Abstract
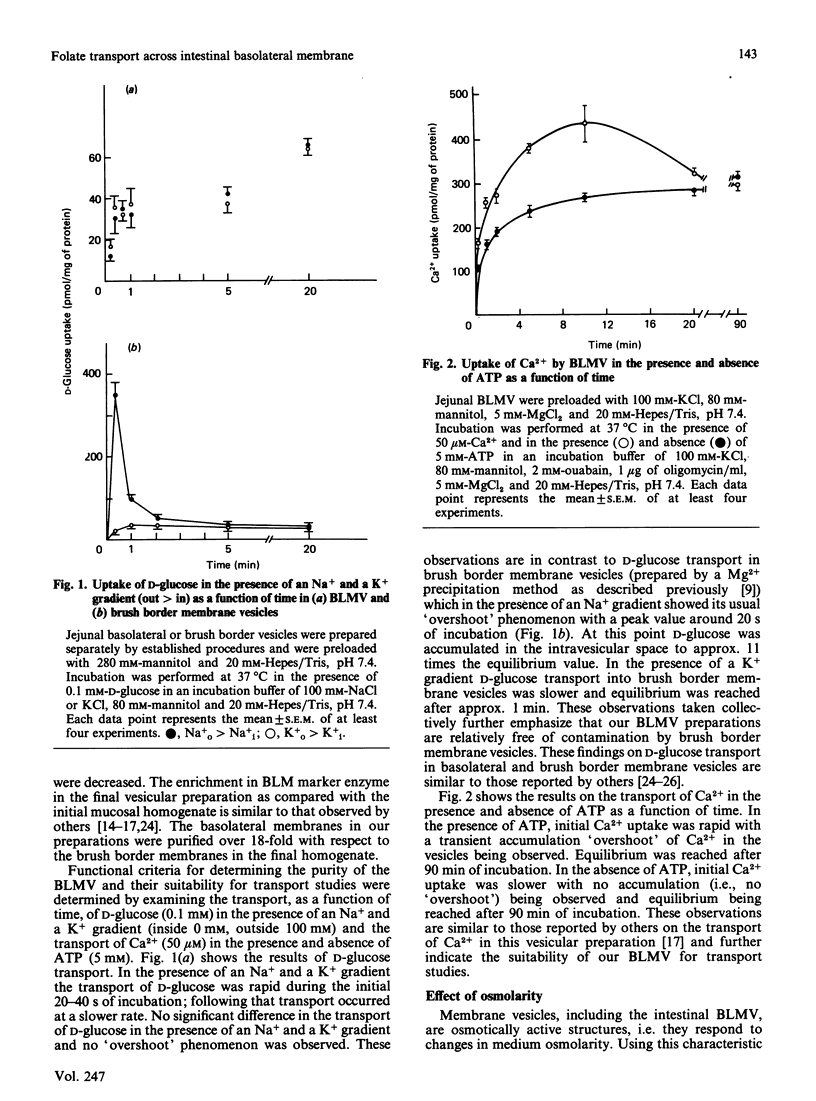
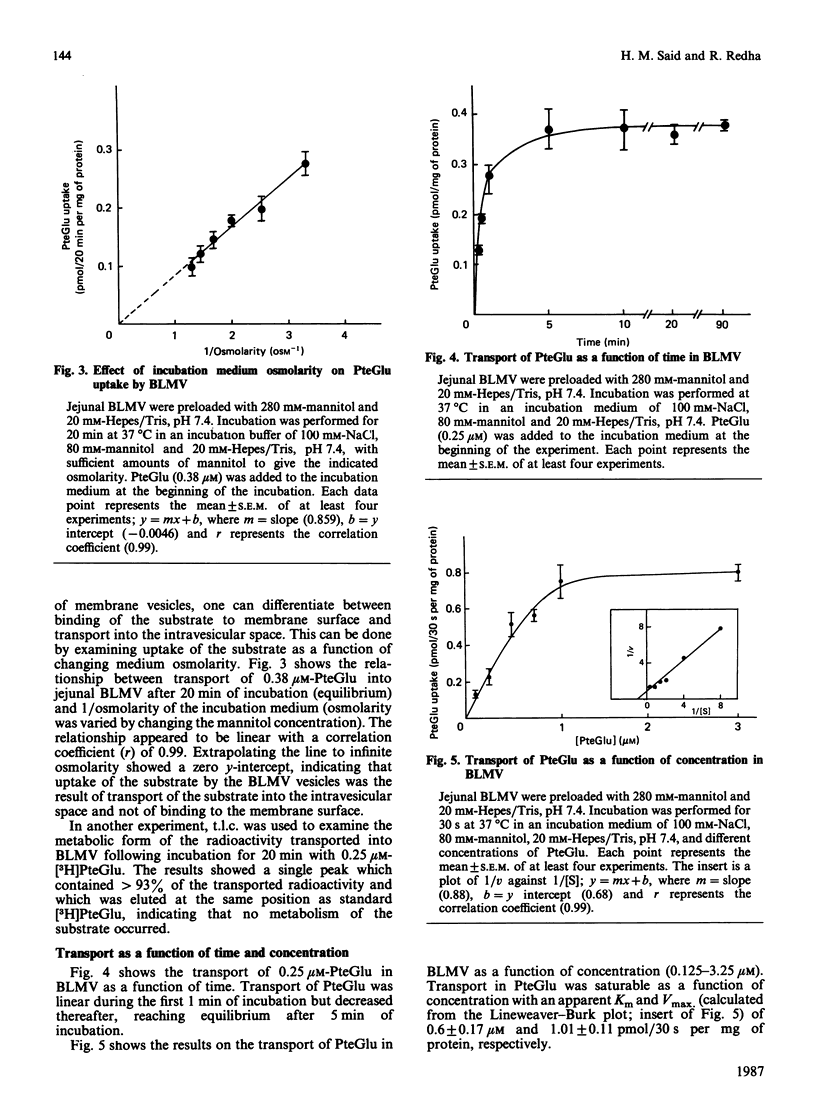
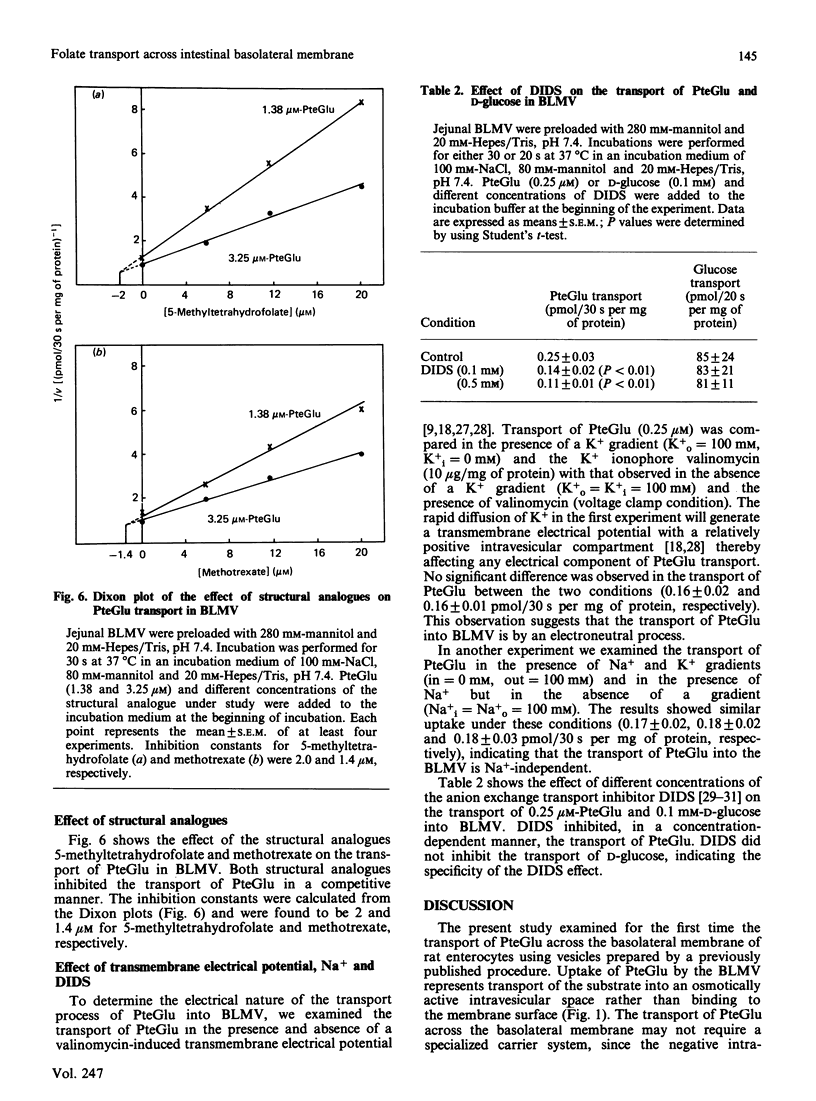
The mechanism of exit of folate from the enterocyte, i.e. transport across the basolateral membrane, is not known. In this study we examined, using basolateral membrane vesicles, the transport of folic acid across the basolateral membrane of rat intestine. Uptake of folic acid by these vesicles represents transport of the substrate into the intravesicular compartment and not binding to the membrane surface. The rate of folic acid transport was linear for the first 1 min of incubation but decreased thereafter, reaching equilibrium after 5 min of incubation. The transport of folic acid was: (1) saturable as a function of concentration with an apparent Km of 0.6 +/- 0.17 microM and Vmax. of 1.01 +/- 0.11 pmol/30 s per mg of protein; (2) inhibited in a competitive manner by the structural analogues 5-methyltetrahydrofolate and methotrexate (Ki = 2 and 1.4 microM, respectively); (4) electroneutral; (5) Na+-independent; (6) sensitive to the effect of the anion exchange inhibitor 4,4'-di-isothiocyanatostilbene-2,2'-disulphonic acid (DIDS). These data indicate the existence of a carrier-mediated transport system for folic acid in rat intestinal basolateral membrane and demonstrate that the transport process is electroneutral, Na+-independent and sensitive to the effect of anion exchange inhibition.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blair J. A., Johnson I. T., Matty A. J. Absorption of folic acid by everted segments of rat jejunum. J Physiol. 1974 Feb;236(3):653–661. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabantchik Z. I., Rothstein A. The nature of the membrane sites controlling anion permeability of human red blood cells as determined by studies with disulfonic stilbene derivatives. J Membr Biol. 1972 Dec 29;10(3):311–330. doi: 10.1007/BF01867863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAHLQVIST A. METHOD FOR ASSAY OF INTESTINAL DISACCHARIDASES. Anal Biochem. 1964 Jan;7:18–25. