Abstract
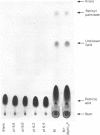
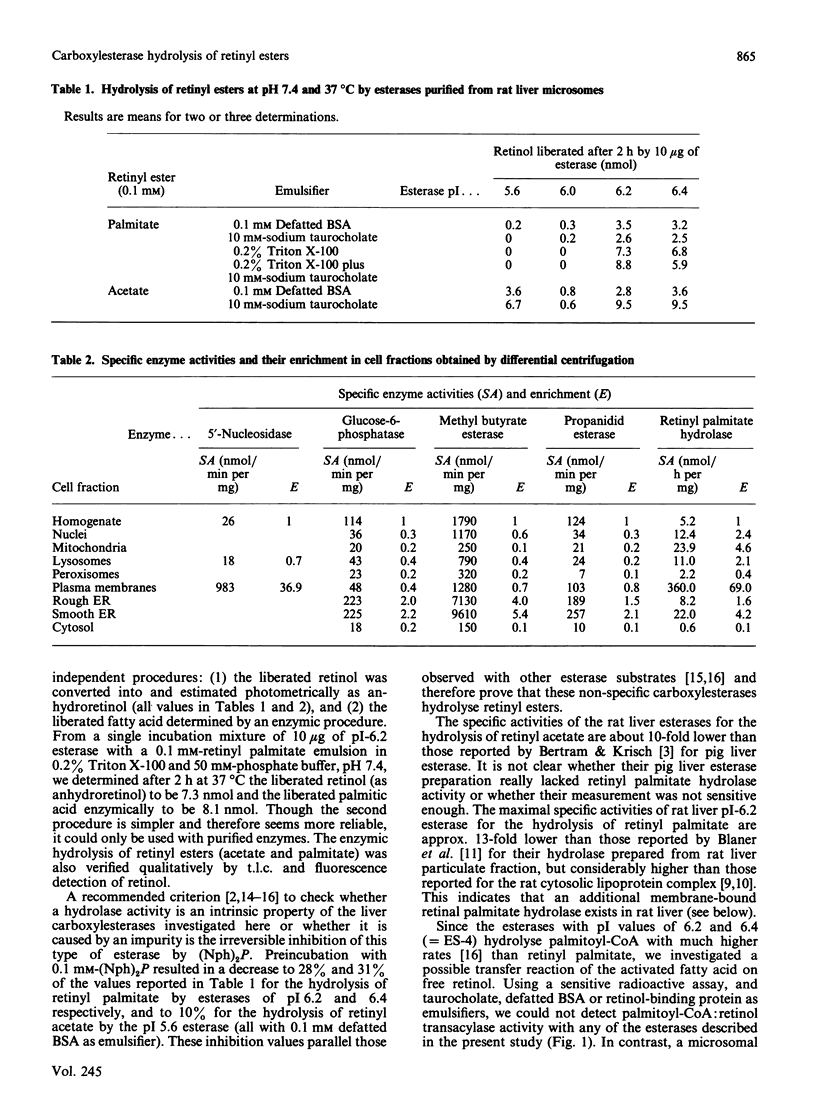
The four most important non-specific carboxylesterases from rat liver were assayed for their ability to hydrolyse retinyl esters. Only the esterases with pI 6.2 and 6.4 (= esterase ES-4) are able to hydrolyse retinyl palmitate. Their specific activities strongly depend on the emulsifier used (maximum rate: 440 nmol of retinol liberated/h per mg of esterase). Beside retinyl palmitate, these esterases cleave palmitoyl-CoA and monoacylglycerols with much higher rates, as well as certain drugs (e.g. aspirin and propanidid). However, no transacylation between palmitoyl-CoA and retinol occurs. Retinyl acetate also is a substrate for the above esterases and for another one with pI 5.6 (= esterase ES-3). Again the emulsifier influences the hydrolysis by these esterases (maximum rates: 475 nmol/h per mg for ES-4 and 200 nmol/h per mg for ES-3). Differential centrifugation of rat liver homogenate reveals that retinyl palmitate hydrolase activity is highly enriched in the plasma membranes, but only moderately so in the endoplasmic reticulum, where the investigated esterases are located. Since the latter activity can be largely inhibited with the selective esterase inhibitor bis-(4-nitrophenyl) phosphate, it is concluded that the esterases with pI 6.2 and 6.4 (ES-4) represent the main retinyl palmitate hydrolase of rat liver endoplasmic reticulum. In view of this cellular localization, the enzyme could possibly be involved in the mobilization of retinol from the vitamin A esters stored in the liver. However, preliminary experiments in vivo have failed to demonstrate such a biological function.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aronson N. N., Jr, Touster O. Isolation of rat liver plasma membrane fragments in isotonic sucrose. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:90–102. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31009-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertram J., Krisch K. Hydrolysis of vitamin A acetate by unspecific carboxylesterases from liver and kidney. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Nov;11(1):122–126. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00748.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhat P. V., Lacroix A. Metabolism of [11-3H]retinyl acetate in liver tissues of vitamin A-sufficient, -deficient and retinoic acid-supplemented rats. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Aug 1;752(3):451–459. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(83)90275-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaner W. S., Halperin G., Stein O., Stein Y., Goodman D. S. Inhibition of rat liver retinyl palmitate hydrolase activity by ether analogs of cholesteryl esters and acylglycerides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jul 26;794(3):428–434. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(84)90009-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaner W. S., Prystowsky J. H., Smith J. E., Goodman D. S. Rat liver retinyl palmitate hydrolase activity. Relationship to cholesteryl oleate and triolein hydrolase activities. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jul 26;794(3):419–427. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(84)90008-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt E., Heymann E., Mentlein R. Selective inhibition of rat liver carboxylesterases by various organophosphorus diesters in vivo and in vitro. Biochem Pharmacol. 1980 Jul 1;29(13):1927–1931. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(80)90105-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büch H., Buzello W., Heymann E., Krisch K. Inhibition of phenacetin- and acetanilide-induced methemoglobinemia in the rat by the carboxylesterase inhibitor bis-[p-nitrophenyl] phosphate. Biochem Pharmacol. 1969 Apr;18(4):801–811. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(69)90050-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. C., Heller J. Retinyl esterase activity of purified rat liver retinyl ester lipoprotein complex. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1979 Dec;198(2):572–579. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(79)90533-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischer S., Kervina M. Subcellular fractionation of rat liver. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:6–41. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31005-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heymann E., Junge W. Characterization of the isoenzymes of pig-liver esterase. 1. Chemical Studies. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Apr;95(3):509–518. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb12991.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heymann E., Mentlein R. Carboxylesterases-amidases. Methods Enzymol. 1981;77:333–344. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)77047-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heymann E., Mentlein R., Schmalz R., Schwabe C., Wagenmann F. A method for the estimation of esterase synthesis and degradation and its application to evaluate the influence of insulin and glucagon. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Dec 17;102(2):509–519. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb04267.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahadevan S., Ayyoub N. I., Roels O. A. Hydrolysis of retinol palmitate by rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jan 10;241(1):57–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mentlein R., Berge R. K., Heymann E. Identity of purified monoacylglycerol lipase, palmitoyl-CoA hydrolase and aspirin-metabolizing carboxylesterase from rat liver microsomal fractions. A comparative study with enzymes purified in different laboratories. Biochem J. 1985 Dec 1;232(2):479–483. doi: 10.1042/bj2320479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mentlein R., Heiland S., Heymann E. Simultaneous purification and comparative characterization of six serine hydrolases from rat liver microsomes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1980 Apr 1;200(2):547–559. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(80)90386-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mentlein R., Heymann E. Hydrolysis of ester- and amide-type drugs by the purified isoenzymes of nonspecific carboxylesterase from rat liver. Biochem Pharmacol. 1984 Apr 15;33(8):1243–1248. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(84)90176-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mentlein R., Schumann M., Heymann E. Comparative chemical and immunological characterization of five lipolytic enzymes (carboxylesterases) from rat liver microsomes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Nov 1;234(2):612–621. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90311-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mentlein R., Suttorp M., Heymann E. Specificity of purified monoacylglycerol lipase, palmitoyl-CoA hydrolase, palmitoyl-carnitine hydrolase, and nonspecific carboxylesterase from rat liver microsomes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Jan;228(1):230–246. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90064-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ong D., Chytil F. Purification of cellular retinol and retinoic acid-binding proteins from rat tissue. Methods Enzymol. 1980;67:288–296. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)67036-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prystowsky J. H., Smith J. E., Goodman D. S. Retinyl palmitate hydrolase activity in normal rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 10;256(9):4498–4503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross A. C. Retinol esterification by rat liver microsomes. Evidence for a fatty acyl coenzyme A: retinol acyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2453–2459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggieri S., Roblin R., Black P. H. Lipids of whole cells and plasma membrane fractions from Balb/c3T3, SV3T3, and concanavalin A-selected revertant cells. J Lipid Res. 1979 Aug;20(6):760–771. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sklan D., Blaner W. S., Adachi N., Smith J. E., Goodman D. S. Association of cellular retinol-binding protein and several lipid hydrolase activities with a vitamin A-containing high-molecular-weight lipid-protein aggregate from rat liver cytosol. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1982 Mar;214(1):35–44. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(82)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]