Abstract
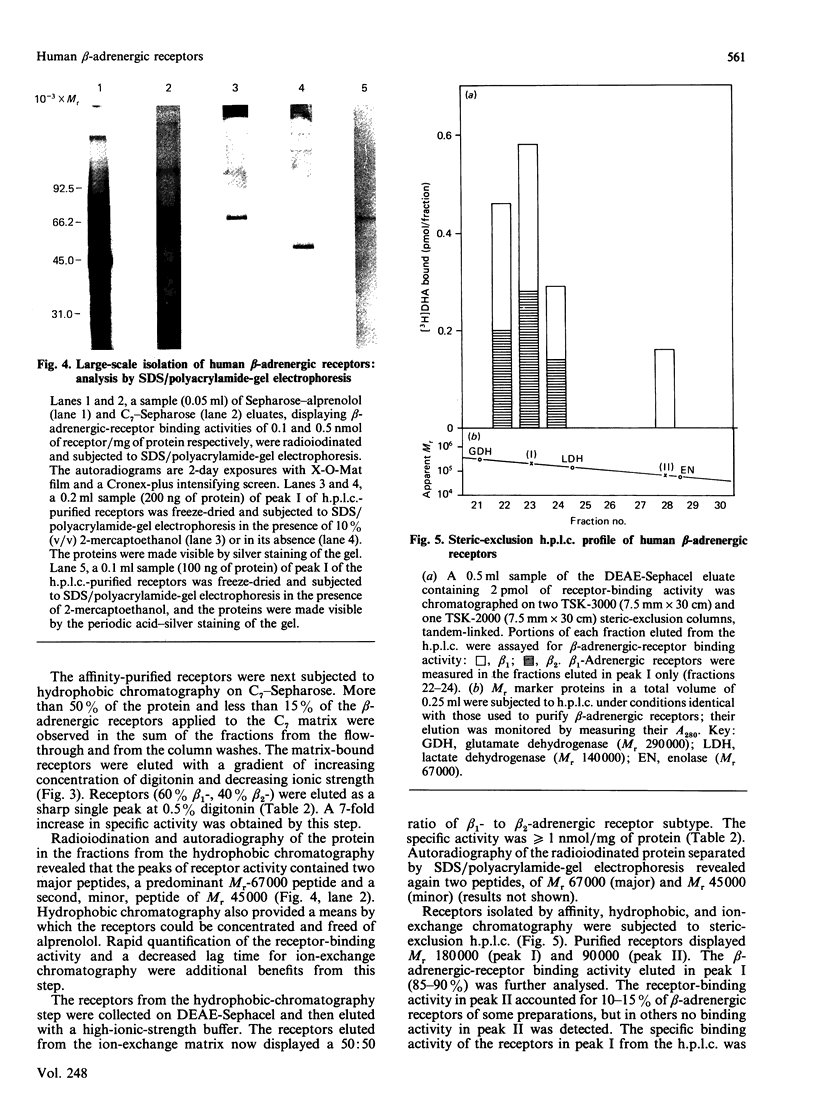
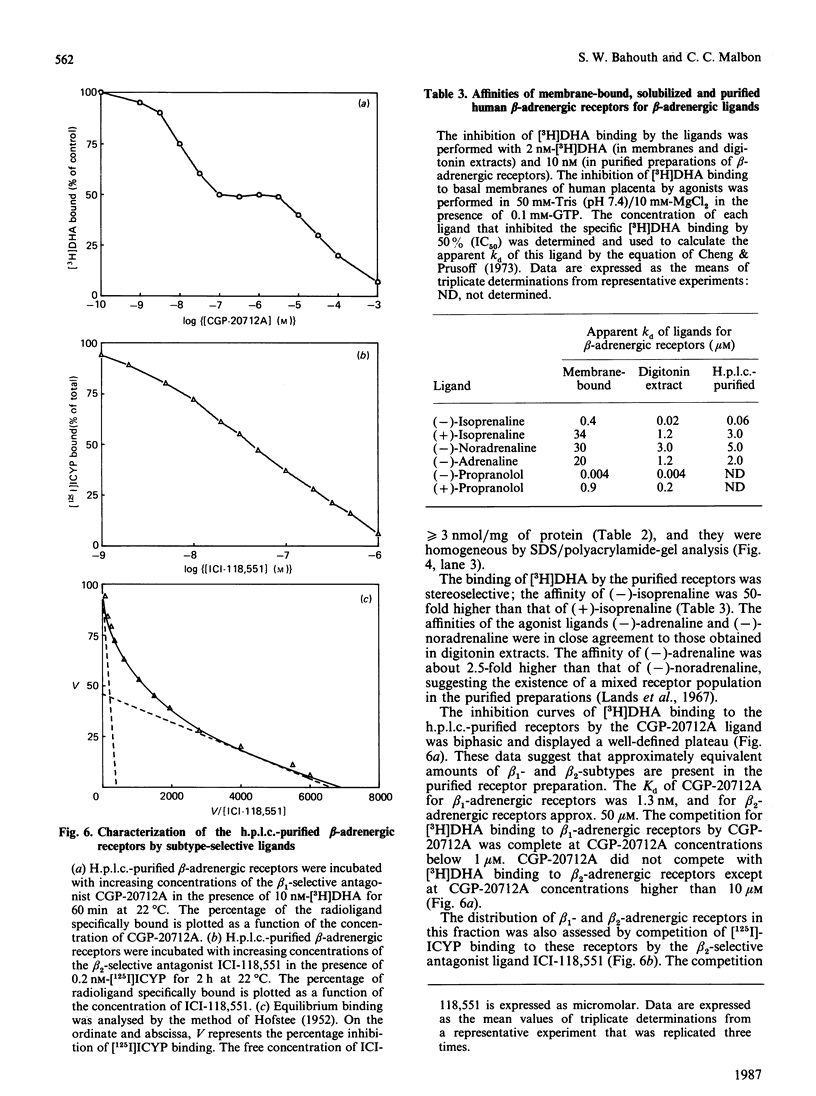
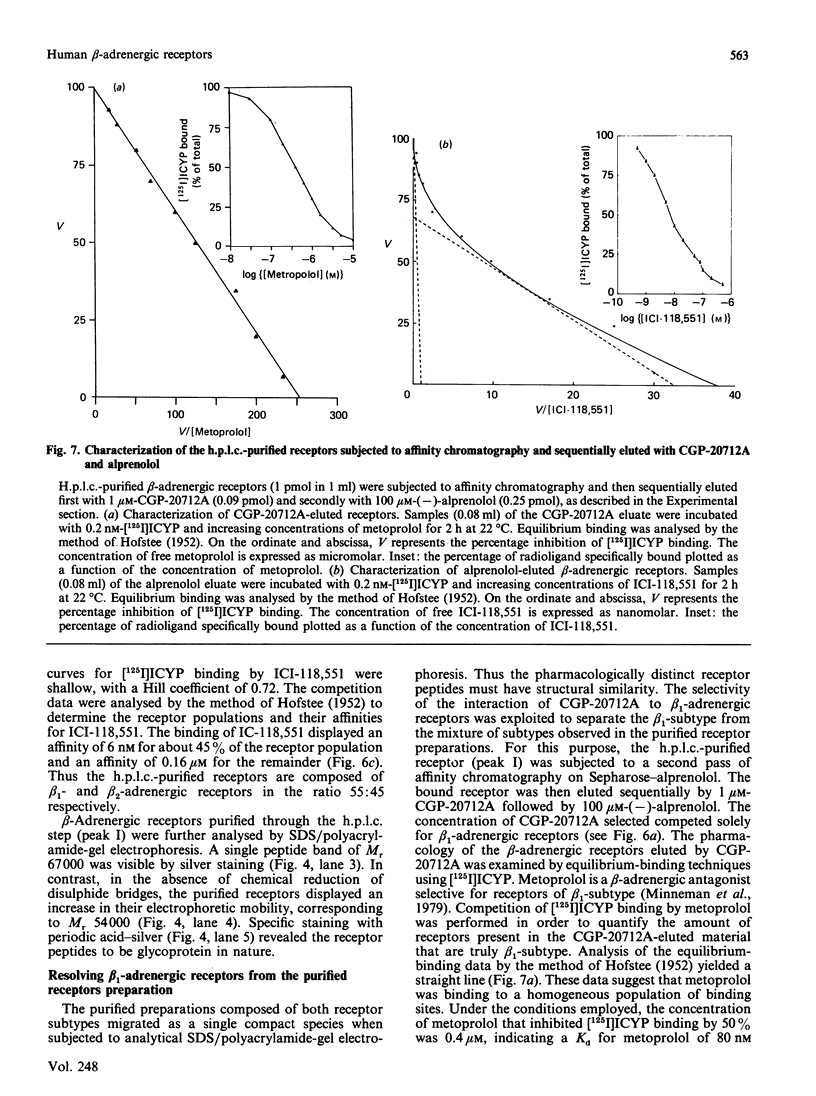
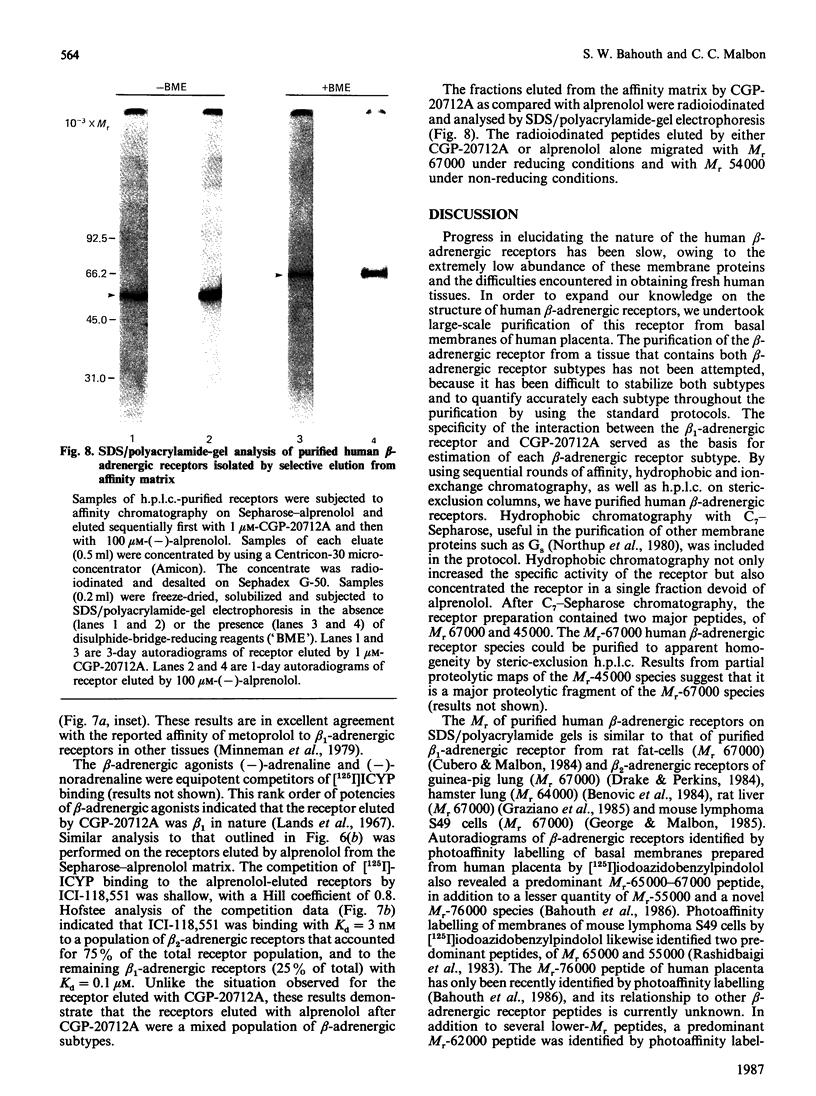
Beta-Adrenergic receptors from basal membranes of human placenta were purified from digitonin extracts by sequential rounds of affinity chromatography, hydrophobic chromatography, ion-exchange chromatography and steric-exclusion h.p.l.c. Basal membranes display both beta 1- and beta 2-adrenergic receptors, in the ratio 65:35. Affinity chromatography, hydrophobic chromatography on heptylamine-Sepharose and ion-exchange chromatography on DEAE-Sephacel removed most of the contaminating proteins, and final purification of the receptor to apparent homogeneity was achieved by steric-exclusion h.p.l.c. The purified receptors showed Mr 67000 on SDS/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis under reducing conditions. Specific binding of radioligand to the purified beta-adrenergic receptors displayed stereoselectivity, and the agonist competition profiles demonstrated the presence of both beta 1- and beta 2-receptors. By using the subtype-selective ligands CGP-20712A (beta 1-selective) and ICI-118,551 (beta 2-selective), the purified Mr-67000 species was shown to be composed of equivalent amounts of beta 1- and beta 2-adrenergic receptors. Affinity chromatography on Sepharose-alprenolol and sequential elution with 1 microM-CGP-20712A followed by 100 microM(-)-alprenolol permitted beta 1-adrenergic receptors to be resolved from the mixture of beta 1-/beta 2-adrenergic receptors. The pharmacologically distinct human beta 1 and beta 2-adrenergic receptors are shown to be structurally very similar peptides.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bahouth S. W., Kelley L. K., Smith C. H., Arbabian M. A., Ruoho A. E., Malbon C. C. Identification of a novel Mr = 76-kDa form of beta-adrenergic receptors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Dec 15;141(2):411–417. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80188-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benovic J. L., Shorr R. G., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. The mammalian beta 2-adrenergic receptor: purification and characterization. Biochemistry. 1984 Sep 25;23(20):4510–4518. doi: 10.1021/bi00315a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caron M. G., Srinivasan Y., Pitha J., Kociolek K., Lefkowitz R. J. Affinity chromatography of the beta-adrenergic receptor. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 25;254(8):2923–2927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y., Prusoff W. H. Relationship between the inhibition constant (K1) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 per cent inhibition (I50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem Pharmacol. 1973 Dec 1;22(23):3099–3108. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(73)90196-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cubero A., Malbon C. C. The fat cell beta-adrenergic receptor. Purification and characterization of a mammalian beta 1-adrenergic receptor. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 25;259(2):1344–1350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. A., Kobilka B. K., Strader D. J., Benovic J. L., Dohlman H. G., Frielle T., Bolanowski M. A., Bennett C. D., Rands E., Diehl R. E. Cloning of the gene and cDNA for mammalian beta-adrenergic receptor and homology with rhodopsin. Nature. 1986 May 1;321(6065):75–79. doi: 10.1038/321075a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. A., Sigal I. S., Rands E., Register R. B., Candelore M. R., Blake A. D., Strader C. D. Ligand binding to the beta-adrenergic receptor involves its rhodopsin-like core. Nature. 1987 Mar 5;326(6108):73–77. doi: 10.1038/326073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubray G., Bezard G. A highly sensitive periodic acid-silver stain for 1,2-diol groups of glycoproteins and polysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 15;119(2):325–329. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90593-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George S. T., Malbon C. C. Large-scale purification of beta-adrenergic receptors from mammalian cells in culture. Prep Biochem. 