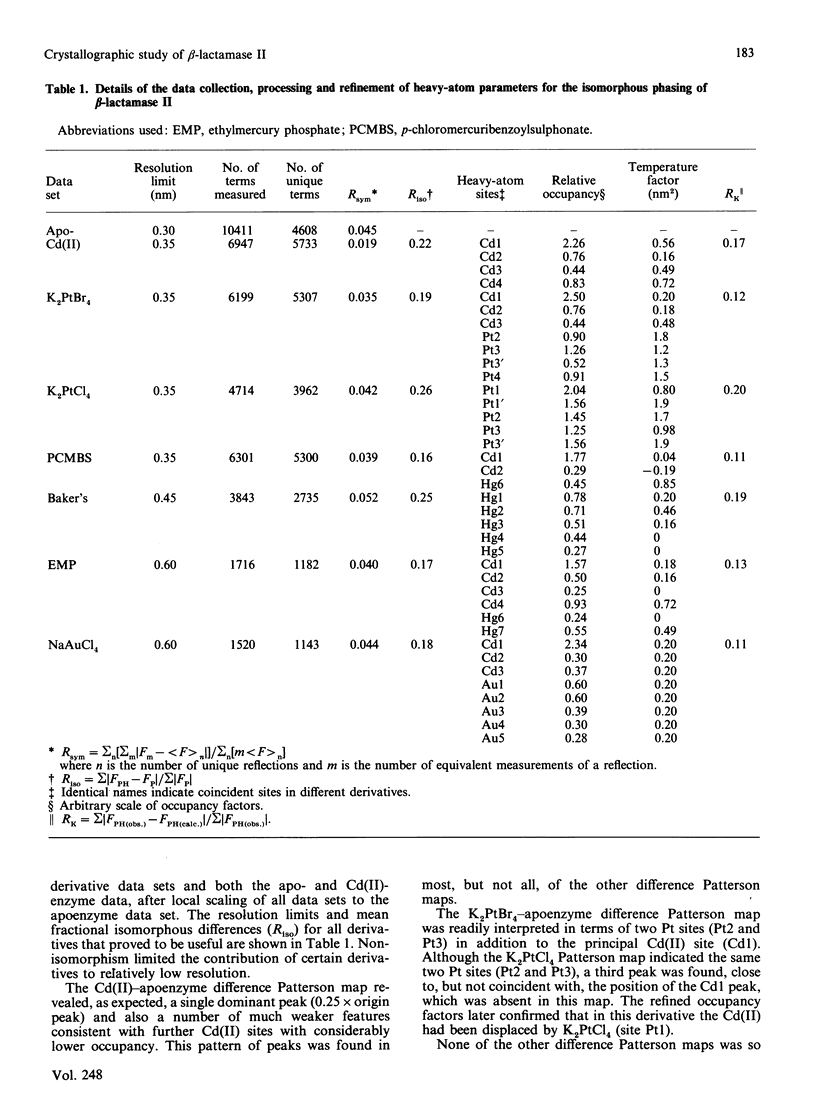
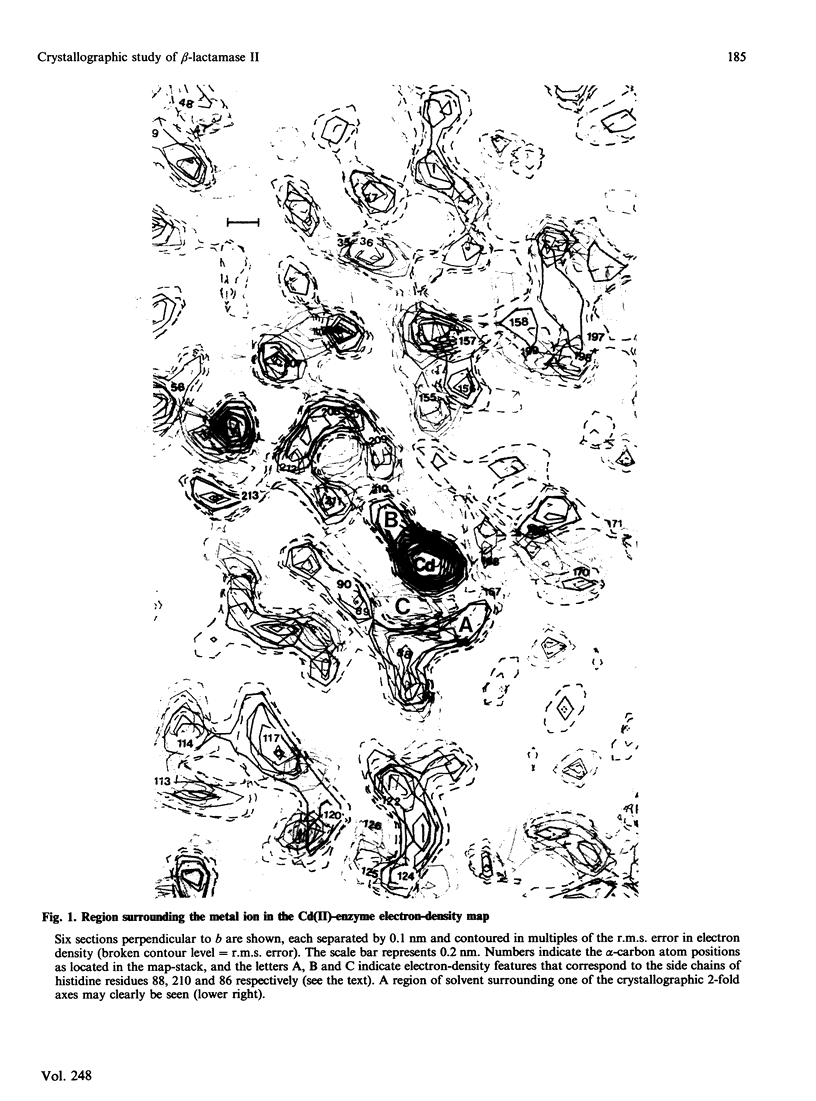
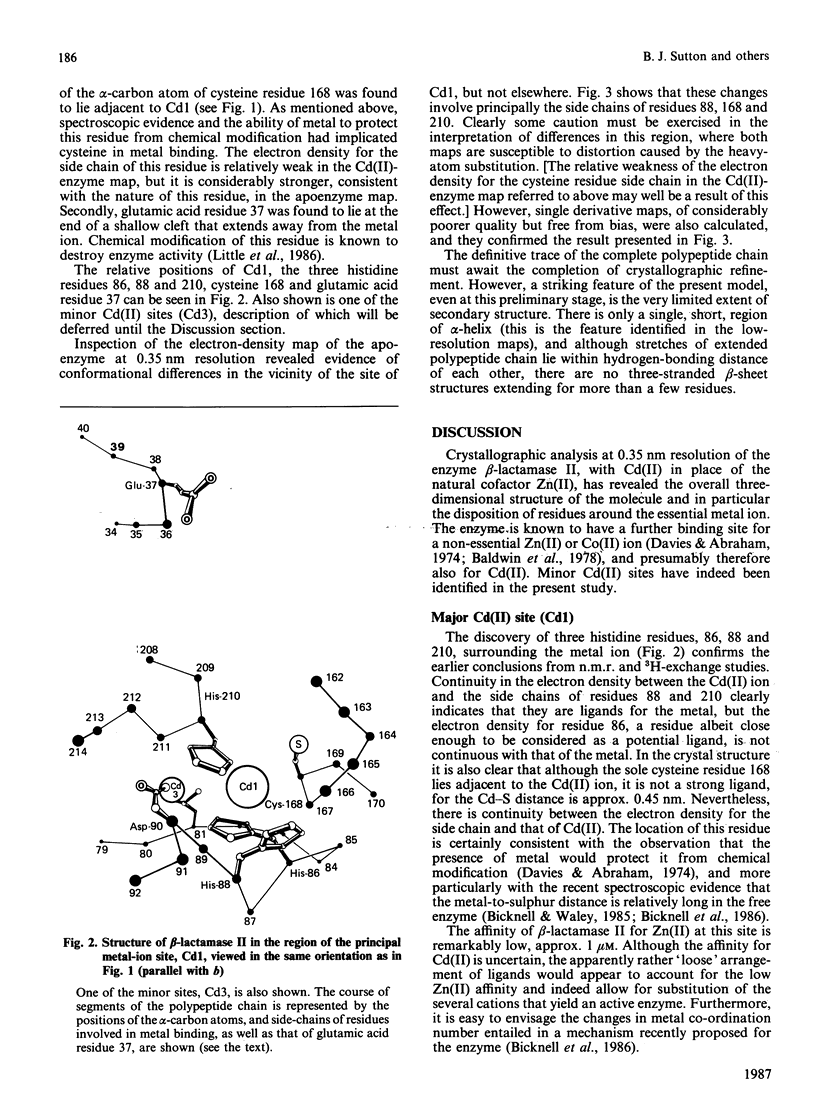
Abstract
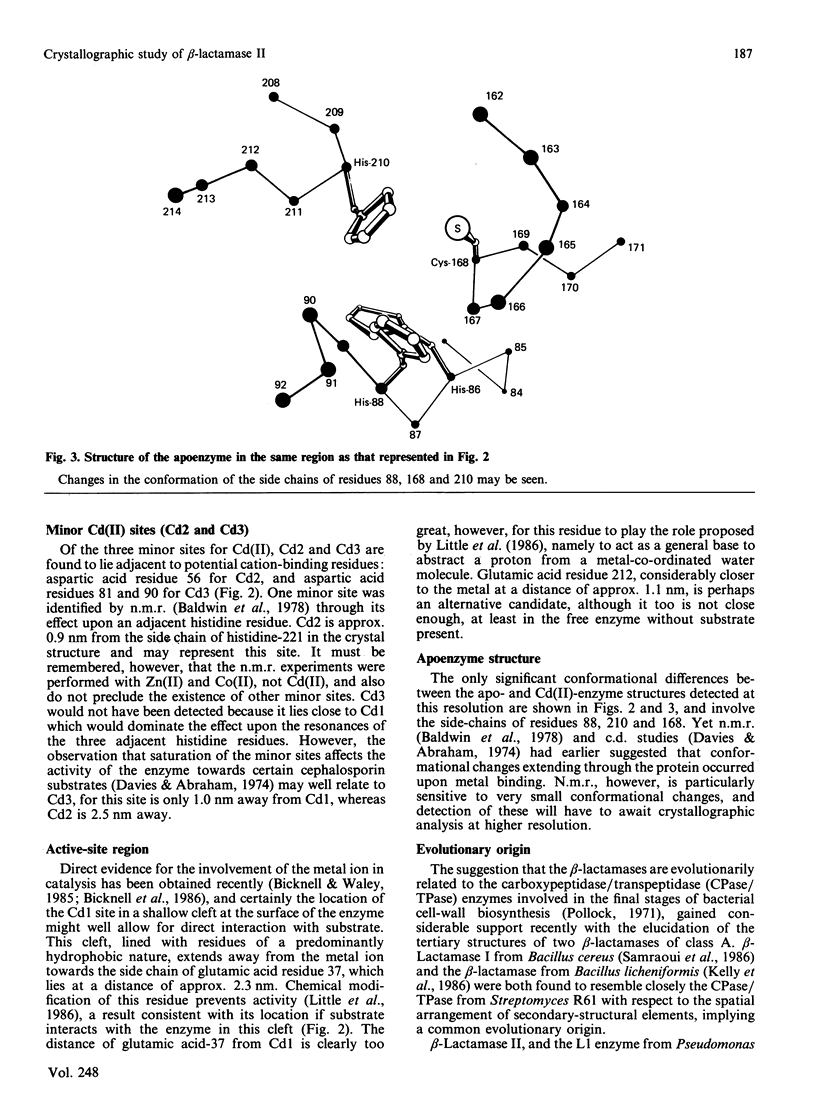
Crystals of beta-lactamase II (EC 3.5.2.6., 'penicillinase') from Bacillus cereus were grown with Cd(II) in place of the natural Zn(II) cofactor and stabilized by cross-linking with glutaraldehyde. Their space group is C2, the cell dimensions are a = 5.44 nm, b = 6.38 nm, c = 7.09 nm and beta = 93.6 degrees, and there is one molecule in the asymmetric unit. Diffraction data were collected from cross-linked crystals of the Cd(II)-enzyme, the apoenzyme and six heavy-atom derivatives. The electron-density map calculated at 0.35 nm resolution reveals the essential Cd(II) ion surrounded by three histidine residues and one cysteine residue. The position of a glutamic acid residue, modification of which destroys activity [Little, Emanuel, Gagnon & Waley (1986) Biochem. J. 233, 465-469], suggests the probable location of the active site of the enzyme. Two minor Cd(II) sites not essential for activity were also located. The structure of the apoenzyme at this resolution appears to differ from that of the Cd(II)-enzyme only in the orientation of two of the histidine residues and the cysteine residue that surround the metal ion.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambler R. P., Daniel M., Fleming J., Hermoso J. M., Pang C., Waley S. G. The amino acid sequence of the zinc-requiring beta-lactamase II from the bacterium Bacillus cereus 569. FEBS Lett. 1985 Sep 23;189(2):207–211. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)81024-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambler R. P. The structure of beta-lactamases. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1980 May 16;289(1036):321–331. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1980.0049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin G. S., Galdes A., Hill H. A., Smith B. E., Waley S. G., Abraham E. P. Histidine residues of zinc ligands in beta-lactamase II. Biochem J. 1978 Nov 1;175(2):441–447. doi: 10.1042/bj1750441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin G. S., Waley S. G., Abraham E. P. Identification of histidine residues that act as zinc ligands in beta-lactamase II by differential tritium exchange. Biochem J. 1979 Jun 1;179(3):459–463. doi: 10.1042/bj1790459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bicknell R., Emanuel E. L., Gagnon J., Waley S. G. The production and molecular properties of the zinc beta-lactamase of Pseudomonas maltophilia IID 1275. Biochem J. 1985 Aug 1;229(3):791–797. doi: 10.1042/bj2290791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bicknell R., Schäffer A., Waley S. G., Auld D. S. Changes in the coordination geometry of the active-site metal during catalysis of benzylpenicillin hydrolysis by Bacillus cereus beta-lactamase II. Biochemistry. 1986 Nov 4;25(22):7208–7215. doi: 10.1021/bi00370a066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bicknell R., Waley S. G. Cryoenzymology of Bacillus cereus beta-lactamase II. Biochemistry. 1985 Nov 19;24(24):6876–6887. doi: 10.1021/bi00345a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuchural G. J., Jr, Malamy M. H., Tally F. P. Beta-lactamase-mediated imipenem resistance in Bacteroides fragilis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Nov;30(5):645–648. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.5.645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies R. B., Abraham E. P. Metal cofactor requirements of beta-lactamase II. Biochem J. 1974 Oct;143(1):129–135. doi: 10.1042/bj1430129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies R. B., Abraham E. P. Separation, purification and properties of beta-lactamase I and beta-lactamase II from