Abstract
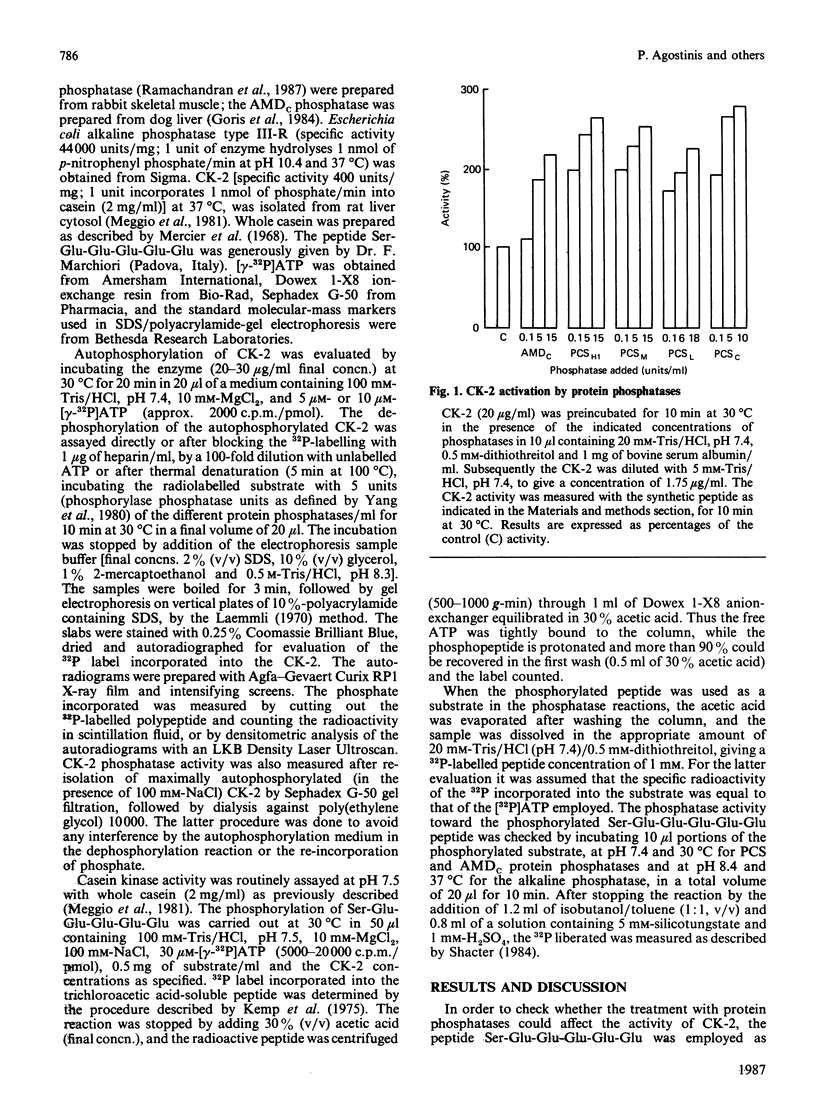
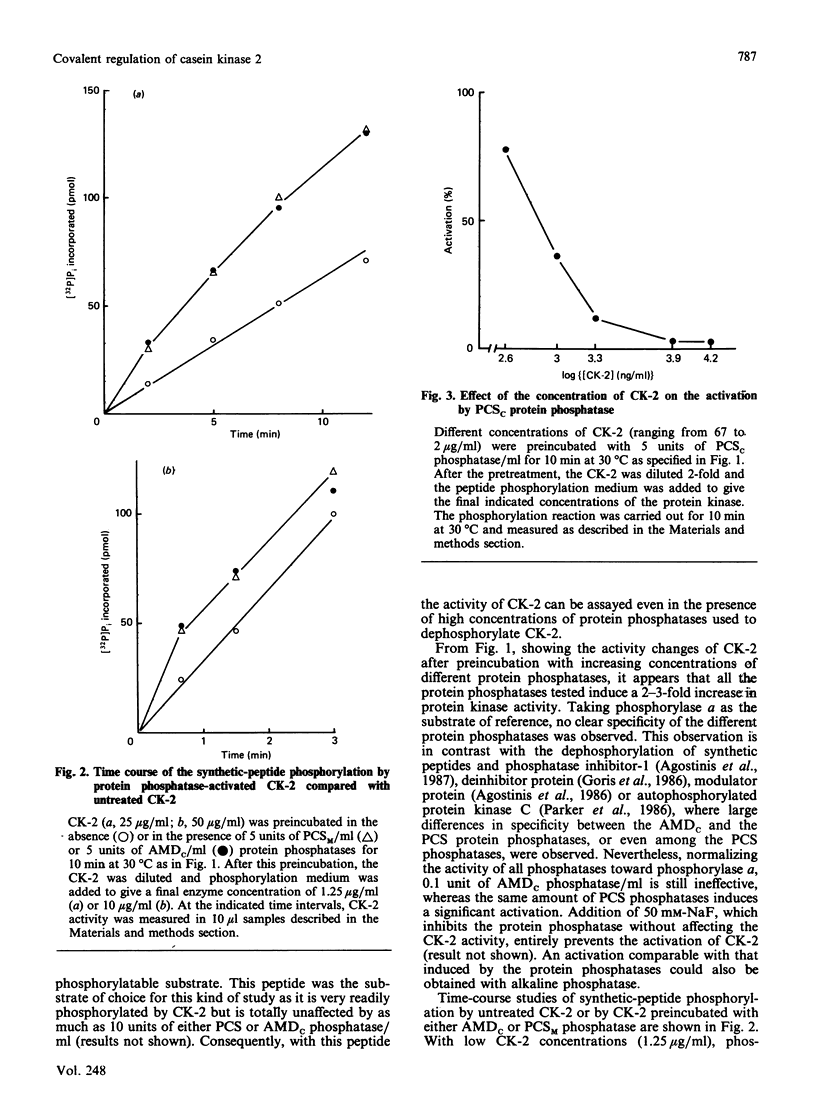
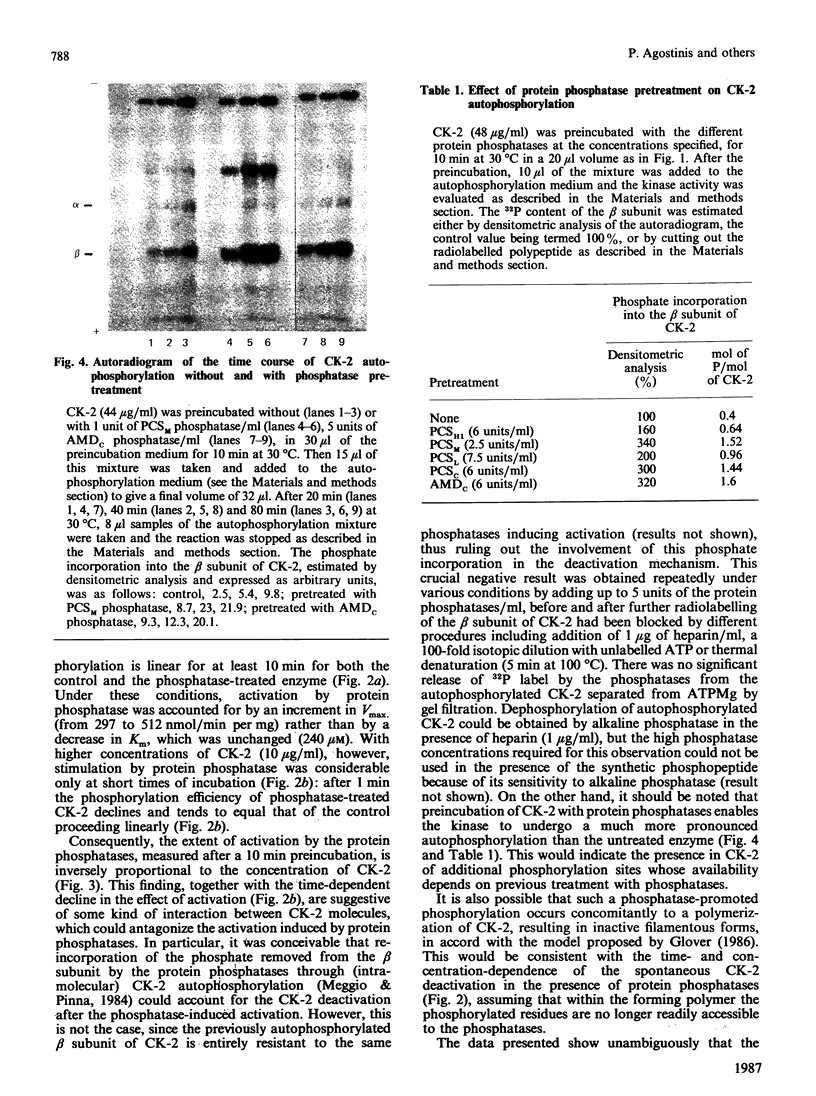
The effects of various polycation-stimulated (PCS) phosphatases and of the active catalytic subunit of the ATPMg-dependent (AMDc) protein phosphatase on the activity of casein kinase 2 (CK-2) were investigated by using the synthetic peptide substrate Ser-Glu-Glu-Glu-Glu-Glu, whose phosphorylated derivative is entirely insensitive to these protein phosphatases. Previous dephosphorylation of native CK-2 enhances its specific activity 2-3-fold. Such an effect, accounted for by an increase in Vmax, is more readily promoted by the PCS phosphatases than by the AMDc phosphatase. The phosphate incorporated by autophosphorylation could not be removed by the protein phosphatases, suggesting the involvement of phosphorylation site(s) other than the one(s) affected by intramolecular autophosphorylation. The activation of CK-2 by the phosphatase pretreatment is neutralized during the kinase assay; the mechanism of this phenomenon, which is highly dependent on the kinase concentration, is discussed.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agostinis P., Goris J., Vandenheede J. R., Waelkens E., Pinna L. A., Merlevede W. Phosphorylation of the modulator protein of the ATP, Mg-dependent protein phosphatase by casein kinase TS. Reversal by PCS phosphatases and control by distinct phosphorylation site(s). FEBS Lett. 1986 Oct 20;207(1):167–172. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80033-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agostinis P., Goris J., Waelkens E., Pinna L. A., Marchiori F., Merlevede W. Dephosphorylation of phosphoproteins and synthetic phosphopeptides. Study of the specificity of the polycation-stimulated and MgATP-dependent phosphorylase phosphatases. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 25;262(3):1060–1064. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmichael D. F., Geahlen R. L., Allen S. M., Krebs E. G. Type II regulatory subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Phosphorylation by casein kinase II at a site that is also phosphorylated in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10440–10445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochet C., Job D., Pirollet F., Chambaz E. M. Adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-independent protein kinase activities in the bovine adrenal cortex cytosol. Endocrinology. 1980 Mar;106(3):750–757. doi: 10.1210/endo-106-3-750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P., Yellowlees D., Aitken A., Donella-Deana A., Hemmings B. A., Parker P. J. Separation and characterisation of glycogen synthase kinase 3, glycogen synthase kinase 4 and glycogen synthase kinase 5 from rabbit skeletal muscle. Eur J Biochem. 1982 May;124(1):21–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb05902.