Abstract
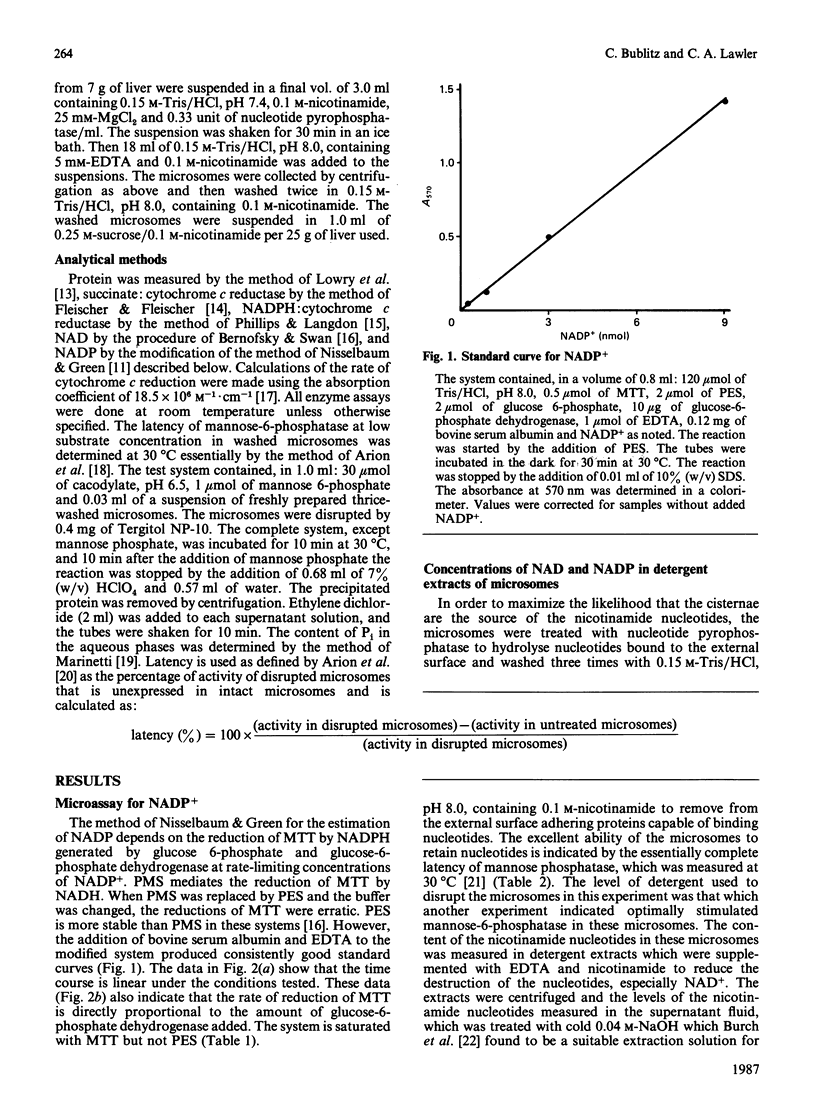
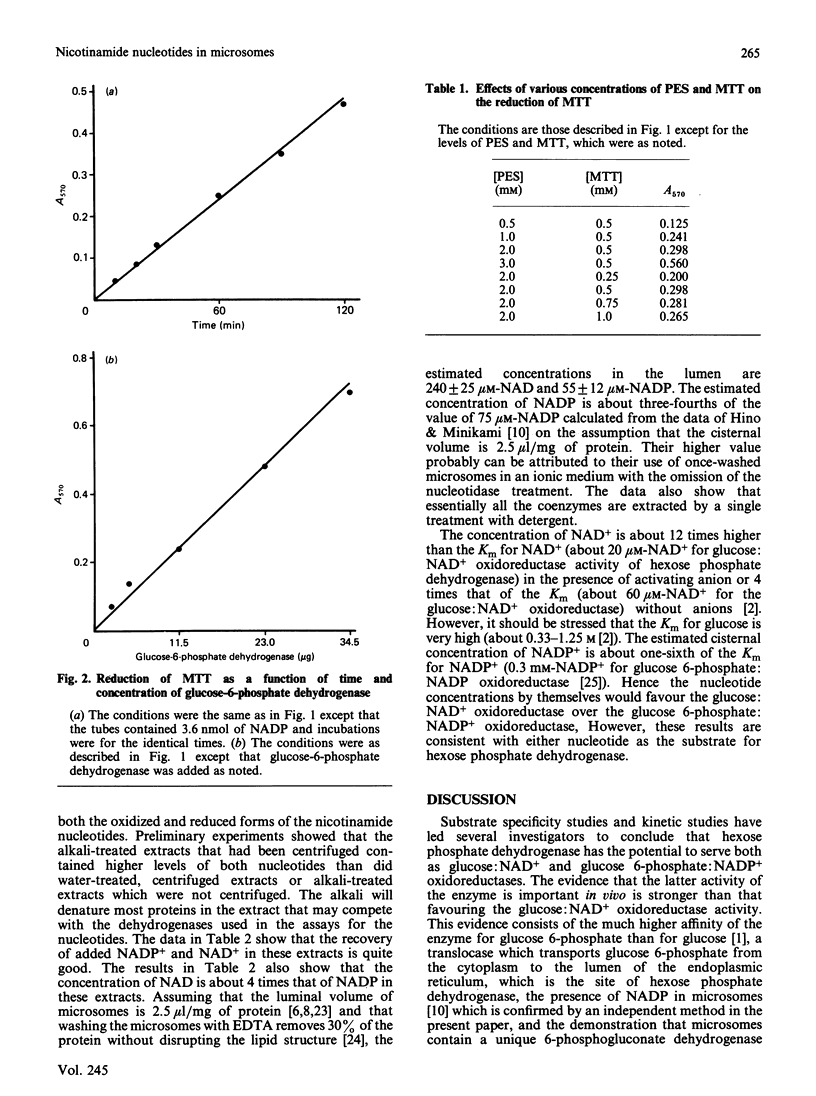
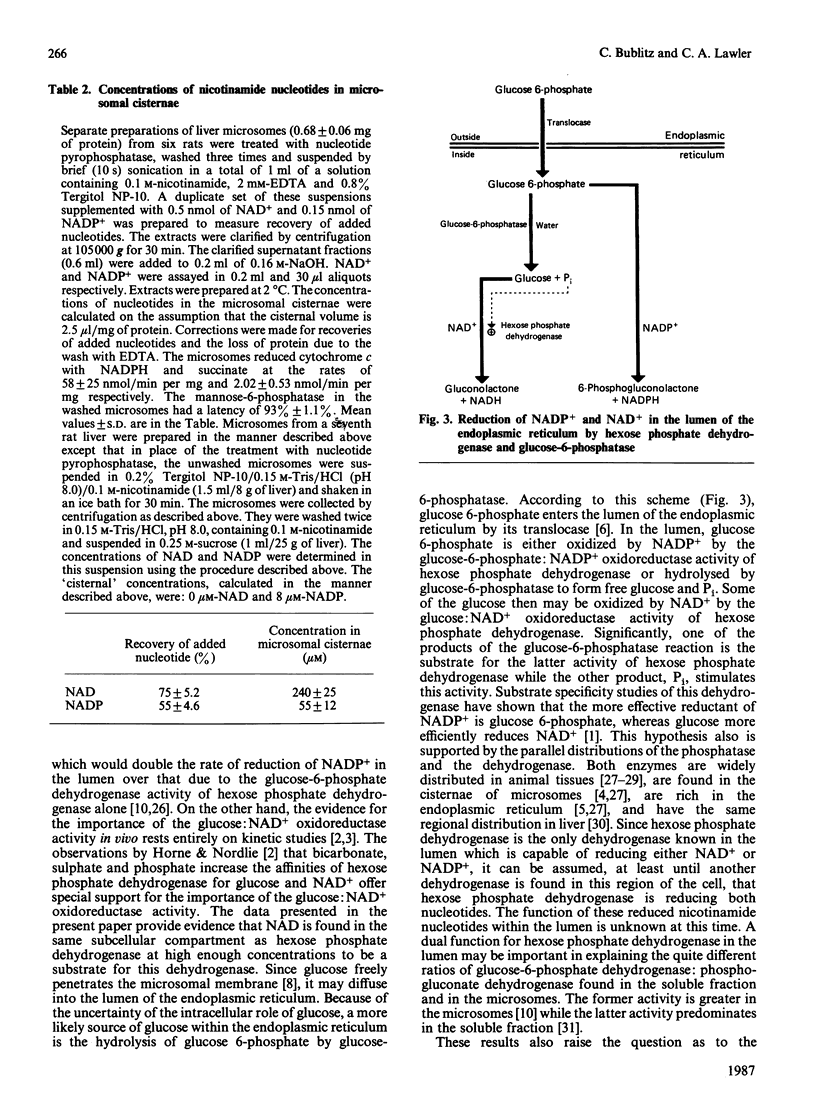
The concentrations of NAD and NADP have been determined in detergent extracts of washed rat liver microsomes. Precautions were taken during the preparation of the microsomes to remove nicotinamide nucleotides from their external surface both by hydrolysis by nucleotide pyrophosphatase (EC 3.6.1.9) and by washing them three times in 0.15 M-Tris/HCl, pH 8.0, to remove soluble proteins which bind these nucleotides. The mannose phosphatase was essentially completely latent, indicating that the microsomes were intact. Assuming these nucleotides are in the cisternae of the microsomes, the concentrations in the cisternae are 240 +/- 25 microM-NAD and 55 +/- 12 microM-NADP. These levels of nucleotides are compatible with both the glucose:NAD+ and the glucose 6-phosphate:NADP+ oxidoreductase activities of hexose phosphate dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.47). Since the organ and subcellular distributions of this dehydrogenase and glucose-6-phosphatase are similar, and Pi stimulates the glucose:NAD+ oxidoreductase activity, it is proposed that the combined action of these two enzymes leads to the reduction of both coenzymes in the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum. A modification of the colorimetric method of Nisselbaum & Green [(1969) Anal. Biochem. 27, 212-217] for the determination of NADP+ is described. Colour formation is linear with the concentration of NADP+ and is sensitive to less than 0.3 nmol of NADP+.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arion W. J., Lange A. J., Walls H. E., Ballas L. M. Evidence for the participation of independent translocation for phosphate and glucose 6-phosphate in the microsomal glucose-6-phosphatase system. Interactions of the system with orthophosphate, inorganic pyrophosphate, and carbamyl phosphate. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10396–10406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arion W. J., Wallin B. K., Lange A. J., Ballas L. M. On the involvement of a glucose 6-phosphate transport system in the function of microsomal glucose 6-phosphatase. Mol Cell Biochem. 1975 Feb 28;6(2):75–83. doi: 10.1007/BF01732001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arion W. J., Walls H. E. The importance of membrane integrity in kinetic characterizations of the microsomal glucose-6-phosphatase system. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11217–11220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballas L. M., Arion W. J. Measurement of glucose 6-phosphate penetration into liver microsomes. Confirmation of substrate transport in the glucose-6-phosphatase system. J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 10;252(23):8512–8518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernofsky C., Swan M. An improved cycling assay for nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide. Anal Biochem. 