Abstract
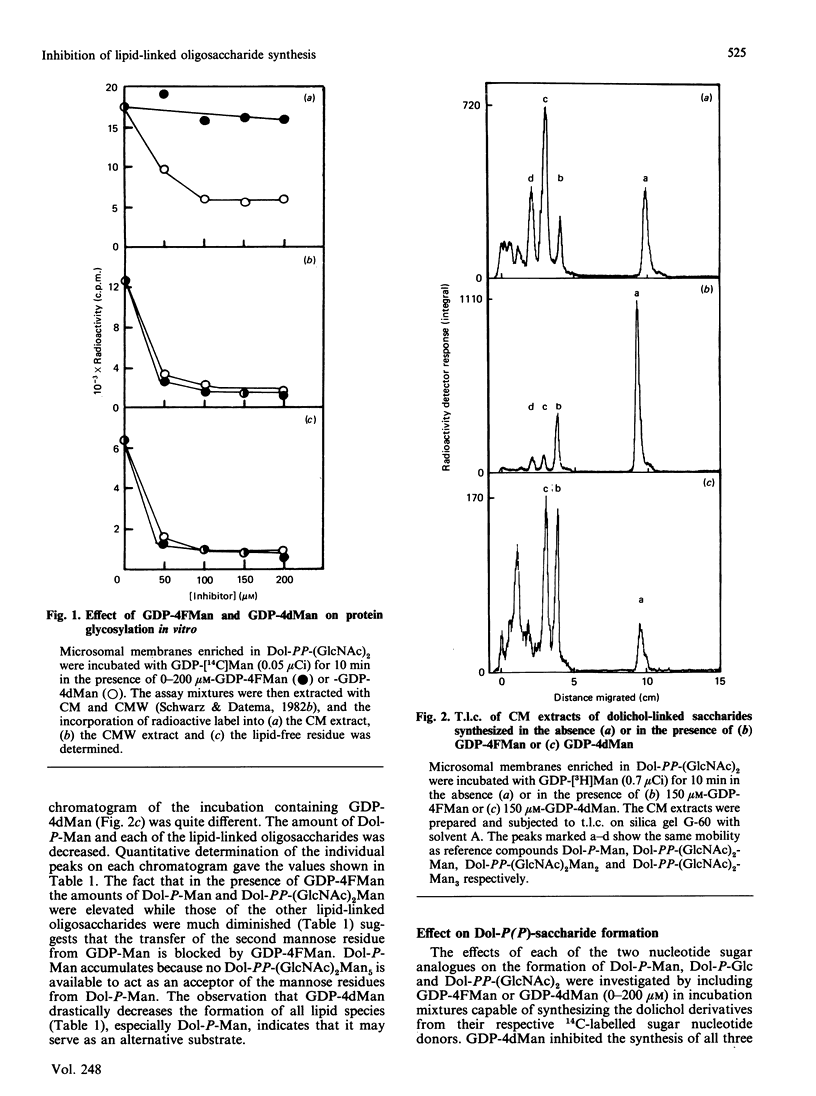
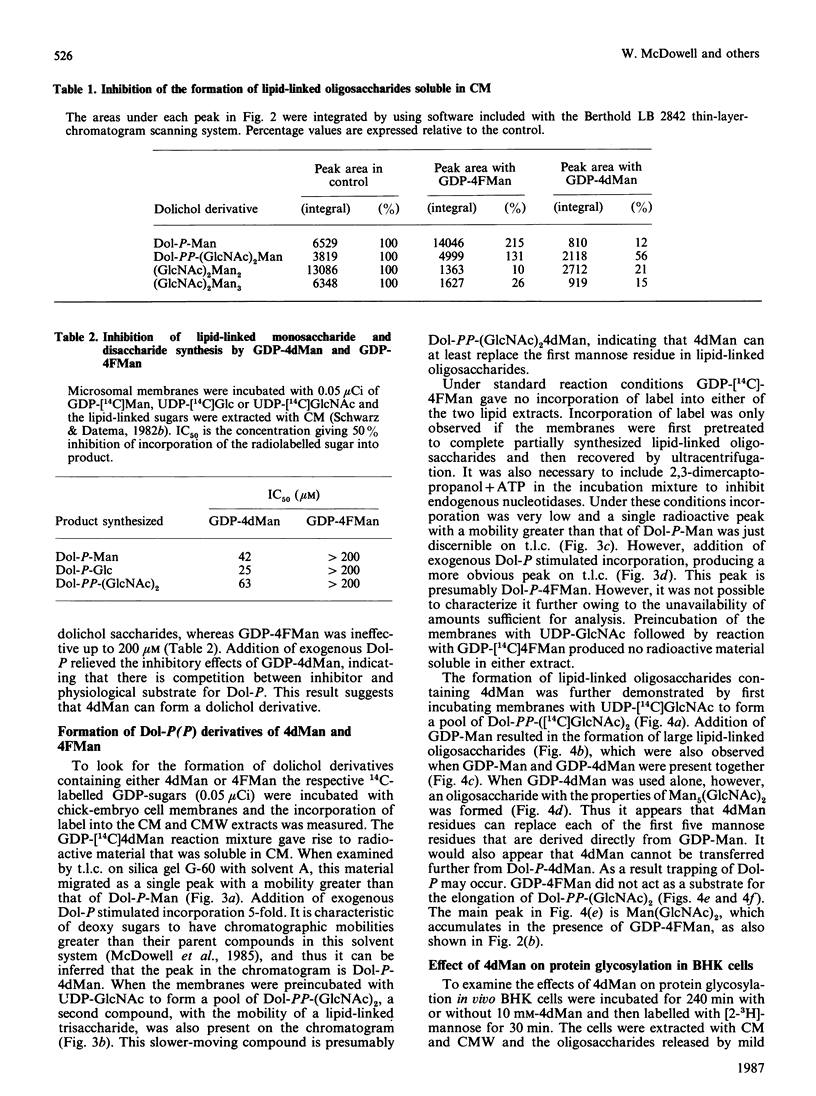
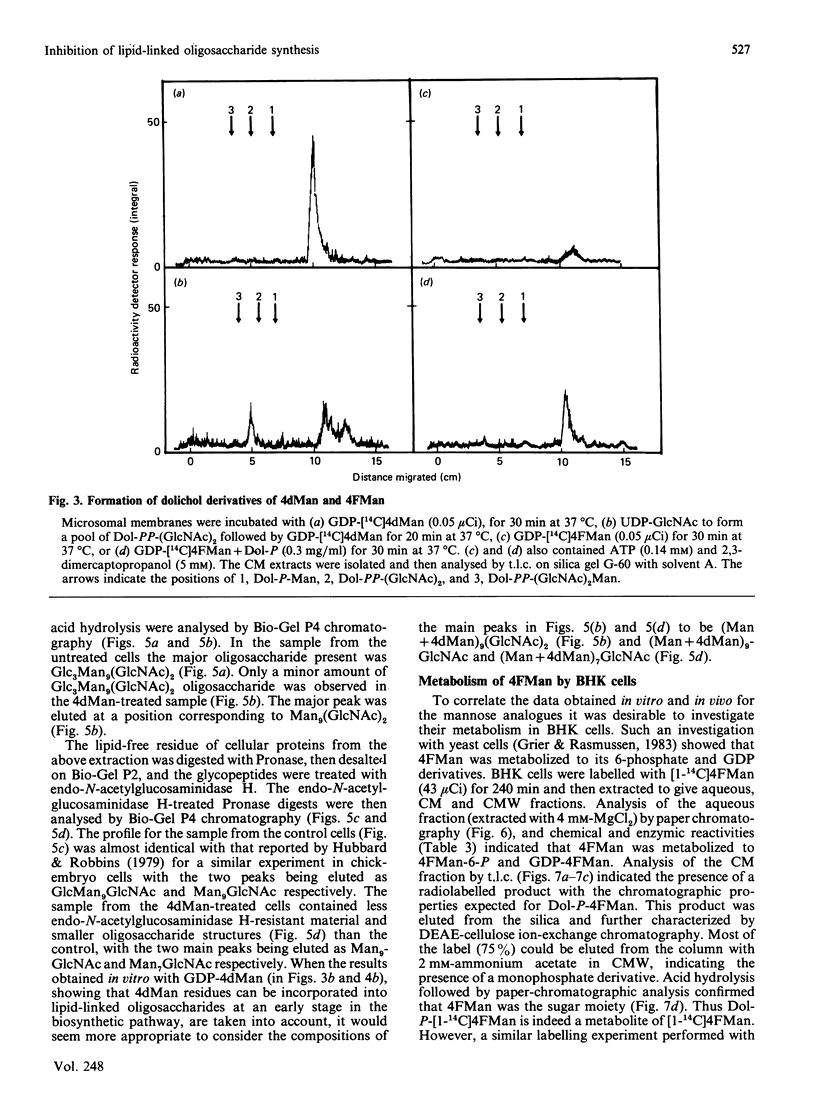
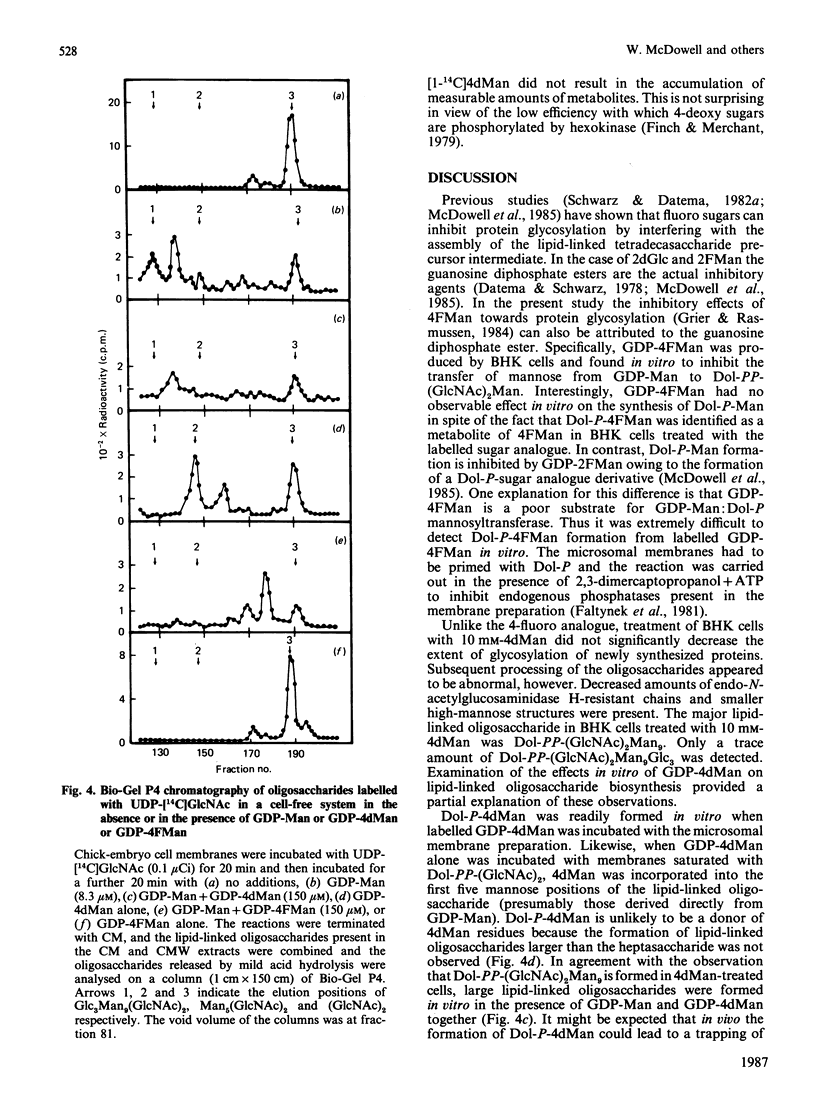
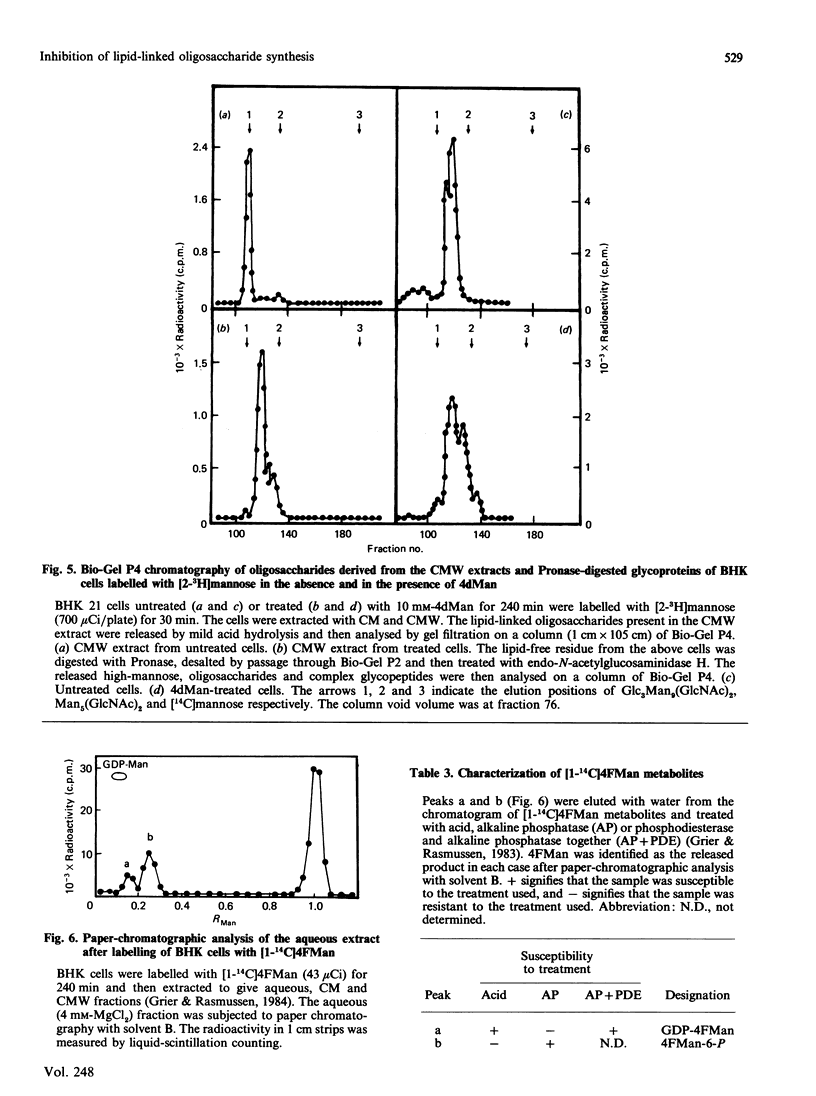
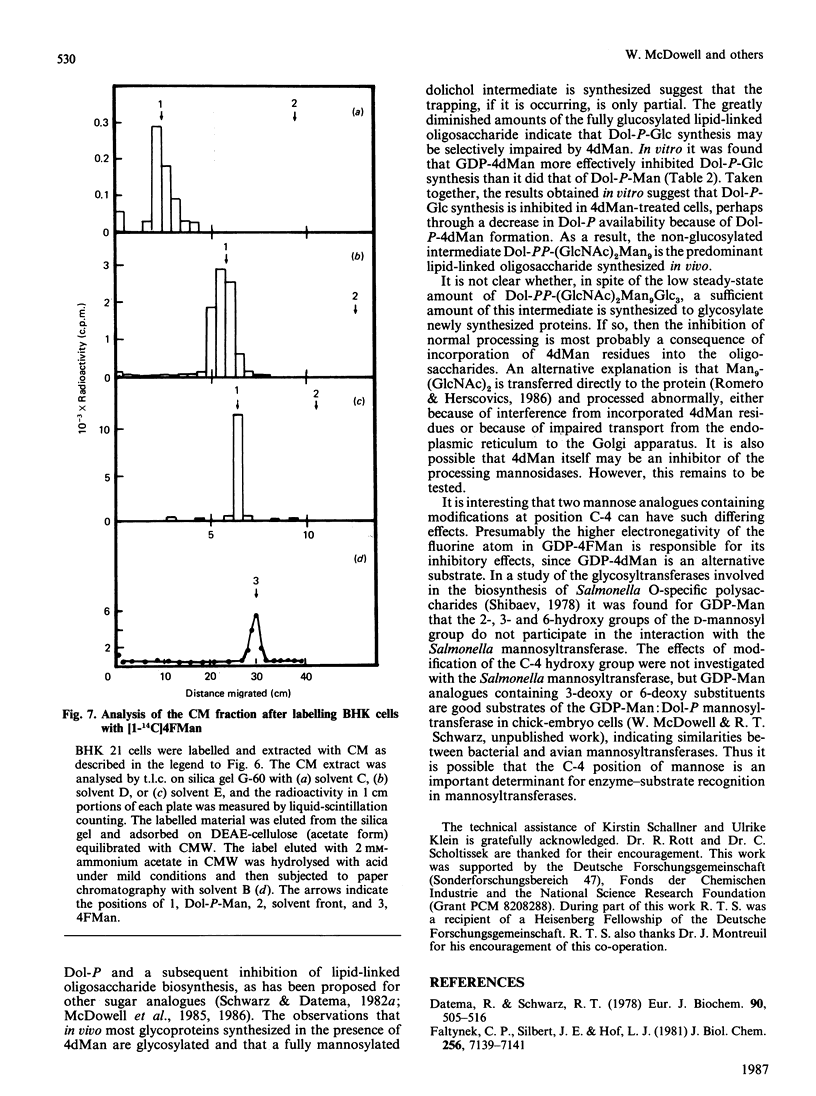
The effects of the guanosine diphosphate esters of 4-deoxy-4-fluoro-D-mannose (GDP-4FMan) and 4-deoxy-D-mannose (GDP-4dMan) on reactions of the dolichol pathway in chick-embryo cell microsomal membranes were investigated by studies with chick-embryo cell microsomal membranes in vitro and in baby-hamster kidney (BHK) cells in vivo. Each nucleotide sugar analogue inhibited lipid-linked oligosaccharide biosynthesis in a concentration-dependent manner. GDP-4FMan blocked in vitro the addition of mannose to Dol-PP-(GlcNAc)2Man from GDP-Man (where Dol represents dolichol), but did not interfere with the formation of Dol-P-Man, Dol-P-Glc and Dol-PP-(GlcNAc)2. Although GDP-4FMan and Dol-P-4FMan were identified as metabolites of 4FMan in BHK cells labelled with [1-14C]4FMan, GDP-4FMan was a very poor substrate for GDP-Man:Dol-P mannosyltransferase and Dol-P-4FMan could only be synthesized in vitro if the chick-embryo cell membranes were primed with Dol-P. It therefore appears that the inhibition of lipid-linked oligosaccharide formation in BHK cells treated with 4FMan [Grier & Rasmussen (1984) J. Biol. Chem. 259, 1027-1030] is due primarily to a blockage in the formation of Dol-PP-(GlcNAc)2Man2 by GDP-4FMan. In contrast, GDP-4dMan was a substrate for those mannosyltransferases that catalyse the transfer of the first five mannose residues to Dol-PP-(GlcNAc)2. In addition, GDP-4dMan was a substrate for GDP-Man:Dol-P mannosyltransferase, which catalysed the formation of Dol-P-4dMan. As a consequence of this, the formation of Dol-P-Man, Dol-P-Glc and Dol-PP-(GlcNAc)2 may be inhibited through competition for Dol-P. In BHK cells treated with 10 mM-4dMan, Dol-PP-(GlcNAc)2Man9 was the major lipid-linked oligosaccharide detected. Nearly normal extents of protein glycosylation were observed, but very little processing to complex oligosaccharides occurred, and the high-mannose structures were smaller than in untreated cells.