Abstract
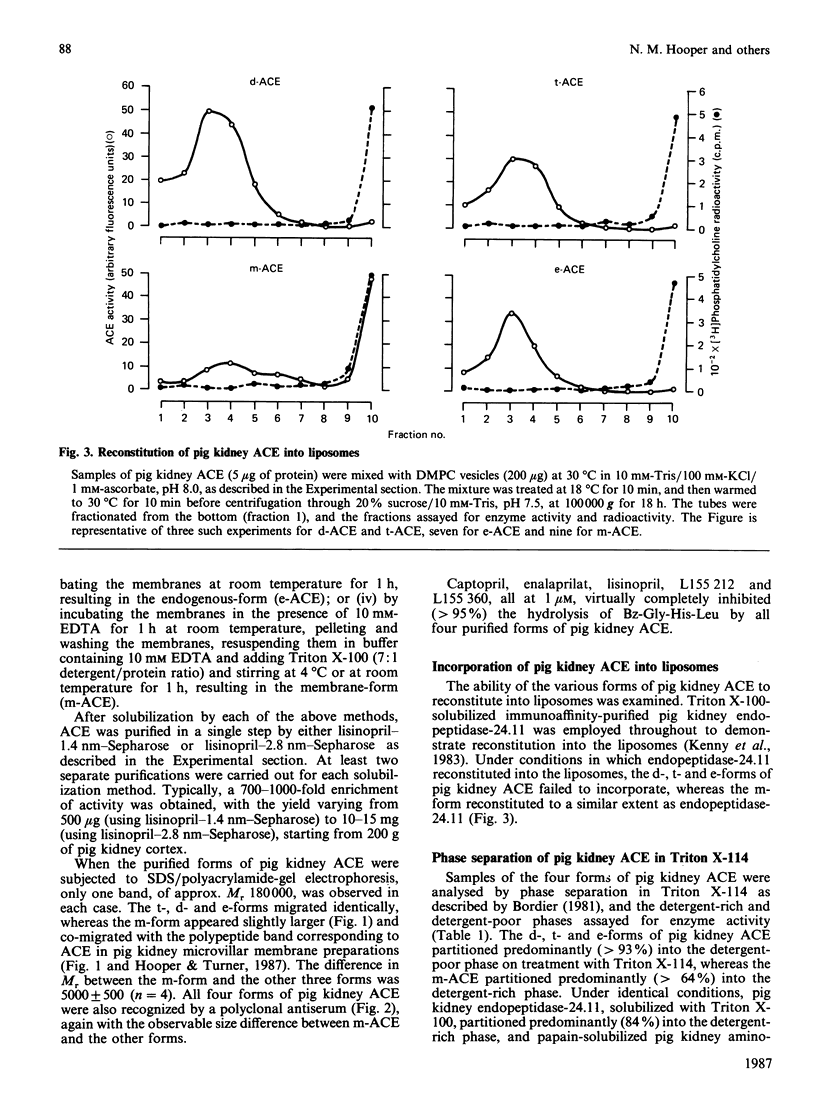
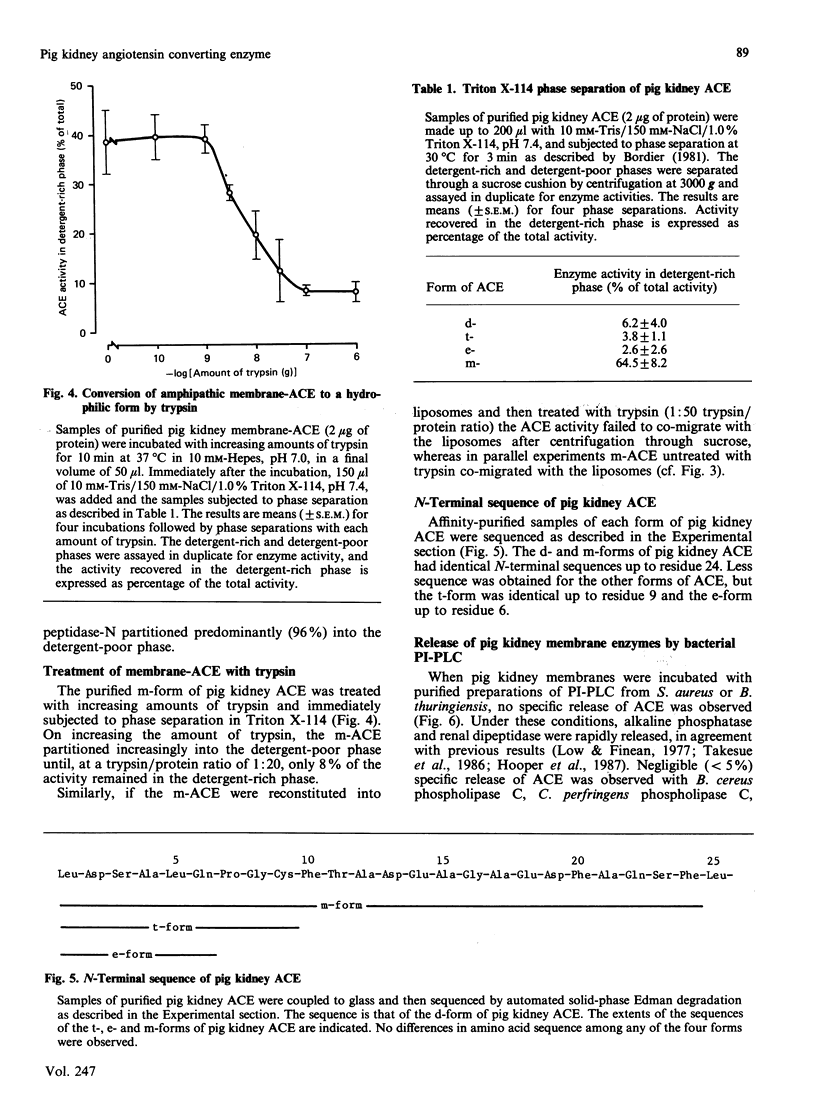
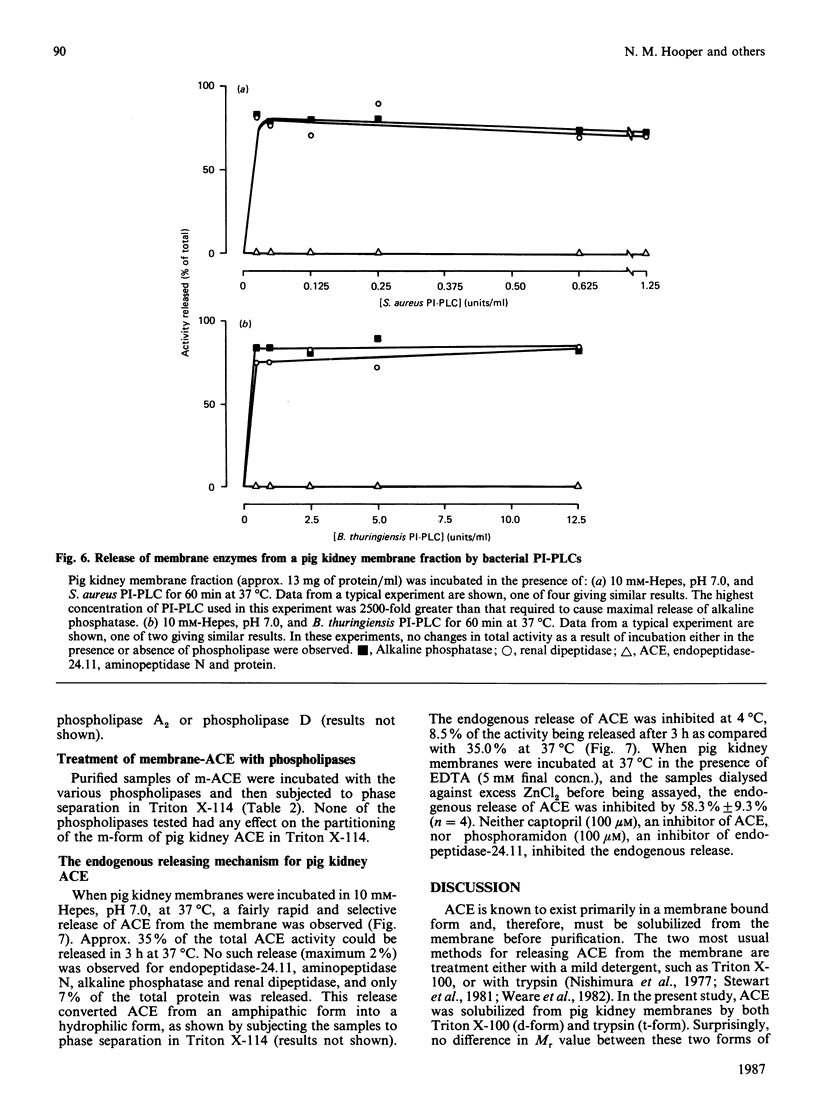
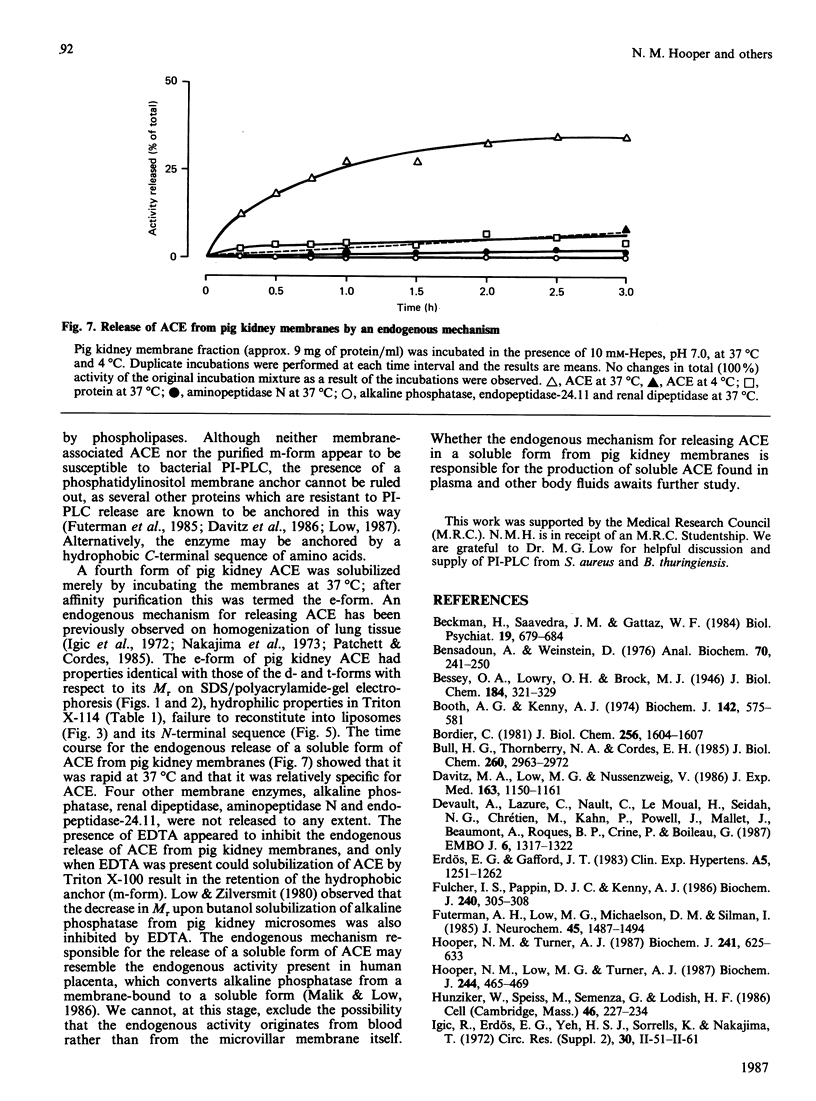
Angiotensin converting enzyme from pig kidney was isolated by affinity chromatography after solubilization from the membrane by one of four different procedures. Solubilization with Triton X-100, trypsin or by an endogenous activity in microvillar membranes all generated hydrophilic forms of the enzyme as assessed by phase separation in Triton X-114 and failure to incorporate into liposomes. Only when solubilization and purification was effected by Triton X-100 in the presence of EDTA (10 mM) could an amphipathic form of the enzyme (membrane- or m-form) be generated. The m-form of angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) appeared slightly larger (Mr approx. 180,000) than the hydrophilic forms (Mr approx. 175,000) after SDS/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis, and the m-form incorporated into liposomes, consistent with retention of the membrane anchor. The m-form of ACE showed an N-terminal sequence identical with that of preparations of enzyme isolated after solubilization with detergent alone (d-form), with trypsin (t-form) or by the endogenous mechanism (e-form). These data imply that ACE is anchored to the plasma membrane via its C-terminus, in contrast with the N-terminal anchorage of endopeptidase-24.11. No release of ACE from the membrane could be detected with a variety of phospholipases, including bacterial phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipases C, although an endogenous EDTA-sensitive membrane-associated hydrolase was capable of releasing a soluble, hydrophilic, form of the enzyme.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beckmann H., Saavedra J. M., Gattaz W. F. Low angiotensin-converting enzyme activity (kininase II) in cerebrospinal fluid of schizophrenics. Biol Psychiatry. 1984 May;19(5):679–684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bensadoun A., Weinstein D. Assay of proteins in the presence of interfering materials. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):241–250. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth A. G., Kenny A. J. A rapid method for the preparation of microvilli from rabbit kidney. Biochem J. 1974 Sep;142(3):575–581. doi: 10.1042/bj1420575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordier C. Phase separation of integral membrane proteins in Triton X-114 solution. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1604–1607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bull H. G., Thornberry N. A., Cordes E. H. Purification of angiotensin-converting enzyme from rabbit lung and human plasma by affinity chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):2963–2972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davitz M. A., Low M. G., Nussenzweig V. Release of decay-accelerating factor (DAF) from the cell membrane by phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C (PIPLC). Selective modification of a complement regulatory protein. J Exp Med. 1986 May 1;163(5):1150–1161. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.5.1150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devault A., Lazure C., Nault C., Le Moual H., Seidah N. G., Chrétien M., Kahn P., Powell J., Mallet J., Beaumont A. Amino acid sequence of rabbit kidney neutral endopeptidase 24.11 (enkephalinase) deduced from a complementary DNA. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1317–1322. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02370.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdös E. G., Gafford J. T. Human converting enzyme. Clin Exp Hypertens A. 1983;5(7-8):1251–1262. doi: 10.3109/10641968309048855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulcher I. S., Pappin D. J., Kenny A. J. The N-terminal amino acid sequence of pig kidney endopeptidase-24.11 shows homology with pro-sucrase-isomaltase. Biochem J. 1986 Nov 15;240(1):305–308. doi: 10.1042/bj2400305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Futerman A. H., Low M. G., Michaelson D. M., Silman I. Solubilization of membrane-bound acetylcholinesterase by a phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C. J Neurochem. 1985 Nov;45(5):1487–1494. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb07217.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper N. M., Low M. G., Turner A. J. Renal dipeptidase is one of the membrane proteins released by phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C. Biochem J. 1987 Jun 1;244(2):465–469. doi: 10.1042/bj2440465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper N. M., Turner A. J. Isolation of two differentially glycosylated forms of peptidyl-dipeptidase A (angiotensin converting enzyme) from pig brain: a re-evaluation of their role in neuropeptide metabolism. Biochem J. 1987 Feb 1;241(3):625–633. doi: 10.1042/bj2410625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunziker W., Spiess M., Semenza G., Lodish H. F. The sucrase-isomaltase complex: primary structure, membrane-orientation, and evolution of a stalked, intrinsic brush border protein. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):227–234. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90739-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igic R., Erdös E. G., Yeh H. S., Sorrells K., Nakajima T. Angiotensin I converting enzyme of the lung. Circ Res. 1972 Sep;31(9 Suppl):51–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwata K., Blacher R., Soffer R. L., Lai C. Y. Rabbit pulmonary angiotensin-converting enzyme: the NH2-terminal fragment with enzymatic activity and its formation from the native enzyme by NH4OH treatment. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Nov;227(1):188–201. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90362-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny A. J., Fulcher I. S., McGill K. A., Kershaw D. Proteins of the kidney microvillar membrane. Reconstitution of endopeptidase in liposomes shows that it is a short-stalked protein. Biochem J. 1983 Jun 1;211(3):755–762. doi: 10.1042/bj2110755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny A. J., Maroux S. Topology of microvillar membrance hydrolases of kidney and intestine. Physiol Rev. 1982 Jan;62(1):91–128. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1982.62.1.91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanzillo J. J., Stevens J., Dasarathy Y., Yotsumoto H., Fanburg B. L. Angiotensin-converting enzyme from human tissues. Physicochemical, catalytic, and immunological properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):14938–14944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laursen R. A. Solid-phase Edman degradation. An automatic peptide sequencer. Eur J Biochem. 1971 May 11;20(1):89–102. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01366.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G. Biochemistry of the glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol membrane protein anchors. Biochem J. 1987 May 15;244(1):1–13. doi: 10.1042/bj2440001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G., Finean J. B. Release of alkaline phosphatase from membranes by a phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C. Biochem J. 1977 Oct 1;167(1):281–284. doi: 10.1042/bj1670281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G., Zilversmit D. B. Role of phosphatidylinositol in attachment of alkaline phosphatase to membranes. Biochemistry. 