Abstract
Infection of H-2b mice with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV) generates an H-2Db-restricted cytotoxic T-lymphocyte (CTL) response whose subdominant component is directed against the GP92-101 (CSANNSHHYI) epitope. The aim of this study was to identify the functional parameters accounting for this subdominance. We found that the two naturally occurring (genetically encoded and posttranslationally modified) forms of LCMV GP92-101 were immunogenic, did not act as T-cell antagonists, and bound efficiently to but were unable to form stable complexes with H-2Db, a crucial factor for immunodominance. Thus, the H-2Db-restricted subdominant CTL response to LCMV resulted not from altered T-cell activation but from impaired major histocompatibility complex presentation properties.
Infection of mice with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV) induces a cellular immune response mediated mainly by CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL). In H-2b mice, the immunodominant component of this CTL response is directed against three H-2Db-restricted epitopes located in the nucleoprotein (NP) or glycoprotein (GP): NP396-404 (FQPQNGQFI), GP33-41 (KAVYNFATC), and GP276-286 (SGVENPGGYCL) (5, 13, 17, 21). More recently, a subdominant component has been identified in the context of H-2Db restriction, which is directed against GP92-101 (CSANNSHHYI) (8, 18, 24). This epitope bears a glycosylation motif (NXS) which is N glycosylated in the mature viral protein (25) and can be subject to posttranslational modification. The genetically encoded (N95) and posttranslationally modified (D95) forms of LCMV GP92-101 are copresented at the surfaces of LCMV-infected H-2b cells (11).
Understanding the mechanisms responsible for the subdominance (versus immunodominance) of this viral antigen is an important goal, not only for a better knowledge of LCMV pathogenesis and its consequent immune response but also for future developments of antiviral vaccination strategies based on the use of subdominant epitopes (22, 24). The aim of this study was therefore to identify the functional parameters that may explain the H-2Db-restricted subdominant component of the CTL response against LCMV.
The two naturally presented forms (N95 and D95) of LCMV GP92-101 are subdominant antigens.
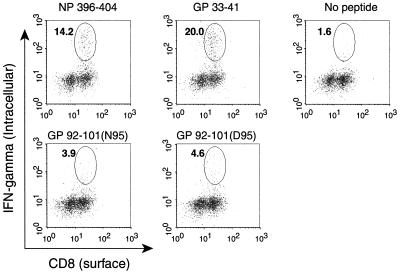
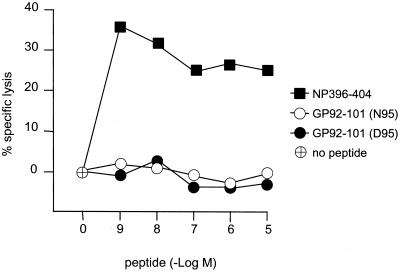
No efficient primary CTL response has been detected against the genetically encoded form N95 of GP92-101 following LCMV infection of H-2b mice (18, 24). However, the ability of the other naturally presented form (D95) of LCMV GP92-101 to induce an anti-LCMV primary CTL response has never been tested. C57BL/6 (H-2b) mice were infected with 2 × 105 PFU of LCMV Arm intraperitoneally. At the peak of the primary response (day 8), spleen cells were explanted and then analyzed in two functional assays. First, an intracellular cytokine staining assay was performed to determine the frequency of CD8+ T cells specific for the LCMV epitopes. Spleens cells were cultured for 5 h in the absence (no stimulation) or presence of peptides representing the LCMV epitopes, stained for surface CD8 and intracellular gamma interferon (IFN-γ), and analyzed by flow cytometry as previously described (16). As illustrated in Fig. 1, we confirmed previous studies (16) by showing that the percentage of the CD8+ T-cell population against the two immunodominant epitopes NP396-404 and GP33-41 was high (13.0% ± 2.9% and 20.2% ± 4.1%, respectively) and that the percentage of the population against the N95 form of GP92-101 was low (3.5% ± 1.6%). We were also able to detect the