Abstract
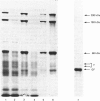
Neurofilaments freshly isolated from bovine spinal cord form a reversible gel in vitro, consisting of nearly parallel and interlinked filaments organized in bundles. This phenomenon is obtained above a critical neurofilament concentration and is highly sensitive to denaturation. No gelation occurs with neurofilaments reconstituted from urea-solubilized subunits. The velocity of the gelation kinetics, optimum at a slightly acidic pH, is inhibited by low and high ionic strength and activated by millimolar concentrations of Mg2+ and other bivalent cations. No protein other than the purified neurofilament preparation itself (80-95% neurofilament triplet) is necessary for the formation of a gel. However, purified cytoskeletal proteins from microtubules and neurofilaments influence the viscosity of the native preparation. These observations suggest a reticulation in vitro between neurofilaments, dependent upon a fragile conformation of the polymers and possibly mediated through the high-Mr neurofilament subunits (200 kDa and 150 kDa). The significance of these results is discussed with regard to the inter-neurofilament cross-bridging in situ involving the 200 kDa subunit described by Hirokawa, Glicksman & Willard [(1984) J. Cell Biol. 98, 1523-1536].
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aamodt E. J., Williams R. C., Jr Microtubule-associated proteins connect microtubules and neurofilaments in vitro. Biochemistry. 1984 Dec 4;23(25):6023–6031. doi: 10.1021/bi00320a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkowitz S. A., Katagiri J., Binder H. K., Williams R. C., Jr Separation and characterization of microtubule proteins from calf brain. Biochemistry. 1977 Dec 13;16(25):5610–5617. doi: 10.1021/bi00644a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. A., Berlin R. D. Packing volume of sedimented microtubules: regulation and potential relationship to an intracellular matrix. J Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;101(4):1492–1500. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.4.1492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carden M. J., Eagles P. A. Neurofilaments from ox spinal nerves. Isolation, disassembly, reassembly and cross-linking properties. Biochem J. 1983 Nov 1;215(2):227–237. doi: 10.1042/bj2150227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu F. C., Norton W. T. Bulk preparation of CNS cytoskeleton and the separation of individual neurofilament proteins by gel filtration: dye-binding characteristics and amino acid compositions. J Neurochem. 1982 Nov;39(5):1252–1260. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb12562.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl D., Bignami A. Neurofilament phosphorylation in development. A sign of axonal maturation? Exp Cell Res. 1986 Jan;162(1):220–230. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(86)90440-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delacourte A., Filliatreau G., Boutteau F., Biserte G., Schrevel J. Study of the 10-nm-filament fraction isolated during the standard microtubule preparation. Biochem J. 1980 Nov 1;191(2):543–546. doi: 10.1042/bj1910543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellisman M. H., Porter K. R. Microtrabecular structure of the axoplasmic matrix: visualization of cross-linking structures and their distribution. J Cell Biol. 1980 Nov;87(2 Pt 1):464–479. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.2.464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Kaufmann E., Fischer S., Plessmann U., Weber K. Neurofilament architecture combines structural principles of intermediate filaments with carboxy-terminal extensions increasing in size between triplet proteins. EMBO J. 1983;2(8):1295–1302. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01584.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin J. W., Fahnestock K. E., Price D. L., Hoffman P. N. Microtubule-neurofilament segregation produced by beta, beta'-iminodipropionitrile: evidence for the association of fast axonal transport with microtubules. J Neurosci. 1983 Mar;3(3):557–566. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.03-03-00557.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heimann R., Shelanski M. L., Liem R. K. Microtubule-associated proteins bind specifically to the 70-kDa neurofilament protein. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 5;260(22):12160–12166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirokawa N. Cross-linker system between neurofilaments, microtubules, and membranous organelles in frog axons revealed by the quick-freeze, deep-etching method. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jul;94(1):129–142. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.1.129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirokawa N., Glicksman M. A., Willard M. B. Organization of mammalian neurofilament polypeptides within the neuronal cytoskeleton. J Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;98(4):1523–1536. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.4.1523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman P. N., Griffin J. W., Gold B. G., Price D. L. Slowing of neurofilament transport and the radial growth of developing nerve fibers. J Neurosci. 1985 Nov;5(11):2920–2929. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-11-02920.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman P. N., Griffin J. W., Price D. L. Control of axonal caliber by neurofilament transport. J Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;99(2):705–714. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.2.705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman P. N., Thompson G. W., Griffin J. W., Price D. L. Changes in neurofilament transport coincide temporally with alterations in the caliber of axons in regenerating motor fibers. J Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;101(4):1332–1340. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.4.1332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julien J. P., Mushynski W. E. The distribution of phosphorylation sites among identified proteolytic fragments of mammalian neurofilaments. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):4019–4025. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasek R. J., Oblinger M. M., Drake P. F. Molecular biology of neuronal geometry: expression of neurofilament genes influences axonal diameter. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;48(Pt 2):731–744. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.048.01.076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leterrier J. F., Liem R. K., Shelanski M. L. Interactions between neurofilaments and microtubule-associated proteins: a possible mechanism for intraorganellar bridging. J Cell Biol. 1982 Dec;95(3):982–986. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.3.982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leterrier J. F., Wong J., Liem R. K., Shelanski M. L. Promotion of microtubule assembly by neurofilament-associated microtubule-associated proteins. J Neurochem. 1984 Nov;43(5):1385–1391. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb05398.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liem R. K., Hutchison S. B. Purification of individual components of the neurofilament triplet: filament assembly from the 70 000-dalton subunit. Biochemistry. 1982 Jun 22;21(13):3221–3226. doi: 10.1021/bi00256a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luca F. C., Bloom G. S., Vallee R. B. A monoclonal antibody that cross-reacts with phosphorylated epitopes on two microtubule-associated proteins and two neurofilament polypeptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):1006–1010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.1006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLean-Fletcher S. D., Pollard T. D. Viscometric analysis of the gelation of Acanthamoeba extracts and purification of two gelation factors. J Cell Biol. 1980 May;85(2):414–428. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.2.414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minami Y., Murofushi H., Sakai H. Interaction of tubulin with neurofilaments: formation of networks by neurofilament-dependent tubulin polymerization. J Biochem. 1982 Sep;92(3):889–898. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minami Y., Sakai H. Effects of microtubule-associated proteins on network formation by neurofilament-induced polymerization of tubulin. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jan 20;195(1-2):68–72. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80132-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minami Y., Sakai H. Network formation by neurofilament-induced polymerization of tubulin: 200K subunit of neurofilament triplet promotes nucleation of tubulin polymerization and enhances microtubule assembly. J Biochem. 1983 Dec;94(6):2023–2033. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris J. R., Lasek R. J. Stable polymers of the axonal cytoskeleton: the axoplasmic ghost. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jan;92(1):192–198. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.1.192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nixon R. A., Logvinenko K. B. Multiple fates of newly synthesized neurofilament proteins: evidence for a stationary neurofilament network distributed nonuniformly along axons of retinal ganglion cell neurons. J Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;102(2):647–659. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.2.647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papasozomenos S. C., Yoon M., Crane R., Autilio-Gambetti L., Gambetti P. Redistribution of proteins of fast axonal transport following administration of beta,beta'-iminodipropionitrile: a quantitative autoradiographic study. J Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;95(2 Pt 1):672–675. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.2.672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnapp B. J., Reese T. S. Cytoplasmic structure in rapid-frozen axons. J Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;94(3):667–669. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.3.667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp G. A., Shaw G., Weber K. Immunoelectronmicroscopical localization of the three neurofilament triplet proteins along neurofilaments of cultured dorsal root ganglion neurones. Exp Cell Res. 1982 Feb;137(2):403–413. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90042-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelanski M. L., Gaskin F., Cantor C. R. Microtubule assembly in the absence of added nucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Mar;70(3):765–768. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.3.765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallee R. B., Borisy G. G. Removal of the projections from cytoplasmic microtubules in vitro by digestion with trypsin. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 10;252(1):377–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weingarten M. D., Lockwood A. H., Hwo S. Y., Kirschner M. W. A protein factor essential for microtubule assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1858–1862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willard M., Simon C. Antibody decoration of neurofilaments. J Cell Biol. 1981 May;89(2):198–205. doi: 10.1083/jcb.89.2.198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willard M., Simon C. Modulations of neurofilament axonal transport during the development of rabbit retinal ganglion cells. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):551–559. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90189-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]