Abstract
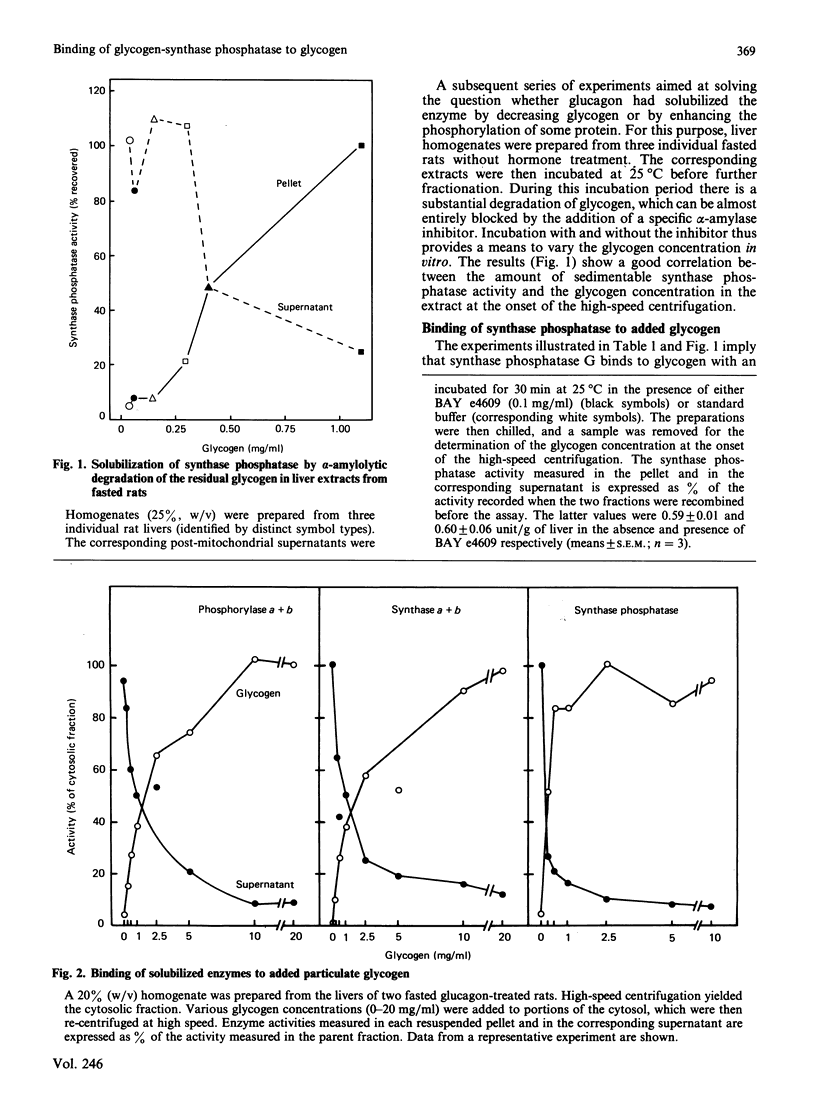
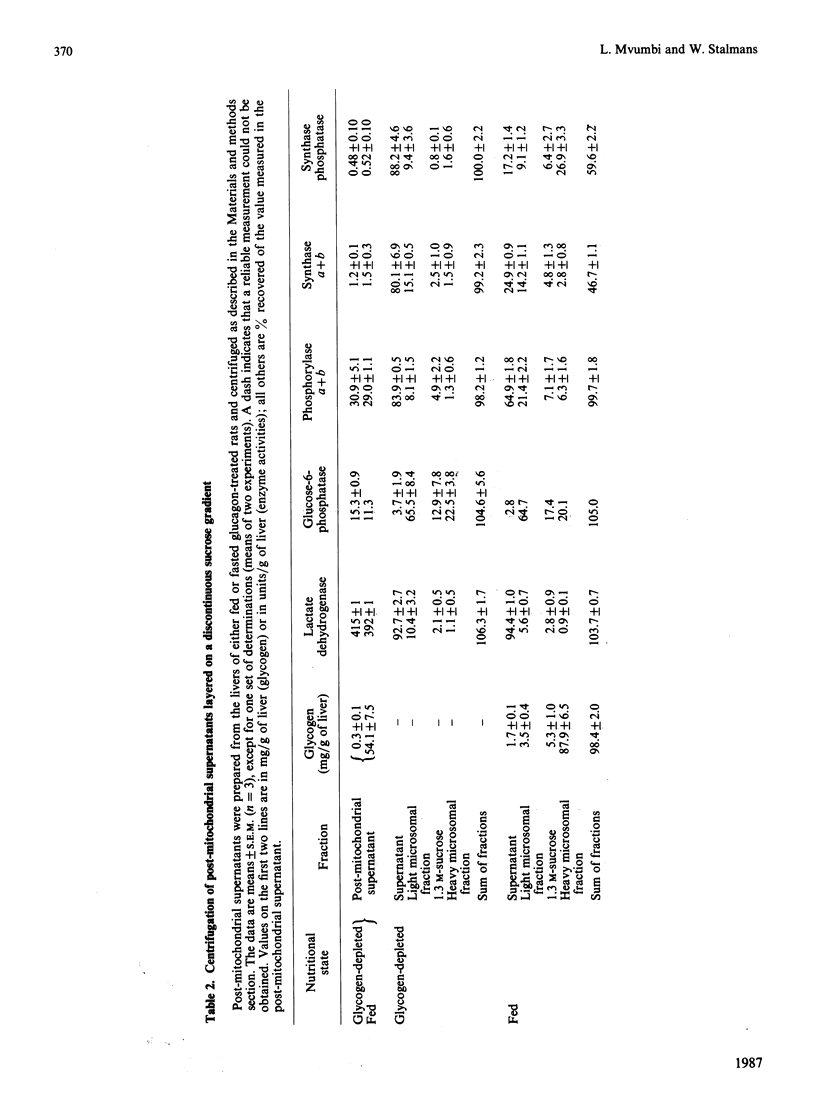
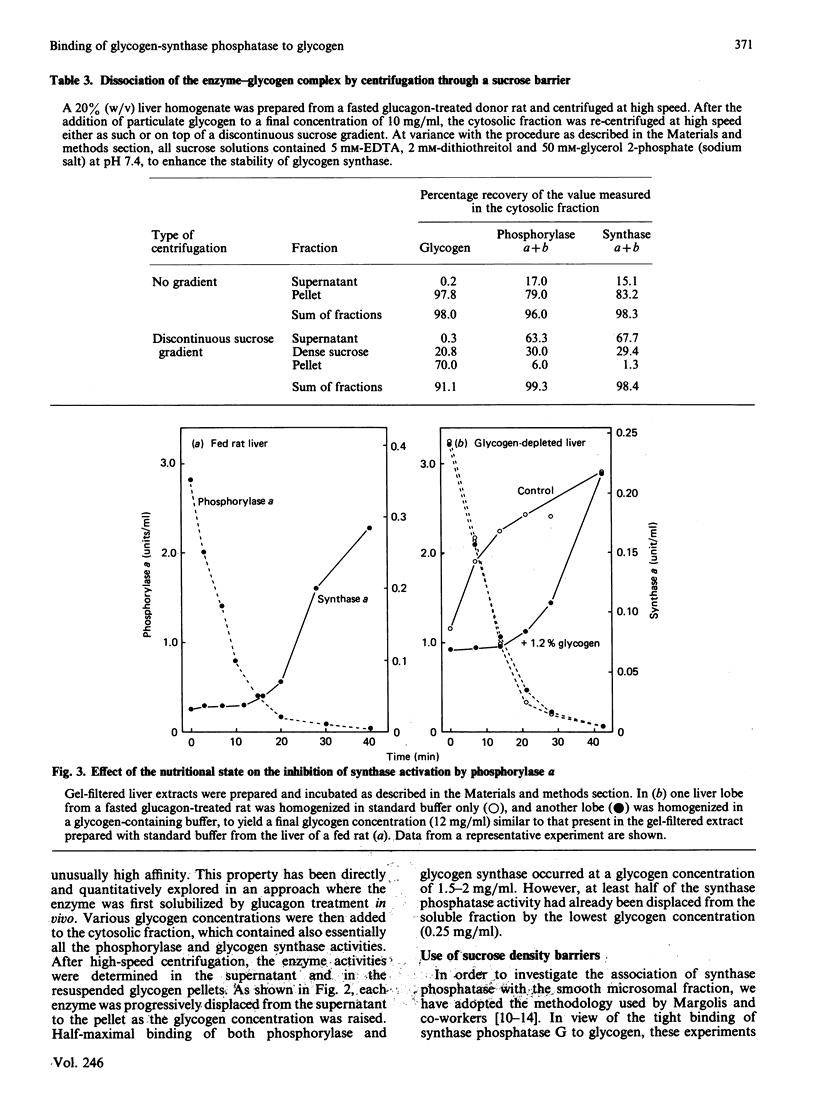
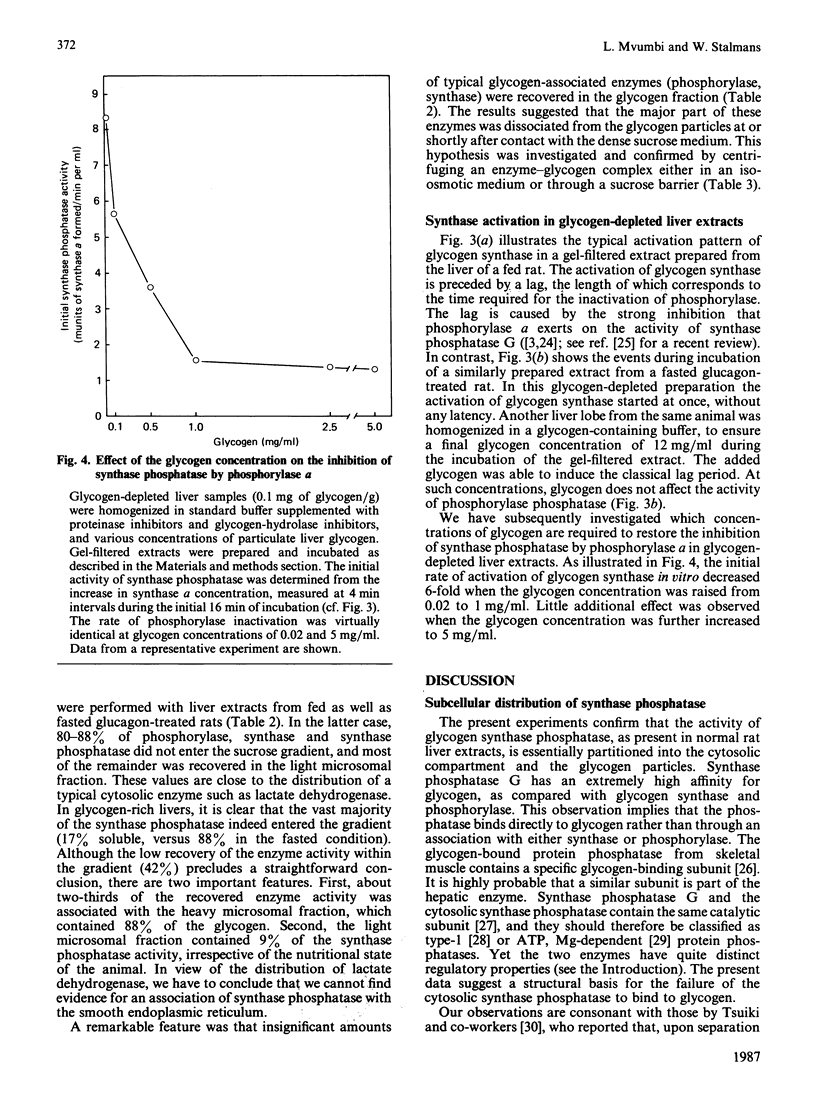
1. Post-mitochondrial supernatants were prepared from the livers of 24 h-fasted rats. Upon centrifugation at high speed, the major part of the glycogen-synthase phosphatase activity sedimented with the microsomal fraction. However, two approaches showed that the enzyme was associated with residual glycogen rather than with vesicles of the endoplasmic reticulum. Indeed, the activity was entirely solubilized when the remaining glycogen was degraded either by glucagon treatment in vivo or by alpha-amylolysis in vitro. No evidence could be found for an association of glycogen-synthase phosphatase with the smooth endoplasmic reticulum, as isolated with the use of discontinuous sucrose gradients. 2. After solubilization by glucagon treatment in vivo, synthase phosphatase could be transferred to glycogen particles with very high affinity. Half-maximal binding occurred at a glycogen concentration of about 0.25 mg/ml, whereas glycogen synthase and phosphorylase required 1.5-2 mg/ml. 3. In gel-filtered extracts prepared from glycogen-depleted livers, the activation of glycogen synthase was not inhibited at all by phosphorylase alpha. The inhibition was restored when the liver homogenates were prepared in a glycogen-containing buffer. The effect was half-maximal at a glycogen concentration of about 0.25 mg/ml, and virtually complete at 1 mg/ml. These findings explain long-standing observations that in fasted animals the liver contains appreciable amounts of both synthase and phosphorylase in the active form.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alemany S., Cohen P. Phosphorylase a is an allosteric inhibitor of the glycogen and microsomal forms of rat hepatic protein phosphatase-1. FEBS Lett. 1986 Mar 31;198(2):194–202. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80404-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alemany S., Pelech S., Brierley C. H., Cohen P. The protein phosphatases involved in cellular regulation. Evidence that dephosphorylation of glycogen phosphorylase and glycogen synthase in the glycogen and microsomal fractions of rat liver are catalysed by the same enzyme: protein phosphatase-1. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Apr 1;156(1):101–110. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09554.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bollen M., Dopere F., Goris J., Merlevede W., Stalmans W. The nature of the decreased activity of glycogen synthase phosphatase in the liver of the adrenalectomized starved rat. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Oct 1;144(1):57–63. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08430.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bollen M., Plana M., Itarte E., Stalmans W. Effect of phosphorylation by different protein kinases on the behaviour of glycogen synthase as a substrate for hepatic synthase phosphatases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Sep 30;139(3):1033–1039. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80281-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bollen M., Stalmans W. The hepatic defect in glycogen synthesis in chronic diabetes involves the G-component of synthase phosphatase. Biochem J. 1984 Jan 15;217(2):427–434. doi: 10.1042/bj2170427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curnow R. T., Nuttall F. Q. Effect of prostaglandin E 1 administration on the liver glycogen synthetase and phosphorylase systems. J Biol Chem. 1972 Mar 25;247(6):1892–1898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallner G. Isolation of rough and smooth microsomes--general. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:191–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doperé F., Vanstapel F., Stalmans W. Glycogen-synthase phosphatase activity in rat liver. Two protein components and their requirement for the activation of different types of substrate. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Feb;104(1):137–146. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04409.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith P. K., Stetten M. R. Different developmental changes in latency for two functions of a single membrane bound enzyme: glucose-6-phosphatase activities as a function of age. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Mar 7;583(2):133–147. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(79)90421-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIZUKURI S., LARNER J. STUDIES ON UDPG: ALPHA-1,4-GLUCAN ALPHA-4-GLUCOSYLTRANSFERASE. VII. CONVERSION OF THE ENZYME FROM GLUCOSE-6-PHOSPHATE-DEPENDENT TO INDEPENDENT FORM IN LIVER. Biochemistry. 1964 Nov;3:1783–1788. doi: 10.1021/bi00899a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hue L., Bontemps F., Hers H. The effects of glucose and of potassium ions on the interconversion of the two forms of glycogen phosphorylase and of glycogen synthetase in isolated rat liver preparations. Biochem J. 1975 Oct;152(1):105–114. doi: 10.1042/bj1520105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutson N. J., Brumley F. T., Assimacopoulos F. D., Harper S. C., Exton J. H. Studies on the alpha-adrenergic activation of hepatic glucose output. I. Studies on the alpha-adrenergic activation of phosphorylase and gluconeogenesis and inactivation of glycogen synthase in isolated rat liver parenchymal cells. J Biol Chem. 1976 Sep 10;251(17):5200–5208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingebritsen T. S., Cohen P. Protein phosphatases: properties and role in cellular regulation. Science. 1983 Jul 22;221(4608):331–338. doi: 10.1126/science.6306765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langdon D. R., Curnow R. T. Impaired glycogenic substrate activation of glycogen synthase is associated with depressed synthase phosphatase activity in diabetic rat liver. Diabetes. 1983 Dec;32(12):1134–1140. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.12.1134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis R. N., Cardell R. R., Curnow R. T. Association of glycogen synthase phosphatase and phosphorylase phosphatase activities with membranes of hepatic smooth endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol. 1979 Nov;83(2 Pt 1):348–356. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.2.348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis R. N., Curnow R. T. Effects of dexamethasone administration on hepatic glycogen synthesis and accumulation in adrenalectomized fasted rats. Endocrinology. 