1985;15(5):349–366. doi: 10.1080/00327488508062451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George S. T., Ruoho A. E., Malbon C. C. N-glycosylation in expression and function of beta-adrenergic receptors. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 15;261(35):16559–16564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graziano M. P., Moxham C. P., Malbon C. C. Purified rat hepatic beta 2-adrenergic receptor. Structural similarities to the rat fat cell beta 1-adrenergic receptor. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7665–7674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOFSTEE B. H. J. On the evaluation of the constants Vm and KM in enzyme reactions. Science. 1952 Sep 26;116(3013):329–331. doi: 10.1126/science.116.3013.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley L. K., Smith C. H., King B. F. Isolation and partial characterization of the basal cell membrane of human placental trophoblast. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Sep 21;734(1):91–98. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90079-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobilka B. K., Dixon R. A., Frielle T., Dohlman H. G., Bolanowski M. A., Sigal I. S., Yang-Feng T. L., Francke U., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. cDNA for the human beta 2-adrenergic receptor: a protein with multiple membrane-spanning domains and encoded by a gene whose chromosomal location is shared with that of the receptor for platelet-derived growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):46–50. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lands A. M., Arnold A., McAuliff J. P., Luduena F. P., Brown T. G., Jr Differentiation of receptor systems activated by sympathomimetic amines. Nature. 1967 May 6;214(5088):597–598. doi: 10.1038/214597a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minneman K. P., Hegstrand L. R., Molinoff P. B. Simultaneous determination of beta-1 and beta-2-adrenergic receptors in tissues containing both receptor subtypes. Mol Pharmacol. 