presence of a small number of CD8+ T cells specific for the D95 form of GP92-101 (4.0% ± 0.8%), comparable to that of N95-specific CTL. The gated cells in the absence of stimulation (no peptide) represented 3.0% ± 1.1% of the CD8+ T cells. These values are the means ± standard errors from five mice. Second, a classical 51Cr release assay was performed to measure the lytic activity of bulk splenocytes in response to target cells pulsed with the LCMV epitopes. As shown in Fig. 2, primary bulk splenocytes from LCMV-infected C57BL/6 mice efficiently lysed target cells coated with the immunodominant epitope NP396-404 but not cells coated with either the N95 or D95 form of GP92-101, even at the highest concentration tested. These findings allow us to extend the subdominant properties of LCMV GP92-101 previously observed for its genetically encoded form, N95 (16, 18, 24), to its posttranslationally modified form, D95. Clearly, however, the subdominance of LCMV GP92-101 does not result from a lack of immunogenicity. Indeed, this viral epitope can efficiently sensitize H-2b target cells to lysis by secondary CTL obtained after in vitro stimulation of spleen cells from LCMV-infected mice with the synthetic peptide corresponding to the genetically encoded sequence (24). Also, LCMV GP92-101-specifc CTL were successfully generated after immunization of C57BL/6 mice with synthetic peptides followed by in vitro restimulation (11; also this study). The GP92-101-specific CTL we generated against N95 or D95 behaved differently. The anti-N95 CTL were not specific for the N95 form used as an immunogen, since they also recognized the D95 form, even more efficiently (about 100-fold; the 50% effective concentration [EC50] of anti-N95 against N95 was 1 nM, while that of anti-N95 against D95 was 0.01 nM). In contrast, the anti-D95 CTL recognized specifically and efficiently (EC50 = 0.03 nM) the D95 peptide used as an immunogen but not the N95 form of the viral antigen (or only at very high concentrations, i.e., an EC50 of >1,000 nM). Regardless of the specificity profile, these results demonstrate that fully functional anti-GP92-101 CTL precursors exist in the T-cell repertoire of H-2b mice.
FIG. 1.
Frequency of CD8+ CTL specific for the N95 and D95 forms of GP92-101 during primary LCMV infection of C57BL/6 mice. C57BL/6 (H-2b) mice were infected with LCMV Arm (2 × 105 PFU) intraperitoneally. At the peak of the primary response (day 8), spleen cells were explanted, cultured in vitro for 5 h either with or without the indicated peptide (0.1 μg/ml), and stained for surface CD8 with anti-CD8 α-Red 613 (Gibco BRL) and for intracellular IFN-γ with anti-IFN-γ XMG1.2-fluorescein isothiocyanate (Pharmingen), by following the procedure described by Murali-Krishna et al. (16). The numbers indicate the percentage of CD8+ cells that were positive for intracellular IFN-γ. Results shown are from a representative individual mouse from a group of five.
FIG. 2.
Sensitization by the LCMV NP396-404 and GP92-101 epitopes of H-2b target cells to lysis by primary CTL. 51Cr-labeled H-2b target cells were incubated in microtiter plates at 37°C with increasing concentrations of GP92-101 N95 and D95 and of NP396-404 used as a positive control. Bulk splenocytes from C57BL/6 mice infected with LCMV 8 days before the experiment were added at an effector/target ratio of 50:1. After 4 h of incubation at 37°C, the 51Cr content of supernatants was determined. The specific lysis was calculated as follows: 100 × [(experimental − spontaneous release)/(total − spontaneous release)].
The N95 form of LCMV GP92-101 does not inhibit the lytic activity of D95-specific CTL.
