Abstract
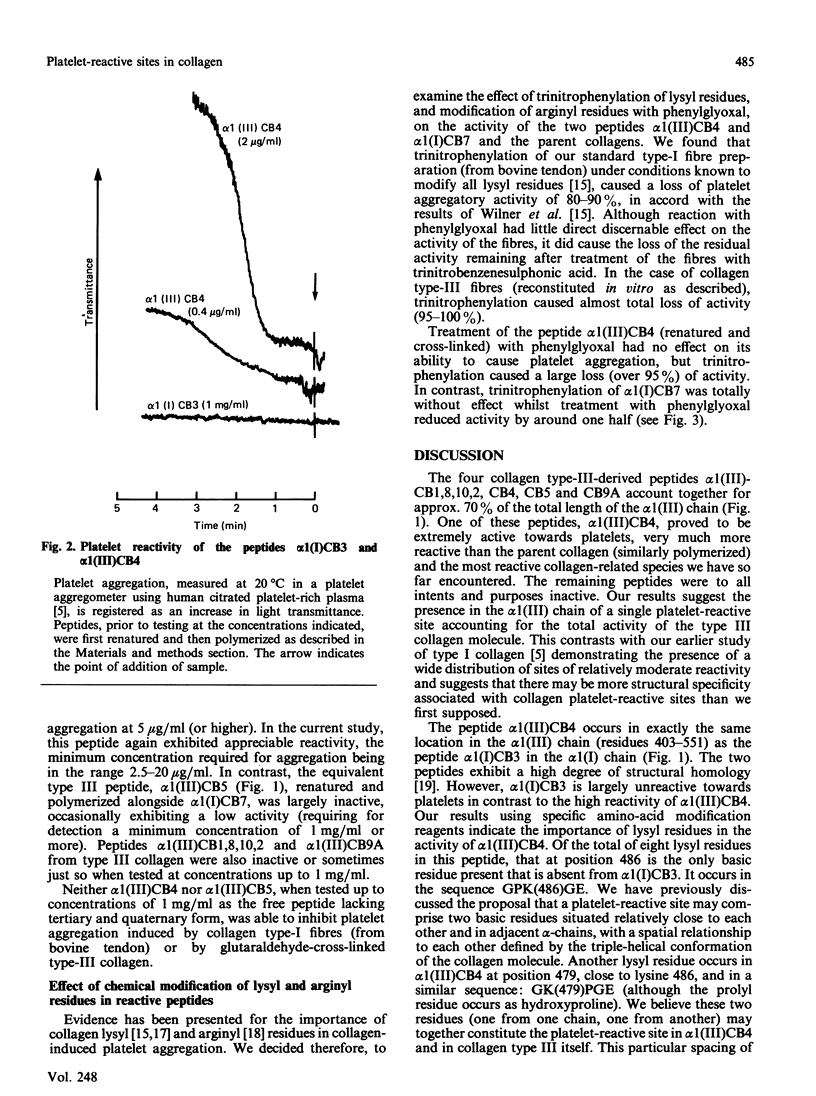
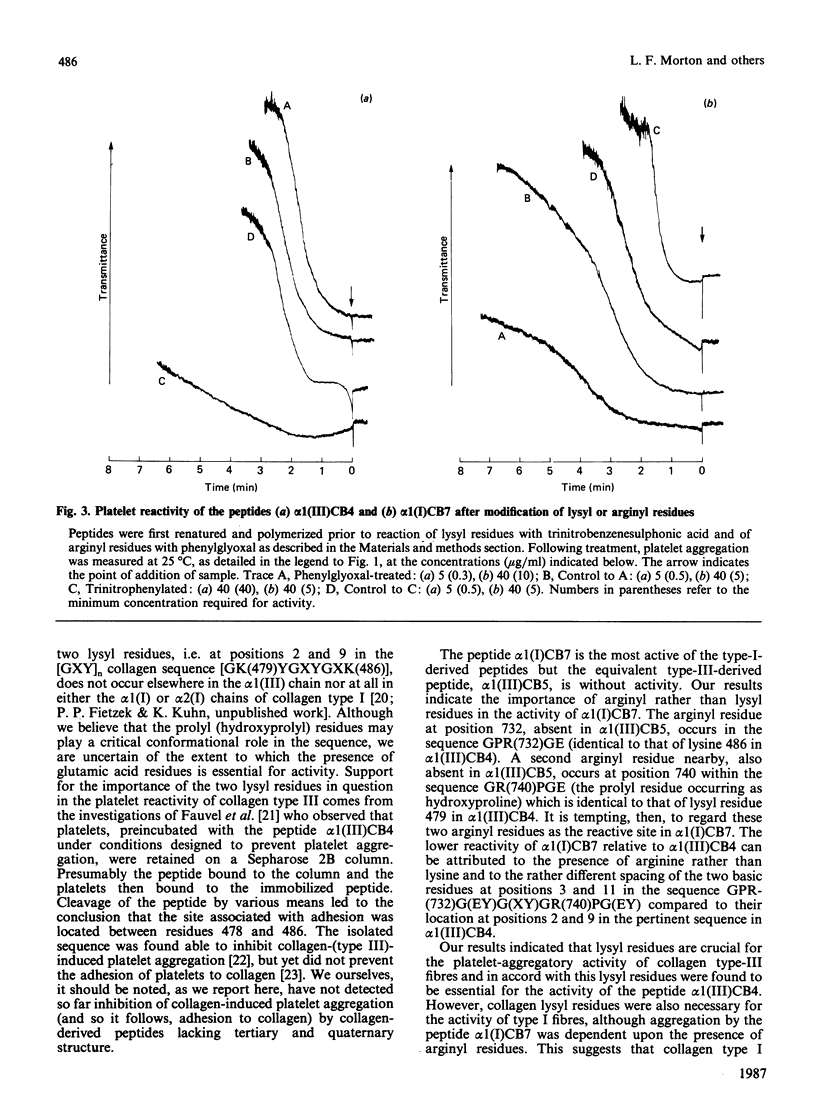
Collagen type III possesses a highly reactive platelet-aggregatory site at a locus which in type I is essentially inactive whilst the latter collagen possesses reactive sites absent in type III. It is proposed that platelet aggregation by collagen involves the sequence GK[or R]PG(EY)GPK[or R]G(EY) or, less favourably, GPK[or R]G(EY)G(XY)GK[or R]PG(EY), one basic residue acting in combination with the second in an adjacent alpha-chain.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnes M. J. Collagens in atherosclerosis. Coll Relat Res. 1985 Jan;5(1):65–97. doi: 10.1016/s0174-173x(85)80048-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes M. J., Gordon J. L., MacIntyre D. E. Platelet-aggregating activity of type I and type III collagens from human aorta and chicken skin. Biochem J. 1976 Dec 15;160(3):647–651. doi: 10.1042/bj1600647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentz H., Fietzek P. P., Kühn K. The covalent structure of calf skin type III collagen. III. The amino acid sequence of the cyanogen bromide peptide alpha 1(III)CB4 (positions 403--551). Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1979 Jul;360(7):833–840. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesney C. M., Pifer D. D., Crofford L. J., Huch K. M. Reevaluation of the role of the polar groups of collagen in the platelet-collagen interaction. Am J Pathol. 1983 Aug;112(2):200–206. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies M. J., Thomas A. Thrombosis and acute coronary-artery lesions in sudden cardiac ischemic death. N Engl J Med. 1984 May 3;310(18):1137–1140. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198405033101801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dedhar S., Ruoslahti E., Pierschbacher M. D. A cell surface receptor complex for collagen type I recognizes the Arg-Gly-Asp sequence. J Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;104(3):585–593. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.3.585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauvel F., Legrand Y. J., Kühn K., Bentz H., Fietzek P. P., Caen J. P. Platelet adhesion to type III collagen : involvement of a sequence of nine aminoacids from alpha 1 (III) CB peptide. Thromb Res. 1979;16(1-2):269–273. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(79)90289-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzsimmons C. M., Barnes M. J. The platelet reactivity of the alpha 2(I)-chain of type I collagen: platelet aggregation induced by polymers of the molecule [alpha 2(I)]3. Thromb Res. 1985 Aug 15;39(4):523–531. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(85)90175-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzsimmons C. M., Cawston T. E., Barnes M. J. The platelet reactivity of collagen type I: evidence for multiple platelet-reactive sites in the type I collagen molecule. Thromb Haemost. 1986 Aug 20;56(1):95–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii T., Kühn K. Isolation and characterization of pepsin-treated type III collagen from calf skin. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1975 Nov;356(11):1793–1801. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1975.356.2.1793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haverstick D. M., Cowan J. F., Yamada K. M., Santoro S. A. Inhibition of platelet adhesion to fibronectin, fibrinogen, and von Willebrand factor substrates by a synthetic tetrapeptide derived from the cell-binding domain of fibronectin. Blood. 