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(64)90115-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Castillo J. R., Robinson J. W. The simultaneous preparation of basolateral and brush-border membrane vesicles from guinea-pig intestinal epithelium, and the determination of the orientation of the basolateral vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 May 21;688(1):45–56. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90577-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan C. C., Faust R. G., Powell D. W. Coupled sodium-chloride transport by rabbit ileal brush-border membrane vesicles. Am J Physiol. 1983 Apr;244(4):G375–G385. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1983.244.4.G375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghishan F. K., Wilson F. A. Developmental maturation of D-glucose transport by rat jejunal brush-border membrane vesicles. Am J Physiol. 1985 Jan;248(1 Pt 1):G87–G92. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1985.248.1.G87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagenbuch B., Stange G., Murer H. Transport of sulphate in rat jejunal and rat proximal tubular basolateral membrane vesicles. Pflugers Arch. 1985 Oct;405(3):202–208. doi: 10.1007/BF00582561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson G. B. Analysis of the transport mechanism for methotrexate in L1210 mouse leukemia cells. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1983;132B:415–423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson G. B., Zevely E. M. Transport of methotrexate in L1210 cells: effect of ions on the rate and extent of uptake. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1980 Mar;200(1):149–155. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(80)90341-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hildmann B., Schmidt A., Murer H. Ca++-transport across basal-lateral plasma membranes from rat small intestinal epithelial cells. J Membr Biol. 1982;65(1-2):55–62. doi: 10.1007/BF01870469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopfer U., Nelson K., Perrotto J., Isselbacher K. J. Glucose transport in isolated brush border membrane from rat small intestine. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 10;248(1):25–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopfer U., Sigrist-Nelson K., Ammann E., Murer H. Differences in neutral amino acid and glucose transport between brush border and basolateral plasma membrane of intestinal epithelial cells. J Cell Physiol. 1976 Dec;89(4):805–810. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040890447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knickelbein R., Aronson P. S., Atherton W., Dobbins J. W. Sodium and chloride transport across rabbit ileal brush border. I. Evidence for Na-H exchange. Am J Physiol. 1983 Oct;245(4):G504–G510. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1983.245.4.G504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murer H., Ammann E., Biber J., Hopfer U. The surface membrane of the small intestinal epithelial cell. I. Localization of adenyl cyclase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 May 21;433(3):509–519. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90277-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg I. H. Folate absorption and malabsorption. N Engl J Med. 1975 Dec 18;293(25):1303–1308. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197512182932509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Said H. M., Ghishan F. K., Murrell J. E. Ontogenesis of intestinal transport of 5-methyltetrahydrofolate in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1985 Nov;249(5 Pt 1):G567–G571. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1985.249.5.G567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Said H. M., Ghishan F. K., Redha R. Folate transport by human intestinal brush-border membrane vesicles. Am J Physiol. 1987 Feb;252(2 Pt 1):G229–G236. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1987.252.2.G229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Said H. M., Hollander D., Katz D. Absorption of 5-methyltetrahydrofolate in rat jejunum with intact blood and lymphatic vessels. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Sep 5;775(3):402–408. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(84)90197-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Said H. M., Strum W. B. A pH-dependent, carrier-mediated system for transport of 5-methyltetrahydrofolate in rat jejunum. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Jul;226(1):95–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scalera V., Storelli C., Storelli-Joss C., Haase W., Murer H. A simple and fast method for the isolation of basolateral plasma membranes from rat small-intestinal epithelial cells. Biochem J. 1980 Jan 15;186(1):177–181. doi: 10.1042/bj1860177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schron C. M., Washington C., Jr, Blitzer B. L. The transmembrane pH gradient drives uphill folate transport in rabbit jejunum. Direct evidence for folate/hydroxyl exchange in brush border membrane vesicles. J Clin Invest. 1985 Nov;76(5):2030–2033. doi: 10.1172/JCI112205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selhub J., Rosenberg I. H. Folate transport in isolated brush border membrane vesicles from rat intestine. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 10;256(9):4489–4493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strum W. B. Enzymatic reduction and methylation of folate following pH-dependent, carrier-mediated transport in rat jejunum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jun 13;554(1):249–257. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90022-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takuwa N., Shimada T., Matsumoto H., Himukai M., Hoshi T. Effect of hydrogen ion-gradient on carrier-mediated transport of glycylglycine across brush border membrane vesicles from rabbit small intestine. Jpn J Physiol. 1985;35(4):629–642. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.35.629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg S. L., Burckhardt G., Wilson F. A. Taurocholate transport by rat intestinal basolateral membrane vesicles. Evidence for the presence of an anion exchange transport system. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jul;78(1):44–50. doi: 10.1172/JCI112571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright E. M., van Os C. H., Mircheff A. K. Sugar uptake by intestinal basolateral membrane vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Mar 27;597(1):112–124. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90155-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


