Abstract
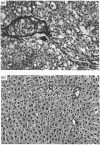
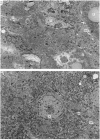
Malotilate is a new drug suggested for use in chronic liver diseases. It is shown here to prevent liver damage caused by CCl4. The concomitant administration of malotilate with CCl4 significantly decreased hydroxyproline accumulation in the liver, liver prolyl 4-hydroxylase and liver and serum galactosylhydroxylysyl glucosyltransferase activities. However, it had no effect on the daily urinary hydroxyproline excretion or the hydroxyproline content of the skin, liver or lungs in normal young growing rats. It also had no specific inhibitory effect on hydroxyproline synthesis or secretion in fibroblast cultures, and did not affect the amount of procollagen-alpha 1(I)-specific mRNAs in these cultures. Thus it seems to have no direct inhibitory effect on collagen metabolism. In addition to inhibition of liver collagen accumulation, malotilate was also able to prevent the development of morphological changes in the liver such as focal necrosis, fatty infiltration and inflammatory changes. It also normalized almost completely the standard liver-function tests. It is possible that malotilate may prevent excessive collagen deposition by inhibiting the inflammation caused by CCl4-induced liver damage.
Full text
PDF


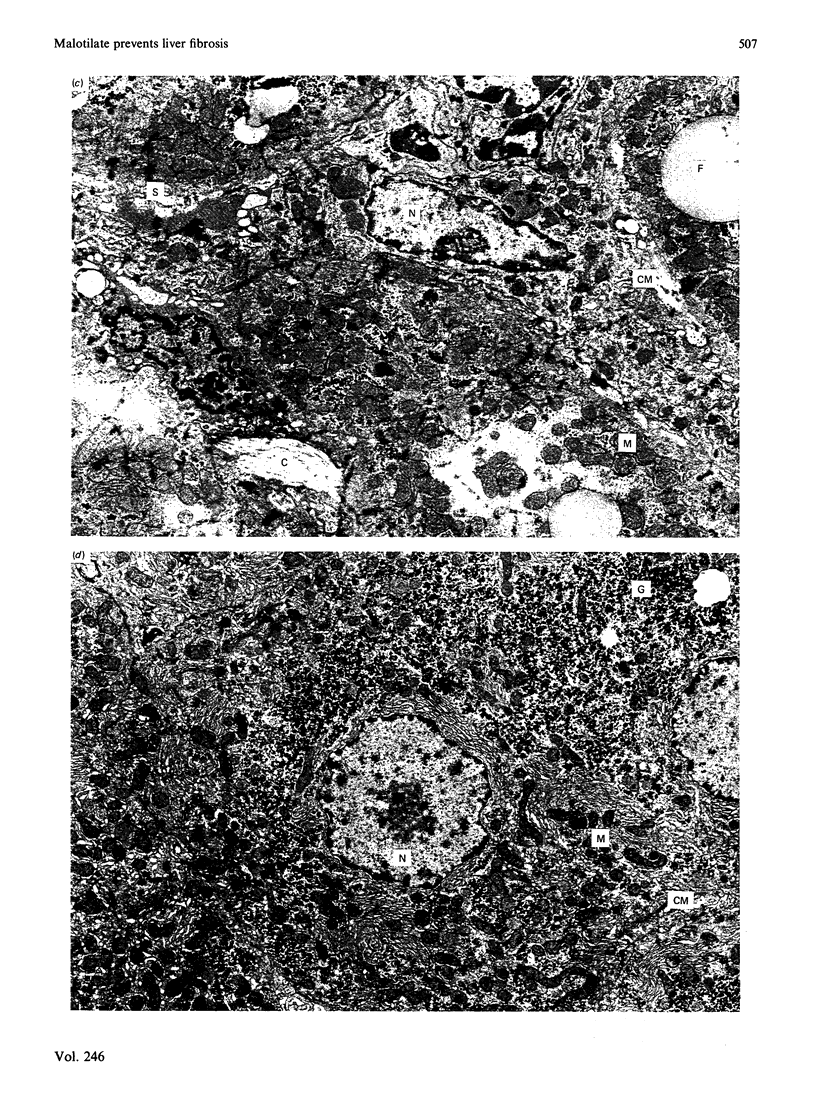


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ATERMAN K. Studies in fibrosis of the liver induced by carbon tetrachloride. I. Relation between hepatocellular injury and new formation of fibrous tissue. AMA Arch Pathol. 1954 Jan;57(1):1–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anttinen H. Collagen glucosyltransferases activity in human serum. Clin Chim Acta. 1977 Jun 15;77(3):323–330. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(77)90236-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anttinen H., Ryhänen L., Puistola U., Arranto A., Oikarinen A. Decrease in liver collagen accumulation in carbon tetrachloride-injured and normal growing rats upon administration of zinc. Gastroenterology. 1984 Mar;86(3):532–539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashburn L. L., Endicott K. M., Daft F. S., Lillie R. D. The Nonportal Distribution of the Trabeculae in Dietary Cirrhosis of Rats and in Carbon Tetrachloride Cirrhosis of Rats and Guinea-Pigs. Am J Pathol. 1947 Jan;23(1):159–171. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu M. L., Myers J. C., Bernard M. P., Ding J. F., Ramirez F. Cloning and characterization of five overlapping cDNAs specific for the human pro alpha 1(I) collagen chain. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 11;10(19):5925–5934. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.19.5925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard R. W., Matthew W. T., Dubowik D. A. Factors influencing the determination of DNA with indole. Anal Biochem. 1970 Nov;38(1):190–201. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90169-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juva K., Prockop D. J. Modified procedure for the assay of H-3-or C-14-labeled hydroxyproline. Anal Biochem. 1966 Apr;15(1):77–83. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90249-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawata S., Sugiyama T., Seki K., Tarui S., Okamoto M., Yamano T. Stimulatory effect of cytochrome b5 induced by p-nitroanisole and diisopropyl 1,3-dithiol-2-ylidenemalonate on rat liver microsomal drug hydroxylations. J Biochem. 1982 Jul;92(1):305–313. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kivirikko K. I., Laitinen O., Prockop D. J. Modifications of a specific assay for hydroxyproline in urine. Anal Biochem. 1967 May;19(2):249–255. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(67)90160-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Hernandez A. The hepatic extracellular matrix. I. Electron immunohistochemical studies in normal rat liver. Lab Invest. 1984 Jul;51(1):57–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Hernandez A. The hepatic extracellular matrix. II. Electron immunohistochemical studies in rats with CCl4-induced cirrhosis. Lab Invest. 1985 Aug;53(2):166–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myllylä R., Risteli L., Kivirikko K. I. Assay of collagen-galactosyltransferase and collagen-glucosyltransferase activities and preliminary characterization of enzymic reactions with transferases from chick-embryo cartilage. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Apr 1;52(3):401–410. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb04008.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oikarinen J., Ryhänen L. Cortisol decreases the concentration of translatable type-I procollagen mRNA species in the developing chick-embryo calvaria. Biochem J. 1981 Sep 15;198(3):519–524. doi: 10.1042/bj1980519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prockop D. J., Kivirikko K. I., Tuderman L., Guzman N. A. The biosynthesis of collagen and its disorders (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1979 Jul 5;301(1):13–23. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197907053010104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUBIN E., HUTTERER F., POPPER H. Cell proliferation and fiber formation in chronic carbon tetrachloride intoxication. A morphologic and chemical study. Am J Pathol. 1963 Jun;42:715–728. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUBINSTEIN H. M., PRYCE J. D. The colorimetric estimation of alpha-amino nitrogen in tissue fluids. J Clin Pathol. 1959 Jan;12(1):80–84. doi: 10.1136/jcp.12.1.80. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risteli J., Kivirikko K. I. Intracellular enzymes of collagen biosynthesis in rat liver as a function of age and in hepatic injury induced by dimethylnitrosamine. Changes in prolyl hydroxylase, lysyl hydroxylase, collagen galactosyltransferase and collagen glucosyltransferase activities. Biochem J. 1976 Aug 15;158(2):361–367. doi: 10.1042/bj1580361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risteli J., Tuderman L., Kivirikko K. I. Intracellular enzymes of collagen biosynthesis in rat liver as a function of age and in hepatic injury induced by dimethylnitrosamine. Purification of rat prolyl hydroxylase and comparison of changes in prolyl hydroxylase activity with changes in immunoreactive prolyl hydroxylase. Biochem J. 1976 Aug 15;158(2):369–376. doi: 10.1042/bj1580369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rojkind M., Pérez-Tamayo R. Liver fibrosis. Int Rev Connect Tissue Res. 1983;10:333–393. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-363710-9.50012-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seyer J. M. Mediators of increased collagen synthesis in fibrosing organs. Fundam Appl Toxicol. 1985 Apr;5(2):228–239. doi: 10.1016/0272-0590(85)90071-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uitto J., Ryhänen L., Tan E. M., Oikarinen A. I., Zaragoza E. J. Pharmacological inhibition of excessive collagen deposition in fibrotic diseases. Fed Proc. 1984 Oct;43(13):2815–2820. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl S. M. Host immune factors regulating fibrosis. Ciba Found Symp. 1985;114:175–195. doi: 10.1002/9780470720950.ch12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weibel E. R., Stäubli W., Gnägi H. R., Hess F. A. Correlated morphometric and biochemical studies on the liver cell. I. Morphometric model, stereologic methods, and normal morphometric data for rat liver. J Cell Biol. 1969 Jul;42(1):68–91. doi: 10.1083/jcb.42.1.68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]