Abstract
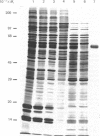
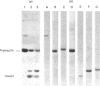
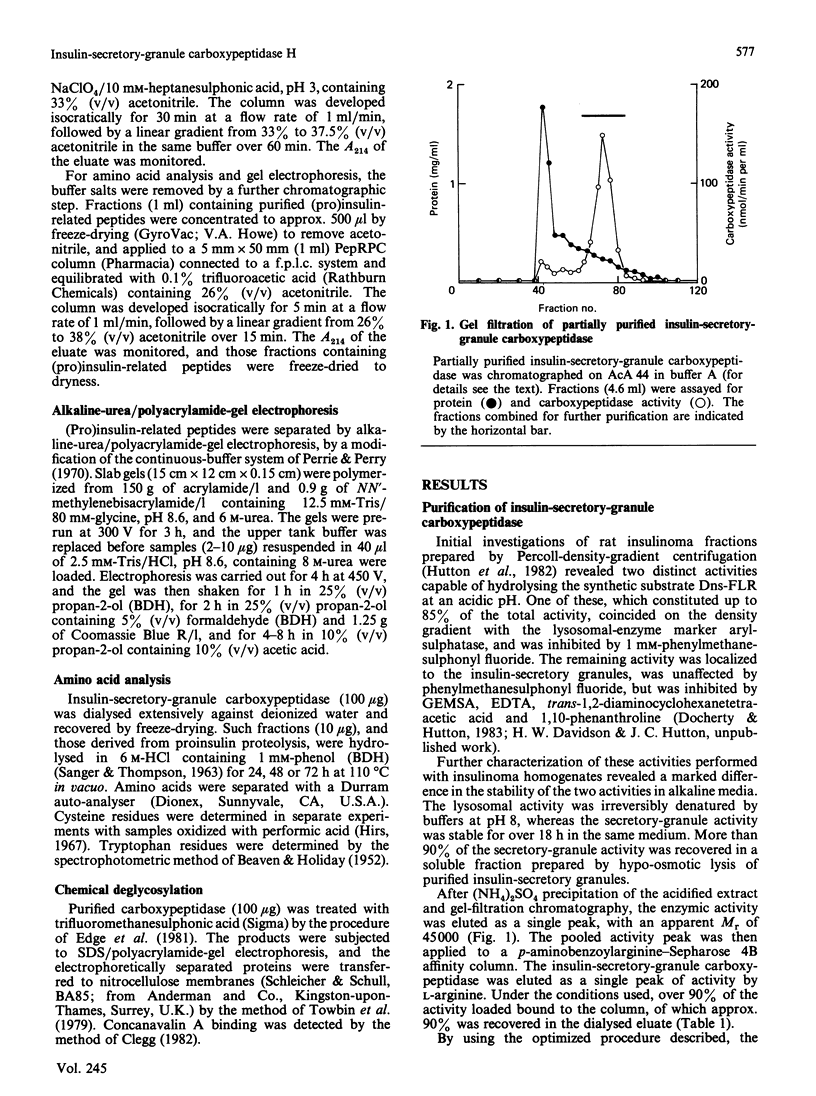
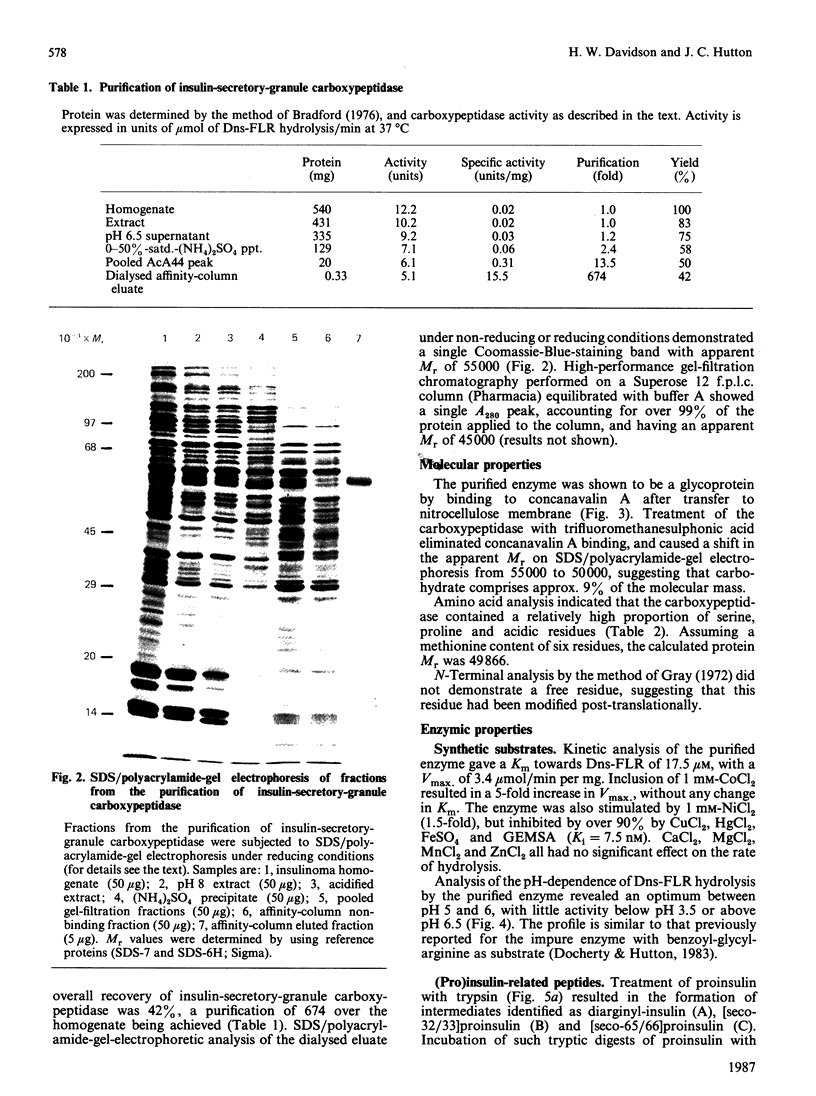
A carboxypeptidase B-like enzyme was detected in the soluble fraction of purified insulin secretory granules, and implicated in insulin biosynthesis. To investigate the role of this activity further, we purified the enzyme from rat insulinoma tissue by gel-filtration chromatography and affinity elution from p-aminobenzoyl-arginine. A yield of 42%, with a purification factor of 674 over the homogenate, was achieved. Analysis of the purified carboxypeptidase by SDS/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis under either reducing or non-reducing conditions showed it to be a monomeric protein of apparent Mr 55,000. The preparation was also homogeneous by high-performance gel-filtration chromatography. The enzyme bound to concanavalin A, showing it to be a glycoprotein. Amino acid analysis or chemical deglycosylation and SDS/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis indicated a protein Mr of 50,000, suggesting a carbohydrate content of approx. 9% by weight. The purified enzyme was able to remove basic amino acids from the C-terminus of proinsulin tryptic peptides to generate insulin, but did not further degrade the mature hormone. It was inhibited by EDTA, 1,10-phenanthroline and guanidinoethylmercaptosuccinic acid, and stimulated 5-fold by CoCl2. The pH optimum of the conversion of diarginyl-insulin into insulin was in the range 5-6, with little activity above pH 6.5. Activity was also expressed towards a dansylated tripeptide substrate (dansyl-phenylalanyl-leucyl-arginine; Km = 17.5 microM), and had a pH optimum of 5.5. These properties are indistinguishable from those of the activity located in secretory granules, and are compatible with the intragranular environment. The insulin-secretory-granule carboxypeptidase shared several properties of carboxypeptidase H from bovine adrenal medulla and pituitary. We propose that the carboxypeptidase that we purified is the pancreatic isoenzyme of carboxypeptidase H (crino carboxypeptidase B; EC 3.4.17.10), and is involved in the biosynthesis of insulin in the pancreatic beta-cell.