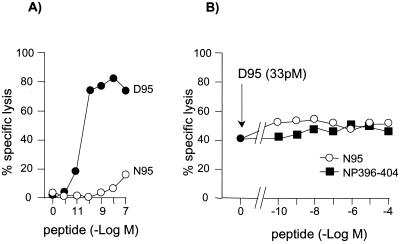
Natural variants generated from multiple processing or mutation of the viral antigen can act as T-cell receptor (TCR) antagonists (12), leading to viral evasion from (1, 14, 15) or immunoregulation of (2) the antiviral CTL response. The question arose of whether copresentation of the two forms of LCMV GP92-101 might be a cause of its subdominance, by means of TCR antagonism (11). The possibility that N95 acts as an antagonist of anti-D95 CTL and may play a role in the regulation of the anti-GP92-101 CTL response was therefore examined. We used a cold target inhibition assay of TCR antagonism (3) in which 51Cr-labeled RMA (a murine H-2b T-lymphoma cell line) were pulsed with a suboptimal concentration of D95 and cold RMA were pulsed with graded concentrations of N95 or control peptide NP396-404. Target cells were washed to remove excess peptide and then mixed with D95-specific CTL. As shown in Fig. 3B, no inhibition of lysis of D95-coated target cells was observed in the presence of NP396-404 (as expected) or N95, even at the highest concentration tested, indicating that N95 was unable to antagonize the lytic activity of anti-D95 CTL. This finding indicated that TCR antagonism was not a valid hypothesis.
FIG. 3.
Activation of anti-LCMV GP92-101, D95-specific CTL. (A) Agonism assay. 51Cr-labeled RMA were pulsed with increasing concentrations of D95 or N95 peptides (10−12 to 10−7 M), and D95-specific CTL were added at an effector/target ratio of 10:1. After 4 h of incubation at 37°C, the 51Cr content of supernatants was determined. (B) Antagonism assay (cold target inhibition assay). 51Cr-labeled RMA were pulsed with a suboptimal concentration (33 pM) of the D95 peptide, and cold RMA were pulsed with increased concentrations (10−10 to 10−4 M) of N95 or NP396-404 for 1 h at 37°C. After three washes in culture medium to remove excess free peptides, 51Cr-labeled RMA and cold RMA were mixed at a 1:3 ratio. CTL were then added at a ratio of 10:1 with 51Cr-labeled RMA. After 4 h at 37°C, the supernatant was analyzed as described above.
Thus, neither a lack of a T-cell response nor altered TCR activation (antagonism) may account for the subdominant CTL response to LCMV GP92-101. An alternative mechanism should therefore be considered. A protective CTL response to a subdominant epitope can be influenced by the overall spectrum of viral peptides generated within infected cells (6). However, no efficient primary CTL response is raised against LCMV GP92-101 even in mice infected with the GPV+NPV variant of LCMV, which lacks all three immunodominant H-2Db epitopes (18), strongly suggesting that intrinsic properties of GP92-101 rather than competition with other antigens may be responsible for its subdominance.
Within the infected cells, major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I presentation of the viral antigen is a crucial step which may control its dominance or subdominance. Two distinct parameters must be considered: (i) the capacity of the peptide to bind to the MHC molecule (binding affinity) and (ii) the ability of the peptide, once bound to the MHC, to form a stable complex with the MHC (complex stability). These two parameters were therefore analyzed.
Both the N95 and D95 forms of LCMV GP92-101 bind to but dissociate rapidly from H-2Db.
By screening of the LCMV glycoprotein sequences for H-2Db motif-fitting peptides, the nonmodified form (N95) of GP92-101 was previously identified as a high (50% inhibitory concentration [IC50], <50 nM) (8) or intermediate (IC50, 50 to 500 nM) (24) H-2Db binder depending on the biochemical assay used. Interestingly, in both studies, the measured affinity of GP92-101 for H-2Db was about 1 log better than that of the immunodominant epitope GP33-41. However, the latter epitope displays somewhat controversial MHC binding properties, and the correlation between its affinity and its immunogenicity remains unclear (8, 9, 24). Nevertheless, the difference observed between the two epitopes suggests that a nonimmunodominant epitope (GP92-101) can compete efficiently with a known immunodominant epitope (GP33-41) for binding to MHC. Furthermore, binding of GP92-101 to H-2Db is not affected by mutation of N95 to D95 (11), a result predictable since the side chain of residues at P4 of H-2Db-restricted peptides has minimal interaction with the MHC binding groove (26). Thus, these data rule out MHC binding deficiency and intermolecular competition for MHC class I presentation as factors responsible for the subdominance of GP92-101.