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Datema R., Schwarz R. T. Formation of 2-deoxyglucose-containing lipid-linked oligosaccharides. Interference with glycosylation of glycoproteins. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Oct 16;90(3):505–516. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12630.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faltynek C. R., Silbert J. E., Hof L. Inhibition of the action of pyrophosphatase and phosphatase on sugar nucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 25;256(14):7139–7141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch P., Merchant Z. M. The substrate specificity of yeast hexokinase: reaction with D-arabinose oxime. Carbohydr Res. 1979 Nov;76:225–232. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(79)80021-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhrmann U., Bause E., Legler G., Ploegh H. Novel mannosidase inhibitor blocking conversion of high mannose to complex oligosaccharides. Nature. 1984 Feb 23;307(5953):755–758. doi: 10.1038/307755a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grier T. J., Rasmussen J. R. 4-Deoxy-4-fluoro-D-mannose inhibits the glycosylation of the G protein of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 25;259(2):1027–1030. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grier T. J., Rasmussen J. R. A convenient enzymic synthesis of guanosine diphosphate-[14C]mannose. Anal Biochem. 1982 Nov 15;127(1):100–104. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90150-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grier T. J., Rasmussen J. R. Metabolism of 3-deoxy-3-fluoro-D-mannose and 4-deoxy-4-fluoro-D-mannose by Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C. Biochem J. 1983 Mar 1;209(3):677–685. doi: 10.1042/bj2090677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard S. C., Robbins P. W. Synthesis and