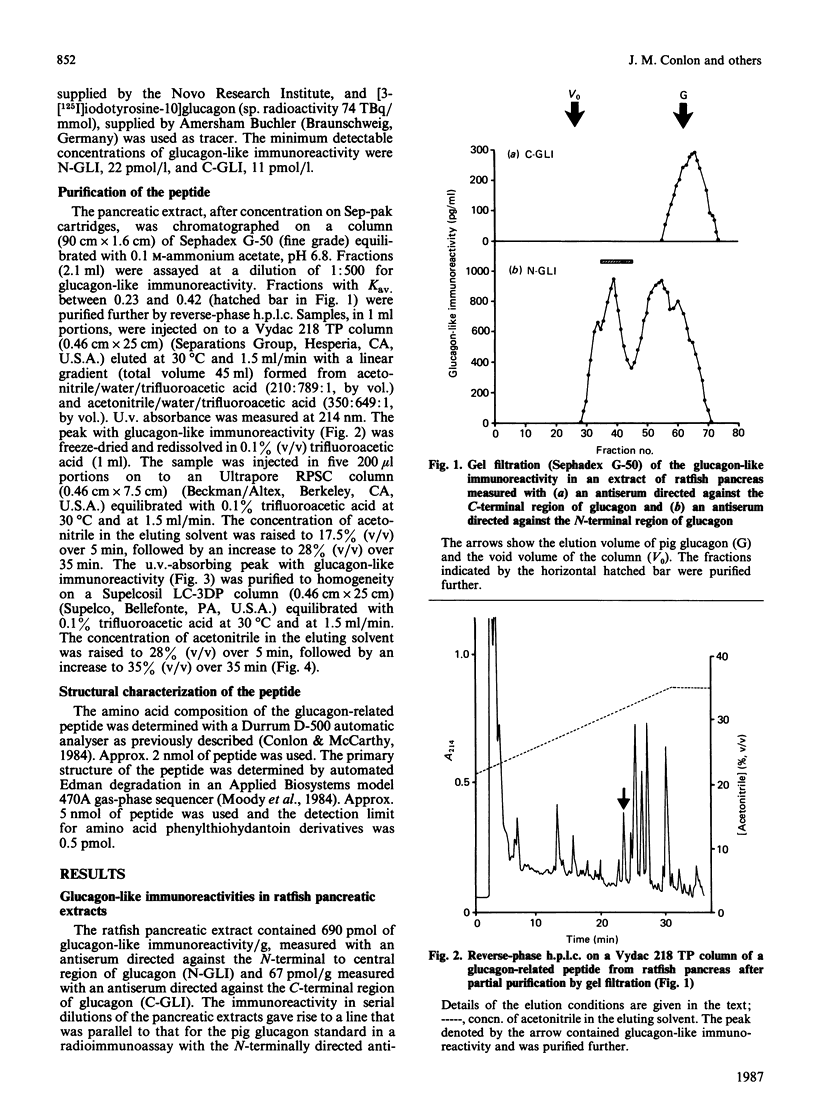
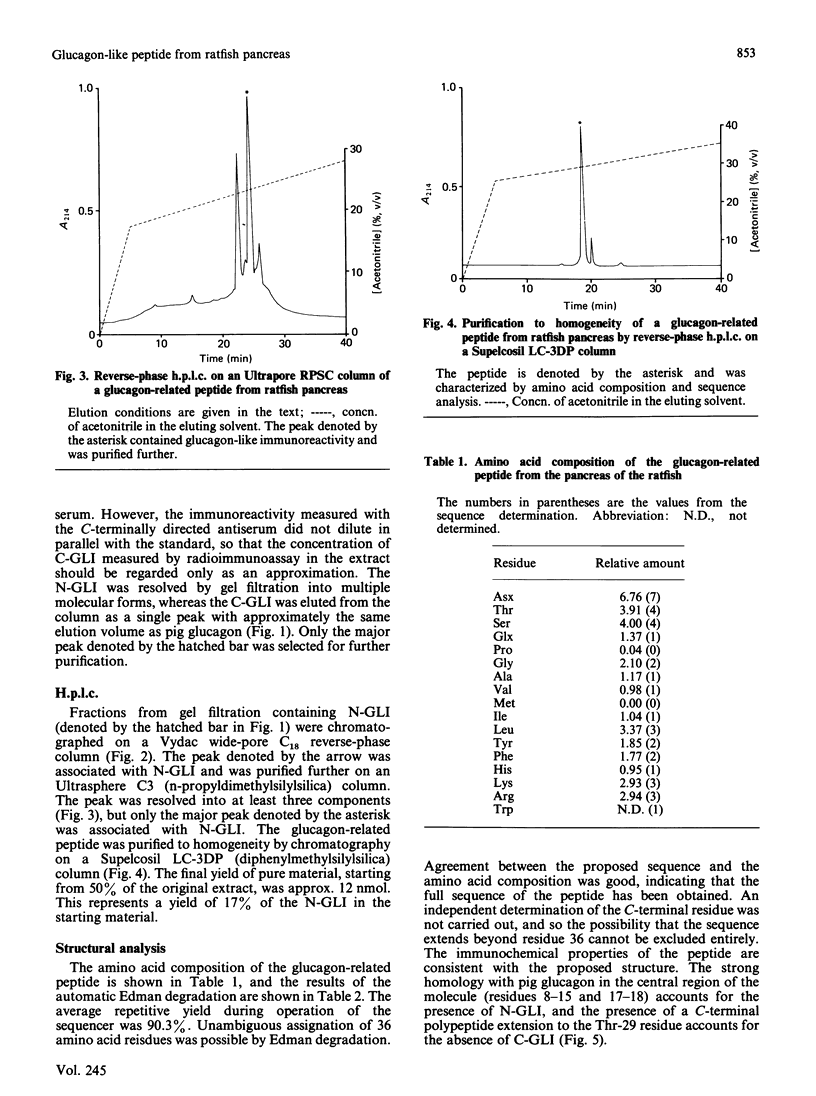
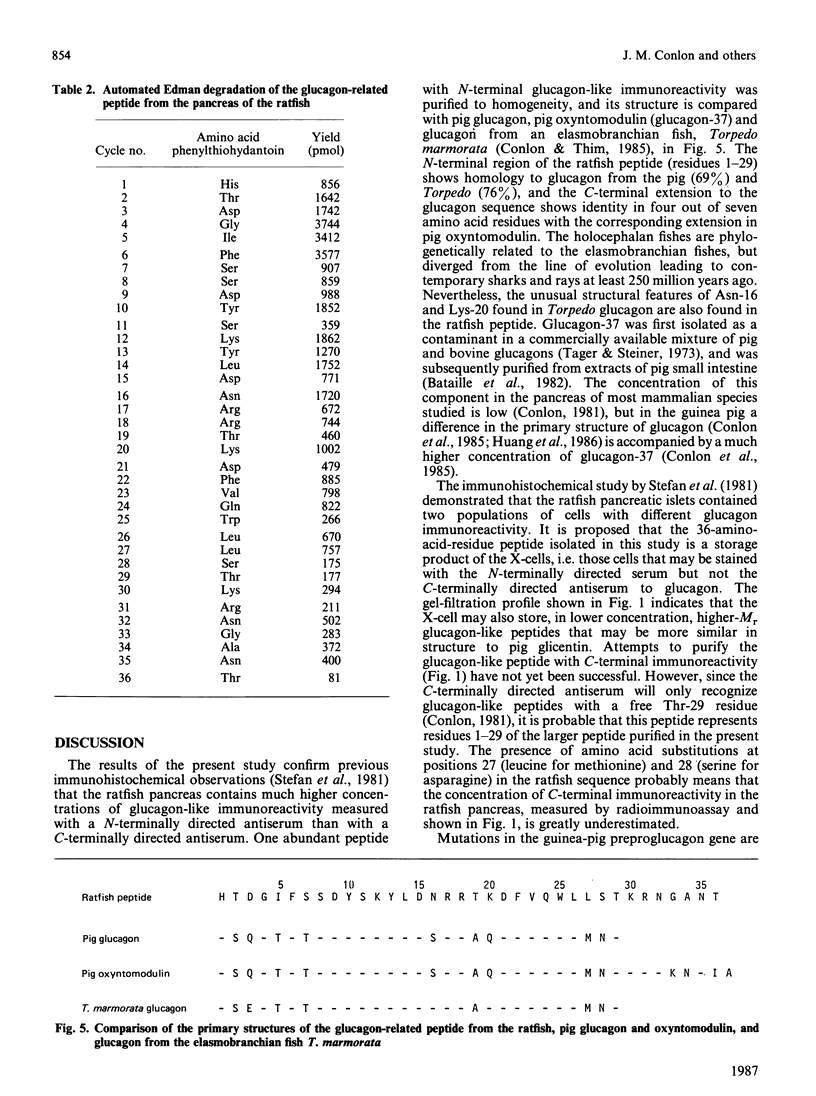
Abstract
The pancreatic islets of the holocephalan fishes contain, in addition to A-, B- and D-cells, X-cells, which are immunoreactive towards antisera directed against the N-terminal region of glucagon but not towards antisera directed against the C-terminal region. A 36-amino-acid-residue peptide was isolated from the pancreas of a holocephalan fish, the Pacific ratfish (Hydrolagus colliei), that shows homology (69%) to mammalian glucagon in its N-terminal region and is reactive towards an N-terminally directed antiserum. Reactivity towards C-terminally directed antisera is prevented by the presence of a 7-residue C-terminal extension to the glucagon sequence that shows limited homology to the C-terminal region of glucagon-37 (oxyntomodulin). It is proposed that this peptide represents a major storage product of the islet X-cell.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bataille D., Coudray A. M., Carlqvist M., Rosselin G., Mutt V. Isolation of glucagon-37 (bioactive enteroglucagon/oxyntomodulin) from porcine jejuno-ileum. Isolation of the peptide. FEBS Lett. 1982 Sep 6;146(1):73–78. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80708-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conlon J. M., Dafgård E., Falkmer S., Thim L. The primary structure of ratfish insulin reveals an unusual mode of proinsulin processing. FEBS Lett. 1986 Nov 24;208(2):445–450. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81066-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conlon J. M., Hansen H. F., Schwartz T. W. Primary structure of glucagon and a partial sequence of oxyntomodulin (glucagon-37) from the guinea pig. Regul Pept. 1985 Aug;11(4):309–320. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(85)90203-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conlon J. M., McCarthy D. M. Fragments of prosomatostatin isolated from a human pancreatic tumour. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1984 Nov;38(1):81–86. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(84)90148-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conlon J. M., Thim L. Primary structure of glucagon from an elasmobranchian fish. Torpedo marmorata. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1985 Dec;60(3):398–405. doi: 10.1016/0016-6480(85)90073-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUJITA T. [On the islet system of the pancreas of Chimaera monstrosa]. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1962;57:487–494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. G., Eng J., Pan Y. C., Hulmes J. D., Yalow R. S. Guinea pig glucagon differs from other mammalian glucagons. Diabetes. 1986 May;35(5):508–512. doi: 10.2337/diab.35.5.508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody A. J., Thim L., Valverde I. The isolation and sequencing of human gastric inhibitory peptide (GIP). FEBS Lett. 1984 Jul 9;172(2):142–148. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)81114-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seino S., Welsh M., Bell G. I., Chan S. J., Steiner D. F. Mutations in the guinea pig preproglucagon gene are restricted to a specific portion of the prohormone sequence. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jul 14;203(1):25–30. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81429-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefan Y., Ravazzola M., Orci L. Primitive islets contain two populations of cells with differing glucagon immunoreactivity. Diabetes. 1981 Mar;30(3):192–195. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.3.192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tager H. S., Markese J. Intestinal and pancreatic glucagon-like peptides. Evidence for identity of higher molecular weight forms. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 10;254(7):2229–2233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tager H. S., Steiner D. F. Isolation of a glucagon-containing peptide: primary structure of a possible fragment of proglucagon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2321–2325. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thim L., Moody A. J. The primary structure of porcine glicentin (proglucagon). Regul Pept. 1981 May;2(2):139–150. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(81)90007-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


