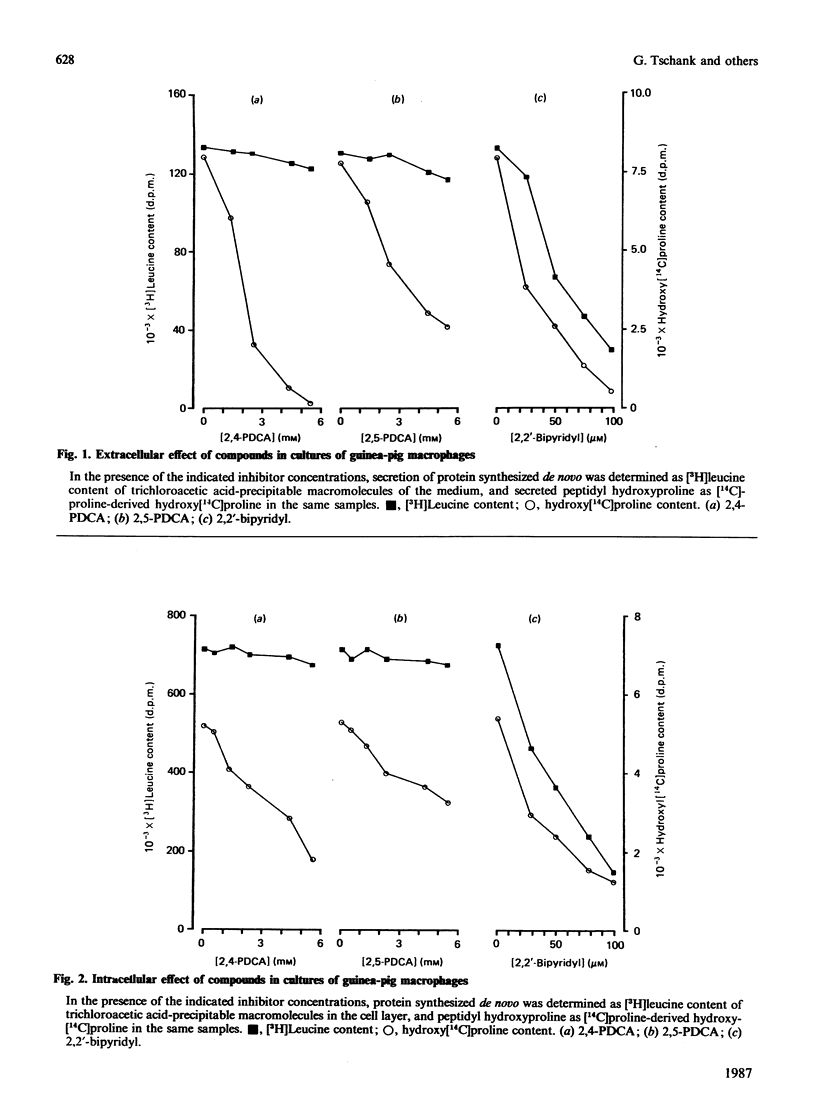
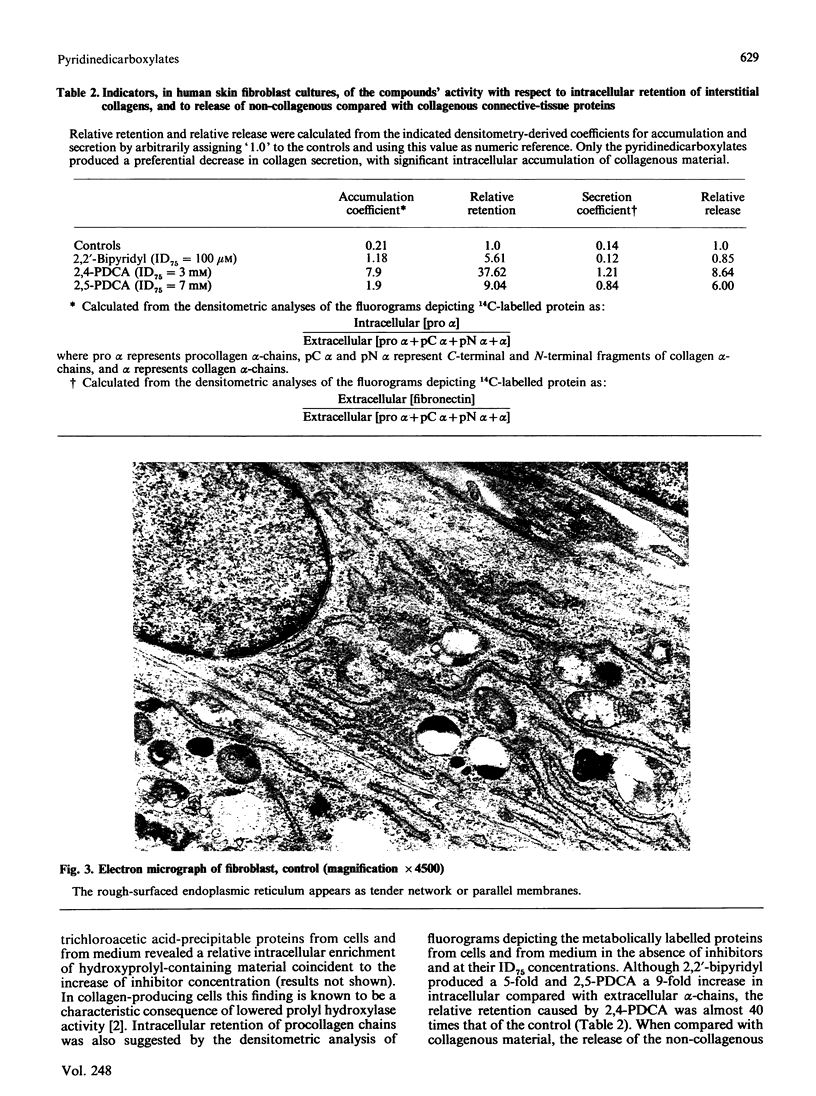
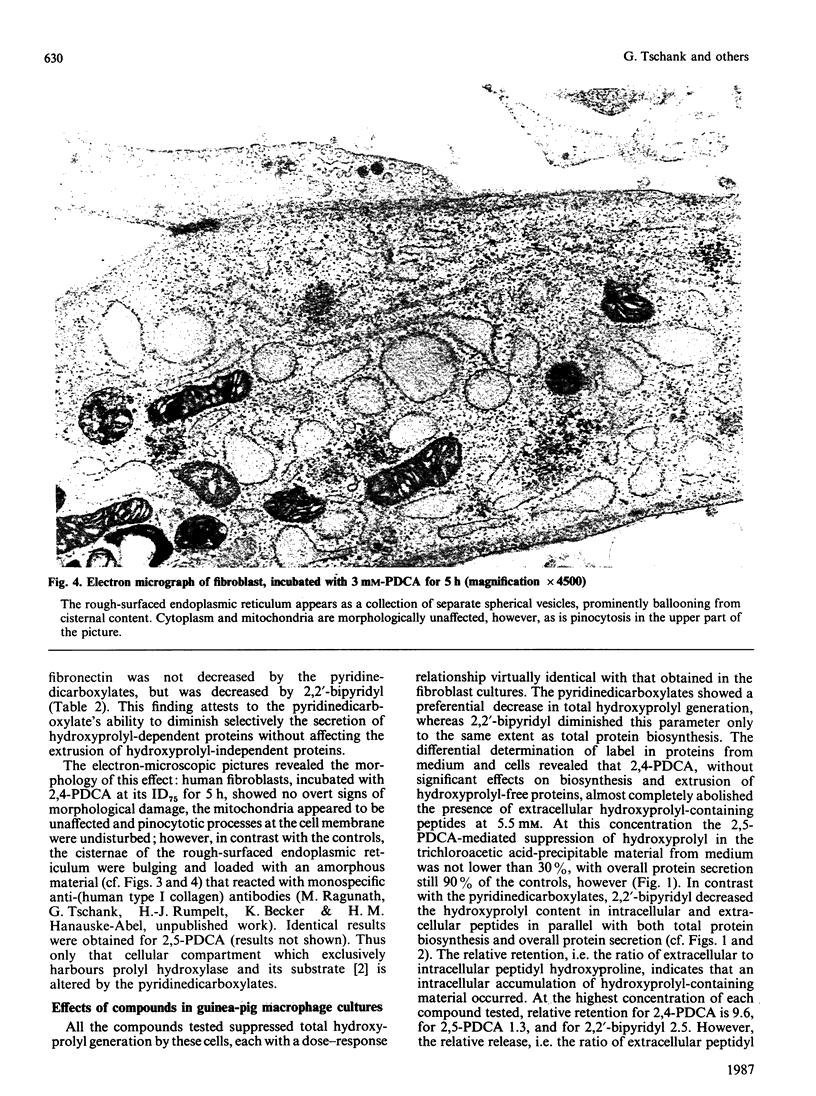
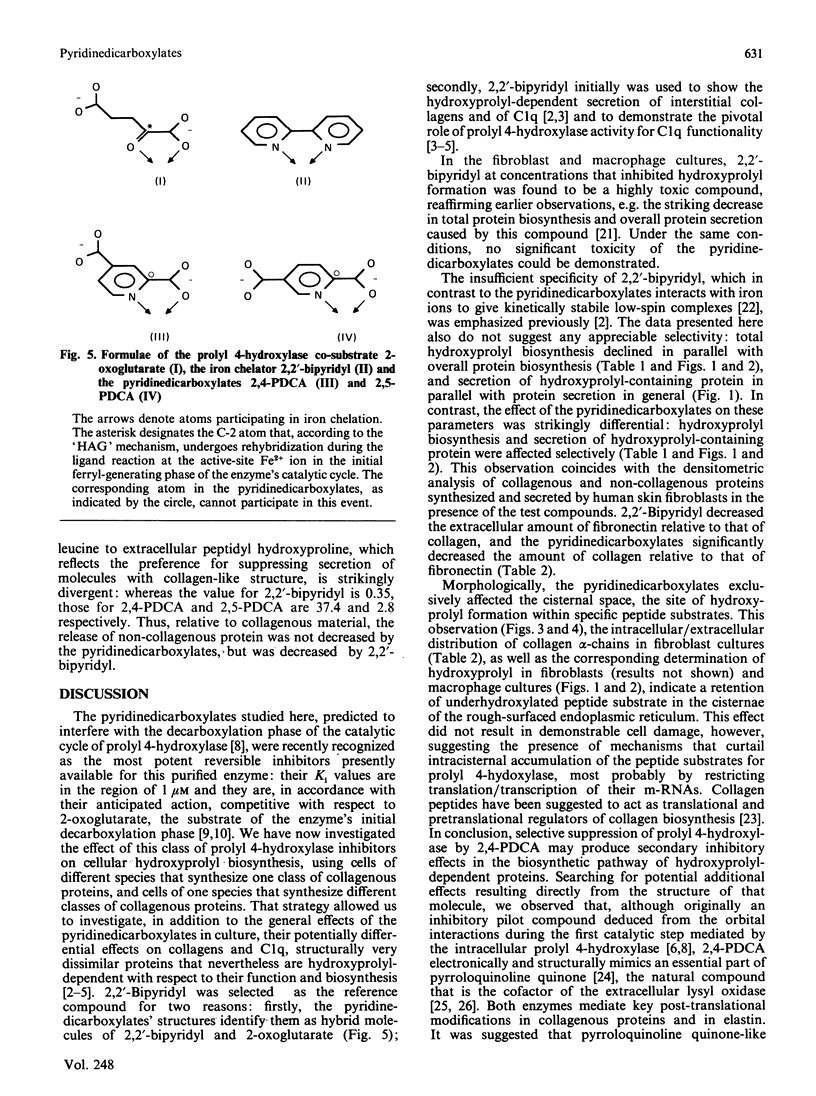
Abstract
Two pyridinedicarboxylates, predicted [Hanauske-Abel (1983) M.D.-Ph.D. Thesis, Philipps Universität Marburg] and later found to be potent reversible inhibitors of purified prolyl 4-hydroxylase [Majaama, Hanauske-Abel, Günzler & Kivirikko (1984) Eur. J. Biochem. 138, 239-245] were investigated with respect to their effect on hydroxyprolyl biosynthesis in the fibroblast/collagen and the macrophage/Clq systems, and the effect was compared with that of the iron chelator 2,2'-dipyridyl, the compound usually employed to inhibit cellular hydroxyprolyl formation. Only the enzyme-mechanism-derived pyridinedicarboxylates were highly selective inhibitors, and only they lacked overt cytotoxicity. Morphologically, their effect was restricted to the site of cellular hydroxyprolyl biosynthesis, i.e. the cisternae of the rough-surfaced endoplasmic reticulum. They were equally effective in the different cell types studied, and human and guinea-pig fibroblasts showed the same sensitivity. The minimal lipophilicity of the pyridinedicarboxylates necessitated high concentrations to achieve suppression of cellular hydroxyprolyl formation, but lipophilic bio-activatable pro-inhibitors may overcome this disadvantage. For the first time, experimental evidence is presented suggesting that, in cell culture, the biosynthesis of interstitial collagens and Clq can be suppressed selectively, identifying the pyridinedicarboxylates as promising pilot compounds for experiments in vivo.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Jong L., Kemp A. Stoicheiometry and kinetics of the prolyl 4-hydroxylase partial reaction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 May 31;787(1):105–111. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(84)90113-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanauske-Abel H. M., Günzler V. A stereochemical concept for the catalytic mechanism of prolylhydroxylase: applicability to classification and design of inhibitors. J Theor Biol. 1982 Jan 21;94(2):421–455. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(82)90320-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanauske-Abel H. M., Pontz B. F., Schorlemmer H. U. Cartilage specific collagen activates macrophages and the alternative pathway of complement: evidence for an immunopathogenic concept of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1982 Apr;41(2):168–176. doi: 10.1136/ard.41.2.168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanauske-Abel H. M., Tschank G., Günzler V., Baader E., Gallop P. Pyrroloquinoline quinone and molecules mimicking its functional domains. Modulators of connective tissue formation? FEBS Lett. 1987 Apr 20;214(2):236–243. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80062-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kivirikko K. I., Myllylä R. Post-translational processing of procollagens. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1985;460:187–201. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1985.tb51167.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majamaa K., Hanauske-Abel H. M., Günzler V., Kivirikko K. I. The 2-oxoglutarate binding site of prolyl 4-hydroxylase. Identification of distinct subsites and evidence for 2-oxoglutarate decarboxylation in a ligand reaction at the enzyme-bound ferrous ion. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jan 16;138(2):239–245. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb07907.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majamaa K., Turpeenniemi-Hujanen T. M., Latipä P., Günzler V., Hanauske-Abel H. M., Hassinen I. E., Kivirikko K. I. Differences between collagen hydroxylases and 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase in their inhibition by structural analogues of 2-oxoglutarate. Biochem J. 1985 Jul 1;229(1):127–133. doi: 10.1042/bj2290127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myllylä R., Seppä H. Studies on enzymes of collagen biosynthesis and the synthesis of hydroxyproline in macrophages and mast cells. Biochem J. 1979 Aug 15;182(2):311–316. doi: 10.1042/bj1820311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller P. K., Meigel W. N., Pontz B. F., Raisch K. Influence of alpha, alpha-dipyridyl on the biosynthesis of collagen in organ cultures. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1974 Aug;355(8):985–996. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1974.355.2.985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller W., Hanauske-Abel H., Loos M. Biosynthesis of the first component of complement by human and guinea pig peritoneal macrophages: evidence for an independent production of the C1 subunits. J Immunol. 1978 Oct;121(4):1578–1584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller W., Hanauske-Abel H., Loos M. Reversible inhibition of C1Q release from guinea pig macrophages by 2,2'-dipyridyl: Evidence for a posttranslational hydroxylation step in the biosynthesis of C1Q, a subcomponent of the first component of complement (C1). FEBS Lett. 1978 Jun 15;90(2):218–222. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80372-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Hayman E. G., Pierschbacher M., Engvall E. Fibronectin: purification, immunochemical properties, and biological activities. Methods Enzymol. 1982;82(Pt A):803–831. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)82103-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson P. R., Moog R. S., Dooley D. M., Kagan H. M. Evidence for pyrroloquinolinequinone as the carbonyl cofactor in lysyl oxidase by absorption and resonance Raman spectroscopy. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 15;261(35):16302–16305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. H., Donovan C. B., Wu G. Y. Evidence for pretranslational regulation of collagen synthesis by procollagen propeptides. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 15;261(23):10482–10484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaragoza E. J., Ryhänen L., Oikarinen A. I., Uitto J. Inhibition of type II procollagen to collagen conversion by lysine derivatives and related compounds. Mapping of the inhibitory structural features. Biochem Pharmacol. 1986 Feb 1;35(3):532–535. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(86)90231-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Waal A., Hartog A. F., de Jong L. Photoaffinity labelling of the 2-oxoglutarate binding site of prolyl 4-hydroxylase with 5-azidopyridine-2-carboxylic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Mar 18;912(1):151–155. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(87)90260-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Meer R. A., Duine J. A. Covalently bound pyrroloquinoline quinone is the organic prosthetic group in human placental lysyl oxidase. Biochem J. 1986 Nov 1;239(3):789–791. doi: 10.1042/bj2390789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




