Abstract
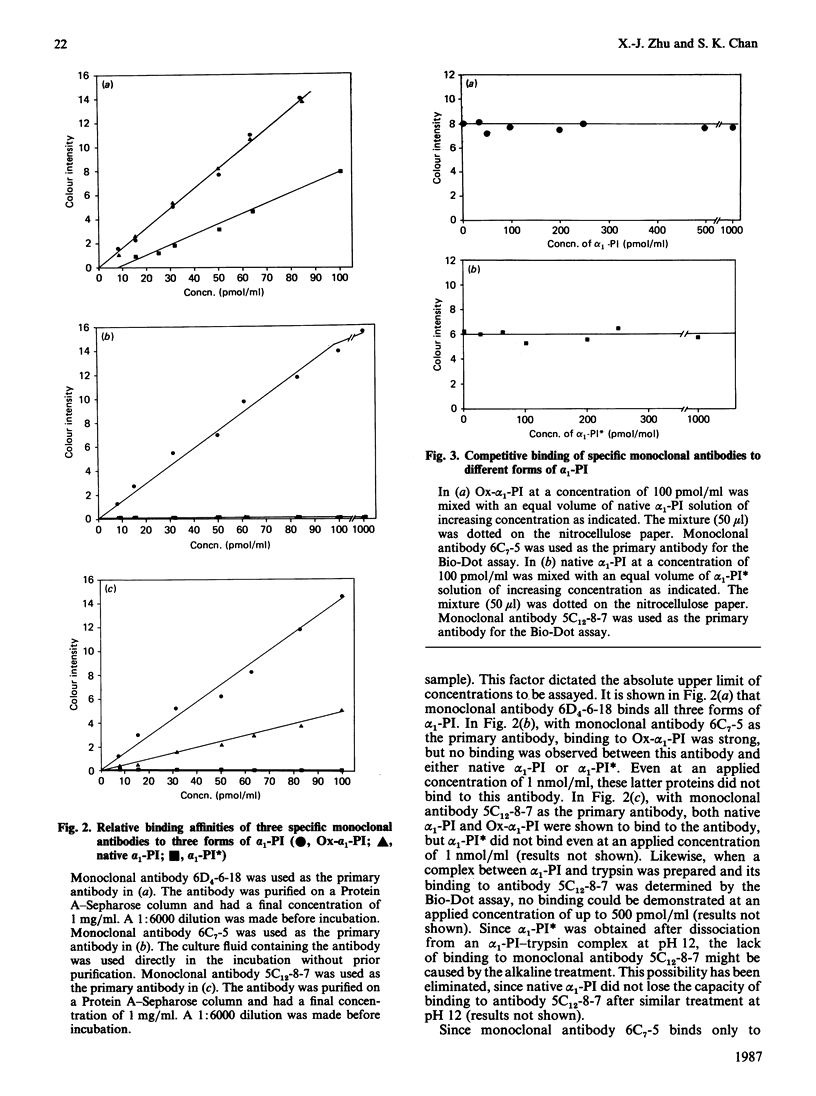
The purpose of our investigation was to obtain monoclonal antibodies that could distinguish three forms of alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor (alpha 1-PI): native alpha 1-PI, N-chlorosuccinimide-oxidized alpha 1-PI (Ox-alpha 1-PI) and proteolytically modified alpha 1-PI (alpha 1-PI). Three specific monoclonal antibodies were characterized as to their binding properties. By using the Bio-Dot assay, it was found that all three forms of alpha 1-PI were capable of binding to antibody 6D4-6-18, that only Ox-alpha 1-PI, but not native alpha 1-PI or alpha 1-PI, could bind to antibody 6C7-5, and that alpha 1-PI and a complex between alpha 1-PI and trypsin uniquely were not able to bind to antibody 5C12-8-7. Thus it was concluded that it is possible to use monoclonal antibodies with different epitopic specificities to distinguish two chemically modified forms of alpha 1-PI from the native protein.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abboud R. T., Fera T., Richter A., Tabona M. Z., Johal S. Acute effect of smoking on the functional activity of alpha1-protease inhibitor in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Jan;131(1):79–85. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.131.1.79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beatty K., Bieth J., Travis J. Kinetics of association of serine proteinases with native and oxidized alpha-1-proteinase inhibitor and alpha-1-antichymotrypsin. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 10;255(9):3931–3934. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnett D., Stockley R. A. The electrophoretic mobility of alpha 1-antitrypsin in sputum and its relationship to protease inhibitory capacity, leucocyte elastase concentrations and acute respiratory infection. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1980 May;361(5):781–789. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1980.361.1.781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carp H., Miller F., Hoidal J. R., Janoff A. Potential mechanism of emphysema: alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor recovered from lungs of cigarette smokers contains oxidized methionine and has decreased elastase inhibitory capacity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):2041–2045. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.2041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadek J. E., Fells G. A., Crystal R. G. Cigarette smoking induces functional antiprotease deficiency in the lower respiratory tract of humans. Science. 1979 Dec 14;206(4424):1315–1316. doi: 10.1126/science.316188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goding J. W. Antibody production by hybridomas. J Immunol Methods. 1980;39(4):285–308. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90230-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes R., Niday E., Gordon J. A dot-immunobinding assay for monoclonal and other antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):142–147. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90677-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janoff A., White R., Carp H., Harel S., Dearing R., Lee D. Lung injury induced by leukocytic proteases. Am J Pathol. 1979 Oct;97(1):111–136. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D., Travis J. Structural evidence for methionine at the reactive site of human alpha-1-proteinase inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 25;253(20):7142–7144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D., Travis J. The oxidative inactivation of human alpha-1-proteinase inhibitor. Further evidence for methionine at the reactive center. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 25;254(10):4022–4026. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lellouch J., Claude J. R., Martin J. P., Orssaud G., Zaoui D., Bieth J. G. Smoking does not reduce the functional activity of serum alpha-1-proteinase inhibitor. An epidemiologic study of 719 healthy men. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Oct;132(4):818–820. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.132.4.818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loebermann H., Tokuoka R., Deisenhofer J., Huber R. Human alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor. Crystal structure analysis of two crystal modifications, molecular model and preliminary analysis of the implications for function. J Mol Biol. 1984 Aug 15;177(3):531–557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shochat D., Staples S., Hargrove K., Kozel J. S., Chan S. K. Primary structure of human alpha1-protease inhibitor. The complete amino acid sequence of cyanogen bromide fragment II. J Biol Chem. 1978 Aug 25;253(16):5630–5634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoclet J. C. L'AMP cyclique intervient-il dans l'effet bronchodilatateur de la théophylline? Bull Eur Physiopathol Respir. 1980 Jan-Feb;16(1):5–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone P. J., Calore J. D., McGowan S. E., Bernardo J., Snider G. L., Franzblau C. Functional alpha 1-protease inhibitor in the lower respiratory tract of cigarette smokers is not decreased. Science. 1983 Sep 16;221(4616):1187–1189. doi: 10.1126/science.6612333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]