Abstract
The susceptibility of a number of human neutrophil granule enzymes to oxidative inactivation was investigated. Addition of H2O2 to the cell-free medium from stimulated neutrophils resulted in inactivation of all enzymes tested. This was inhibited by azide and methionine, indicating that inactivation was due to myeloperoxidase-derived oxidants. Lysozyme was more than 50% inactivated by one addition of 100 nmol of H2O2/ml, whereas myeloperoxidase, beta-glucuronidase, gelatinase and collagenase were almost completely inactivated by three additions. Cathepsin G was slightly less susceptible, whereas elastase was extremely resistant to oxidative attack. Myeloperoxidase-dependent enzyme inactivation may be a means whereby the neutrophil can terminate the activity of its granule enzymes and control the release of degradative enzymes into the tissues.
Full text
PDF

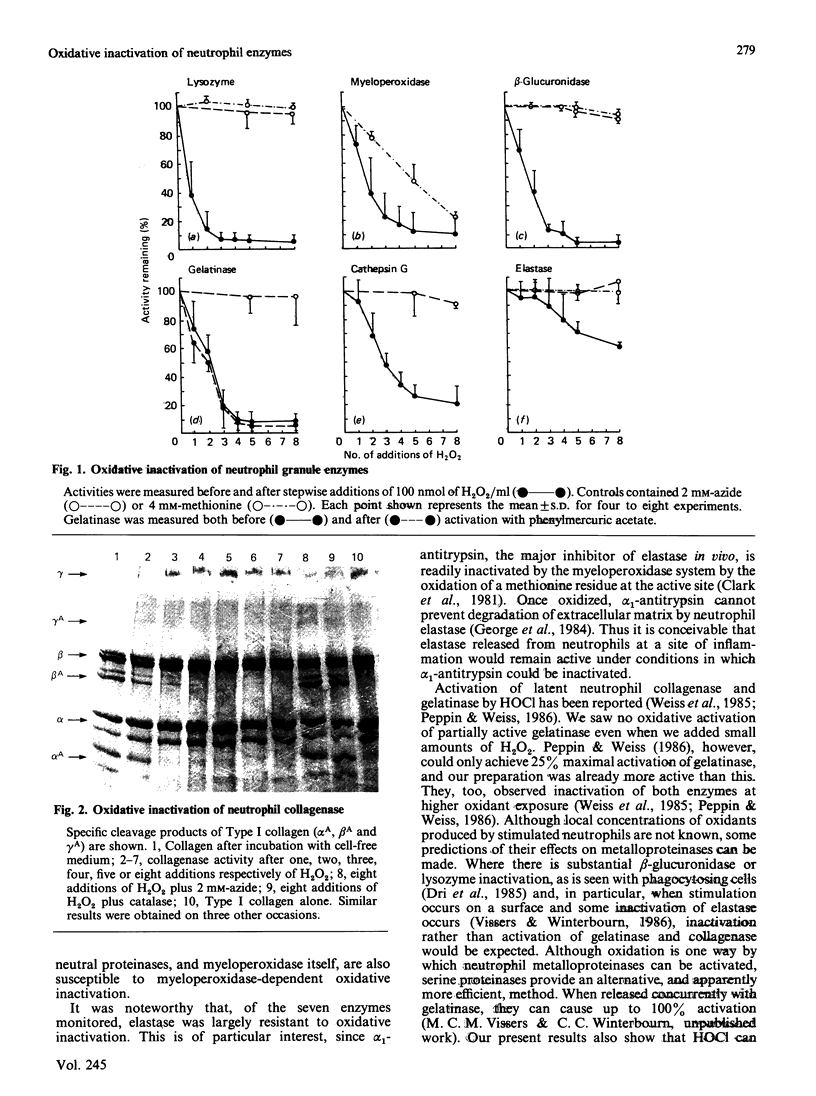

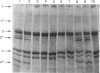
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albrich J. M., Hurst J. K. Oxidative inactivation of Escherichia coli by hypochlorous acid. Rates and differentiation of respiratory from other reaction sites. FEBS Lett. 1982 Jul 19;144(1):157–161. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80591-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baggiolini M., Hirsch J. G., De Duve C. Resolution of granules from rabbit heterophil leukocytes into distinct populations by zonal sedimentation. J Cell Biol. 1969 Feb;40(2):529–541. doi: 10.1083/jcb.40.2.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A., Borregaard N. Neutrophils autoinactivate secretory products by myeloperoxidase-catalyzed oxidation. Blood. 1985 Feb;65(2):375–381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A., Stone P. J., El Hag A., Calore J. D., Franzblau C. Myeloperoxidase-catalyzed inactivation of alpha 1-protease inhibitor by human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 10;256(7):3348–3353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dri P., Cramer R., Menegazzi R., Patriarca P. Increased degranulation of human myeloperoxidase-deficient polymorphonuclear leucocytes. Br J Haematol. 1985 Jan;59(1):115–125. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1985.tb02971.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George P. M., Vissers M. C., Travis J., Winterbourn C. C., Carrell R. W. A genetically engineered mutant of alpha 1-antitrypsin protects connective tissue from neutrophil damage and may be useful in lung disease. Lancet. 1984 Dec 22;2(8417-8418):1426–1428. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91623-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibbs M. S., Hasty K. A., Seyer J. M., Kang A. H., Mainardi C. L. Biochemical and immunological characterization of the secreted forms of human neutrophil gelatinase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2493–2500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jandl R. C., André-Schwartz J., Borges-DuBois L., Kipnes R. S., McMurrich B. J., Babior B. M. Termination of the respiratory burst in human neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1978 May;61(5):1176–1185. doi: 10.1172/JCI109033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebanoff S. J. Oxygen metabolism and the toxic properties of phagocytes. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Sep;93(3):480–489. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-93-3-480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peppin G. J., Weiss S. J. Activation of the endogenous metalloproteinase, gelatinase, by triggered human neutrophils. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4322–4326. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal A. W. Variations on the theme of chronic granulomatous disease. Lancet. 1985 Jun 15;1(8442):1378–1383. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91796-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas E. L., Jefferson M. M., Grisham M. B. Myeloperoxidase-catalyzed incorporation of amines into proteins: role of hypochlorous acid and dichloramines. Biochemistry. 1982 Nov 23;21(24):6299–6308. doi: 10.1021/bi00267a040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas E. L. Myeloperoxidase, hydrogen peroxide, chloride antimicrobial system: nitrogen-chlorine derivatives of bacterial components in bactericidal action against Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1979 Feb;23(2):522–531. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.2.522-531.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vissers M. C., Winterbourn C. C. The effect of oxidants on neutrophil-mediated degradation of glomerular basement membrane collagen. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Dec 19;889(3):277–286. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(86)90190-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voetman A. A., Weening R. S., Hamers M. N., Meerhof L. J., Bot A. A., Roos D. Phagocytosing human neutrophils inactivate their own granular enzymes. J Clin Invest. 1981 May;67(5):1541–1549. doi: 10.1172/JCI110185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J., Peppin G., Ortiz X., Ragsdale C., Test S. T. Oxidative autoactivation of latent collagenase by human neutrophils. Science. 1985 Feb 15;227(4688):747–749. doi: 10.1126/science.2982211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winterbourn C. C. Comparative reactivities of various biological compounds with myeloperoxidase-hydrogen peroxide-chloride, and similarity of the oxidant to hypochlorite. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jun 18;840(2):204–210. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(85)90120-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winterbourn C. C., Garcia R. C., Segal A. W. Production of the superoxide adduct of myeloperoxidase (compound III) by stimulated human neutrophils and its reactivity with hydrogen peroxide and chloride. Biochem J. 1985 Jun 15;228(3):583–592. doi: 10.1042/bj2280583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]