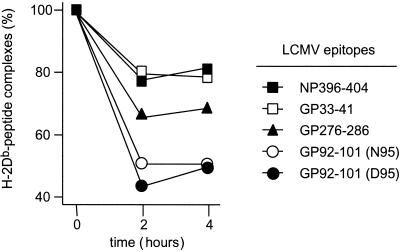
The stability of peptide-MHC complexes is another important binding parameter which has been shown to correlate with the immunogenicity of the antigenic peptide (23). We therefore analyzed the stability of the complexes formed between LCMV GP92-101 and H-2Db and compared it with that obtained with the three immunodominant H-2Db-restricted LCMV epitopes NP396-404, GP33-41, and GP276-286. For that, the RMA-S mutant cells previously cultivated at 26°C were pulsed with the different peptides (1 μM) for 4 h at 37°C, washed, resuspended in culture medium, and incubated for different periods of time at 37°C. At this temperature, peptides unable to form stable complexes with MHC molecules rapidly dissociate and the empty MHC molecules disappear from the cell surface, whereas stable complexes in which peptides are tightly bound to the MHC remain at the cell surface. As shown in Fig. 4 and summarized in Table 1, the two immunodominant epitopes NP396-404 and GP33-41 formed very stable complexes with H-2Db, in agreement with previous studies (6). In contrast, the complexes between H-2Db and any of the two forms of GP92-101 dissociated rapidly, with a half-life of less than 2 h. Interestingly, GP276-286, which induces an immunodominant but moderate CTL response (7, 16), formed molecular complexes of intermediate stability with H-2Db. Thus, the inability to form stable complexes with the MHC molecule is likely the main factor responsible for the subdominance of the LCMV GP92-101 epitope. However, the contribution of other factors, such as an intermediate binding affinity (24), to subdominance cannot be excluded.
FIG. 4.
Stability of the complexes formed between H-2Db and the LCMV epitopes. RMA-S previously incubated at 26°C were pulsed with 1 μM peptide for 4 h at 37°C. After three washes at 4°C in phosphate-buffered saline containing 2% fetal calf serum, cells were resuspended in medium without fetal calf serum and then transferred to 37°C. At different times (0, 2, and 4 h), aliquots (2.5 × 105 cells) were removed and stained for H-2Db expression using the 28-14-8S mouse monoclonal antibody. Cells were then stained with a fluorescent (fluorescein isothiocyanate) secondary anti-mouse antibody and analyzed by flow cytometry. Results are expressed as percent fluorescence (100% at 0 h).
TABLE 1.
Characteristics of the H-2Db-restricted primary CTL response to LCMV infection
| LCMV epitope
|
Primary CTL response
|
MHC binding affinity | Peptide-MHC complex stability | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Status | CTL frequency | Efficiency | ||
| NP396-404 | Immunodominant | High (16; also this study) | Strong (21) | High (5, 8, 24) | Strong |
| GP33-41 | Immunodominant | High (16; also this study) | Strong (13) | Intermediate/weak (5, 8, 24) | Strong |
| GP276-286 | Immunodominant | Moderate (16) | Moderate (7, 16) | High (5, 8, 24) | Moderate |
| GP92-101 (N95) | Subdominant | Low (16; also this study) | Inefficient (8, 18, 24) | High/intermediate (8, 11, 24) | Weak |
| GP92-101 (D95) | Subdominant | Low (this study) | Inefficient (this study) | High (8, 11) | Weak |
The use of subdominant (versus dominant) epitopes presents a certain number of advantages for antiviral vaccination (22). Our demonstration that the H-2Db-restricted subdominant component of the cytotoxic T-cell response against LCMV does not result from a lack of a T-cell response or altered T-cell activation but from impaired MHC presentation properties of GP92-101 is of interest not only for fundamental knowledge but also for potential therapeutic application. Indeed, manipulating an antigenic sequence to compensate for a defect in T-cell activation is far from mastered, since the rules governing TCR recognition are not fully elucidated. In contrast, the structural rules governing peptide-MHC interactions are now well established and can be manipulated for therapeutic purposes (10). For example, enhanced MHC presentation of viral or tumor antigens can be successfully achieved by modifying MHC anchor residues (20, 22). van der Most and coworkers showed that vaccination with LCMV GP92-101 conferred protective immunity on mice (24). The two anchor residues (N at P5 and I at the C terminus) of LCMV GP92-101 are already optimal for H-2Db binding (19). However, other structural elements, such as peptide conformation (4) or nonanchor residues (8), also control the presentation of viral peptides by H-2Db. Identification and manipulation of these elements will help in the design of a modified analog of LCMV GP92-101 with improved MHC presentation properties (more specifically MHC complex stability) and thus with potentially increased immunogenicity.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by grants from the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique and Association pour la Recherche sur le Cancer (contract 5485).