1973 Jun;53(2):452–458. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90094-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler E., Morrison M. Localization and characteristics of hexose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase (glucose dehydrogenase). J Biol Chem. 1967 Nov 25;242(22):5289–5293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bublitz C. Physical separation of cytoplasmic and microsomal 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenases from rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Feb 12;98(3):588–594. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91155-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burch H. B., Bradley M. E., Lowry O. H. The measurement of triphosphopyridine nucleotide and reduced triphosphopyridine nucleotide and the role of hemoglobin in producing erroneous triphosphopyridine nucleotide values. J Biol Chem. 1967 Oct 10;242(19):4546–4554. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell D. P., Carper W. R., Thompson R. E. Bovine liver glucose dehydrogenase: isolation and characterization. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1982 Apr 15;215(1):289–301. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(82)90307-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallner G. Isolation of rough and smooth microsomes--general. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:191–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLOCK G. E., MCLEAN P. A preliminary investigation of the hormonal control of the hexose monophosphate oxidative pathway. Biochem J. 1955 Nov;61(3):390–397. doi: 10.1042/bj0610390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLOCK G. E., MCLEAN P. The intracellular distribution of pyridine nucleotides in rat liver. Exp Cell Res. 1956 Aug;11(1):234–236. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(56)90214-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hino Y., Minakami S. Hexose-6-phosphate and 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenases of rat liver microsomes. Involvement in NADPH and carbon dioxide generation in the luminal space of microsomal vesicles. J Biochem. 1982 Aug;92(2):547–557. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hino Y., Minakami S. Hexose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase of rat liver microsomes. Isolation by affinity chromatography and properties. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2563–2568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horne R. N., Nordlie R. C. Activation by bicarbonate orthophosphate, and sulfate of rat liver microsomal glucose dehydrogenase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jul 21;242(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(71)90082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandula B., Srivastava S. K., Beutler E. Hexose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase: distribution in rat tissues and effect of diet, age and steroids. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Nov;141(1):155–161. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90118-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manns E. The histochemical localization of glucose dehydrogenase activity in sheep liver. Histochem J. 1972 Jan;4(1):25–33. doi: 10.1007/BF01005266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner G., Allen R. Evidence for two types of rat liver microsomes with differing permeability to glucose and other small molecules. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 25;256(12):6413–6422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson R., Peterson E., Dallner G. Permeability of microsomal membranes isolated from rat liver. J Cell Biol. 1973 Mar;56(3):762–776. doi: 10.1083/jcb.56.3.762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nisselbaum J. S., Green S. A simple ultramicro method for determination of pyridine nucleotides in tissues. Anal Biochem. 1969 Feb;27(2):212–217. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90025-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordlie R. C. Metabolic regulation by multifunctional glucose-6-phosphatase. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1974;8(0):33–117. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152808-9.50009-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PALADE G. E., SIEKEVITZ P. Liver microsomes; an integrated morphological and biochemical study. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1956 Mar 25;2(2):171–200. doi: 10.1083/jcb.2.2.171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PHILLIPS A. H., LANGDON R. G. Hepatic triphosphopyridine nucleotide-cytochrome c reductase: isolation, characterization, and kinetic studies. J Biol Chem. 1962 Aug;237:2652–2660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw C. R. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase: homologous molecules in deer mouse and man. Science. 1966 Aug 26;153(3739):1013–1015. doi: 10.1126/science.153.3739.1013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi T., Hori S. H. Intramembraneous localization of rat liver microsomal hexose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase and membrane permeability to its substrates. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jun 9;524(2):262–276. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(78)90163-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanahashi K., Hori S. H. Immunohistochemical localization of hexose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase in various organs of the rat. J Histochem Cytochem. 1980 Nov;28(11):1175–1182. doi: 10.1177/28.11.7430614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