1979 Jul;16(1):34–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molinoff P. B., Wolfe B. B., Weiland G. A. Quantitative analysis of drug-receptor interactions: II. Determination of the properties of receptor subtypes. Life Sci. 1981 Aug 3;29(5):427–443. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90208-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore J. J., Whitsett J. A. The beta-adrenergic receptor in human placenta: receptor subtype analysis (beta 1 and beta 2) and partial characterization of the solubilized receptor. Placenta Suppl. 1981;3:103–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moxham C. P., George S. T., Graziano M. P., Brandwein H. J., Malbon C. C. Mammalian beta 1- and beta 2-adrenergic receptors. Immunological and structural comparisons. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14562–14570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moxham C. P., Malbon C. C. Fat cell beta 1-adrenergic receptor: structural evidence for existence of disulfide bridges essential for ligand binding. Biochemistry. 1985 Oct 22;24(22):6072–6077. doi: 10.1021/bi00343a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northup J. K., Sternweis P. C., Smigel M. D., Schleifer L. S., Ross E. M., Gilman A. G. Purification of the regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6516–6520. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rashidbaigi A., Ruoho A. E., Green D. A., Clark R. B. Photoaffinity labeling of the beta-adrenergic receptor from cultured lymphoma cells with [125I]iodoazidobenzylpindolol: loss of the label with desensitization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):2849–2853. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.2849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross E. M., Gilman A. G. Biochemical properties of hormone-sensitive adenylate cyclase. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:533–564. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.002533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner W., Weissmann C. A rapid, sensitive, and specific method for the determination of protein in dilute solution. Anal Biochem. 1973 Dec;56(2):502–514. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90217-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaltiel S. Hydrophobic chromatography. Methods Enzymol. 1974;34:126–140. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(74)34012-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiles G. L., Benovic J. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Mammalian beta-adrenergic receptors. Distinct glycoprotein populations containing high mannose or complex type carbohydrate chains. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8655–8663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiles G. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Beta-adrenergic receptors: biochemical mechanisms of physiological regulation. Physiol Rev. 1984 Apr;64(2):661–743. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1984.64.2.661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiles G. L., Strasser R. H., Lavin T. N., Jones L. R., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. The cardiac beta-adrenergic receptor. Structural similarities of beta 1 and beta 2 receptor subtypes demonstrated by photoaffinity labeling. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):8443–8449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vauquelin G., Geynet P., Hanoune J., Strosberg A. D. Affinity chromatography of the beta-adrenergic receptor from turkey erythrocytes. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Aug 1;98(2):543–556. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13215.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E. R., Hadcock J. R., Johnson G. L., Malbon C. C. Antipeptide antibodies directed against cytoplasmic rhodopsin sequences recognize the beta-adrenergic receptor. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 25;262(9):4319–4323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]