We thank J.-C. Guery for his kind gift of anti-IFN-γ XMG1.2-fluorescein isothiocyanate antibody.
REFERENCES
- 1.Bertoletti A, Sette A, Chisari F V, Penna A, Levrero M, De Carli M, Fiaccadori F, Ferrari C. Natural variants of cytotoxic epitopes are T-cell receptor antagonists for antiviral cytotoxic T cells. Nature. 1994;369:407–410. doi: 10.1038/369407a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Carson R T, Desai D D, Vignali K M, Vignali D A. Immunoregulation of Th cells by naturally processed peptide antagonists. J Immunol. 1999;162:1–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.De Magistris M T, Alexander J, Coggeshall M, Altman A, Gaeta F C, Grey H M, Sette A. Antigen analog-major histocompatibility complexes act as antagonists of the T cell receptor. Cell. 1992;68:625–634. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90139-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Gairin J E, Oldstone M B A. Virus and cytotoxic T lymphocytes: crucial role of viral peptide secondary structure in major histocompatibility complex class I interactions. J Virol. 1993;67:2903–2907. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.5.2903-2907.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Gairin J E, Mazarguil H, Hudrisier D, Oldstone M B A. Optimal lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus sequences restricted by H-2Db major histocompatibility complex class I molecules and presented to cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Virol. 1995;69:2297–2305. doi: 10.1128/jvi.69.4.2297-2305.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Gallimore A, Hombach J, Dumrese T, Rammensee H G, Zinkernagel R M, Hengartner H. A protective cytotoxic T cell response to a subdominant epitope is influenced by the stability of the MHC class I/peptide complex and the overall spectrum of viral peptides generated within infected cells. Eur J Immunol. 1998;28:3301–3311. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1521-4141(199810)28:10<3301::AID-IMMU3301>3.0.CO;2-Q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Gallimore A, Dumrese T, Hengartner H, Zinkernagel R M, Rammensee H G. Protective immunity does not correlate with the hierarchy of virus-specific cytotoxic T cell responses to naturally processed peptides. J Exp Med. 1998;187:1647–1657. doi: 10.1084/jem.187.10.1647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Hudrisier D, Mazarguil H, Laval F, Oldstone M B A, Gairin J E. Binding of viral antigens to major histocompatibility complex class I H-2Db molecules is controlled by dominant negative elements at peptide non-anchor residues. Implications for peptide selection and presentation. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:17829–17836. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.30.17829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Hudrisier D, Oldstone M B A, Gairin J E. The signal sequence of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus contains an immunodominant cytotoxic T cell epitope that is restricted by both H-2Db and H-2Kb molecules. Virology. 1997;234:62–73. doi: 10.1006/viro.1997.8627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Hudrisier D, Gairin J E. Peptide-major histocompatibility complex class I complex: from the structural and molecular basis to pharmacological principles and therapeutic applications. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1998;232:75–97. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-72045-1_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Hudrisier D, Riond J, Mazarguil H, Oldstone M B A, Gairin J E. Genetically encoded and posttranslationally modified forms of a major histocompatibility complex class I-restricted antigen bearing a glycosylation motif are independently processed and copresented to cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:36274–36280. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.51.36274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Jameson S C, Carbone F R, Bevan M J. Clone-specific T cell receptor antagonists of major histocompatibility complex class I-restricted cytotoxic T cells. J Exp Med. 1993;177:1541–1550. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.6.1541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Klavinskis L S, Whitton J L, Joly E, Oldstone M B A. Vaccination and protection from a lethal viral infection: identification, incorporation, and use of a cytotoxic T lymphocyte glycoprotein epitope. Virology. 