Bacillus cereus 569/H/9. Biochem J. 1974 Oct;143(1):115–127. doi: 10.1042/bj1430115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dideberg O., Charlier P., Dive G., Joris B., Frère J. M., Ghuysen J. M. Structure of a Zn2+-containing D-alanyl-D-alanine-cleaving carboxypeptidase at 2.5 A resolution. Nature. 1982 Sep 30;299(5882):469–470. doi: 10.1038/299469a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galdes A., Hill H. A., Baldwin G. S., Waley S. G., Abraham E. P. The 1H nuclear-magnetic-resonance spectroscopy of cobalt(II)-beta-lactamase II. Biochem J. 1980 Jun 1;187(3):789–795. doi: 10.1042/bj1870789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hussain M., Carlino A., Madonna M. J., Lampen J. O. Cloning and sequencing of the metallothioprotein beta-lactamase II gene of Bacillus cereus 569/H in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Oct;164(1):223–229. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.1.223-229.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaurin B., Grundström T. ampC cephalosporinase of Escherichia coli K-12 has a different evolutionary origin from that of beta-lactamases of the penicillinase type. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4897–4901. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly J. A., Dideberg O., Charlier P., Wery J. P., Libert M., Moews P. C., Knox J. R., Duez C., Fraipont C., Joris B. On the origin of bacterial resistance to penicillin: comparison of a beta-lactamase and a penicillin target. Science. 1986 Mar 21;231(4744):1429–1431. doi: 10.1126/science.3082007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little C., Emanuel E. L., Gagnon J., Waley S. G. Identification of an essential glutamic acid residue in beta-lactamase II from Bacillus cereus. Biochem J. 1986 Jan 15;233(2):465–469. doi: 10.1042/bj2330465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews B. W. Solvent content of protein crystals. J Mol Biol. 1968 Apr 28;33(2):491–497. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90205-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock M. R. The function and evolution of penicillinase. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1971 Dec 31;179(1057):385–401. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1971.0104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proceedings of the biochemical society. Biochem J. 1966 Jan;98(1):1–16P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- QUIOCHO F. A., RICHARDS F. M. INTERMOLECULAR CROSS LINKING OF A PROTEIN IN THE CRYSTALLINE STATE: CARBOXYPEPTIDASE-A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Sep;52:833–839. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.3.833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saino Y., Kobayashi F., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. Purification and properties of inducible penicillin beta-lactamase isolated from Pseudomonas maltophilia. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Oct;22(4):564–570. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.4.564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samraoui B., Sutton B. J., Todd R. J., Artymiuk P. J., Waley S. G., Phillips D. C. Tertiary structural similarity between a class A beta-lactamase and a penicillin-sensitive D-alanyl carboxypeptidase-transpeptidase. 1986 Mar 27-Apr 2Nature. 320(6060):378–380. doi: 10.1038/320378a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato K., Fujii T., Okamoto R., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. Biochemical properties of beta-lactamase produced by Flavobacterium odoratum. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Apr;27(4):612–614. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.4.612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]