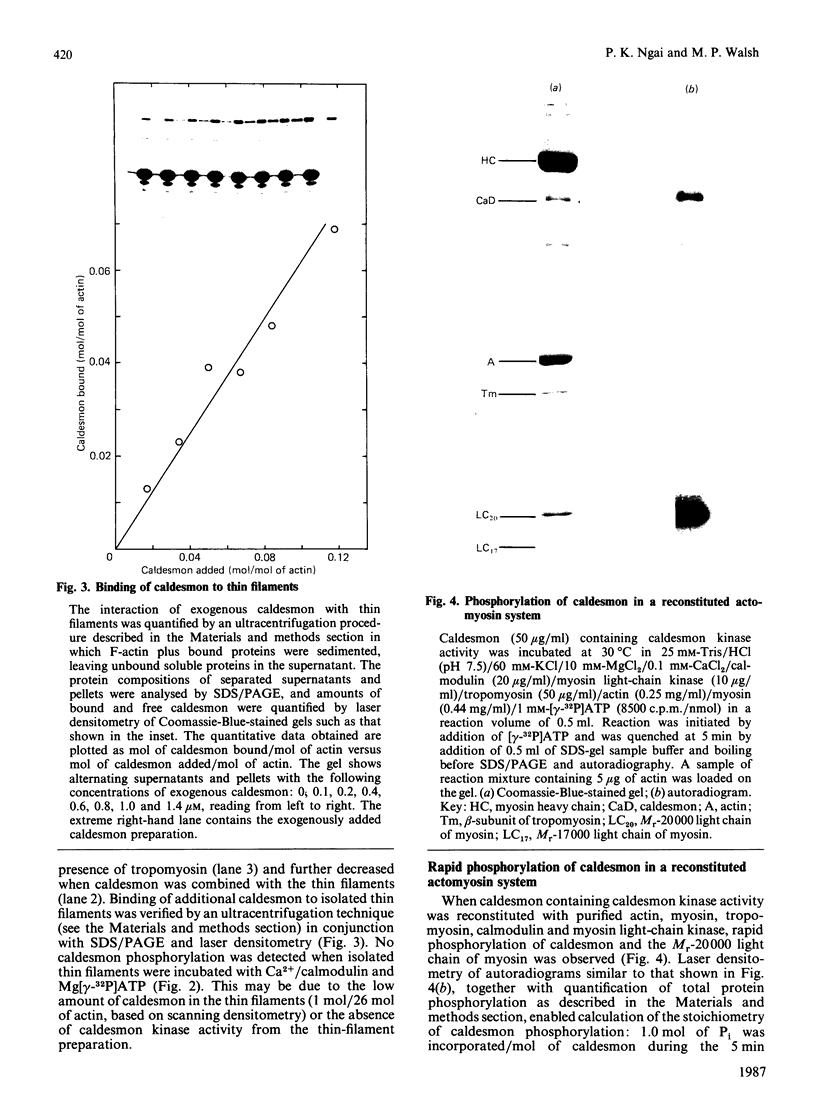
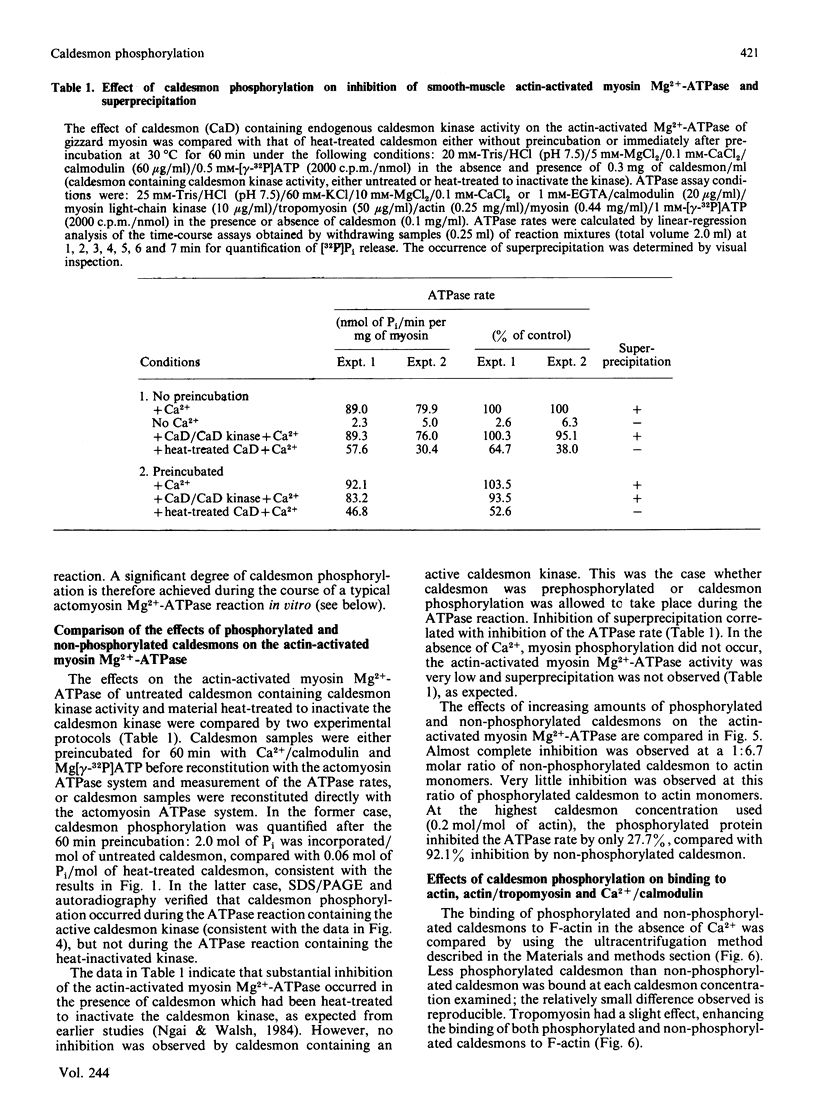
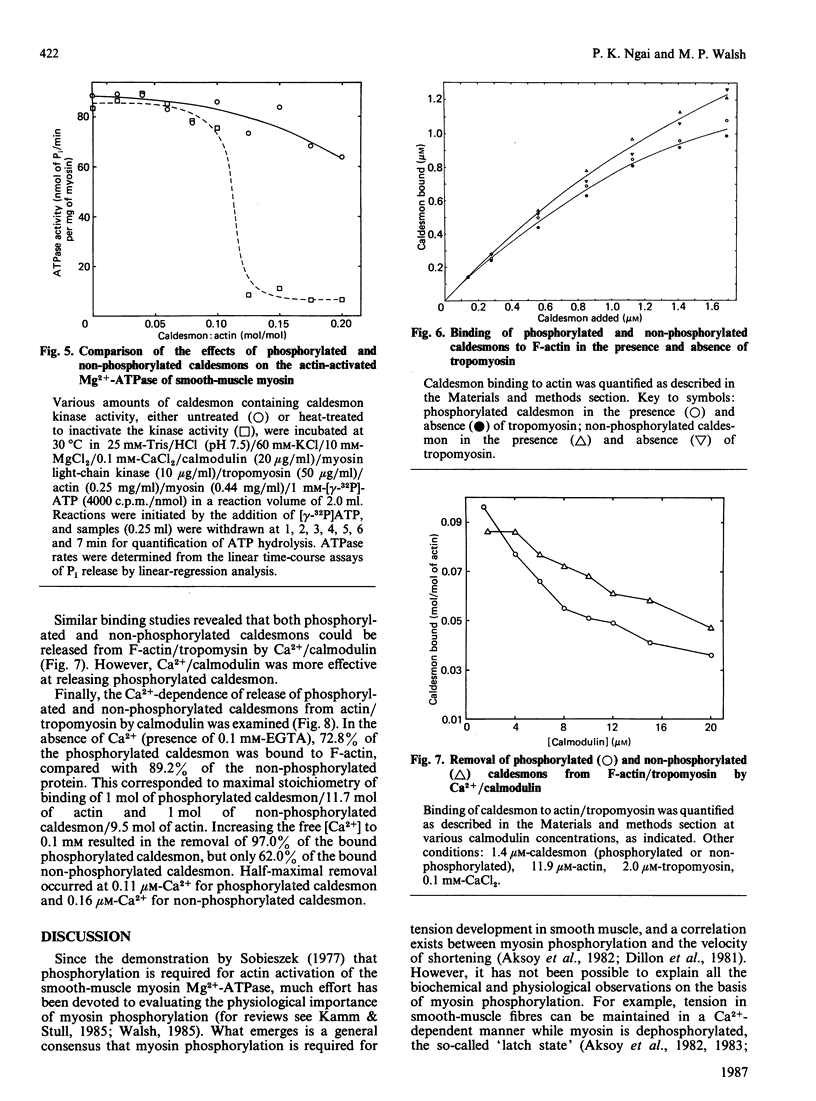
Caldesmon is a major calmodulin- and actin-binding protein of smooth muscle which interacts with calmodulin in a Ca2+-dependent manner or with actin in a Ca2+-independent manner. Isolated caldesmon is capable of inhibiting the actin-activated Mg2+-ATPase of smooth-muscle myosin, suggesting a possible physiological role for caldesmon in regulating the contractile state of smooth-muscle. Caldesmon can be phosphorylated in vitro by a co-purifying Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase and dephosphorylated by a protein phosphatase, both of which are present in smooth muscle. We investigated further the phosphorylation of caldesmon and the effects which phosphorylation has on the functional properties of the protein. The kinetics of caldesmon phosphorylation were similar whether the caldesmon substrate was free or bound to actin, actin/tropomyosin or thin filaments. Caldesmon containing endogenous kinase activity was rapidly phosphorylated (to approx. 1 mol of Pi/mol of caldesmon in 5 min) when reconstituted with actin, myosin, tropomyosin, calmodulin and myosin light-chain kinase in the presence of Ca2+ and MgATP2-. Under conditions in which unphosphorylated caldesmon showed substantial inhibition of the actin-activated myosin Mg2+-ATPase, no inhibition was observed with phosphorylated caldesmon. This was the case whether caldesmon was phosphorylated before addition to the actomyosin Mg2+-ATPase system, or phosphorylation was allowed to take place during the ATPase reaction. Binding studies revealed maximal binding of 1 mol of unphosphorylated caldesmon/9.5 mol of actin and 1 mol of phosphorylated caldesmon/11.7 mol of actin. All the bound phosphorylated caldesmon could be released by Ca2+/calmodulin, with half-maximal release at 0.11 microM-Ca2+, whereas only 62% of the bound unphosphorylated caldesmon could be removed, with half-maximal release at 0.16 microM-Ca2+. However, under conditions in which inhibition of actomyosin Mg2+-ATPase activity by non-phosphorylated but not by phosphorylated caldesmon was observed, both forms of caldesmon would remain bound to the thin filament. These observations suggest a possible mechanism whereby caldesmon phosphorylation may prevent its inhibitory action on the actomyosin Mg2+-ATPase.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adelstein R. S., Eisenberg E. Regulation and kinetics of the actin-myosin-ATP interaction. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:921–956. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.004421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aksoy M. O., Mras S., Kamm K. E., Murphy R. A. Ca2+, cAMP, and changes in myosin phosphorylation during contraction of smooth muscle. Am J Physiol. 1983 Sep;245(3):C255–C270. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1983.245.3.C255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aksoy M. O., Murphy R. A., Kamm K. E. Role of Ca2+ and myosin light chain phosphorylation in regulation of smooth muscle. Am J Physiol. 1982 Jan;242(1):C109–C116. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1982.242.1.C109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aksoy M. O., Stewart G. J., Harakal C. Myosin light chain phosphorylation and evidence for latchbridge formation in norepinephrine stimulated canine veins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Mar 28;135(3):735–741. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90990-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher A., Lynch W. Identification and localization of immunoreactive forms of caldesmon in smooth and nonmuscle cells: a comparison with the distributions of tropomyosin and alpha-actinin. J Cell Biol. 1985 May;100(5):1656–1663. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.5.1656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher A. Smooth muscle caldesmon. Rapid purification and F-actin cross-linking properties. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 25;259(20):12873–12880. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler T. M., Siegman M. J., Mooers S. U. Chemical energy usage during shortening and work production in mammalian smooth muscle. Am J Physiol. 1983 Mar;244(3):C234–C242. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1983.244.3.C234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee M., Murphy R. A. Calcium-dependent stress maintenance without myosin phosphorylation in skinned smooth muscle. Science. 1983 Jul 29;221(4609):464–466. doi: 10.1126/science.6867722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark T., Ngai P. K., Sutherland C., Gröschel-Stewart U., Walsh M. P. Vascular smooth muscle caldesmon. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 15;261(17):8028–8035. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark T., Ngai P. K., Sutherland C., Gröschel-Stewart U., Walsh M. P. Vascular smooth muscle caldesmon. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 15;261(17):8028–8035. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillon P. F., Aksoy M. O., Driska S. P., Murphy R. A. Myosin phosphorylation and the cross-bridge cycle in arterial smooth muscle. Science. 