1990;178:393–400. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90336-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Klenerman P, Rowland-Jones S, McAdam S, Edwards J, Daenke S, Lalloo D, Koppe B, Rosenberg W, Boyd D, Edwards A, et al. Cytotoxic T-cell activity antagonized by naturally occurring HIV-1 Gag variants. Nature. 1994;369:403–407. doi: 10.1038/369403a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Meier U C, Klenerman P, Griffin P, James W, Koppe B, Larder B, McMichael A, Phillips R. Cytotoxic T lymphocyte lysis inhibited by viable HIV mutants. Science. 1995;270:1360–1362. doi: 10.1126/science.270.5240.1360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Murali-Krishna K, Altman J D, Suresh M, Sourdive D J, Zajac A J, Miller J D, Slansky J, Ahmed R. Counting antigen-specific CD8 T cells: a reevaluation of bystander activation during viral infection. Immunity. 1998;8:177–187. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80470-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Oldstone M B A, Whitton J L, Lewicki H, Tishon A. Fine dissection of a nine amino acid glycoprotein epitope, a major determinant recognized by lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus-specific class I-restricted H-2Db cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1988;168:559–570. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.2.559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Oldstone M B A, Lewicki H, Borrow P, Hudrisier D, Gairin J E. Discriminated selection among viral peptides with the appropriate anchor residues: implications for the size of the cytotoxic T-lymphocyte repertoire and control of viral infection. J Virol. 1995;69:7423–7429. doi: 10.1128/jvi.69.12.7423-7429.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Rammensee H G, Friede T, Stevanoviic S. MHC ligands and peptide motifs: first listing. Immunogenetics. 1995;41:178–228. doi: 10.1007/BF00172063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Rosemberg S A, Yang J C, Schartzentruber D J, Hwu P, Marincola F M, Topalian S L, Restifo N P, Dudley M E, Scharz S L, Spiess P J, Wunderlich J R, Parkhurst M R, Kawakami Y, Seipp C A, Einhorn J H, White D E. Immunologic and therapeutic evaluation of a synthetic peptide vaccine for the treatment of patients with metastatic melanoma. Nat Med. 1998;4:321–327. doi: 10.1038/nm0398-321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Schulz M, Aichele P, Vollenweider M, Bobe F W, Cardinaux F, Hengartner H, Zinkernagel R M. Major histocompatibility complex-dependent T cell epitopes of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus nucleoprotein and their protective capacity against viral disease. Eur J Immunol. 1989;19:1657–1667. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Tourdot S, Oukka M, Manuguerra J C, Magafa V, Vergnon I, Riche N, Bruley-Rosset M, Cordopatis P, Kosmatopoulos K. Chimeric peptides: a new approach to enhancing the immunogenicity of peptides with low MHC class I affinity: application in antiviral vaccination. J Immunol. 1997;159:2391–2398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.van der Burg S H, Visseren M J, Brandt R M, Kast W M, Melief C J. Immunogenicity of peptides bound to MHC class I molecules depends on the MHC-peptide complex stability. J Immunol. 1996;156:3308–3314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.van der Most R G, Murali-Krishna K, Whitton J L, Oseroff C, Alexander J, Southwood S, Sidney J, Chesnut R W, Sette A, Ahmed R. Identification of Db- and Kb-restricted subdominant cytotoxic T-cell responses in lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus-infected mice. Virology. 1998;240:158–167. doi: 10.1006/viro.1997.8934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Wright K E, Spiro R C, Burns J W, Buchmeier M J. Post-translational processing of the glycoproteins of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. Virology. 1990;177:175–183. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90471-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Young A C, Zhang W, Sacchettini J C, Nathenson S G. The three-dimensional structure of H-2Db at 2.4 A resolution: implications for antigen-determinant selection. Cell. 1994;76:39–50. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90171-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]