1984 Aug;115(2):625–629. doi: 10.1210/endo-115-2-625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis R. N., Curnow R. T. The role of insulin and glucocorticoids in the regulation of hepatic glycogen metabolism: effect of fasting, refeeding, and adrenalectomy. Endocrinology. 1983 Dec;113(6):2113–2119. doi: 10.1210/endo-113-6-2113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis R. N., Selawry H. P., Curnow R. T. Regulation of hepatic glycogen metabolism: effects of diabetes, insulin infusion, and pancreatic islet transplantation. Metabolism. 1985 Jan;34(1):62–68. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(85)90062-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer F., Heilmeyer L. M., Jr, Haschke R. H., Fischer E. H. Control of phosphorylase activity in a muscle glycogen particle. I. Isolation and characterization of the protein-glycogen complex. J Biol Chem. 1970 Dec 25;245(24):6642–6648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mvumbi L., Bollen M., Stalmans W. Calcium ions and glycogen act synergistically as inhibitors of hepatic glycogen-synthase phosphatase. Biochem J. 1985 Dec 15;232(3):697–704. doi: 10.1042/bj2320697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mvumbi L., Doperé F., Stalmans W. The inhibitory effect of phosphorylase a on the activation of glycogen synthase depends on the type of synthase phosphatase. Biochem J. 1983 May 15;212(2):407–416. doi: 10.1042/bj2120407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuttall F. Q., Theen J. W., Niewoehner C., Gilboe D. P. Response of liver glycogen synthase and phosphorylase to in vivo glucose and glucose analogues. Am J Physiol. 1983 Nov;245(5 Pt 1):E521–E527. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1983.245.5.E521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalmans W., Bollen M., Mvumbi L. Control of glycogen synthesis in health and disease. Diabetes Metab Rev. 1987 Jan;3(1):127–161. doi: 10.1002/dmr.5610030107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalmans W. The role of the liver in the homeostasis of blood glucose. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1976;11:51–97. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152811-9.50009-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strålfors P., Hiraga A., Cohen P. The protein phosphatases involved in cellular regulation. Purification and characterisation of the glycogen-bound form of protein phosphatase-1 from rabbit skeletal muscle. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Jun 3;149(2):295–303. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08926.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan A. W., Nuttall F. Q. Evidence for the non-identity of proteins having synthase phosphatase, phosphorylase phosphatase and histone phosphatase activity in rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jan 12;522(1):139–150. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(78)90330-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van de Werve G., Jeanrenaud B. Synthase activation is not a prerequisite for glycogen synthesis in the starved liver. Am J Physiol. 1984 Aug;247(2 Pt 1):E271–E275. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1984.247.2.E271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandebroeck A., Bollen M., De Wulf H., Stalmans W. An assessment of the importance of intralysosomal and of alpha-amylolytic glycogenolysis in the liver of normal rats and of rats with a glycogen-storage disease. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Dec 16;153(3):621–628. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09345.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanstapel F., Doperé F., Stalmans W. The role of glycogen synthase phosphatase in the glucocorticoid-induced deposition of glycogen in foetal rat liver. Biochem J. 1980 Nov 15;192(2):607–612. doi: 10.1042/bj1920607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanson J. C., Drochmans P. Rabbit skeletal muscle glycogen. A morphological and biochemical study of glycogen beta-particles isolated by the precipitation-centrifugation method. J Cell Biol. 1968 Jul;38(1):130–150. doi: 10.1083/jcb.38.1.130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


