Abstract
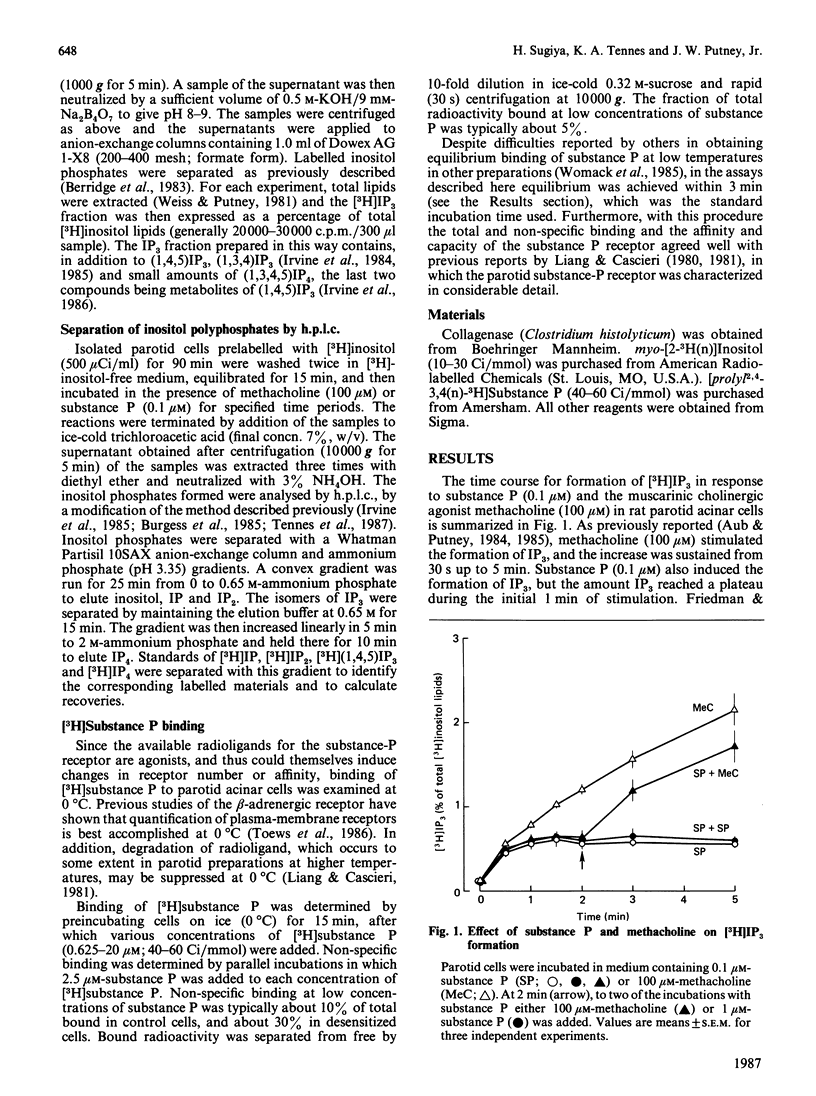
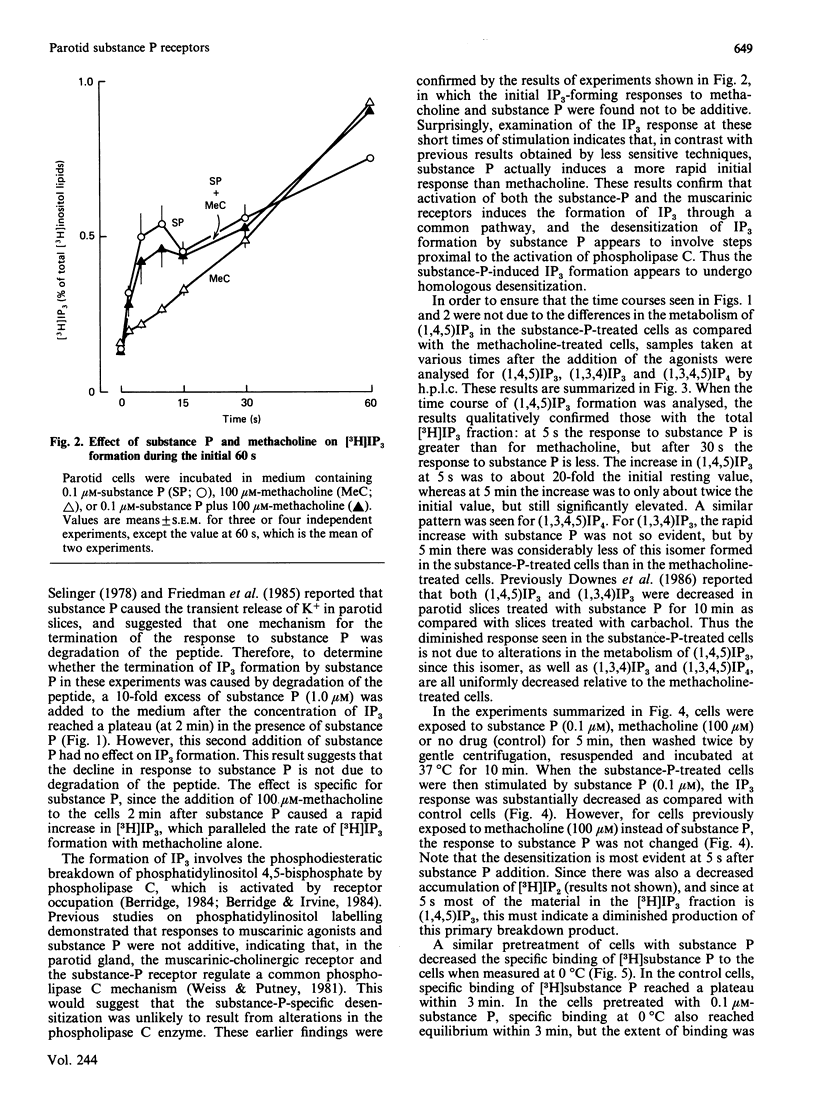
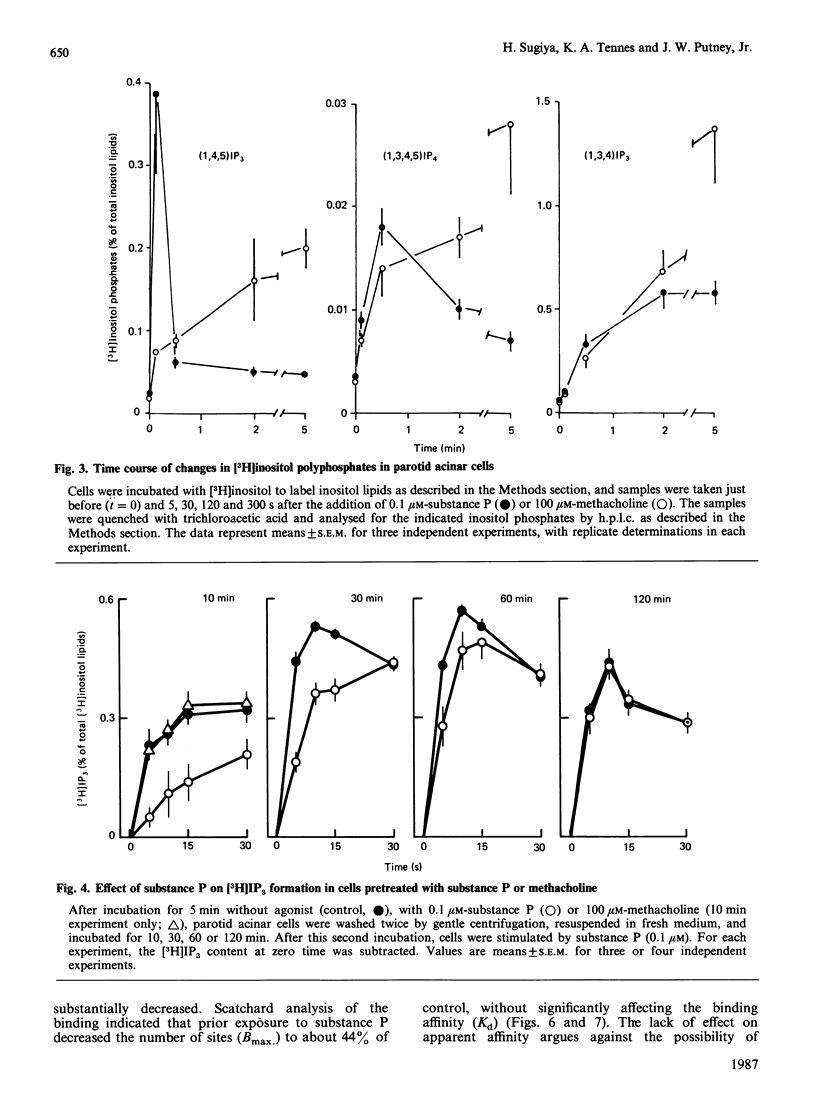
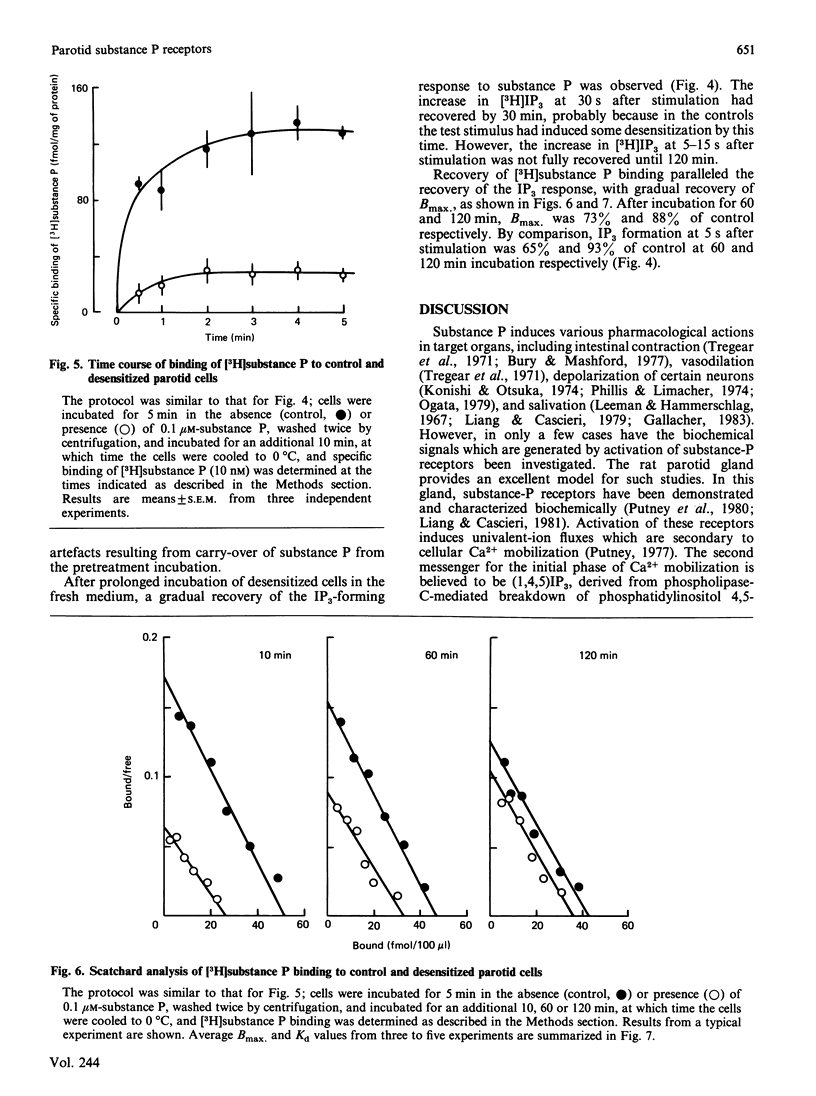
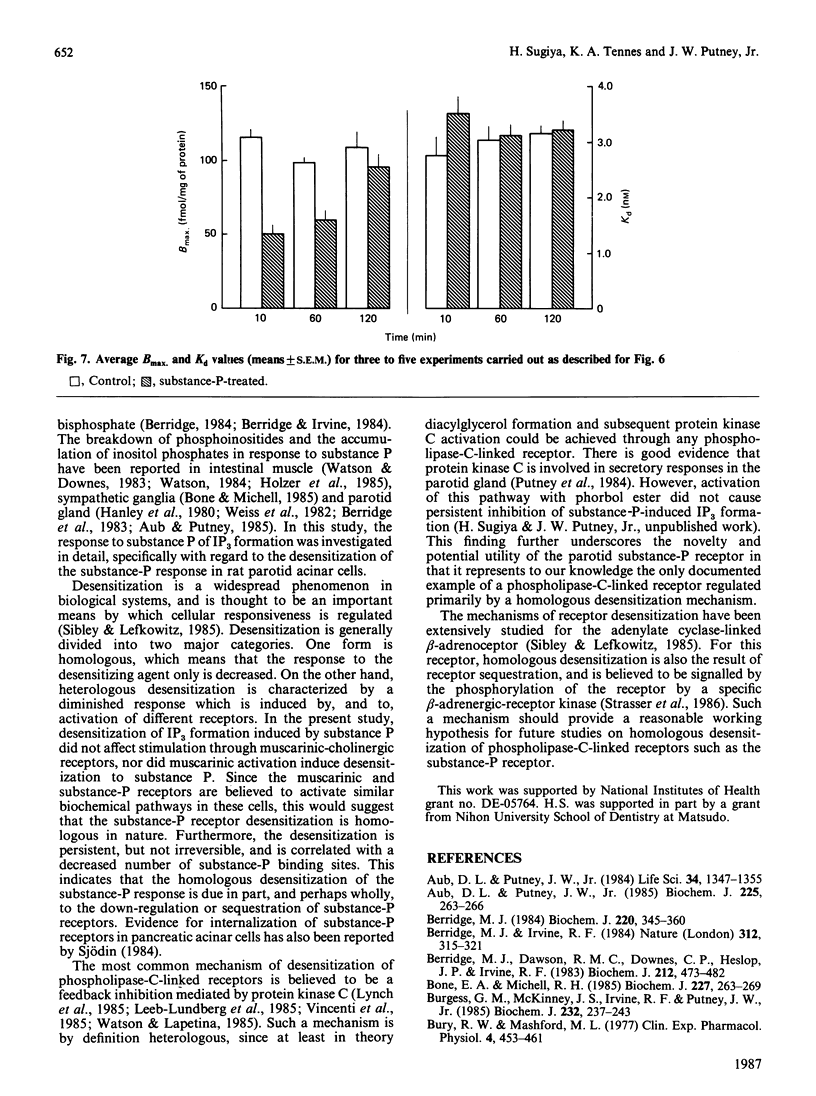
Maximal concentrations of substance P and methacholine induced a rapid increase in [3H]inositol trisphosphate ([3H]IP3) formation. After about 1 min, the [3H]IP3 in the substance-P-treated cells ceased to increase further, whereas in the methacholine-treated cells [3H]IP3 continued to increase. Addition of methacholine to the substance-P-treated cells caused a rapid increase in [3H]IP3, whereas a second addition of a 10-fold excess of substance P had no effect. Pretreatment of cells with substance P, followed by removal of the substance P by washing, resulted in a decreased response to a second application of substance P. A similar protocol involving pretreatment with methacholine had no effect on subsequent responsiveness to substance P. Analysis of [3H]substance P binding to substance-P-treated cells indicated that the number of receptors for substance P was decreased, but the affinity of the receptors for substance P was unaffected. After substance P pretreatment, a prolonged incubation (2 h) restored responsiveness of the cells to substance P, measured as [3H]IP3 formation, and restored the number of binding sites to control values. These findings indicate that, in the rat parotid gland, substance P induces a homologous desensitization of its receptor, which involves a slowly reversible down-regulation or sequestration of substance-P-binding sites.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aub D. L., Putney J. W., Jr Metabolism of inositol phosphates in parotid cells: implications for the pathway of the phosphoinositide effect and for the possible messenger role of inositol trisphosphate. Life Sci. 1984 Apr 2;34(14):1347–1355. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(84)90006-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aub D. L., Putney J. W., Jr Properties of receptor-controlled inositol trisphosphate formation in parotid acinar cells. Biochem J. 1985 Jan 1;225(1):263–266. doi: 10.1042/bj2250263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Dawson R. M., Downes C. P., Heslop J. P., Irvine R. F. Changes in the levels of inositol phosphates after agonist-dependent hydrolysis of membrane phosphoinositides. Biochem J. 1983 May 15;212(2):473–482. doi: 10.1042/bj2120473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol as second messengers. Biochem J. 1984 Jun 1;220(2):345–360. doi: 10.1042/bj2200345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):315–321. doi: 10.1038/312315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bone E. A., Michell R. H. Accumulation of inositol phosphates in sympathetic ganglia. Effects of depolarization and of amine and peptide neurotransmitters. Biochem J. 1985 Apr 1;227(1):263–269. doi: 10.1042/bj2270263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess G. M., McKinney J. S., Irvine R. F., Putney J. W., Jr Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate formation in Ca2+-mobilizing-hormone-activated cells. Biochem J. 1985 Nov 15;232(1):237–243. doi: 10.1042/bj2320237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bury R. W., Mashford M. L. A pharmacological investigation of synthetic substance P on the isolated guinea-pig ileum. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1977 Sep-Oct;4(5):453–461. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.1977.tb02409.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downes C. P., Hawkins P. T., Irvine R. F. Inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate and not phosphatidylinositol 3,4-bisphosphate is the probable precursor of inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate in agonist-stimulated parotid gland. Biochem J. 1986 Sep 1;238(2):501–506. doi: 10.1042/bj2380501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman Z. Y., Selinger Z. A transient release of potassium mediated by the action of substance P on rat parotid slices. J Physiol. 1978 May;278:461–469. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman Z. Y., Wormser U., Rubini E., Chorev M., Gilon C., Selinger Z. Desensitization of substance P-induced K+ release in rat parotid. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Nov 19;117(3):323–328. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90005-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallacher D. V. Substance P is a functional neurotransmitter in the rat parotid gland. J Physiol. 1983 Sep;342:483–498. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanley M. R., Lee C. M., Michell R. H., Jones L. M. Similar effects of substance P and related peptides on salivation and on phosphatidylinositol turnover in rat salivary glands. Mol Pharmacol. 1980 Jul;18(1):78–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Anggård E. E., Letcher A. J., Downes C. P. Metabolism of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate in rat parotid glands. Biochem J. 1985 Jul 15;229(2):505–511. doi: 10.1042/bj2290505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Letcher A. J., Heslop J. P., Berridge M. J. The inositol tris/tetrakisphosphate pathway--demonstration of Ins(1,4,5)P3 3-kinase activity in animal tissues. Nature. 1986 Apr 17;320(6063):631–634. doi: 10.1038/320631a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Letcher A. J., Lander D. J., Downes C. P. Inositol trisphosphates in carbachol-stimulated rat parotid glands. Biochem J. 1984 Oct 1;223(1):237–243. doi: 10.1042/bj2230237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konishi S., Otsuka M. The effects of substance P and other peptides on spinal neurons of the frog. Brain Res. 1974 Jan 18;65(3):397–410. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90231-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leeb-Lundberg L. M., Cotecchia S., Lomasney J. W., DeBernardis J. F., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G. Phorbol esters promote alpha 1-adrenergic receptor phosphorylation and receptor uncoupling from inositol phospholipid metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5651–5655. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leeman S. E., Hammerschlag R. Stimulation of salivary secretion by a factor extracted from hypothalamic tissue. Endocrinology. 