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahmus M. E. Phosphorylation of eukaryotic DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Identification of calf thymus RNA polymerase subunits phosphorylated by two purified protein kinases, correlation with in vivo sites of phosphorylation in HeLa cell RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 10;256(7):3332–3339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePaoli-Roach A. A., Ahmad Z., Roach P. J. Characterization of a rabbit skeletal muscle protein kinase (PC0.7) able to phosphorylate glycogen synthase and phosvitin. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):8955–8962. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePaoli-Roach A. A. Synergistic phosphorylation and activation of ATP-Mg-dependent phosphoprotein phosphatase by F A/GSK-3 and casein kinase II (PC0.7). J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):12144–12152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISCHER E. H., KREBS E. G. The isolation and crystallization of rabbit skeletal muscle phosphorylase b. J Biol Chem. 1958 Mar;231(1):65–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glover C. V. A filamentous form of Drosophila casein kinase II. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 25;261(30):14349–14354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goris J., Waelkens E., Camps T., Merlevede W. Regulation of protein phosphatase activity by the deinhibitor protein. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1984;22:467–484. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(84)90026-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goris J., Waelkens E., Merlevede W. Identification of the phosphatase deinhibitor protein phosphatases in rabbit skeletal muscle. Biochem J. 1986 Oct 1;239(1):109–114. doi: 10.1042/bj2390109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara T., Endo H. Polyamines alter the substrate preference of nuclear protein kinase NII. Biochemistry. 1982 May 25;21(11):2632–2637. doi: 10.1021/bi00540a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hathaway G. M., Lubben T. H., Traugh J. A. Inhibition of casein kinase II by heparin. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 10;255(17):8038–8041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hathaway G. M., Traugh J. A. Casein kinases--multipotential protein kinases. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1982;21:101–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hathaway G. M., Traugh J. A. Kinetics of activation of casein kinase II by polyamines and reversal of 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate inhibition. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):7011–7015. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmings B. A., Aitken A., Cohen P., Rymond M., Hofmann F. Phosphorylation of the type-II regulatory subunit of cyclic-AMP-dependent protein kinase by glycogen synthase kinase 3 and glycogen synthase kinase 5. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Oct;127(3):473–481. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06896.