1980 Aug 19;19(17):3913–3918. doi: 10.1021/bi00558a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malfroy B., Schofield P. R., Kuang W. J., Seeburg P. H., Mason A. J., Henzel W. J. Molecular cloning and amino acid sequence of rat enkephalinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Apr 14;144(1):59–66. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80475-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malik A. S., Low M. G. Conversion of human placental alkaline phosphatase from a high Mr form to a low Mr form during butanol extraction. An investigation of the role of endogenous phosphoinositide-specific phospholipases. Biochem J. 1986 Dec 1;240(2):519–527. doi: 10.1042/bj2400519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsas R., Stephenson S. L., Hryszko J., Kenny A. J., Turner A. J. The metabolism of neuropeptides. Phase separation of synaptic membrane preparations with Triton X-114 reveals the presence of aminopeptidase N. Biochem J. 1985 Oct 15;231(2):445–449. doi: 10.1042/bj2310445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura K., Yoshida N., Hiwada K., Ueda E., Kokubu T. Purification of angiotensin I-converting enzyme from human lung. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Aug 11;483(2):398–408. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(77)90067-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons W. H., Davidson J. L., Taub D., Aster S. D., Thorsett E. D., Patchett A. A., Ulm E. H., Lamont B. I. Benzolactams. A new class of converting enzyme inhibitors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Nov 30;117(1):108–113. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91547-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patchett A. A., Cordes E. H. The design and properties of N-carboxyalkyldipeptide inhibitors of angiotensin-converting enzyme. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1985;57:1–84. doi: 10.1002/9780470123034.ch1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Relton J. M., Gee N. S., Matsas R., Turner A. J., Kenny A. J. Purification of endopeptidase-24.11 ('enkephalinase') from pig brain by immunoadsorbent chromatography. Biochem J. 1983 Dec 1;215(3):519–523. doi: 10.1042/bj2150519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scotto A. W., Zakim D. Reconstitution of membrane proteins. Spontaneous association of integral membrane proteins with preformed unilamellar lipid bilayers. Biochemistry. 