1967 Oct;81(4):803–810. doi: 10.1210/endo-81-4-803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang T., Cascieri M. A. Specific binding of an immunoreactive and biologically active 125I-labeled N(1)acylated substance P derivative to parotid cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Oct 31;96(4):1793–1799. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91382-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang T., Cascieri M. A. Substance P receptor on parotid cell membranes. J Neurosci. 1981 Oct;1(10):1133–1141. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.01-10-01133.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang T., Cascieri M. A. Substance P stimulation of amylase release by isolated parotid cells and inhibition of substance P induction of salivation by vasoactive peptides. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1979 Sep;15(3):151–162. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(79)90035-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch C. J., Charest R., Bocckino S. B., Exton J. H., Blackmore P. F. Inhibition of hepatic alpha 1-adrenergic effects and binding by phorbol myristate acetate. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):2844–2851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata N. Substance P causes direct depolarisation of neurones of guinea pig interpeduncular nucleus in vitro. Nature. 1979 Feb 8;277(5696):480–481. doi: 10.1038/277480a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillis J. W., Limacher J. J. Substance P excitation of cerebral cortical Betz cells. Brain Res. 1974 Mar 29;69(1):158–163. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90383-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney J. W., Jr, Aub D. L., Taylor C. W., Merritt J. E. Formation and biological action of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Fed Proc. 1986 Oct;45(11):2634–2638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney J. W., Jr, McKinney J. S., Aub D. L., Leslie B. A. Phorbol ester-induced protein secretion in rat parotid gland. Relationship to the role of inositol lipid breakdown and protein kinase C activation in stimulus-secretion coupling. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 Sep;26(2):261–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney J. W., Jr Muscarinic, alpha-adrenergic and peptide receptors regulate the same calcium influx sites in the parotid gland. J Physiol. 1977 Jun;268(1):139–149. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney J. W., Jr, Van de Walle C. M., Wheeler C. S. Binding of 125I-physalaemin to rat parotid acinar cells. J Physiol. 1980 Apr;301:205–212. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney J. W., Jr, VanDeWalle C. M., Leslie B. A. Receptor control of calcium influx in parotid acinar cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1978 Nov;14(6):1046–1053. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley D. R., Lefkowitz R. J. Molecular mechanisms of receptor desensitization using the beta-adrenergic receptor-coupled adenylate cyclase system as a model. Nature. 1985 Sep 12;317(6033):124–129. doi: 10.1038/317124a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strasser R. H., Sibley D. R., Lefkowitz R. J. A novel catecholamine-activated adenosine cyclic 3',5'-phosphate independent pathway for beta-adrenergic receptor phosphorylation in wild-type and mutant S49 lymphoma cells: mechanism of homologous desensitization of adenylate cyclase. Biochemistry. 1986 Mar 25;25(6):1371–1377. doi: 10.1021/bi00354a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tennes K. A., McKinney J. S., Putney J. W., Jr Metabolism of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate in guinea-pig hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1987 Mar 15;242(3):797–802. doi: 10.1042/bj2420797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toews M. L., Waldo G. L., Harden T. K., Perkins J. P. Comparison of binding of 125I-iodopindolol to control and desensitized cells at 37 degrees and on ice. J Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphor Res. 1986;11(1):47–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tregear G. W., Niall H. D., Potts J. T., Jr, Leeman S. E., Chang M. M. Synthesis of substance P. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jul 21;232(29):87–89. doi: 10.1038/newbio232087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vicentini L. M., Di Virgilio F., Ambrosini A., Pozzan T., Meldolesi J. Tumor promoter phorbol 12-myristate, 13-acetate inhibits phosphoinositide hydrolysis and cytosolic Ca2+ rise induced by the activation of muscarinic receptors in PC12 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Feb 28;127(1):310–317. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(85)80160-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. P., Downes C. P. Substance P induced hydrolysis of inositol phospholipids in guinea-pig ileum and rat hypothalamus. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Sep 30;93(3-4):245–253. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90144-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. P., Lapetina E. G. 1,2-Diacylglycerol and phorbol ester inhibit agonist-induced formation of inositol phosphates in human platelets: possible implications for negative feedback regulation of inositol phospholipid hydrolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2623–2626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. P. The action of substance P on contraction, inositol phospholipids and adenylate cyclase in rat small intestine. Biochem Pharmacol. 1984 Dec 1;33(23):3733–3737. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(84)90033-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J., McKinney J. S., Putney J. W., Jr Receptor-mediated net breakdown of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in parotid acinar cells. Biochem J. 1982 Sep 15;206(3):555–560. doi: 10.1042/bj2060555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J., Putney J. W., Jr The relationship of phosphatidylinositol turnover to receptors and calcium-ion channels in rat parotid acinar cells. Biochem J. 1981 Feb 15;194(2):463–468. doi: 10.1042/bj1940463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Womack M. D., Hanley M. R., Jessell T. M. Functional substance P receptors on a rat pancreatic acinar cell line. J Neurosci. 1985 Dec;5(12):3370–3378. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-12-03370.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


