Abstract
1. We have studied the metabolism of Ins(1,3,4,5)P4 (inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate) by rat liver homogenates incubated in a medium resembling intracellular ionic strength and pH. 2. Ins(1,3,4,5)P4 was dephosphorylated to a single inositol trisphosphate product, Ins(1,3,4)P3 (inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate), the identity of which was confirmed by periodate degradation, followed by reduction and dephosphorylation to yield altritol. 3. The major InsP2 (inositol bisphosphate) product was inositol 3,4-bisphosphate [Shears, Storey, Morris, Cubitt, Parry, Michell & Kirk (1987) Biochem. J. 242, 393-402]. Small quantities of a second InsP2 product was also detected in some experiments, but its isomeric configuration was not identified. 4. The Ins(1,3,4,5)P4 5-phosphatase activity was primarily associated with plasma membranes. 5. ATP (5 mM) decreased the membrane-associated Ins(1,4,5)P3 5-phosphatase and Ins(1,3,4,5)P4 5-phosphatase activities by 40-50%. This inhibition was imitated by AMP, adenosine 5'-[beta gamma-imido]triphosphate, adenosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate or PPi, but not by adenosine or Pi. A decrease in [ATP] from 7 to 3 mM halved the inhibition of Ins(1,3,4,5)P4 5-phosphatase activity, but the extent of inhibition was not further decreased unless [ATP] less than 0.1 mM. 6. Ins(1,3,4,5)P4 5-phosphatase was insensitive to 50 mM-Li+, but was inhibited by 5 mM-2,3-bisphosphoglycerate. 7. The Ins(1,3,4,5)P4 5-phosphatase activity was unchanged by cyclic AMP, GTP, guanosine 5'-[beta gamma-imido]triphosphate or guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate, or by increasing [Ca2+] from 0.1 to 1 microM. 8. Ins(1,3,4)P3 was phosphorylated in an ATP-dependent manner to an isomer of InsP4 that was partially separable on h.p.l.c. from Ins(1,3,4,5)P4. The novel InsP4 appears to be Ins(1,3,4,6)P4. Its metabolic fate and function are not known.
Full text
PDF

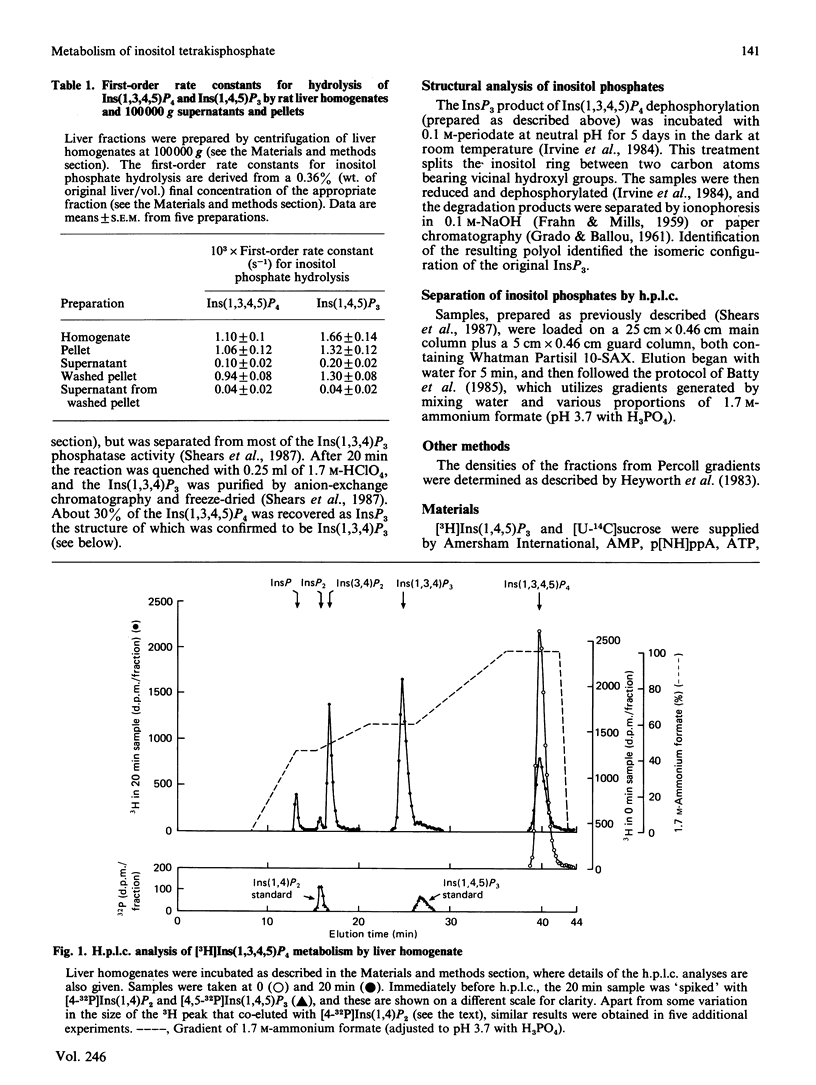
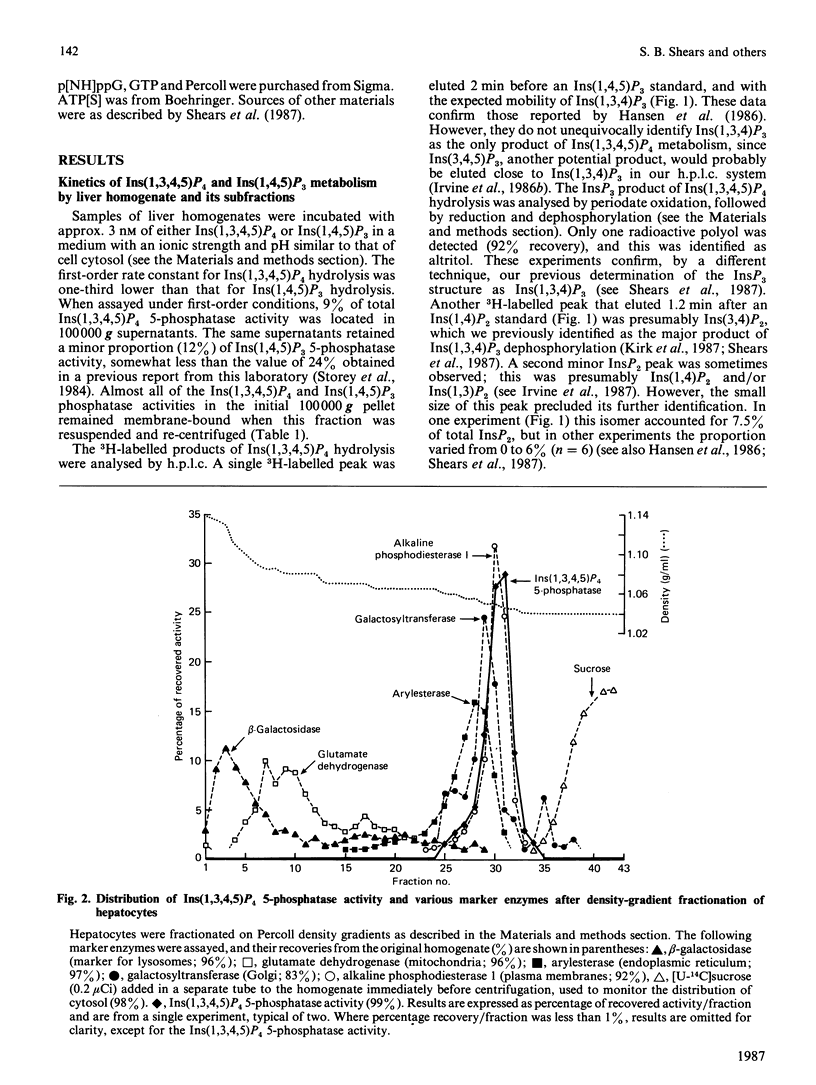
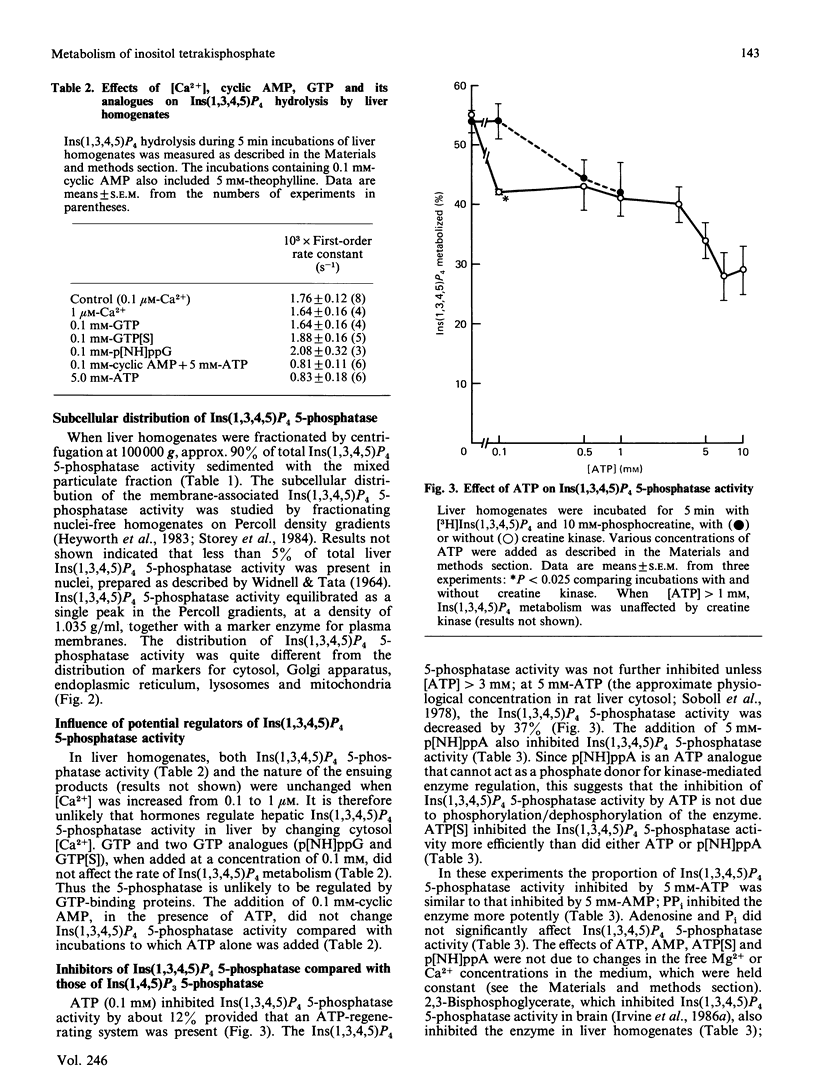

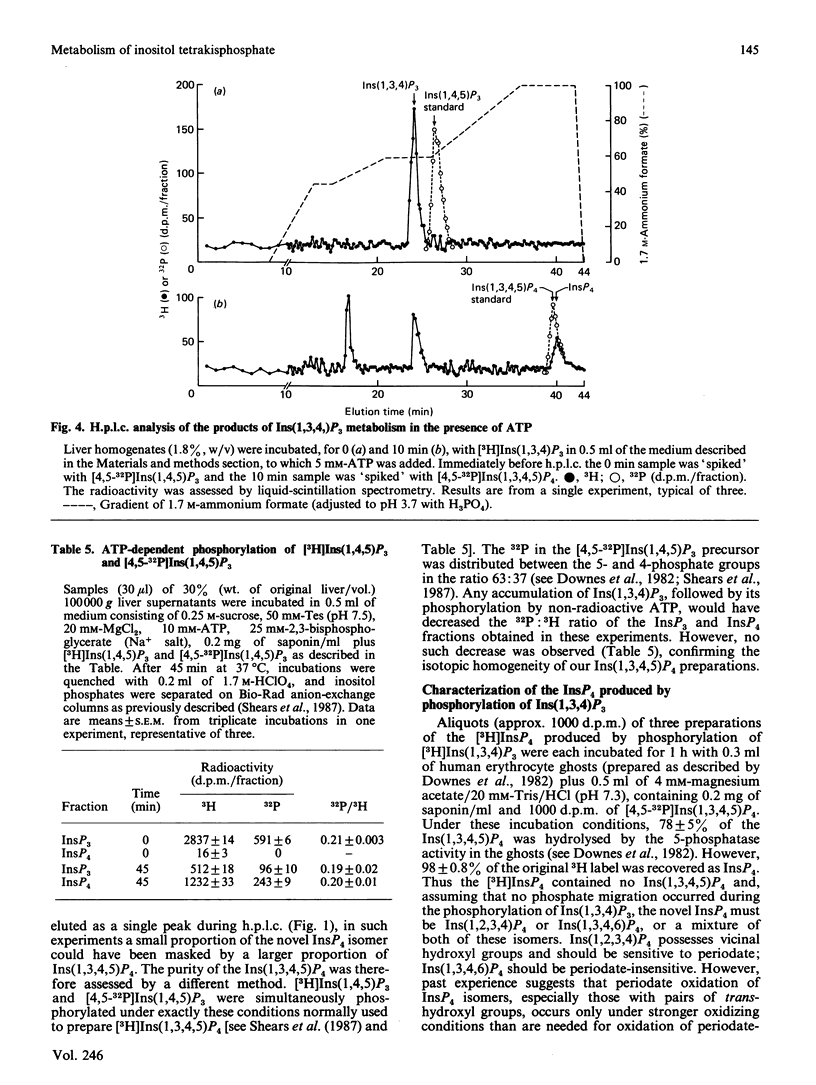


