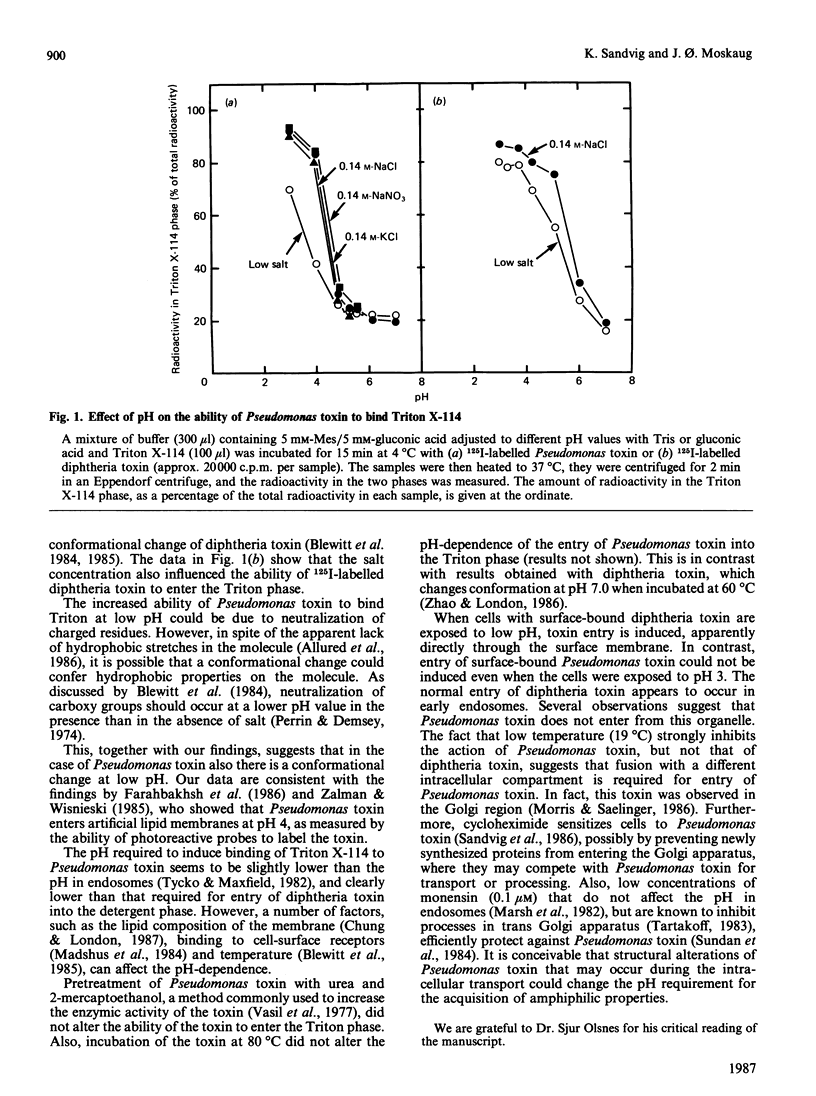
Abstract
Pseudomonas toxin was found to bind Triton X-114 at pH values below pH 5.0, whereas much less binding was observed at higher pH values. The toxin bound Triton X-114 at a higher pH value in the presence of 0.14 M-NaCl, -KCl or -NaNO3 than at low salt concentrations. The results suggest that low pH in an intracellular compartment facilitates the transport of Pseudomonas toxin across the membrane and into the cytosol by inducing a conformational change in the molecule.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allured V. S., Collier R. J., Carroll S. F., McKay D. B. Structure of exotoxin A of Pseudomonas aeruginosa at 3.0-Angstrom resolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1320–1324. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blewitt M. G., Chao J. M., McKeever B., Sarma R., London E. Fluorescence characterization of the low pH-induced change in diphtheria toxin conformation: effect of salt. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Apr 16;120(1):286–290. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91446-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blewitt M. G., Chung L. A., London E. Effect of pH on the conformation of diphtheria toxin and its implications for membrane penetration. Biochemistry. 1985 Sep 24;24(20):5458–5464. doi: 10.1021/bi00341a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordier C. Phase separation of integral membrane proteins in Triton X-114 solution. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1604–1607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draper R. K., Simon M. I. The entry of diphtheria toxin into the mammalian cell cytoplasm: evidence for lysosomal involvement. J Cell Biol. 1980 Dec;87(3 Pt 1):849–854. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.3.849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draper R. K., Simon M. I. The entry of diphtheria toxin into the mammalian cell cytoplasm: evidence for lysosomal involvement. J Cell Biol. 1980 Dec;87(3 Pt 1):849–854. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.3.849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farahbakhsh Z. T., Baldwin R. L., Wisnieski B. J. Pseudomonas exotoxin A. Membrane binding, insertion, and traversal. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 25;261(24):11404–11408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Speck J. C., Jr Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloroamide, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3a,6a-diphrenylglycoluril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iglewski B. H., Kabat D. NAD-dependent inhibition of protein synthesis by Pseudomonas aeruginosa toxin,. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2284–2288. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madshus I. H., Olsnes S., Sandvig K. Requirements for entry of poliovirus RNA into cells at low pH. EMBO J. 1984 Sep;3(9):1945–1950. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02074.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manhart M. D., Morris R. E., Bonventre P. F., Leppla S., Saelinger C. B. Evidence for pseudomonas exotoxin A receptors on plasma membrane of toxin-sensitive lm fibroblasts. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):596–603. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.596-603.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh M., Wellsteed J., Kern H., Harms E., Helenius A. Monensin inhibits Semliki Forest virus penetration into culture cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5297–5301. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris R. E., Saelinger C. B. Reduced temperature alters Pseudomonas exotoxin A entry into the mouse LM cell. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):445–453. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.445-453.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappenheimer A. M., Jr Diphtheria toxin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:69–94. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandvig K., Brown J. E. Ionic requirements for entry of Shiga toxin from Shigella dysenteriae 1 into cells. Infect Immun. 1987 Feb;55(2):298–303. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.2.298-303.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandvig K., Olsnes S. Rapid entry of nicked diphtheria toxin into cells at low pH. Characterization of the entry process and effects of low pH on the toxin molecule. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):9068–9076. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandvig K., Tønnessen T. I., Olsnes S. Ability of inhibitors of glycosylation and protein synthesis to sensitize cells to abrin, ricin, Shigella toxin, and Pseudomonas toxin. Cancer Res. 1986 Dec;46(12 Pt 1):6418–6422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundan A., Sandvig K., Olsnes S. Calmodulin antagonists sensitize cells to pseudomonas toxin. J Cell Physiol. 1984 Apr;119(1):15–22. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041190104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartakoff A. M. Perturbation of vesicular traffic with the carboxylic ionophore monensin. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1026–1028. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90286-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tycko B., Maxfield F. R. Rapid acidification of endocytic vesicles containing alpha 2-macroglobulin. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):643–651. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90219-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasil M. L., Kabat D., Iglewski B. H. Structure-activity relationships of an exotoxin of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1977 Apr;16(1):353–361. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.1.353-361.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zalman L. S., Wisnieski B. J. Characterization of the insertion of Pseudomonas exotoxin A into membranes. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):630–635. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.630-635.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao J. M., London E. Similarity of the conformation of diphtheria toxin at high temperature to that in the membrane-penetrating low-pH state. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2002–2006. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


