Abstract
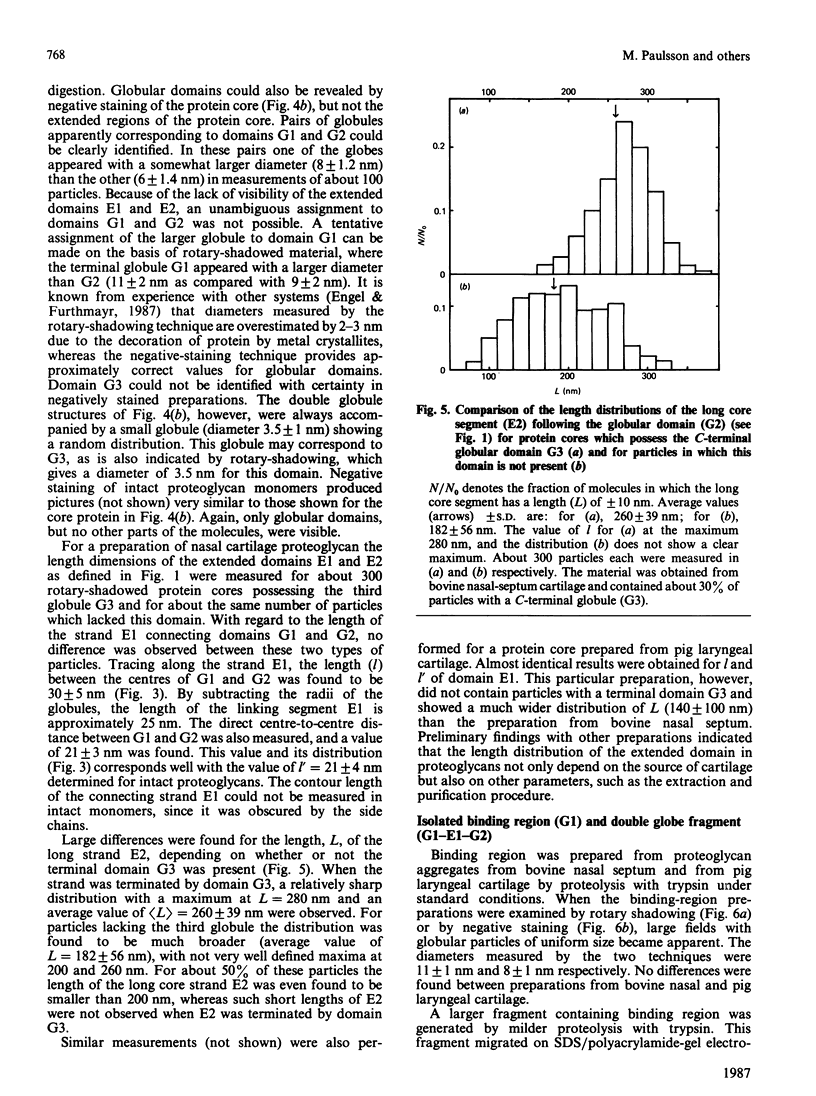
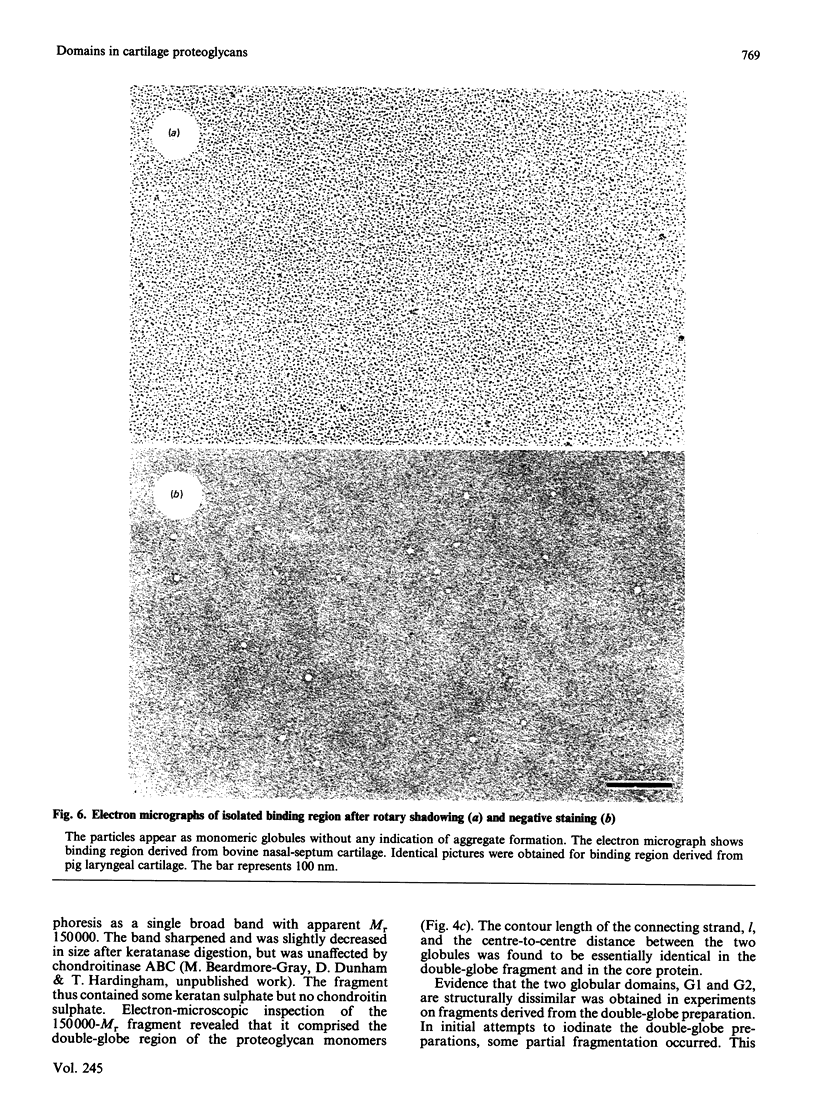
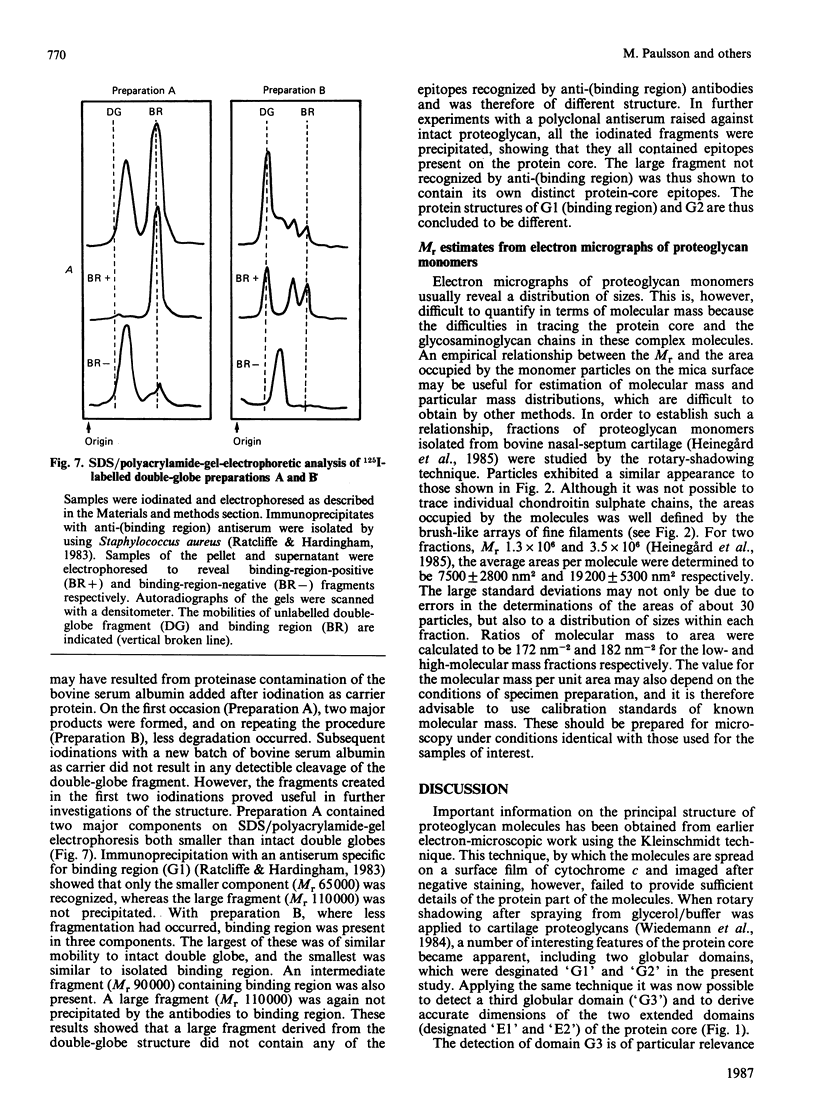
Electron microscopy after rotary shadowing and negative staining of the large chondroitin sulphate proteoglycan from rat chondrosarcoma, bovine nasal cartilage and pig laryngeal cartilage demonstrated a unique multidomain structure for the protein core. A main characteristic is a pair of globular domains (diameter 6-8 nm), one of which forms the N-terminal hyaluronate-binding region. They are connected by a 25 nm-long rod-like domain of limited flexibility. This segment is continued by a 280 nm-long polypeptide strand containing most chondroitin sulphate chains (average length 40 nm) in a brush-like array and is terminated by a small C-terminal globular domain. The core protein showed a variable extent of degradation, including the loss of the C-terminal globular domain and sections of variable length of the chondroitin sulphate-bearing strand. The high abundance (30-50%) of the C-terminal domain in some extracted proteoglycan preparations indicated that this structure is present in the cartilage matrix rather than being a precursor-specific segment. It may contain the hepatolectin-like segment deduced from cDNA sequences corresponding to the 3'-end of protein core mRNA [Doege, Fernandez, Hassell, Sasaki & Yamada (1986) J. Biol. Chem. 261, 8108-8111; Sai, Tanaka, Kosher & Tanzer (1986) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 83, 5081-5085; Oldberg, Antonsson & Heinegård (1987) Biochem. J. 243, 255-259].
