Abstract
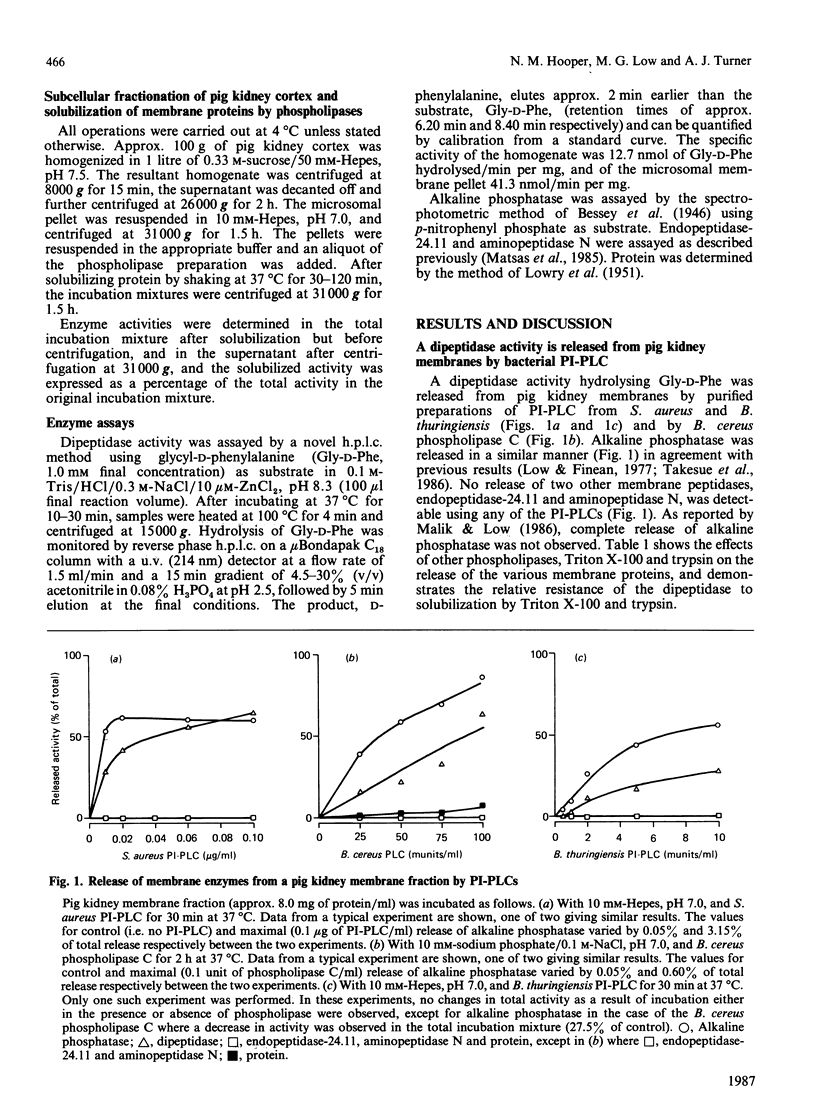
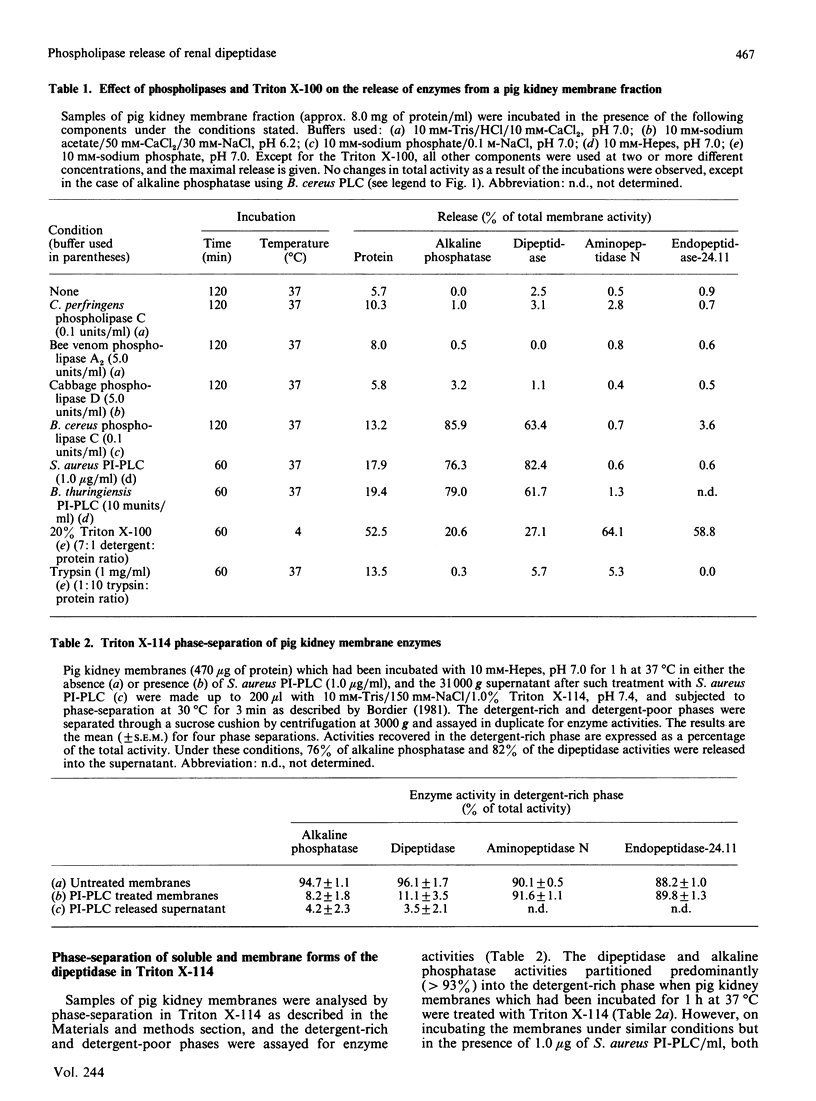
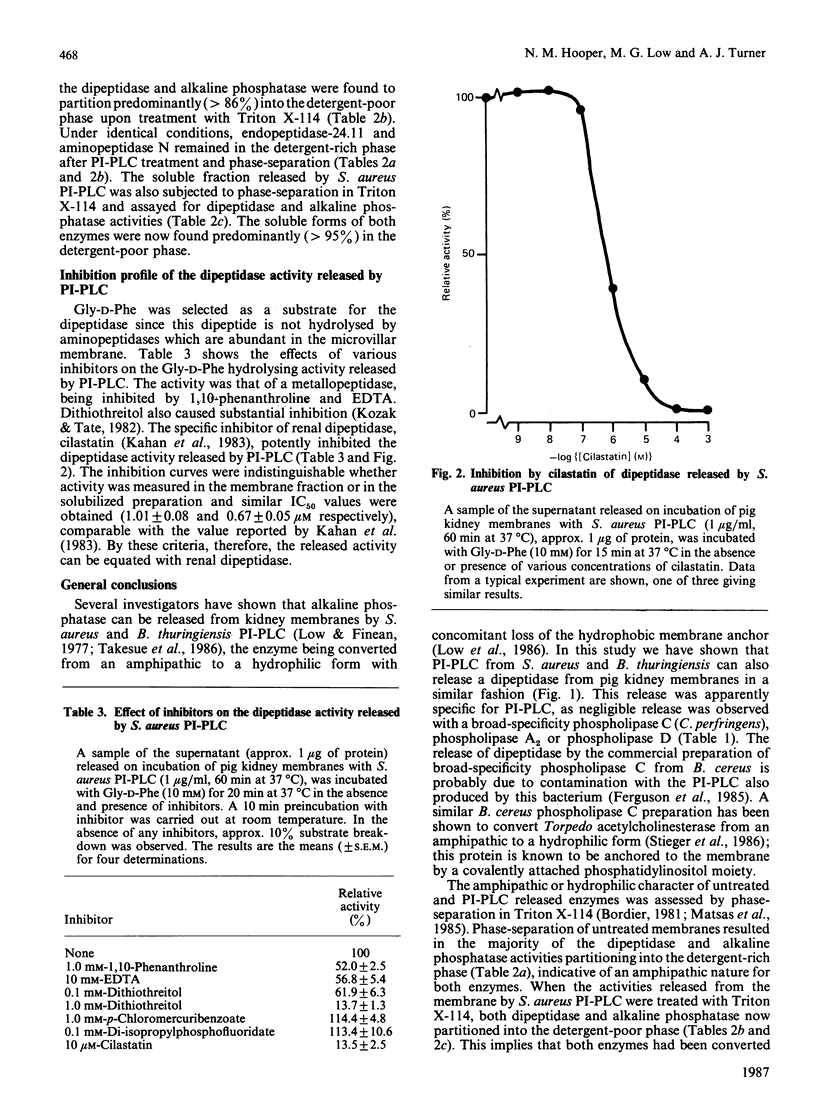
Renal dipeptidase (dehydropeptidase-I, EC 3.4.13.11) was released from pig kidney membrane preparations by treatment with phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C from Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus thuringiensis and a phospholipase C preparation from Bacillus cereus to a similar extent as alkaline phosphatase. Endopeptidase-24.11 and aminopeptidase N were not released by this treatment. After treatment of the membrane fraction with the S. aureus phospholipase C the dipeptidase was converted from an amphipathic to a hydrophilic form, as deduced from phase-separation experiments in Triton X-114. It is concluded that renal dipeptidase is anchored to the microvillar membrane by covalently attached phosphatidylinositol.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bordier C. Phase separation of integral membrane proteins in Triton X-114 solution. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1604–1607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson M. A., Low M. G., Cross G. A. Glycosyl-sn-1,2-dimyristylphosphatidylinositol is covalently linked to Trypanosoma brucei variant surface glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14547–14555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulcher I. S., Pappin D. J., Kenny A. J. The N-terminal amino acid sequence of pig kidney endopeptidase-24.11 shows homology with pro-sucrase-isomaltase. Biochem J. 1986 Nov 15;240(1):305–308. doi: 10.1042/bj2400305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Futerman A. H., Low M. G., Michaelson D. M., Silman I. Solubilization of membrane-bound acetylcholinesterase by a phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C. J Neurochem. 1985 Nov;45(5):1487–1494. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb07217.