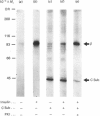
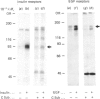
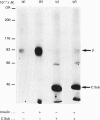
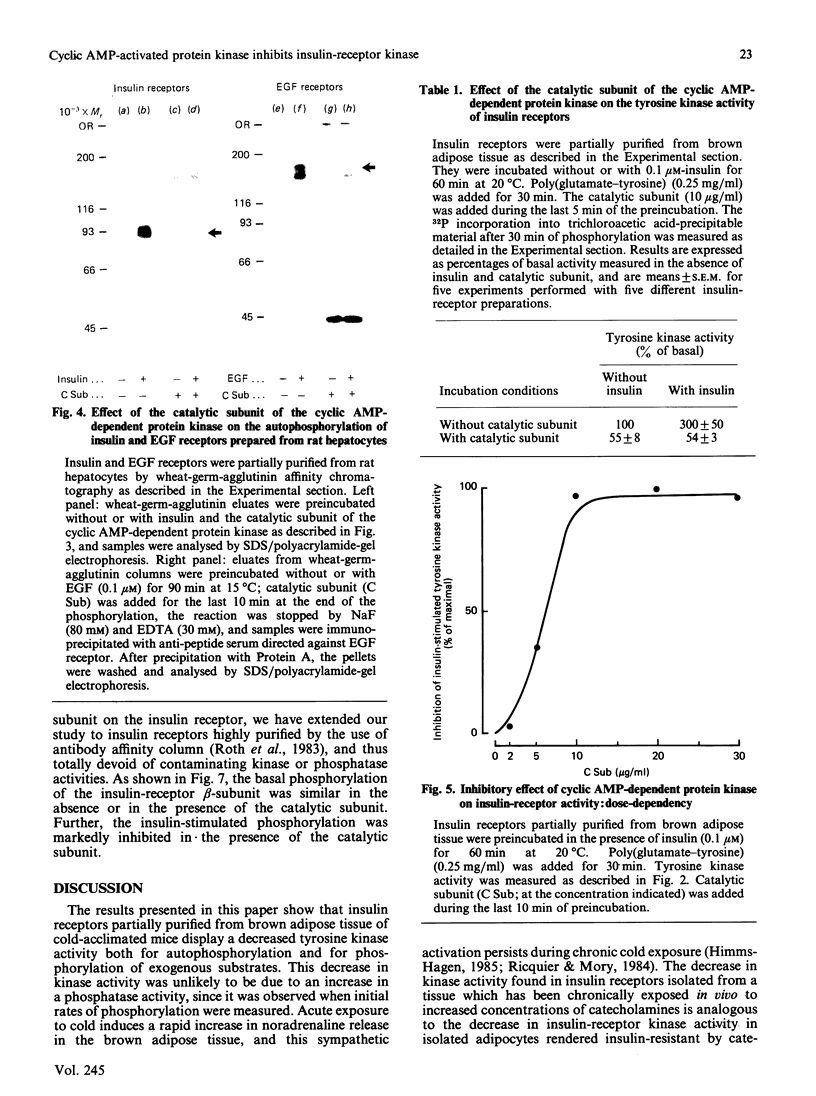
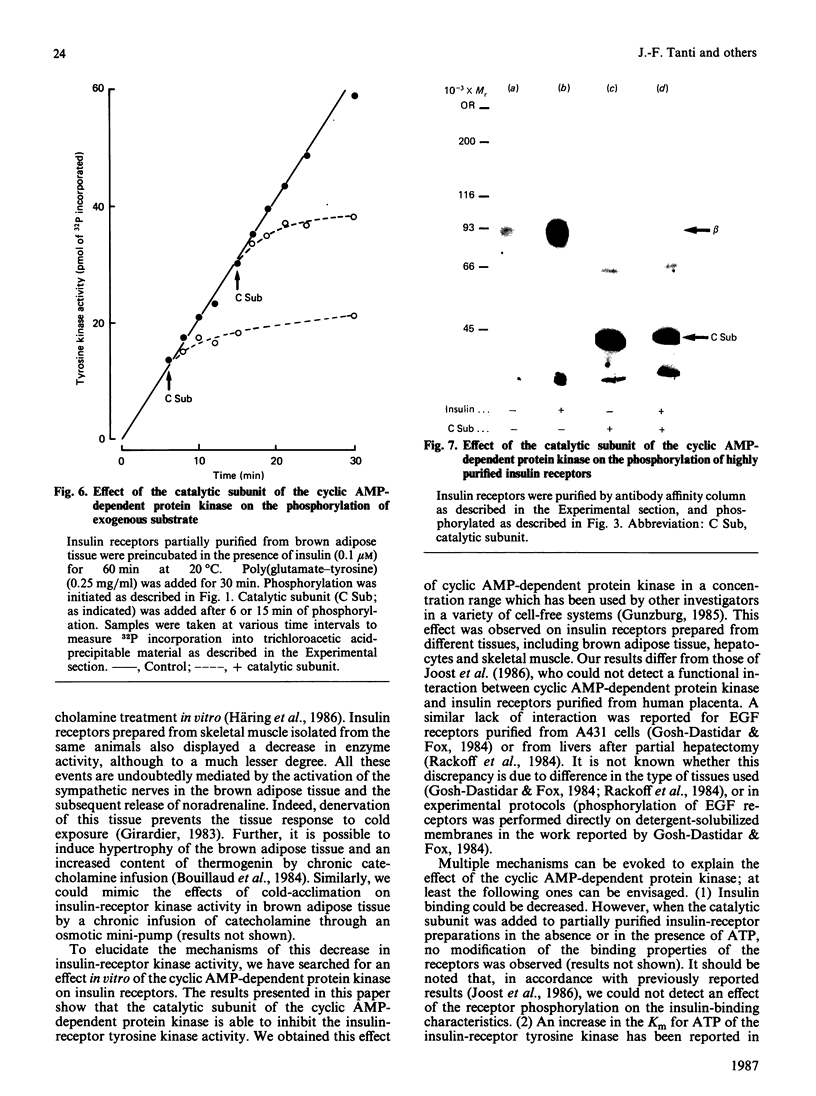
Abstract
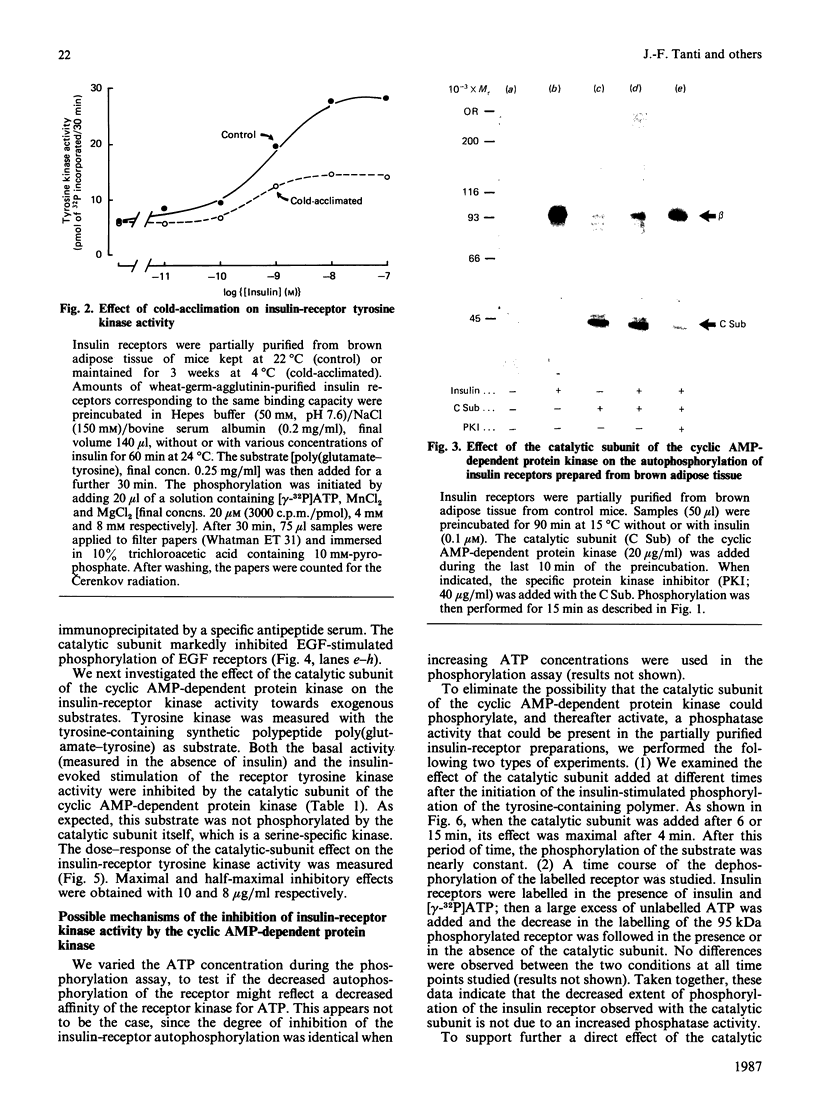
To explain the insulin resistance induced by catecholamines, we studied the tyrosine kinase activity of insulin receptors in a state characterized by elevated noradrenaline concentrations in vivo, i.e. cold-acclimation. Insulin receptors were partially purified from brown adipose tissue of 3-week- or 48 h-cold-acclimated mice. Insulin-stimulated receptor autophosphorylation and tyrosine kinase activity of insulin receptors prepared from cold-acclimated mice were decreased. Since the effect of noradrenaline is mediated by cyclic AMP and cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase, we tested the effect of the purified catalytic subunit of this enzyme on insulin receptors purified by wheat-germ agglutinin chromatography. The catalytic subunit had no effect on basal phosphorylation, but completely inhibited the insulin-stimulated receptor phosphorylation. Similarly, receptor kinase activity towards exogenous substrates such as histone or a tyrosine-containing copolymer was abolished. This inhibitory effect was observed with receptors prepared from brown adipose tissue, isolated hepatocytes and skeletal muscle. The same results were obtained on epidermal-growth-factor receptors. Further, the catalytic subunit exerted a comparable effect on the phosphorylation of highly purified insulin receptors. To explain this inhibition, we were able to rule out the following phenomena: a change in insulin binding, a change in the Km of the enzyme for ATP, activation of a phosphatase activity present in the insulin-receptor preparation, depletion of ATP, and phosphorylation of a serine residue of the receptor. These results suggest that the alteration in the insulin-receptor tyrosine kinase activity induced by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase could contribute to the insulin resistance produced by catecholamines.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bouillaud F., Ricquier D., Mory G., Thibault J. Increased level of mRNA for the uncoupling protein in brown adipose tissue of rats during thermogenesis induced by cold exposure or norepinephrine infusion. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 25;259(18):11583–11586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun S., Raymond W. E., Racker E. Synthetic tyrosine polymers as substrates and inhibitors of tyrosine-specific protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2051–2054. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiasson J. L., Shikama H., Chu D. T., Exton J. H. Inhibitory effect of epinephrine on insulin-stimulated glucose uptake by rat skeletal muscle. J Clin Invest. 1981 Sep;68(3):706–713. doi: 10.1172/JCI110306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deibert D. C., DeFronzo R. A. Epinephrine-induced insulin resistance in man. J Clin Invest. 1980 Mar;65(3):717–721. doi: 10.1172/JCI109718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demaille J. G., Peters K. A., Fischer E. H. Isolation and properties of the rabbit skeletal muscle protein inhibitor of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate dependent protein kinases. Biochemistry. 1977 Jul 12;16(14):3080–3086. doi: 10.1021/bi00633a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebina Y., Ellis L., Jarnagin K., Edery M., Graf L., Clauser E., Ou J. H., Masiarz F., Kan Y. W., Goldfine I. D. The human insulin receptor cDNA: the structural basis for hormone-activated transmembrane signalling. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):747–758. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90334-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh-Dastidar P., Fox C. F. cAMP-dependent protein kinase stimulates epidermal growth factor-dependent phosphorylation of epidermal growth factor receptors. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3864–3869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haring H. U., Kasuga M., White M. F., Crettaz M., Kahn C. R. Phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of the insulin receptor: evidence against an intrinsic phosphatase activity. Biochemistry. 1984 Jul 3;23(14):3298–3306. doi: 10.1021/bi00309a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Himms-Hagen J. Brown adipose tissue metabolism and thermogenesis. Annu Rev Nutr. 1985;5:69–94. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nu.05.070185.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häring H., Kirsch D., Obermaier B., Ermel B., Machicao F. Decreased tyrosine kinase activity of insulin receptor isolated from rat adipocytes rendered insulin-resistant by catecholamine treatment in vitro. Biochem J. 1986 Feb 15;234(1):59–66. doi: 10.1042/bj2340059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joost H. G., Steinfelder H. J., Schmitz-Salue C. Tyrosine kinase activity of insulin receptors from human placenta. Effects of autophosphorylation and cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. Biochem J. 1986 Feb 1;233(3):677–681. doi: 10.1042/bj2330677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsch D. M., Baumgarten M., Deufel T., Rinninger F., Kemmler W., Häring H. U. Catecholamine-induced insulin resistance of glucose transport in isolated rat adipocytes. Biochem J. 1983 Dec 15;216(3):737–745. doi: 10.1042/bj2160737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsch D., Kemmler W., Häring H. U. Cyclic AMP modulates insulin binding and induces post-receptor insulin resistance of glucose transport in isolated rat adipocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Aug 30;115(1):398–405. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91017-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowalski A., Gazzano H., Fehlmann M., Van Obberghen E. Dephosphorylation of the hepatic insulin receptor: absence of intrinsic phosphatase activity in purified receptors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Dec 28;117(3):885–893. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91679-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kris R. M., Lax I., Gullick W., Waterfield M. D., Ullrich A., Fridkin M., Schlessinger J. Antibodies against a synthetic peptide as a probe for the kinase activity of the avian EGF receptor and v-erbB protein. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):619–625. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90210-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Marchand-Brustel Y., Grémeaux T., Ballotti R., Van Obberghen E. Insulin receptor tyrosine kinase is defective in skeletal muscle of insulin-resistant obese mice. Nature. 1985 Jun 20;315(6021):676–679. doi: 10.1038/315676a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pessin J. E., Gitomer W., Oka Y., Oppenheimer C. L., Czech M. P. beta-Adrenergic regulation of insulin and epidermal growth factor receptors in rat adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 25;258(12):7386–7394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rackoff W. R., Rubin R. A., Earp H. S. Phosphorylation of the hepatic EGF receptor with cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1984 Feb;34(2):113–119. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(84)90062-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricquier D., Mory G. Factors affecting brown adipose tissue activity in animals and man. Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1984 Nov;13(3):501–520. doi: 10.1016/s0300-595x(84)80035-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizza R. A., Cryer P. E., Haymond M. W., Gerich J. E. Adrenergic mechanisms for the effects of epinephrine on glucose production and clearance in man. J Clin Invest. 1980 Mar;65(3):682–689. doi: 10.1172/JCI109714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth R. A., Beaudoin J. Phosphorylation of purified insulin receptor by cAMP kinase. Diabetes. 1987 Jan;36(1):123–126. doi: 10.2337/diab.36.1.123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth R. A., Mesirow M. L., Cassell D. J. Preferential degradation of the beta subunit of purified insulin receptor. Effect on insulin binding and protein kinase activities of the receptor. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14456–14460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadtmauer L., Rosen O. M. Increasing the cAMP content of IM-9 cells alters the phosphorylation state and protein kinase activity of the insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 5;261(7):3402–3407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanti J. F., Grémeaux T., Brandenburg D., Van Obberghen E., Le Marchand-Brustel Y. Brown adipose tissue in lean and obese mice. Insulin-receptor binding and tyrosine kinase activity. Diabetes. 1986 Nov;35(11):1243–1248. doi: 10.2337/diab.35.11.1243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Bell J. R., Chen E. Y., Herrera R., Petruzzelli L. M., Dull T. J., Gray A., Coussens L., Liao Y. C., Tsubokawa M. Human insulin receptor and its relationship to the tyrosine kinase family of oncogenes. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):756–761. doi: 10.1038/313756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Obberghen E., Kowalski A. Phosphorylation of the hepatic insulin receptor: stimulating effect of insulin on intact cells and in a cell-free system. FEBS Lett. 1982 Jul 5;143(2):179–182. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80094-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Obberghen E., Ksauga M., Le Cam A., Hedo J. A., Itin A., Harrison L. C. Biosynthetic labeling of insulin receptor: studies of subunits in cultured human IM-9 lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1052–1056. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Gunzburg J. Le mode d'action de l'AMP cyclique chez les procaryotes et les eucaryotes, CAP et protéine kinases AMPc dépendantes. Biochimie. 1985 Jun;67(6):563–582. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(85)80196-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]