1985 Oct;66(4):946–952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen A. M., Borders C. L., Jr, Fish W. W. Arginine residues are critical for the heparin-cofactor activity of antithrombin III. Biochem J. 1985 Oct 1;231(1):59–63. doi: 10.1042/bj2310059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karniguian A., Legrand Y. J., Lefrancier P., Caen J. P. Effect of a collagen derived octapeptide on different steps of the platelet/collagen interaction. Thromb Res. 1983 Dec 15;32(6):593–604. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(83)90061-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K., Favre M. Maturation of the head of bacteriophage T4. I. DNA packaging events. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 15;80(4):575–599. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legrand Y. J., Karniguian A., Le Francier P., Fauvel F., Caen J. P. Evidence that a collagen-derived nonapeptide is a specific inhibitor of platelet-collagen interaction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Oct 31;96(4):1579–1585. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91354-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton L. F., Griffin B., Pepper D. S., Barnes M. J. The interaction between collagens and factor VIII/von Willebrand factor: investigation of the structural requirements for interaction. Thromb Res. 1983 Dec 15;32(6):545–556. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(83)90056-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauterberg J., Allmann H., Henkel W., Fietzek P. P. Isolation and characterization of CNBr derived peptides of the alpha1 (III) chain of pepsin-solubilized calf skin collagen. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1976 Dec;357(10):1401–1407. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1976.357.2.1401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Pierschbacher M. D. Arg-Gly-Asp: a versatile cell recognition signal. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):517–518. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90259-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoro S. A., Cunningham L. W. Collagen-mediated platelet aggregation: the role of multiple interactions between the platelet surface and collagen. Thromb Haemost. 1980 Jun 18;43(2):158–162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tkocz C., Kühn K. The formation of triple-helical collagen molecules from alpha-1 or alpha-2 polypeptide chains. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Feb;7(4):454–462. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb19631.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C. L., Miyata T., Weksler B., Rubin A. L., Stenzel K. H. Collagen-induced platelet aggregation and release. I Effects of side-chain modifications and role of arginyl residues. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Dec 18;544(3):555–567. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90330-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilner G. D., Nossel H. L., Procupez T. L. Aggregation of platelets by collagen: polar active sites of insoluble human collagen. Am J Physiol. 1971 Apr;220(4):1074–1079. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.220.4.1074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


