Abstract
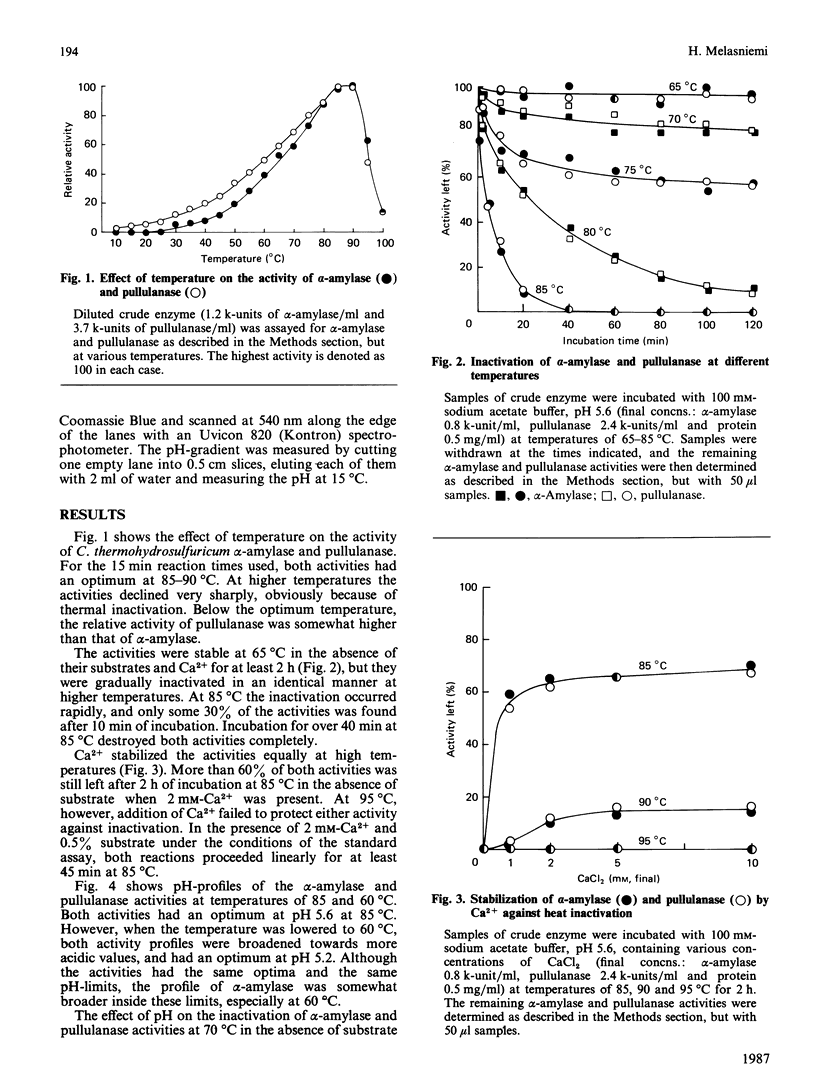
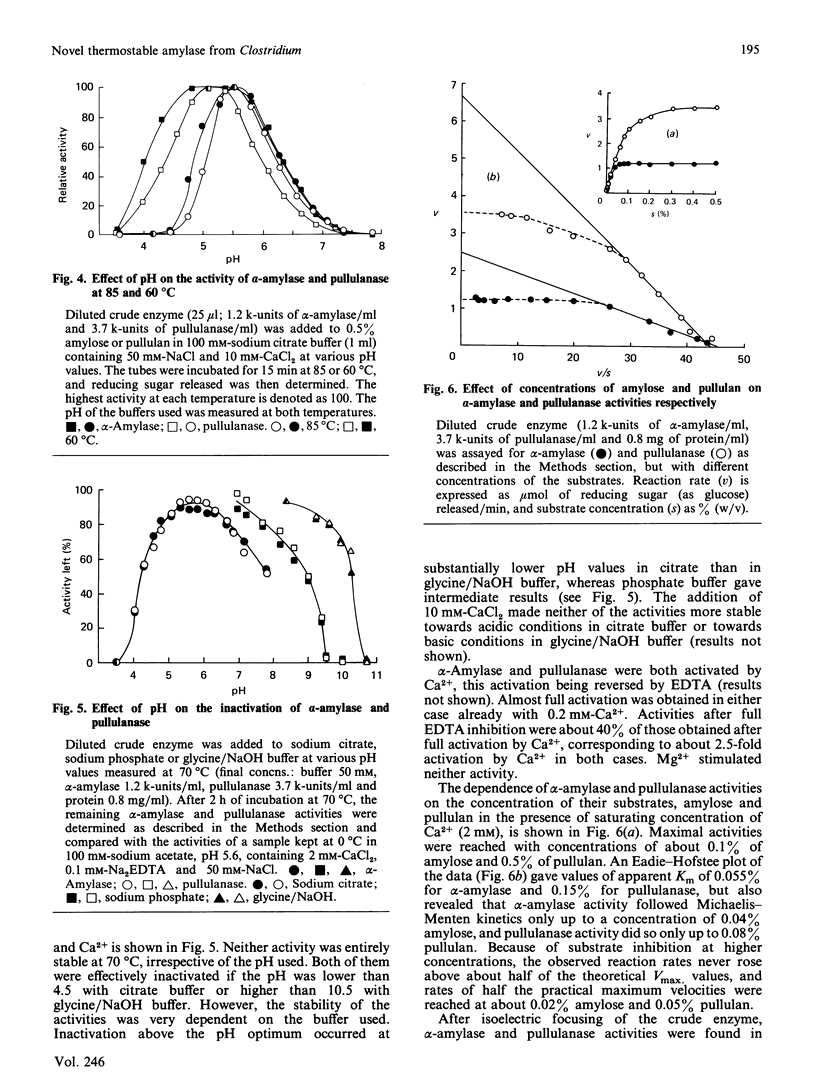
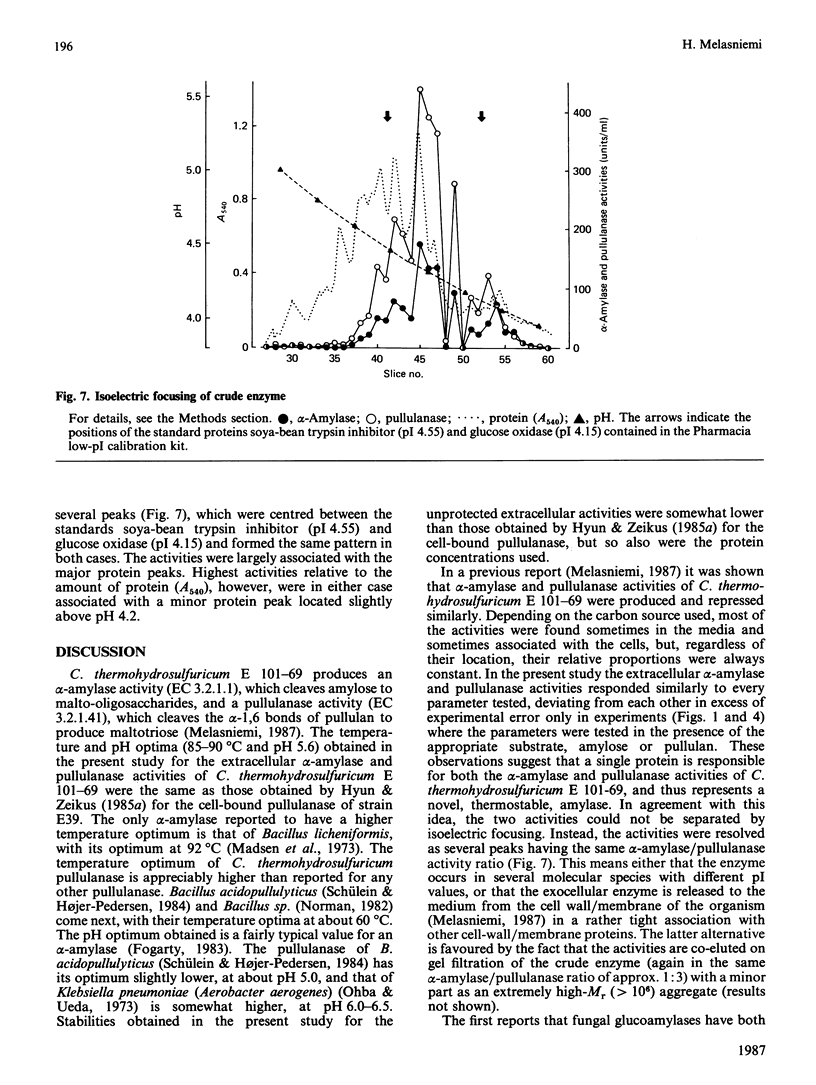
Thermostable extracellular alpha-amylase and pullulanase activities of Clostridium thermohydrosulfuricum E 101-69 were characterized in a crude enzyme preparation. The activities responded similarly to temperature and pH, with optima at 85-90 degrees C and pH 5.6. The activities were stable at 65 degrees C, but were inactivated gradually in an identical manner at higher temperatures in the absence of Ca2+ and substrate. Ca2+ stabilized both activities similarly at high temperatures. Ca2+ also stimulated both activities, whereas EDTA reversed this stimulation. The activities were similarly inactivated at pH extremes. The two activities distributed in the same way during isoelectric focusing. The results suggest that the two activities are properties of the same protein, representing a novel, thermostable, amylase.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Hollaus F., Sleytr U. On the taxonomy and fine structure of some hyperthermophilic saccharolytic Clostridia. Arch Mikrobiol. 1972;86(2):129–146. doi: 10.1007/BF00413368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyun H. H., Shen G. J., Zeikus J. G. Differential amylosaccharide metabolism of Clostridium thermosulfurogenes and Clostridium thermohydrosulfuricum. J Bacteriol. 1985 Dec;164(3):1153–1161. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.3.1153-1161.