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes C. F., Kuret J., Chisholm A. A., Cohen P. Identification of the sites on rabbit skeletal muscle protein phosphatase inhibitor-2 phosphorylated by casein kinase-II. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Apr 22;870(3):408–416. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(86)90248-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp B. E., Bylund D. B., Huang T. S., Krebs E. G. Substrate specificity of the cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3448–3452. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King M. M., Fitzgerald T. J., Carlson G. M. Characterization of initial autophosphorylation events in rabbit skeletal muscle phosphorylase kinase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):9925–9930. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lou L. L., Lloyd S. J., Schulman H. Activation of the multifunctional Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase by autophosphorylation: ATP modulates production of an autonomous enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9497–9501. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marin O., Meggio F., Marchiori F., Borin G., Pinna L. A. Site specificity of casein kinase-2 (TS) from rat liver cytosol. A study with model peptide substrates. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Oct 15;160(2):239–244. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09962.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meggio F., Deana A. D., Pinna L. A. Endogenous phosphate acceptor proteins for rat liver cytosolic casein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):11958–11961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meggio F., Flamigni F., Caldarera C. M., Guarnieri C., Pinna L. A. Phosphorylation of rat heart ornithine decarboxylase by type-2 casein kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Aug 16;122(3):997–1004. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91190-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meggio F., Marchiori F., Borin G., Chessa G., Pinna L. A. Synthetic peptides including acidic clusters as substrates and inhibitors of rat liver casein kinase TS (type-2). J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14576–14579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meggio F., Pinna L. A., Marchiori F., Borin G. Polyglutamyl peptides: a new class of inhibitors of type-2 casein kinases. FEBS Lett. 1983 Oct 17;162(2):235–238. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80762-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meggio F., Pinna L. A. Subunit structure and autophosphorylation mechanism of casein kinase-TS (type-2) from rat liver cytosol. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Dec 17;145(3):593–599. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08598.