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He H. T., Barbet J., Chaix J. C., Goridis C. Phosphatidylinositol is involved in the membrane attachment of NCAM-120, the smallest component of the neural cell adhesion molecule. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2489–2494. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04526.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahan F. M., Kropp H., Sundelof J. G., Birnbaum J. Thienamycin: development of imipenen-cilastatin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Dec;12 (Suppl 500):1–35. doi: 10.1093/jac/12.suppl_d.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny A. J., Maroux S. Topology of microvillar membrance hydrolases of kidney and intestine. Physiol Rev. 1982 Jan;62(1):91–128. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1982.62.1.91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H. S., Campbell B. J. Association of renal dipeptidase with the Triton-insoluble fraction of kidney microvilli. J Membr Biol. 1983;75(2):115–122. doi: 10.1007/BF01995631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kropp H., Sundelof J. G., Hajdu R., Kahan F. M. Metabolism of thienamycin and related carbapenem antibiotics by the renal dipeptidase, dehydropeptidase. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Jul;22(1):62–70. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.1.62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G. Biochemistry of the glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol membrane protein anchors. Biochem J. 1987 May 15;244(1):1–13. doi: 10.1042/bj2440001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G., Finean J. B. Release of alkaline phosphatase from membranes by a phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C. Biochem J. 1977 Oct 1;167(1):281–284. doi: 10.1042/bj1670281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G., Kincade P. W. Phosphatidylinositol is the membrane-anchoring domain of the Thy-1 glycoprotein. Nature. 