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Batty I. R., Nahorski S. R., Irvine R. F. Rapid formation of inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate following muscarinic receptor stimulation of rat cerebral cortical slices. Biochem J. 1985 Nov 15;232(1):211–215. doi: 10.1042/bj2320211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol as second messengers. Biochem J. 1984 Jun 1;220(2):345–360. doi: 10.1042/bj2200345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):315–321. doi: 10.1038/312315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Best L. A role for calcium in the breakdown of inositol phospholipids in intact and digitonin-permeabilized pancreatic islets. Biochem J. 1986 Sep 15;238(3):773–779. doi: 10.1042/bj2380773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brew K., Vanaman T. C., Hill R. L. The role of alpha-lactalbumin and the A protein in lactose synthetase: a unique mechanism for the control of a biological reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Feb;59(2):491–497. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.2.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess G. M., McKinney J. S., Fabiato A., Leslie B. A., Putney J. W., Jr Calcium pools in saponin-permeabilized guinea pig hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 25;258(24):15336–15345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly T. M., Bansal V. S., Bross T. E., Irvine R. F., Majerus P. W. The metabolism of tris- and tetraphosphates of inositol by 5-phosphomonoesterase and 3-kinase enzymes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 15;262(5):2146–2149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly T. M., Bross T. E., Majerus P. W. Isolation of a phosphomonoesterase from human platelets that specifically hydrolyzes the 5-phosphate of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 5;260(13):7868–7874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downes C. P., Hawkins P. T., Irvine R. F. Inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate and not phosphatidylinositol 3,4-bisphosphate is the probable precursor of inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate in agonist-stimulated parotid gland. Biochem J. 1986 Sep 1;238(2):501–506. doi: 10.1042/bj2380501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downes C. P., Mussat M. C., Michell R. H. The inositol trisphosphate phosphomonoesterase of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochem J. 1982 Apr 1;203(1):169–177. doi: 10.1042/bj2030169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flodgaard H., Torp-Pedersen C. A calcium ion-dependent adenosine triphosphate pyrophosphohydrolase in plasma membrane from rat