Full text
PDF

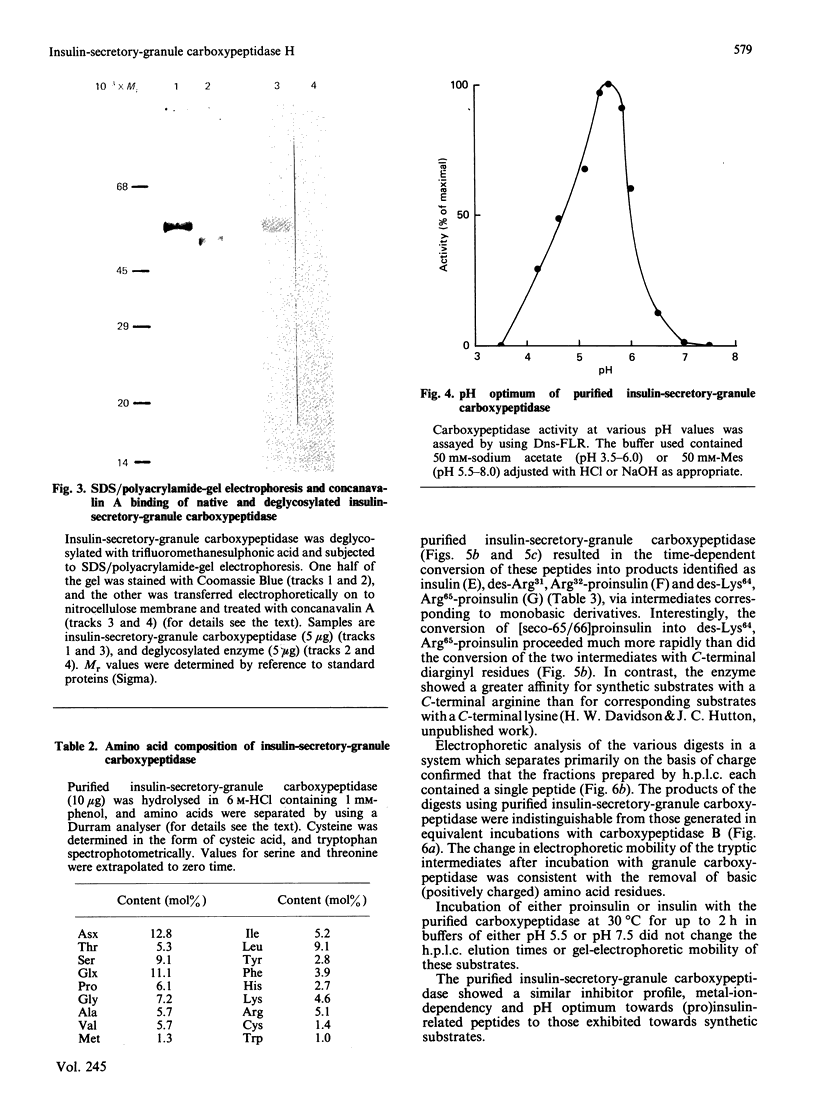
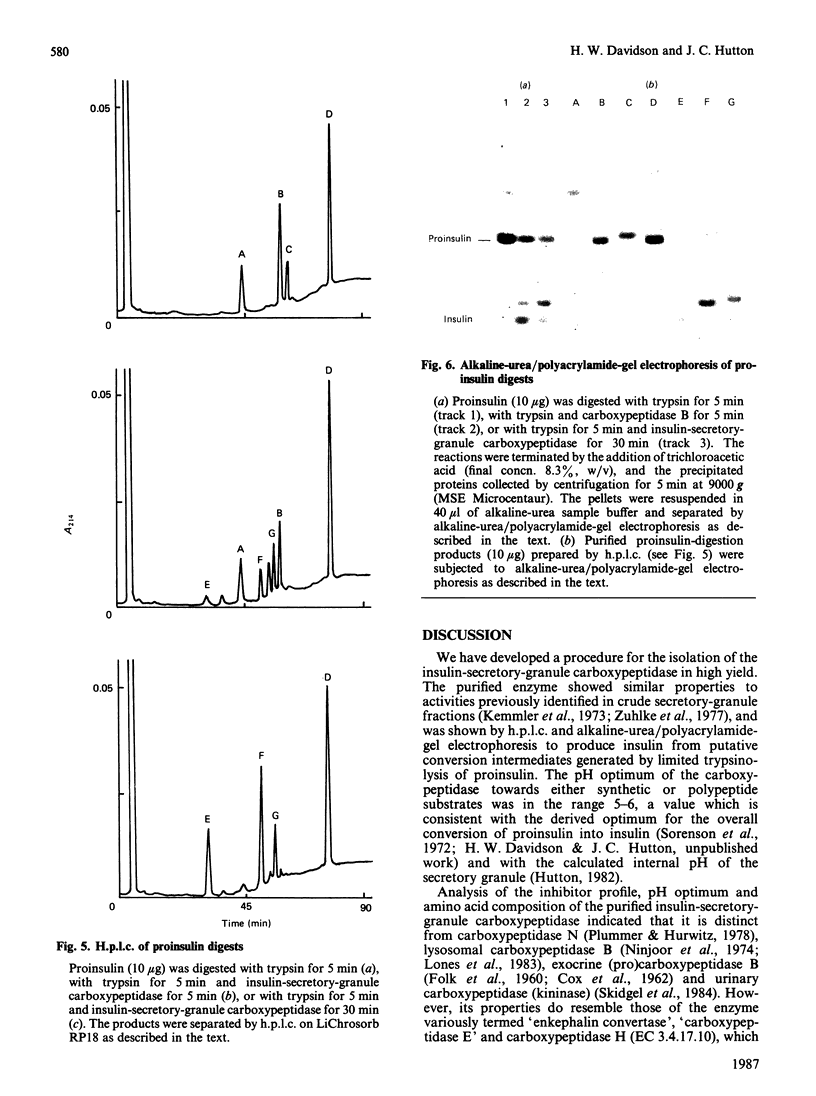


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BEAVEN G. H., HOLIDAY E. R. Ultraviolet absorption spectra of proteins and amino acids. Adv Protein Chem. 1952;7:319–386. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60022-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COX D. J., WINTERSBERGER E., NEURATH H. Bovine pancreatic procarboxypeptidase B. II. Mechanism of activation. Biochemistry. 1962 Nov;1:1078–1082. doi: 10.1021/bi00912a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chick W. L., Warren S., Chute R. N., Like A. A., Lauris V., Kitchen K. C. A transplantable insulinoma in the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):628–632. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg J. C. Glycoprotein detection in nitrocellulose transfers of electrophoretically separated protein mixtures using concanavalin A and peroxidase: application to arenavirus and flavivirus proteins. Anal Biochem. 1982 Dec;127(2):389–394. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90192-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Docherty K., Hutton J. C. Carboxypeptidase activity in the insulin secretory granule. FEBS Lett. 1983 Oct 3;162(1):137–141. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)81065-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Docherty K., Steiner D. F. Post-translational proteolysis in polypeptide hormone biosynthesis. Annu Rev Physiol. 1982;44:625–638. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.44.030182.003205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edge A. S., Faltynek C. R., Hof L., Reichert L. E., Jr, Weber P. Deglycosylation of glycoproteins by trifluoromethanesulfonic acid. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):131–137. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90168-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLK J. E., PIEZ K. A., CARROLL W. R., GLADNER J. A. Carboxy-peptidase B. 4. Purification and characterization of the porcine enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1960 Aug;235:2272–2277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fricker L. D., Evans C. J., Esch F. S., Herbert E. Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA for bovine carboxypeptidase E. Nature. 