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercier J. C., Maubois J. L., Poznanski S., Ribadeau-Dumas B. Fractionnement préparatif des caséines de vache et de brebis par chromatographie sur D.E.A.E. cellulose, en milieu urée et 2-mercaptoéthanol. Bull Soc Chim Biol (Paris) 1968;50(3):521–530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesterova M. V., Ulmasov K. A., Shlyapnikov S. V., Severin E. S. The autophosphorylation reaction in the mechanism of activation of pig brain cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jul 24;660(1):110–116. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(81)90115-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker P. J., Goris J., Merlevede W. Specificity of protein phosphatases in the dephosphorylation of protein kinase C. Biochem J. 1986 Nov 15;240(1):63–67. doi: 10.1042/bj2400063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinna L. A., Meggio F., Dediukina M. M. Phosphorylation of troponin T by casein kinase TS. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 May 15;100(1):449–454. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(81)80117-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qi S. L., Yukioka M., Morisawa S., Inoue A. Heterogeneity of protein kinase NII. Multiple subunit-polypeptides. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jul 14;203(1):104–108. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81446-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramachandran C., Goris J., Waelkens E., Merlevede W., Walsh D. A. The interrelationship between cAMP-dependent alpha and beta subunit phosphorylation in the regulation of phosphorylase kinase activity. Studies using subunit specific phosphatases. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3210–3218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen O. M., Herrera R., Olowe Y., Petruzzelli L. M., Cobb M. H. Phosphorylation activates the insulin receptor tyrosine protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3237–3240. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shacter E. Organic extraction of Pi with isobutanol/toluene. Anal Biochem. 1984 May 1;138(2):416–420. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90831-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waelkens E., Goris J., Merlevede W. Purification and properties of polycation-stimulated phosphorylase phosphatases from rabbit skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 25;262(3):1049–1059. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto M., Criss W. E., Takai Y., Yamamura H., Nishizuka Y. A hepatic soluble cyclic nucleotide-independent protein kinase. Stimulation by basic polypeptides. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):5049–5052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang S. D., Vandenheede J. R., Goris J., Merlevede W. ATP x Mg-dependent protein phosphatase from rabbit skeletal muscle. I. Purification of the enzyme and its regulation by the interaction with an activating protein factor. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11759–11767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]