liver. Demonstration that the adenosine triphosphate analogues adenosine 5'-[betagamma-imido]triphosphate and adenosine 5'-[betagamma-methylene]-triphosphate are substrates for the enzyme. Biochem J. 1978 Jun 1;171(3):817–820. doi: 10.1042/bj1710817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRADO C., BALLOU C. E. Myo-inositol phosphates obtained by alkaline hydrolysis of beef brain phosphoinositide. J Biol Chem. 1961 Jan;236:54–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guynn R. W., Veloso D., Lawson J. W., Veech R. L. The concentration and control of cytoplasmic free inorganic pyrophosphate in rat liver in vivo. Biochem J. 1974 Jun;140(3):369–375. doi: 10.1042/bj1400369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen C. A., Mah S., Williamson J. R. Formation and metabolism of inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate in liver. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8100–8103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins P. T., Stephens L., Downes C. P. Rapid formation of inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate and inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate in rat parotid glands may both result indirectly from receptor-stimulated release of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate from phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate. Biochem J. 1986 Sep 1;238(2):507–516. doi: 10.1042/bj2380507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heslop J. P., Irvine R. F., Tashjian A. H., Jr, Berridge M. J. Inositol tetrakis- and pentakisphosphates in GH4 cells. J Exp Biol. 1985 Nov;119:395–401. doi: 10.1242/jeb.119.1.395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyworth C. M., Neumann E. F., Wynn C. H. The stability and aggregation properties of human liver acid beta-D-galactosidase. Biochem J. 1981 Mar 1;193(3):773–779. doi: 10.1042/bj1930773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyworth C. M., Wallace A. V., Houslay M. D. Insulin and glucagon regulate the activation of two distinct membrane-bound cyclic AMP phosphodiesterases in hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1983 Jul 15;214(1):99–110. doi: 10.1042/bj2140099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Letcher A. J., Heslop J. P., Berridge M. J. The inositol tris/tetrakisphosphate pathway--demonstration of Ins(1,4,5)P3 3-kinase activity in animal tissues. Nature. 