Full text
PDF

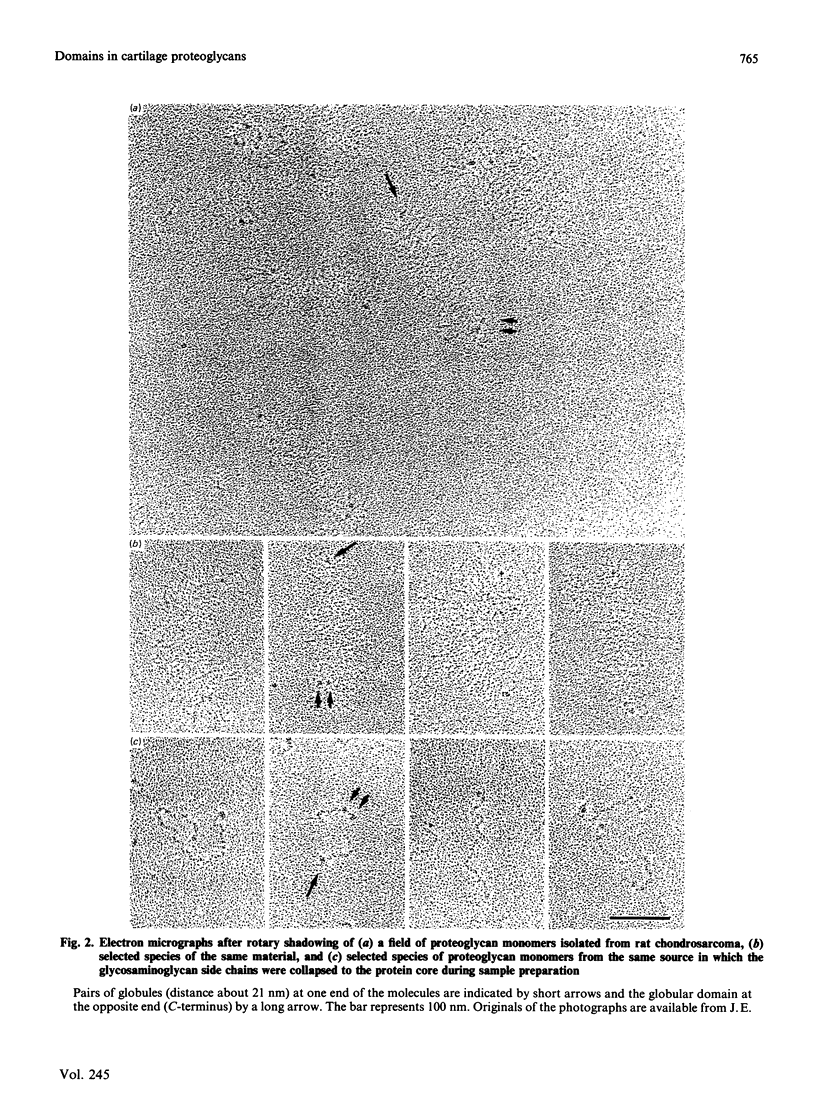


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonnet F., Dunham D. G., Hardingham T. E. Structure and interactions of cartilage proteoglycan binding region and link protein. Biochem J. 1985 May 15;228(1):77–85. doi: 10.1042/bj2280077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckwalter J. A., Rosenberg L. C. Electron microscopic studies of cartilage proteoglycans. Direct evidence for the variable length of the chondroitin sulfate-rich region of proteoglycan subunit core protein. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 25;257(16):9830–9839. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doege K., Fernandez P., Hassell J. R., Sasaki M., Yamada Y. Partial cDNA sequence encoding a globular domain at the C terminus of the rat cartilage proteoglycan. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8108–8111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel J., Odermatt E., Engel A., Madri J. A., Furthmayr H., Rohde H., Timpl R. Shapes, domain organizations and flexibility of laminin and fibronectin, two multifunctional proteins of the extracellular matrix. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jul 25;150(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90326-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fellini S. A., Kimura J. H., Hascall V. C. Polydispersity of proteoglycans synthesized by chondrocytes from the Swarm rat chondrosarcoma. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):7883–7889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara S., Wiedemann H., Timpl R., Lustig A., Engel J. Structure and interactions of heparan sulfate proteoglycans from a mouse tumor basement membrane. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Aug 15;143(1):145–157. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08353.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardingham T. E., Beardmore-Gray M., Dunham D. G., Ratcliffe A. Cartilage proteoglycans. Ciba Found Symp. 1986;124:30–46. doi: 10.1002/9780470513385.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardingham T. E. The role of link-protein in the structure of cartilage proteoglycan aggregates. Biochem J. 1979 Jan 1;177(1):237–247. doi: 10.1042/bj1770237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassell J. R., Kimura J. H., Hascall V. C. Proteoglycan core protein families. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:539–567. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.002543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinegård D., Axelsson I. Distribution of keratan sulfate in cartilage proteoglycans. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 25;252(6):1971–1979. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinegård D., Hascall V. C. Aggregation of cartilage proteoglycans. 3. Characteristics of the proteins isolated from trypsin digests of aggregates. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 10;249(13):4250–4256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinegård D., Lohmander S., Thyberg J. Cartilage proteoglycan aggregates. Electron-microscopic studies of native and fragmented molecules. Biochem J. 1978 Dec 1;175(3):913–919. doi: 10.1042/bj1750913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinegård D. Polydispersity of cartilage proteoglycans. Structural variations with size and buoyant density of the molecules. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 25;252(6):1980–1989. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinegård D., Wieslander J., Sheehan J., Paulsson M., Sommarin Y. Separation and characterization of two populations of aggregating proteoglycans from cartilage. Biochem J. 1985 Jan 1;225(1):95–106. doi: 10.1042/bj2250095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey J. H. Silver stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels: a modified procedure with enhanced uniform sensitivity. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 1;117(2):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90783-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oegema T. R., Jr, Hascall V. C., Dziewiatkowski D. D. Isolation and characterization of proteoglycans from the swarm rat chondrosarcoma. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 10;250(15):6151–6159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulsson M., Fujiwara S., Dziadek M., Timpl R., Pejler G., Bäckström G., Lindahl U., Engel J. Structure and function of basement membrane proteoglycans. Ciba Found Symp. 1986;124:189–203. doi: 10.1002/9780470513385.ch11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Périn J. P., Bonnet F., Jollès J., Jollès P. Sequence data concerning the protein core of the cartilage proteoglycan monomers. Characterization of a sequence allowing the synthesis of an oligonucleotide probe. FEBS Lett. 1984 Oct 15;176(1):37–42. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80907-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratcliffe A., Hardingham T. Cartilage proteoglycan binding region and link protein. Radioimmunoassays and the detection of masked determinants in aggregates. Biochem J. 1983 Aug 1;213(2):371–378. doi: 10.1042/bj2130371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg L., Hellmann W., Kleinschmidt A. K. Electron microscopic studies of proteoglycan aggregates from bovine articular cartilage. J Biol Chem. 1975 Mar 10;250(5):1877–1883. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg L., Hellmann W., Kleinschmidt A. K. Macromolecular models of proteinpolysaccharides from bovine nasal cartilage based on electron microscopic studies. J Biol Chem. 1970 Aug 25;245(16):4123–4130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sai S., Tanaka T., Kosher R. A., Tanzer M. L. Cloning and sequence analysis of a partial cDNA for chicken cartilage proteoglycan core protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5081–5085. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Structural and contractile proteins. Part E. Extracellular matrix. Methods Enzymol. 1987;145:1–453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thyberg J., Lohmander S., Heinegård D. Proteoglycans of hyaline cartilage: Electron-microscopic studies on isolated molecules. Biochem J. 1975 Oct;151(1):157–166. doi: 10.1042/bj1510157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treadwell B. V., Mankin D. P., Ho P. K., Mankin H. J. Cell-free synthesis of cartilage proteins: partial identification of proteoglycan core and link proteins. Biochemistry. 1980 May 13;19(10):2269–2275. doi: 10.1021/bi00551a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upholt W. B., Vertel B. M., Dorfman A. Translation and characterization of messenger RNAs in differentiating chicken cartilage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4847–4851. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedemann H., Paulsson M., Timpl R., Engel J., Heinegård D. Domain structure of cartilage proteoglycans revealed by rotary shadowing of intact and fragmented molecules. Biochem J. 1984 Nov 15;224(1):331–333. doi: 10.1042/bj2240331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]