1985 Nov 7;318(6041):62–64. doi: 10.1038/318062a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malik A. S., Low M. G. Conversion of human placental alkaline phosphatase from a high Mr form to a low Mr form during butanol extraction. An investigation of the role of endogenous phosphoinositide-specific phospholipases. Biochem J. 1986 Dec 1;240(2):519–527. doi: 10.1042/bj2400519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsas R., Stephenson S. L., Hryszko J., Kenny A. J., Turner A. J. The metabolism of neuropeptides. Phase separation of synaptic membrane preparations with Triton X-114 reveals the presence of aminopeptidase N. Biochem J. 1985 Oct 15;231(2):445–449. doi: 10.1042/bj2310445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medof M. E., Walter E. I., Roberts W. L., Haas R., Rosenberry T. L. Decay accelerating factor of complement is anchored to cells by a C-terminal glycolipid. Biochemistry. 1986 Nov 4;25(22):6740–6747. doi: 10.1021/bi00370a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stieger A., Cardoso de Almeida M. L., Blatter M. C., Brodbeck U., Bordier C. The membrane-anchoring systems of vertebrate acetylcholinesterase and variant surface glycoproteins of African trypanosomes share a common antigenic determinant. FEBS Lett. 1986 Apr 21;199(2):182–186. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80476-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taguchi R., Asahi Y., Ikezawa H. Purification and properties of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C of Bacillus thuringiensis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jul 14;619(1):48–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takesue Y., Yokota K., Nishi Y., Taguchi R., Ikezawa H. Solubilization of trehalase from rabbit renal and intestinal brush-border membranes by a phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C. FEBS Lett. 1986 May 26;201(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80560-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