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyun H. H., Zeikus J. G. General Biochemical Characterization of Thermostable Pullulanase and Glucoamylase from Clostridium thermohydrosulfuricum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 May;49(5):1168–1173. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.5.1168-1173.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyun H. H., Zeikus J. G. Regulation and genetic enhancement of glucoamylase and pullulanase production in Clostridium thermohydrosulfuricum. J Bacteriol. 1985 Dec;164(3):1146–1152. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.3.1146-1152.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyun H. H., Zeikus J. G. Simultaneous and Enhanced Production of Thermostable Amylases and Ethanol from Starch by Cocultures of Clostridium thermosulfurogenes and Clostridium thermohydrosulfuricum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 May;49(5):1174–1181. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.5.1174-1181.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi H., Sano T., Ii K., Hizawa K., Yamanoi A., Otsuka T. Mixed connective tissue disease with fatal pulmonary hypertension. Acta Pathol Jpn. 1982 Nov;32(6):1121–1129. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.1982.tb02093.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCleary B. V., Anderson M. A. Hydrolysis of alpha-D-glucans and alpha-D-gluco-oligosaccharides by Cladosporium resinae glucoamylases. Carbohydr Res. 1980 Nov 1;86(1):77–96. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)84583-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAZUR J. H., ANDO T. The hydrolysis of glucosyl oligosaccharides with alpha-D-(1-4) and alpha-D-(1-6) bonds by fungal amyloglucosidase. J Biol Chem. 1960 Feb;235:297–302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAZUR J. H., KLEPPE K. The hydrolysis of alpha-D-glucosides by amyloglucosidase from Aspergillus niger. J Biol Chem. 1962 Apr;237:1002–1006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMOGYI M. Notes on sugar determination. J Biol Chem. 1952 Mar;195(1):19–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schülein M., Højer-Pedersen B. Characterization of a new class of thermophilic pullulanases from Bacillus acidopullulyticus. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1984;434:271–274. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1984.tb29842.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TSUJISAKA Y., FUKUMOTO J., YAMAMCTO T. Specificity of crystalline saccharogenic amylase of moulds. Nature. 1958 Mar 15;181(4611):770–771. doi: 10.1038/181770a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiegel J., Ljungdahl L. G., Rawson J. R. Isolation from soil and properties of the extreme thermophile Clostridium thermohydrosulfuricum. J Bacteriol. 1979 Sep;139(3):800–810. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.3.800-810.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