1985 Jul 16;24(15):4066–4075. doi: 10.1021/bi00336a040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Clair D. K., Presper K. A., Smith P. L., Stump D. C., Heath E. C. Bovine angiotensin-converting enzyme: amino-terminal sequence analysis and preliminary characterization of a hybridization-selected primary translation product. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Dec 30;141(3):968–972. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80138-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart T. A., Weare J. A., Erdös E. G. Human peptidyl dipeptidase (converting enzyme, kininase II). Methods Enzymol. 1981;80(Pt 100):450–460. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)80039-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takesue Y., Yokota K., Nishi Y., Taguchi R., Ikezawa H. Solubilization of trehalase from rabbit renal and intestinal brush-border membranes by a phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C. FEBS Lett. 1986 May 26;201(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80560-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wachter E., Machleidt W., Hofner H., Otto J. Aminopropyl glass and its p-phenylene diisothiocyanate derivative, a new support in solid-phase Edman degradation of peptides and proteins. FEBS Lett. 1973 Sep 1;35(1):97–102. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80585-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weare J. A., Gafford J. T., Lu H. S., Erdös E. G. Purification of human kidney angiotensin I converting enzyme using reverse-immunoadsorption chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jul 1;123(2):310–319. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90451-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang H. Y., Neff N. H. Distribution and properties of angiotensin converting enzyme of rat brain. J Neurochem. 1972 Oct;19(10):2443–2450. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1972.tb01298.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman C. L., Appella E., Pisano J. J. Rapid analysis of amino acid phenylthiohydantoins by high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1977 Feb;77(2):569–573. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90276-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zubenko G. S., Volicer L., Direnfeld L. K., Freeman M., Langlais P. J., Nixon R. A. Cerebrospinal fluid levels of angiotensin-converting enzyme in Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease and progressive supranuclear palsy. Brain Res. 1985 Mar 4;328(2):215–221. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)91032-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]