processing of protein-linked oligosaccharides in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 10;254(11):4568–4576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld R., Kornfeld S. Assembly of asparagine-linked oligosaccharides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:631–664. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krag S. S., Robbins P. W. Sindbis envelope proteins as endogenous acceptors in reactions of guanosine diphosphate-[14C]Mannose with preparations of infected chicken embryo fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1977 Apr 25;252(8):2621–2629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDowell W., Datema R., Romero P. A., Schwarz R. T. Mechanism of inhibition of protein glycosylation by the antiviral sugar analogue 2-deoxy-2-fluoro-D-mannose: inhibition of synthesis of man(GlcNAc)2-PP-Dol by the guanosine diphosphate ester. Biochemistry. 1985 Dec 31;24(27):8145–8152. doi: 10.1021/bi00348a046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDowell W., Weckbecker G., Keppler D. O., Schwarz R. T. UDP-glucosamine as a substrate for dolichyl monophosphate glucosamine synthesis. Biochem J. 1986 Feb 1;233(3):749–754. doi: 10.1042/bj2330749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romero P. A., Herscovics A. Transfer of nonglucosylated oligosaccharide from lipid to protein in a mammalian cell. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 5;261(34):15936–15940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz R. T., Datema R. Inhibition of the dolichol pathway of protein glycosylation. Methods Enzymol. 1982;83:432–443. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)83041-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz R. T., Datema R. The lipid pathway of protein glycosylation and its inhibitors: the biological significance of protein-bound carbohydrates. Adv Carbohydr Chem Biochem. 1982;40:287–379. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2318(08)60111-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