1986 Oct 2;323(6087):461–464. doi: 10.1038/323461a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fricker L. D., Snyder S. H. Purification and characterization of enkephalin convertase, an enkephalin-synthesizing carboxypeptidase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 25;258(18):10950–10955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold G., Gishizky M. L., Chick W. L., Grodsky G. M. Contrasting patterns of insulin biosynthesis, compartmental storage, and secretion. Rat tumor versus islet cells. Diabetes. 1984 Jun;33(6):556–561. doi: 10.2337/diab.33.6.556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hook V. Y., Loh Y. P. Carboxypeptidase B-like converting enzyme activity in secretory granules of rat pituitary. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2776–2780. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutton J. C., Penn E. J., Jackson P., Hales C. N. Isolation and characterization of calmodulin from an insulin-secreting tumour. Biochem J. 1981 Mar 1;193(3):875–885. doi: 10.1042/bj1930875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutton J. C., Penn E. J., Peshavaria M. Isolation and characterisation of insulin secretory granules from a rat islet cell tumour. Diabetologia. 1982 Oct;23(4):365–373. doi: 10.1007/BF00253746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutton J. C. The internal pH and membrane potential of the insulin-secretory granule. Biochem J. 1982 Apr 15;204(1):171–178. doi: 10.1042/bj2040171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemmler W., Steiner D. F., Borg J. Studies on the conversion of proinsulin to insulin. 3. Studies in vitro with a crude secretion granule fraction isolated from rat islets of Langerhans. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jul 10;248(13):4544–4551. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loh Y. P., Brownstein M. J., Gainer H. Proteolysis in neuropeptide processing and other neural functions. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1984;7:189–222. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.07.030184.001201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lones M., Chatterjee R., Singh H., Kalnitsky G. Lysosomal carboxypeptidase B from rabbit lung purification and characterization. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Feb 15;221(1):64–78. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90122-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ninjoor V., Taylor S. L., Tappel A. L. Purification and characterization of rat liver lysosomal cathepsin B2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Nov 25;370(1):308–321. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(74)90055-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolan C., Margoliash E., Peterson J. D., Steiner D. F. The structure of bovine proinsulin. J Biol Chem. 1971 May 10;246(9):2780–2795. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrie W. T., Perry S. V. An electrophoretic study of the low-molecular-weight components of myosin. Biochem J. 1970 Aug;119(1):31–38. doi: 10.1042/bj1190031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plummer T. H., Jr, Hurwitz M. Y. Human plasma carboxypeptidase N. Isolation and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 10;253(11):3907–3912. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANGER F., THOMPSON E. O. Halogenation of tyrosine during acid hydrolysis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 May 14;71:468–471. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91108-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skidgel R. A., Davis R. M., Erdös E. G. Purification of a human urinary carboxypeptidase (kininase) distinct from carboxypeptidases A, B, or N. Anal Biochem. 1984 Aug 1;140(2):520–531. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90203-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorenson R. L., Shank R. D., Lindall A. W. Effect of pH on conversion of proinsulin to insulin by a subcellular fraction of rat islets. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Feb;139(2):652–655. doi: 10.3181/00379727-139-36207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Supattapone S., Fricker L. D., Snyder S. H. Purification and characterization of a membrane-bound enkephalin-forming carboxypeptidase, "enkephalin convertase". J Neurochem. 1984 Apr;42(4):1017–1023. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb12705.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zühlke H., Kohnert K. D., Jahr H., Schmidt S., Kirschke H., Steiner D. F. Proteolytic and transhydrogenolytic activities in isolated pancreatic islets of rats. Acta Biol Med Ger. 1977;36(11-12):1695–1703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]