Abstract
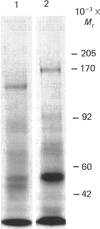
Several reports have indicated that Factor H has specific effects on certain cell populations, suggesting that Factor H receptors may exist. Lambris & Ross [(1982) J. Exp. Med. 155, 1400-1411] purified a protein from Raji B-lymphoblastoid cell culture supernatants, using Factor H-Sepharose affinity chromatography. This species appeared to consist of two disulphide-linked components each of Mr 50,000, with an additional 50,000-Mr chain attached non-covalently. The existence of cell-surface Factor H-binding proteins has now been re-investigated with 125I surface-labelled Raji and tonsil B cells. Non-ionic-detergent extracts of the cells, in 0.1% Nonidet P40/10 mM-sodium phosphate buffer, pH 7.4, were incubated with Factor H-Sepharose in the presence of proteinase inhibitors. After the beads had been washed, bound components were eluted with 50 mM-NaCl. A single radioactive species was eluted from the resin, which migrates identically with Factor H (apparent Mr 170,000) in SDS/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis under reducing and non-reducing conditions. Biosynthetic radiolabelling studies confirmed that this species was synthesized by Raji cells. Examination of culture supernatants from biosynthetically radiolabelled Raji cells showed again the presence of a single soluble species that bound to Factor H-Sepharose, but this species was of lower Mr (approx. 105,000) than the membrane-derived protein. The soluble form may be produced by proteolysis of the membrane form, or may be of separate origin. The similarity in size of the cell-surface protein to Factor H was initially confusing, but it is distinct from cell-surface Factor H on the basis of three criteria: (1) it is not recognized by anti-(Factor H) monoclonal antibodies MRC OX23 and MRC OX24, nor by polyclonal F(ab')2 anti-(Factor H); (2) it does not bind to Zn2+-chelate resin, whereas Factor H does; (3) cell-surface Factor H present on U937 cells does not bind to Factor H-Sepharose.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Fearon D. T. Regulation of the amplification C3 convertase of human complement by an inhibitory protein isolated from human erythrocyte membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5867–5871. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartung H. P., Hadding U., Bitter-Suermann D., Gemsa D. Release of prostaglandin E and thromboxane from macrophages by stimulation with factor H. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 May;56(2):453–458. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka K. Regulation of IgE synthesis. Annu Rev Immunol. 1984;2:159–182. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.02.040184.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambris J. D., Dobson N. J., Ross G. D. Release of endogenous C3b inactivator from lymphocytes in response to triggering membrane receptors for beta 1H globulin. J Exp Med. 1980 Dec 1;152(6):1625–1644. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.6.1625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambris J. D., Ross G. D. Characterization of the lymphocyte membrane receptor for factor H (beta 1H-globulin) with an antibody to anti-factor H idiotype. J Exp Med. 1982 May 1;155(5):1400–1411. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.5.1400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malhotra V., Sim R. B. Expression of complement factor H on the cell surface of the human monocytic cell line U937. Eur J Immunol. 1985 Sep;15(9):935–941. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830150913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Fox C. F. Surface-specific iodination of membrane proteins of viruses and eucaryotic cells using 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3alpha,6alpha-diphenylglycoluril. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 31;17(22):4807–4817. doi: 10.1021/bi00615a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Micklem K. J., Sim R. B., Sim E. Analysis of C3-receptor activity on human B-lymphocytes and isolation of the complement receptor type 2 (CR2). Biochem J. 1984 Nov 15;224(1):75–86. doi: 10.1042/bj2240075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Micklem K., Sim E., Sim R. B. The generation of active fragments of complement receptor type 2 by trypsin digestion. FEBS Lett. 1985 Sep 23;189(2):195–201. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)81022-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neauport-Sautes C., Rabourdin-Combe C., Fridman W. H. T-cell hybrids bear Fcgamma receptors and secrete suppressor immunoglobulin binding factor. Nature. 1979 Feb 22;277(5698):656–659. doi: 10.1038/277656a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pangburn M. K., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Complement C3 convertase: cell surface restriction of beta1H control and generation of restriction on neuraminidase-treated cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2416–2420. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ripoche J., Al Salihi A., Rousseaux J., Fontaine M. Isolation of two molecular populations of human complement factor H by hydrophobic affinity chromatography. Biochem J. 1984 Jul 1;221(1):89–96. doi: 10.1042/bj2210089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ripoche J., Day A. J., Willis A. C., Belt K. T., Campbell R. D., Sim R. B. Partial characterization of human complement factor H by protein and cDNA sequencing: homology with other complement and non-complement proteins. Biosci Rep. 1986 Jan;6(1):65–72. doi: 10.1007/BF01145180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schopf R. E., Hammann K. P., Scheiner O., Lemmel E. M., Dierich M. P. Activation of human monocytes by both human beta 1H and C3b. Immunology. 1982 Jun;46(2):307–312. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seya T., Turner J. R., Atkinson J. P. Purification and characterization of a membrane protein (gp45-70) that is a cofactor for cleavage of C3b and C4b. J Exp Med. 1986 Apr 1;163(4):837–855. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.4.837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sim E., Palmer M. S., Puklavec M., Sim R. B. Monoclonal antibodies against the complement control protein factor H (beta 1 H). Biosci Rep. 1983 Dec;3(12):1119–1131. doi: 10.1007/BF01120205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sim R. B., DiScipio R. G. Purification and structural studies on the complement-system control protein beta 1H (Factor H). Biochem J. 1982 Aug 1;205(2):285–293. doi: 10.1042/bj2050285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sim R. B., Malhotra V., Ripoche J., Day A. J., Micklem K. J., Sim E. Complement receptors and related complement control proteins. Biochem Soc Symp. 1986;51:83–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sunderland C. A., McMaster W. R., Williams A. F. Purification with monoclonal antibody of a predominant leukocyte-common antigen and glycoprotein from rat thymocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Feb;9(2):155–159. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsokos G. C., Inghirami G., Tsoukas C. D., Balow J. E., Lambris J. D. Regulation of immunoglobulin secretion by factor H of human complement. Immunology. 1985 Jul;55(3):419–426. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whaley K., Ruddy S. Modulation of C3b hemolytic activity by a plasma protein distinct from C3b inactivator. Science. 1976 Sep 10;193(4257):1011–1013. doi: 10.1126/science.948757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoon S. H., Fearon D. T. Characterization of a soluble form of the C3b/C4b receptor (CR1) in human plasma. J Immunol. 1985 May;134(5):3332–3338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]