1986 Apr 17;320(6063):631–634. doi: 10.1038/320631a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Letcher A. J., Lander D. J., Berridge M. J. Specificity of inositol phosphate-stimulated Ca2+ mobilization from Swiss-mouse 3T3 cells. Biochem J. 1986 Nov 15;240(1):301–304. doi: 10.1042/bj2400301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Letcher A. J., Lander D. J., Downes C. P. Inositol trisphosphates in carbachol-stimulated rat parotid glands. Biochem J. 1984 Oct 1;223(1):237–243. doi: 10.1042/bj2230237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Letcher A. J., Lander D. J., Heslop J. P., Berridge M. J. Inositol(3,4)bisphosphate and inositol(1,3)bisphosphate in GH4 cells--evidence for complex breakdown of inositol(1,3,4)trisphosphate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Feb 27;143(1):353–359. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90672-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Moor R. M. Micro-injection of inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate activates sea urchin eggs by a mechanism dependent on external Ca2+. Biochem J. 1986 Dec 15;240(3):917–920. doi: 10.1042/bj2400917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph S. K., Williams R. J. Subcellular localization and some properties of the enzymes hydrolysing inositol polyphosphates in rat liver. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jan 28;180(2):150–154. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)81061-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirk C. J., Michell R. H., Parry J. B., Shears S. B. Inositol trisphosphate and tetrakisphosphate phosphomonoesterases of rat liver. Biochem Soc Trans. 1987 Feb;15(1):28–32. doi: 10.1042/bst0150028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim P. E., Tate M. E. The phytases. II. Properties of phytase fractions F 1 and F 2 from wheat bran and the myoinositol phosphates produced by fraction F 2 . Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Apr 12;302(2):316–328. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(73)90160-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer S., Hawkins P. T., Michell R. H., Kirk C. J. The labelling of polyphosphoinositides with [32P]Pi and the accumulation of inositol phosphates in vasopressin-stimulated hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1986 Sep 1;238(2):491–499. doi: 10.1042/bj2380491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seyfred