1981 Jan 30;211(4481):495–497. doi: 10.1126/science.6893872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A. Myoplasmic free calcium concentration reached during the twitch of an intact isolated cardiac cell and during calcium-induced release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum of a skinned cardiac cell from the adult rat or rabbit ventricle. J Gen Physiol. 1981 Nov;78(5):457–497. doi: 10.1085/jgp.78.5.457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fürst D. O., Cross R. A., De Mey J., Small J. V. Caldesmon is an elongated, flexible molecule localized in the actomyosin domains of smooth muscle. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):251–257. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04206.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerthoffer W. T., Murphy R. A. Myosin phosphorylation and regulation of cross-bridge cycle in tracheal smooth muscle. Am J Physiol. 1983 Mar;244(3):C182–C187. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1983.244.3.C182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gopalakrishna R., Anderson W. B. Ca2+-induced hydrophobic site on calmodulin: application for purification of calmodulin by phenyl-Sepharose affinity chromatography. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jan 29;104(2):830–836. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)90712-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. E., Sellers J. R., Eisenberg E., Adelstein R. S. Binding of gizzard smooth muscle myosin subfragment 1 to actin in the presence and absence of adenosine 5'-triphosphate. Biochemistry. 1983 Feb 1;22(3):530–535. doi: 10.1021/bi00272a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikebe M., Hartshorne D. J. Proteolysis of smooth muscle myosin by Staphylococcus aureus protease: preparation of heavy meromyosin and subfragment 1 with intact 20 000-dalton light chains. Biochemistry. 1985 Apr 23;24(9):2380–2387. doi: 10.1021/bi00330a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamm K. E., Stull J. T. The function of myosin and myosin light chain kinase phosphorylation in smooth muscle. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1985;25:593–620. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.25.040185.003113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klee C. B. Conformational transition accompanying the binding of Ca2+ to the protein activator of 3',5'-cyclic adenosine monophosphate phosphodiesterase. Biochemistry. 1977 Mar 8;16(5):1017–1024. doi: 10.1021/bi00624a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lash J. A., Sellers J. R., Hathaway D. R. The effects of caldesmon on smooth muscle heavy actomeromyosin ATPase activity and binding of heavy meromyosin to actin. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 5;261(34):16155–16160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehman W. Caldesmon association with smooth muscle thin filaments isolated in the presence and absence of calcium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jan 23;885(1):88–90. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(86)90042-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehman W., Szent-Györgyi A. G. Regulation of muscular contraction. Distribution of actin control and myosin control in the animal kingdom. J Gen Physiol. 1975 Jul;66(1):1–30. doi: 10.1085/jgp.66.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim M. S., Walsh M. P. The effects of caldesmon on the ATPase activities of rabbit skeletal-muscle myosin. Biochem J. 1986 Sep 1;238(2):523–530. doi: 10.1042/bj2380523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marston S. B. Ca2+ can control vascular smooth-muscle thin filaments without caldesmon phosphorylation. Biochem J. 1986 Jul 15;237(2):605–607. doi: 10.1042/bj2370605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marston S. B., Lehman W. Caldesmon is a Ca2+-regulatory component of native smooth-muscle thin filaments. Biochem J. 1985 Nov 1;231(3):517–522. doi: 10.1042/bj2310517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marston S. B., Smith C. W. Purification and properties of Ca2+-regulated thin filaments and F-actin from sheep aorta smooth muscle. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1984 Oct;5(5):559–575. doi: 10.1007/BF00713261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marston S. B., Smith C. W. The thin filaments of smooth muscles. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1985 Dec;6(6):669–708. doi: 10.1007/BF00712237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marston S. B., Trevett R. M., Walters M. Calcium ion-regulated thin filaments from vascular smooth muscle. Biochem J. 1980 Feb 1;185(2):355–365. doi: 10.1042/bj1850355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan J. P., Morgan K. G. Vascular smooth muscle: the first recorded Ca2+ transients. Pflugers Arch. 1982 Oct;395(1):75–77. doi: 10.1007/BF00584972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ngai P. K., Carruthers C. A., Walsh M. P. Isolation of the native form of chicken gizzard myosin light-chain kinase. Biochem J. 1984 Mar 15;218(3):863–870. doi: 10.1042/bj2180863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ngai P. K., Gröschel-Stewart U., Walsh M. P. Comparison of the effects of smooth and skeletal muscle actins on smooth muscle actomyosin Mg2+-ATPase. Biochem Int. 1986 Jan;12(1):89–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ngai P. K., Walsh M. P. Inhibition of smooth muscle actin-activated myosin Mg2+-ATPase activity by caldesmon. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13656–13659. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ngai P. K., Walsh M. P. Properties of caldesmon isolated from chicken gizzard. Biochem J. 1985 Sep 15;230(3):695–707. doi: 10.1042/bj2300695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persechini A., Hartshorne D. J. Phosphorylation of smooth muscle myosin: evidence for cooperativity between the myosin heads. Science. 1981 Sep 18;213(4514):1383–1385. doi: 10.1126/science.6455737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver P. J., Stull J. T. Regulation of myosin light chain and phosphorylase phosphorylation in tracheal smooth muscle. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6145–6150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobue K., Muramoto Y., Fujita M., Kakiuchi S. Purification of a calmodulin-binding protein from chicken gizzard that interacts with F-actin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5652–5655. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector T. Refinement of the coomassie blue method of protein quantitation. A simple and linear spectrophotometric assay for less than or equal to 0.5 to 50 microgram of protein. Anal Biochem. 1978 May;86(1):142–146. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90327-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szpacenko A., Wagner J., Dabrowska R., Rüegg J. C. Caldesmon-induced inhibition of ATPase activity of actomyosin and contraction of skinned fibres of chicken gizzard smooth muscle. FEBS Lett. 1985 Nov 11;192(1):9–12. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80032-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh M. P., Hinkins S., Dabrowska R., Hartshorne D. J. Smooth muscle myosin light chain kinase. Methods Enzymol. 1983;99:279–288. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)99063-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh M. P., Valentine K. A., Ngai P. K., Carruthers C. A., Hollenberg M. D. Ca2+-dependent hydrophobic-interaction chromatography. Isolation of a novel Ca2+-binding protein and protein kinase C from bovine brain. Biochem J. 1984 Nov 15;224(1):117–127. doi: 10.1042/bj2240117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. A., Fay F. S. Calcium transients and resting levels in isolated smooth muscle cells as monitored with quin 2. Am J Physiol. 1986 May;250(5 Pt 1):C779–C791. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.250.5.C779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]