M. A., Farrell L. E., Wells W. W. Characterization of D-myo-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate phosphatase in rat liver plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13204–13208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shears S. B., Kirk C. J. Characterization of a rapid cellular-fractionation technique for hepatocytes. Application in the measurement of mitochondrial membrane potential in situ. Biochem J. 1984 Apr 15;219(2):375–382. doi: 10.1042/bj2190375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shears S. B., Storey D. J., Morris A. J., Cubitt A. B., Parry J. B., Michell R. H., Kirk C. J. Dephosphorylation of myo-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and myo-inositol 1,3,4-triphosphate. Biochem J. 1987 Mar 1;242(2):393–402. doi: 10.1042/bj2420393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shephard E. H., Hübscher G. Phosphatidate biosynthesis in mitochondrial subfractions of rat liver. Biochem J. 1969 Jun;113(2):429–440. doi: 10.1042/bj1130429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soboll S., Scholz R., Heldt H. W. Subcellular metabolite concentrations. Dependence of mitochondrial and cytosolic ATP systems on the metabolic state of perfused rat liver. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(2):377–390. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12387.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storey D. J., Shears S. B., Kirk C. J., Michell R. H. Stepwise enzymatic dephosphorylation of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate to inositol in liver. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):374–376. doi: 10.1038/312374a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOMLINSON R. V., BALLOU C. E. Myoinositol polyphosphate intermediates in the dephosphorylation of phytic acid by phytase. Biochemistry. 1962 Jan;1:166–171. doi: 10.1021/bi00907a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turk J., Wolf B. A., McDaniel M. L. Glucose-induced accumulation of inositol trisphosphates in isolated pancreatic islets. Predominance of the 1,3,4-isomer. Biochem J. 1986 Jul 1;237(1):259–263. doi: 10.1042/bj2370259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widnell C. C., Tata J. R. A procedure for the isolation of enzymically active rat-liver nuclei. Biochem J. 1964 Aug;92(2):313–317. doi: 10.1042/bj0920313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


